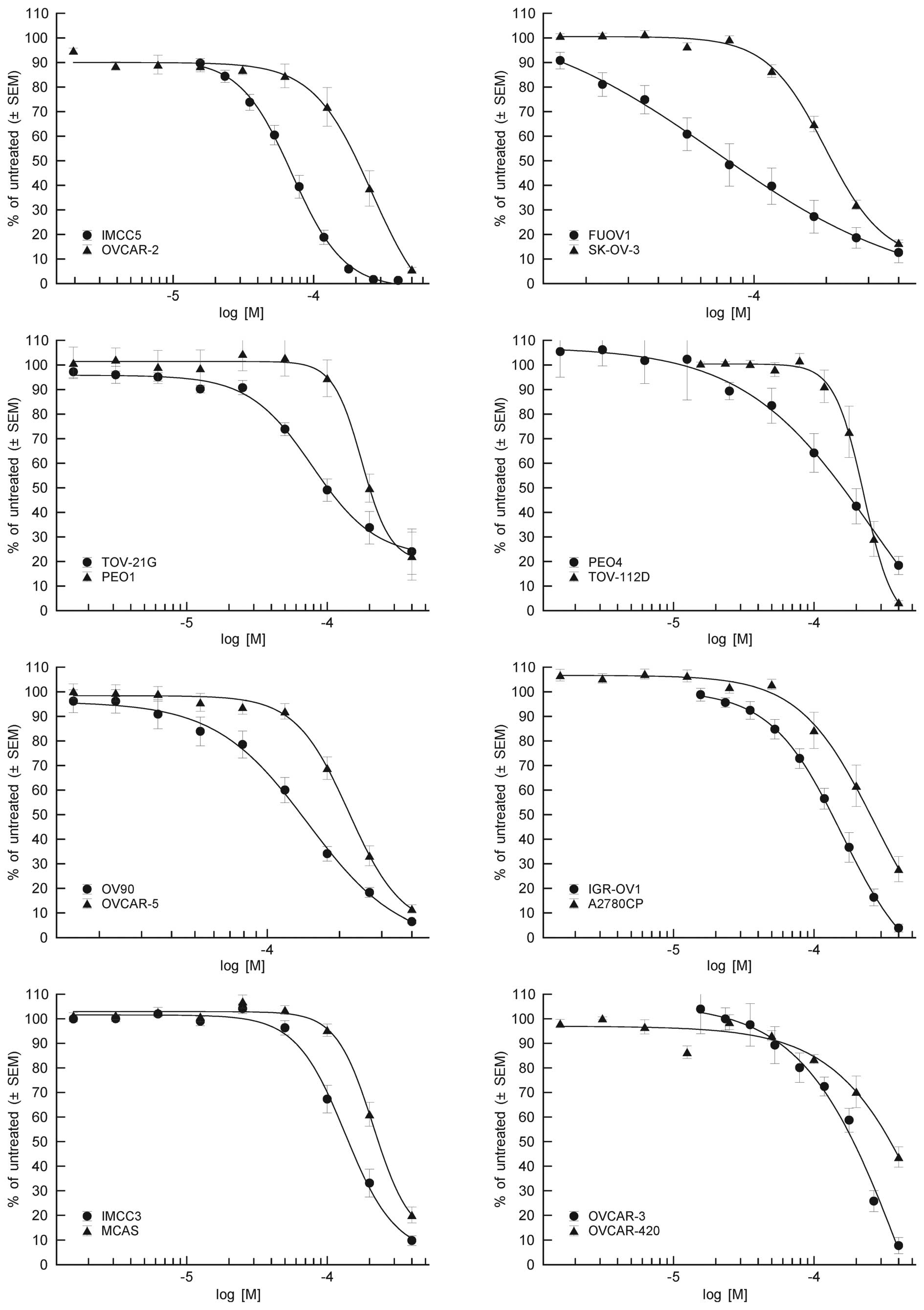
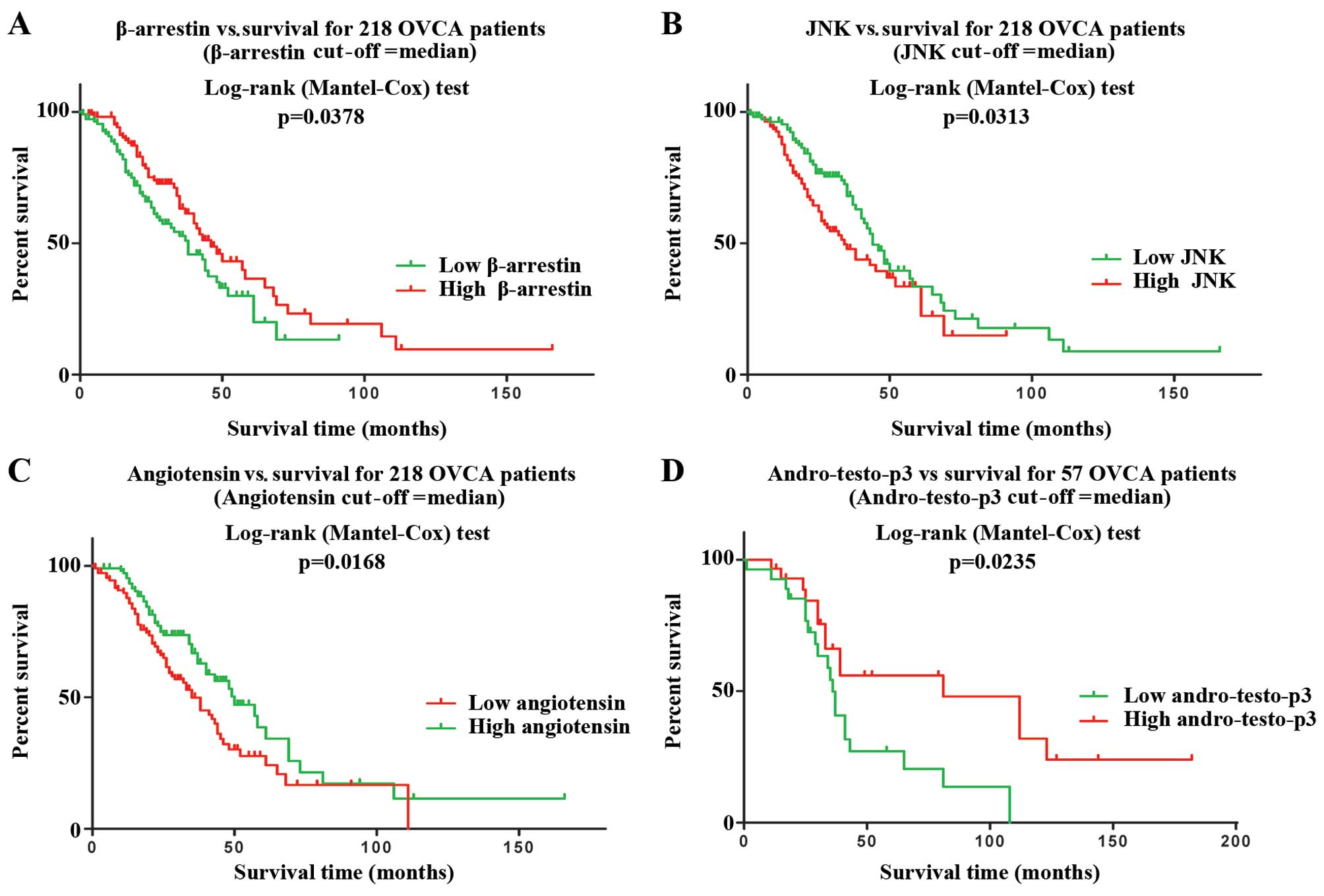
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ozols RF, Bundy BN, Greer BE, Fowler JM,
Clarke-Pearson D, Burger RA, Mannel RS, DeGeest K, Hartenbach EM
and Baergen R: Gynecologic Oncology Group: Phase III trial of
carboplatin and paclitaxel compared with cisplatin and paclitaxel
in patients with optimally resected stage III ovarian cancer: A
Gynecologic Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol. 21:3194–3200. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McGuire WP, Hoskins WJ, Brady MF, Kucera
PR, Partridge EE, Look KY, Clarke-Pearson DL and Davidson M:
Cyclophosphamide and cisplatin compared with paclitaxel and
cisplatin in patients with stage III and stage IV ovarian cancer. N
Engl J Med. 334:1–6. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu YJ, Neuwelt AJ, Muldoon LL and Neuwelt
EA: Acetaminophen enhances cisplatin- and paclitaxel-mediated
cytotoxicity to SKOV3 human ovarian carcinoma. Anticancer Res.
33:2391–2400. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Spooner JB and Harvey JG: The history and
usage of paracetamol. J Int Med Res. 4(Suppl 4): 1–6.
