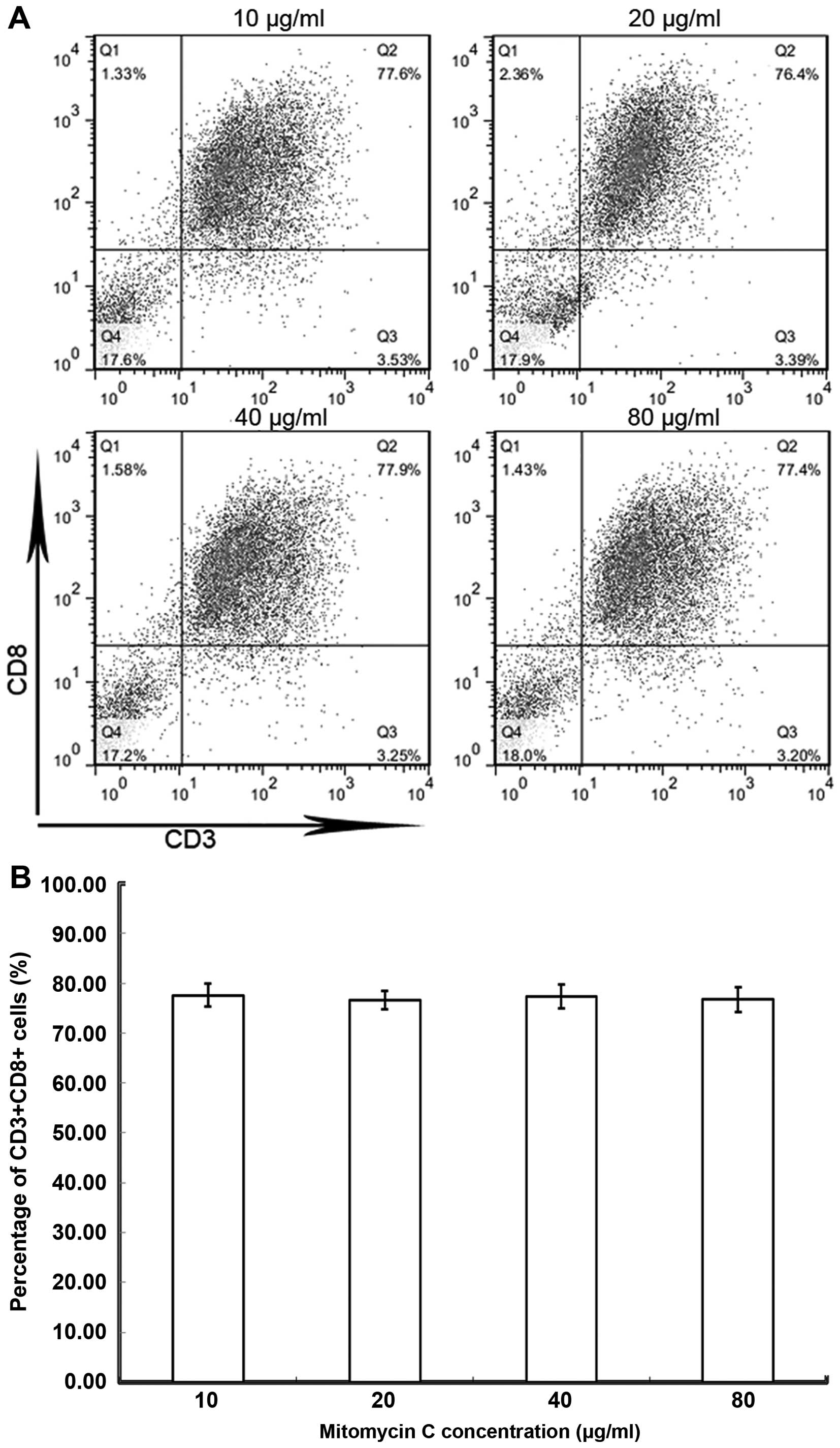
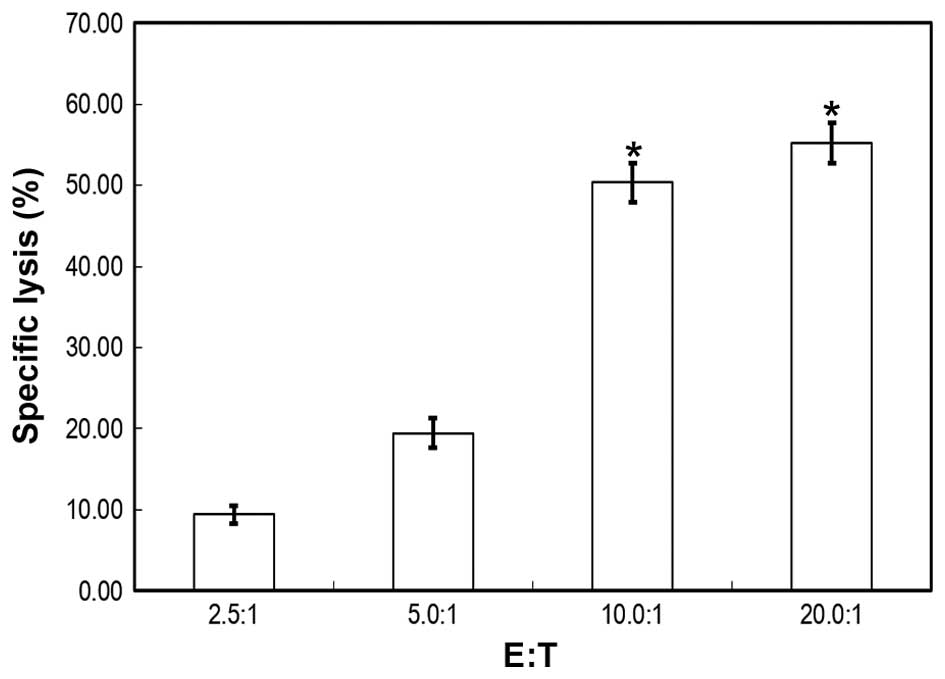
|
1
|
Heslop HE: Biology and treatment of
Epstein-Barr virus-associated non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Hematology Am
Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2005:260–266. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Doherty PC and Christensen JP: Accessing
complexity: The dynamics of virus-specific T cell responses. Annu
Rev Immunol. 18:561–592. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Russell JH and Ley TJ: Lymphocyte-mediated
cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 20:323–370. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun Y, Iglesias E, Samri A, Kamkamidze G,
Decoville T, Carcelain G and Autran B: A systematic comparison of
methods to measure HIV-1 specific CD8 T cells. J Immunol Methods.
272:23–34. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Subklewe M, Chahroudi A, Schmaljohn A,
Kurilla MG, Bhardwaj N and Steinman RM: Induction of Epstein-Barr
virus-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses using dendritic
cells pulsed with EBNA-3A peptides or UV-inactivated, recombinant
EBNA-3A vaccinia virus. Blood. 94:1372–1381. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tabi Z, Moutaftsi M and Borysiewicz LK:
Human cytomegalovirus pp65 and immediate early 1 antigen-specific
