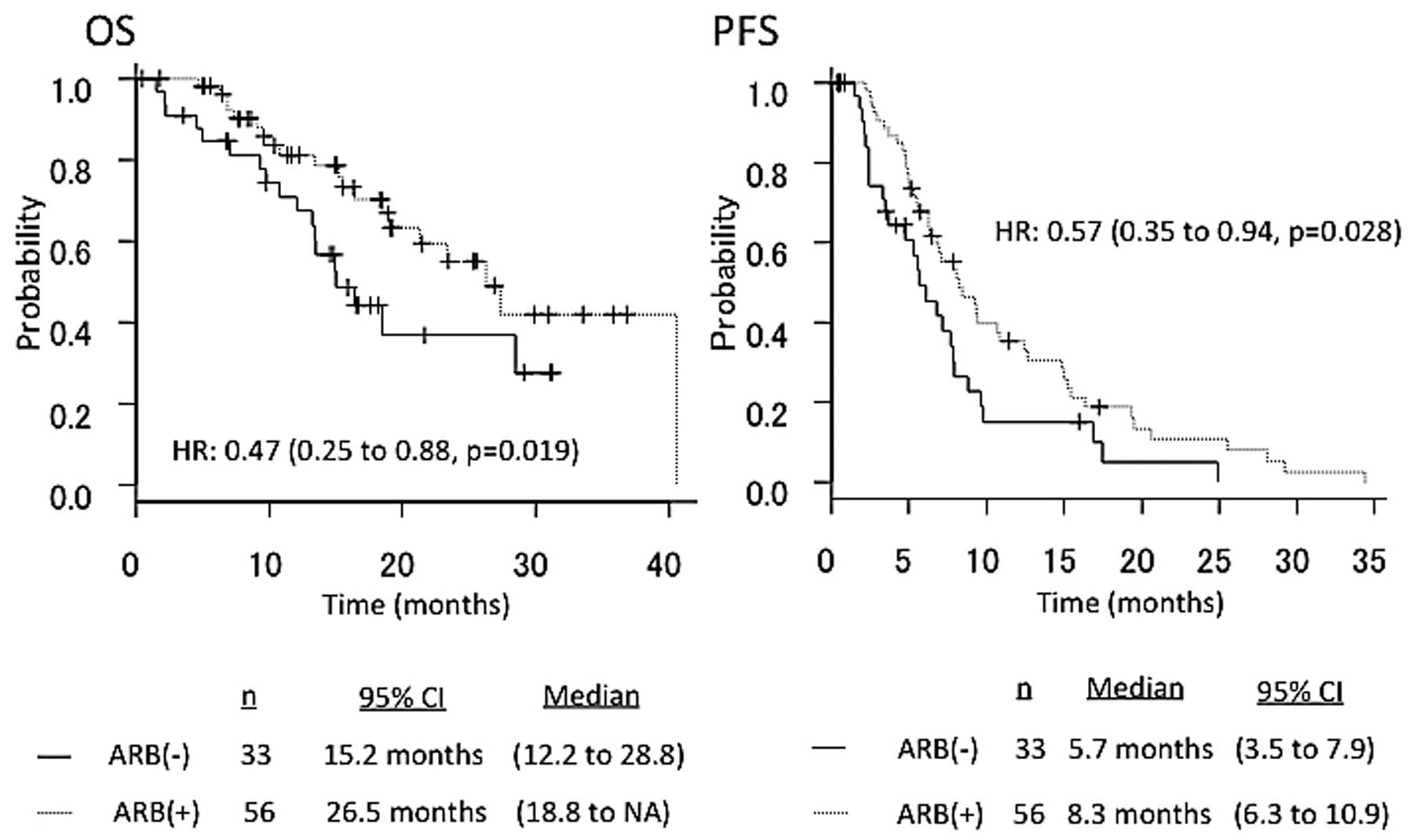
|
1
|
Ager EI, Neo J and Christophi C: The
renin-angiotensin system and malignancy. Carcinogenesis.
29:1675–1684. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khakoo AY, Sidman RL, Pasqualini R and
Arap W: Does the renin-angiotensin system participate in regulation
of human vasculogenesis and angiogenesis? Cancer Res. 68:9112–9115.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lever AF, Hole DJ, Gillis CR, McCallum IR,
McInnes GT, MacKinnon PL, Meredith PA, Murray LS, Reid JL and
Robertson JW: Do inhibitors of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme
protect against risk of cancer? Lancet. 352:179–184. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang W, Wu YL, Zhong J, Jiang FX, Tian XL
and Yu LF: Angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist suppress
angiogenesis and growth of gastric cancer xenografts. Dig Dis Sci.