1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ameer B and Greenblatt DJ: Acetaminophen.
Ann Int Med. 87:202–209. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Botting RM: Mechanism of action of
acetaminophen: Is there a cyclooxygenase 3? Clin Infect Dis.
31(Suppl 5): S202–S210. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moysich KB, Mettlin C, Piver MS, Natarajan
N, Menezes RJ and Swede H: Regular use of analgesic drugs and
ovarian cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 10:903–906.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rodriguez-Burford C, Barnes MN,
Oelschlager DK, Myers RB, Talley LI, Partridge EE and Grizzle WE:
Effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs) on
ovarian carcinoma cell lines: Preclinical evaluation of NSAIDs as
chemopreventive agents. Clin Cancer Res. 8:202–209. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cramer DW, Harlow BL, Titus-Ernstoff L,
Bohlke K, Welch WR and Greenberg ER: Over-the-counter analgesics
and risk of ovarian cancer. Lancet. 351:104–107. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Baandrup L, Friis S, Dehlendorff C,
Andersen KK, Olsen JH and Kjaer SK: Prescription use of paracetamol
and risk for ovarian cancer in Denmark. J Natl Cancer Inst.
106:dju1112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lo-Ciganic WH, Zgibor JC, Bunker CH,
Moysich KB, Edwards RP and Ness RB: Aspirin, nonaspirin
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or acetaminophen and risk of
ovarian cancer. Epidemiology. 23:311–319. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hannibal CG, Rossing MA, Wicklund KG and
Cushing-Haugen KL: Analgesic drug use and risk of epithelial
ovarian cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 167:1430–1437. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Marchion DC, Cottrill HM, Xiong Y, Chen N,
Bicaku E, Fulp WJ, Bansal N, Chon HS, Stickles XB, Kamath SG, et
al: BAD phosphorylation determines ovarian cancer chemosensitivity
and patient survival. Clin Cancer Res. 17:6356–6366. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen DT, Nasir A, Culhane A, Venkataramu
C, Fulp W, Rubio R, Wang T, Agrawal D, McCarthy SM, Gruidl M, et
al: Proliferative genes dominate malignancy-risk gene signature in
histologically-normal breast tissue. Breast Cancer Res Treatment.
119:335–346. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tothill RW, Tinker AV, George J, Brown R,
Fox SB, Lade S, Johnson DS, Trivett MK, Etemadmoghadam D, Locandro
B, et al: Novel molecular subtypes of serous and endometrioid
ovarian cancer linked to clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res.
14:5198–5208. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Win S, Than TA, Han D, Petrovic LM and
Kaplowitz N: c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-dependent acute liver
injury from acetaminophen or tumor necrosis factor (TNF) requires
mitochondrial Sab protein expression in mice. J Biol Chem.
286:35071–35078. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Johnson GL and Nakamura K: The c-jun
kinase/stress-activated pathway: Regulation, function and role in
human disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1773:1341–1348. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Weston CR and Davis RJ: The JNK signal
transduction pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 19:142–149. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Czaja MJ: Cell signaling in oxidative
stress-induced liver injury. Semin Liver Dis. 27:378–389. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Han D, Ybanez MD, Ahmadi S, Yeh K and
Kaplowitz N: Redox regulation of tumor necrosis factor signaling.
Antioxidants Redox Signal. 11:2245–2263. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gunawan BK, Liu ZX, Han D, Hanawa N,
Gaarde WA and Kaplowitz N: c-Jun N-terminal kinase plays a major
role in murine acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Gastroenterology.
131:165–178. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shibata W, Maeda S, Hikiba Y, Yanai A,
Sakamoto K, Nakagawa H, Ogura K, Karin M and Omata M: c-Jun
NH2-terminal kinase 1 is a critical regulator for the development
of gastric cancer in mice. Cancer Res. 68:5031–5039. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vivas-Mejia P, Benito JM, Fernandez A, Han
HD, Mangala L, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Chavez-Reyes A, Lin YG, Carey
MS, Nick AM, et al: c-Jun-NH2-kinase-1 inhibition leads
to antitumor activity in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
16:184–194. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mansouri A, Ridgway LD, Korapati AL, Zhang
Q, Tian L, Wang Y, Siddik ZH, Mills GB and Claret FX: Sustained
activation of JNK/p38 MAPK pathways in response to cisplatin leads
to Fas ligand induction and cell death in ovarian carcinoma cells.
J Biol Chem. 278:19245–19256. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|