HLA class I-restricted cytotoxic T cell responses induced by
cross-presentation of viral antigens. J Immunol. 166:5695–5703.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rehermann B, Chang K-M, McHutchinson J,
Kokka R, Houghton M, Rice CM and Chisari FV: Differential cytotoxic
T-lymphocyte responsiveness to the hepatitis B and C viruses in
chronically infected patients. J Virol. 70:7092–7102.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nijmeijer BA, Mollevanger P, van
Zelderen-Bhola SL, Kluin-Nelemans HC, Willemze R and Falkenburg JH:
Monitoring of engraftment and progression of acute lymphoblastic
leukemia in individual NOD/SCID mice. Exp Hematol. 29:322–329.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Markasz L, Skribek H, Uhlin M, Otvos R,
Flaberg E, Eksborg S, Olah E, Stuber G and Szekely L: Effect of
frequently used chemotherapeutic drugs on cytotoxic activity of
human cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. J Immunother. 31:283–293. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sánchez-Aguilera A, Montalbán C, de la
Cueva P, Sánchez-Verde L, Morente MM, García-Cosío M, García-Laraña
J, Bellas C, Provencio M, Romagosa V, et al: Spanish Hodgkin
Lymphoma Study Group: Tumor microenvironment and mitotic checkpoint
are key factors in the outcome of classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood.