53:1206–1210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kosugi M, Miyajima A, Kikuchi E, Kosaka T,
Horiguchi Y, Murai M and Oya M: Angiotensin II type 1 receptor
antagonist enhances cis-dichlorodiammineplatinum-induced
cytotoxicity in mouse xenograft model of bladder cancer. Urology.
73:655–660. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fujita M, Hayashi I, Yamashina S, Itoman M
and Majima M: Blockade of angiotensin AT1a receptor signaling
reduces tumor growth, angiogenesis and metastasis. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 294:441–447. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Noguchi R, Yoshiji H, Ikenaka Y, Namisaki
T, Kitade M, Kaji K, Yoshii J, Yanase K, Yamazaki M, Tsujimoto T,
et al: Synergistic inhibitory effect of gemcitabine and angiotensin
type-1 receptor blocker, losartan, on murine pancreatic tumor
growth via anti-angiogenic activities. Oncol Rep. 22:355–360.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nakai Y, Isayama H, Ijichi H, Sasaki T,
Sasahira N, Hirano K, Kogure H, Kawakubo K, Yagioka H, Yashima Y,
et al: Inhibition of renin-angiotensin system affects prognosis of
advanced pancreatic cancer receiving gemcitabine. Br J Cancer.
103:1644–1648. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ohta T, Amaya K, Yi S, Kitagawa H,
Kayahara M, Ninomiya I, Fushida S, Fujimura T, Nishimura G, Shimizu
K, et al: Angiotensin converting enzyme-independent, local
angiotensin II-generation in human pancreatic ductal cancer
tissues. Int J Oncol. 23:593–598. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fujimoto Y, Sasaki T, Tsuchida A and
Chayama K: Angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression in human
pancreatic cancer and growth inhibition by angiotensin II type 1
receptor antagonist. FEBS Lett. 495:197–200. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Arafat HA, Gong Q, Chipitsyna G, Rizvi A,
Saa CT and Yeo CJ: Antihypertensives as novel antineoplastics:
angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II type
1 receptor blockers in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Am Coll
Surg. 204:996–1006. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fendrich V, Chen NM, Neef M, Waldmann J,
Buchholz M, Feldmann G, Slater EP, Maitra A and Bartsch DK: The
angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitor enalapril and aspirin
delay progression of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and
cancer formation in a genetically engineered mouse model of
pancreatic cancer. Gut. 59:630–637. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yanase K, Yoshiji H, Ikenaka Y, Noguchi R,
Kitade M, Kaji K, Yoshii J, Namisaki T, Yamazaki M, Asada K, et al:
Synergistic inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma growth and
hepatocarcinogenesis by combination of 5-fluorouracil and
angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor via anti-angiogenic
activities. Oncol Rep. 17:441–446. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Amaya K, Ohta T, Kitagawa H, Kayahara M,
Takamura H, Fujimura T, Nishimura G, Shimizu K and Miwa K:
Angiotensin II activates MAP kinase and NF-κB through angiotensin
II type I receptor in human pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
25:849–856. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gong Q, Davis M, Chipitsyna G, Yeo CJ and
Arafat HA: Blocking angiotensin II type 1 receptor triggers
apoptotic cell death in human pancreatic cancer cells. Pancreas.
39:581–594. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Österlund P, Soveri LM, Isoniemi H, Poussa
T, Alanko T and Bono P: Hypertension and overall survival in
metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with
bevacizumab-containing chemotherapy. Br J Cancer. 104:599–604.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tahover E, Uziely B, Salah A, Temper M,
Peretz T and Hubert A: Hypertension as a predictive biomarker in
bevacizumab treatment for colorectal cancer patients. Med Oncol.
30:3272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dewdney A, Cunningham D, Barbachano Y and
Chau I: Correlation of bevacizumab-induced hypertension and outcome
in the BOXER study, a phase II study of capecitabine, oxaliplatin
(CAPOX) plus bevacizumab as peri-operative treatment in 45 patients
with poor-risk colorectal liver-only metastases unsuitable for
upfront resection. Br J Cancer. 106:1718–1721. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu Ryanne R, Lindenberg PA, Slack R, Noone
AM, Marshall JL and He AR: Evaluation of hypertension as a marker
of bevacizumab efficacy. J Gastrointest Cancer. 40:101–108. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Scartozzi M, Galizia E, Chiorrini S,
Giampieri R, Berardi R, Pierantoni C and Cascinu S: Arterial
hypertension correlates with clinical outcome in colorectal cancer
patients treated with first-line bevacizumab. Ann Oncol.
20:227–230. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|