108:662–668. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guedez L, McMarlin AJ, Kingma DW, Bennett
TA, Stetler-Stevenson M and Stetler-Stevenson WG: Tissue inhibitor
of metalloproteinase-1 alters the tumorigenicity of Burkitt's
lymphoma via divergent effects on tumor growth and angiogenesis. Am
J Pathol. 158:1207–1215. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mori F, Ishida T, Ito A, Sato F, Masaki A,
Takino H, Ri M, Kusumoto S, Komatsu H, Ueda R, et al: Potent
antitumor effects of bevacizumab in a microenvironment-dependent
human lymphoma mouse model. Blood Cancer J. 2:e672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Canioni D, Salles G, Mounier N, Brousse N,
Keuppens M, Morchhauser F, Lamy T, Sonet A, Rousselet MC, Foussard
C, et al: High numbers of tumor-associated macrophages have an
adverse prognostic value that can be circumvented by rituximab in
patients with follicular lymphoma enrolled onto the GELA-GOELAMS
FL-2000 trial. J Clin Oncol. 26:440–446. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mohammad RM, Wall NR, Dutcher JA and
Al-Katib AM: The addition of bryostatin 1 to cyclophosphamide,
doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) chemotherapy
improves response in a CHOP-resistant human diffuse large cell
lymphoma xenograft model. Clin Cancer Res. 6:4950–4956.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Israel BF and Kenney SC: Virally targeted
therapies for EBV-associated malignancies. Oncogene. 22:5122–5130.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Frisan T, Sjöberg J, Dolcetti R, Boiocchi
M, De Re V, Carbone A, Brautbar C, Battat S, Biberfeld P, Eckman M,
et al: Local suppression of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-specific
cytotoxicity in biopsies of EBV-positive Hodgkin's disease. Blood.
86:1493–1501. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sing AP, Ambinder RF, Hong DJ, Jensen M,
Batten W, Petersdorf E and Greenberg PD: Isolation of Epstein-Barr
virus (EBV)-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes that lyse
Reed-Sternberg cells: Implications for immune-mediated therapy of
EBV+ Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 89:1978–1986. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Heslop HE, Slobod KS, Pule MA, Hale GA,
Rousseau A, Smith CA, Bollard CM, Liu H, Wu MF, Rochester RJ, et
al: Long-term outcome of EBV-specific T-cell infusions to prevent
or treat EBV-related lymphoproliferative disease in transplant
recipients. Blood. 115:925–935. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Doubrovina E, Oflaz-Sozmen B, Prockop SE,
Kernan NA, Abramson S, Teruya-Feldstein J, Hedvat C, Chou JF,
Heller G, Barker JN, et al: Adoptive immunotherapy with unselected
or EBV-specific T cells for biopsy-proven EBV+ lymphomas after
allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood.
119:2644–2656. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Icheva V, Kayser S, Wolff D, Tuve S,
Kyzirakos C, Bethge W, Greil J, Albert MH, Schwinger W, Nathrath M,
et al: Adoptive transfer of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear
antigen 1-specific T cells as treatment for EBV reactivation and
lymphoproliferative disorders after allogeneic stem-cell
transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 31:39–48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Steidl C, Connors JM and Gascoyne RD:
Molecular pathogenesis of Hodgkin's lymphoma: Increasing evidence
of the importance of the microenvironment. J Clin Oncol.
29:1812–1826. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Staudt MR, Kanan Y, Jeong JH, Papin JF,
Hines-Boykin R and Dittmer DP: The tumor microenvironment controls
primary effusion lymphoma growth in vivo. Cancer Res. 64:4790–4799.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Carreras J, Lopez-Guillermo A, Fox BC,
Colomo L, Martinez A, Roncador G, Montserrat E, Campo E and Banham
AH: High numbers of tumor-infiltrating FOXP3-positive regulatory T
cells are associated with improved overall survival in follicular
lymphoma. Blood. 108:2957–2964. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Steidl C, Lee T, Shah SP, Farinha P, Han
G, Nayar T, Delaney A, Jones SJ, Iqbal J, Weisenburger DD, et al:
Tumor-associated macrophages and survival in classic Hodgkin's
lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 362:875–885. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|