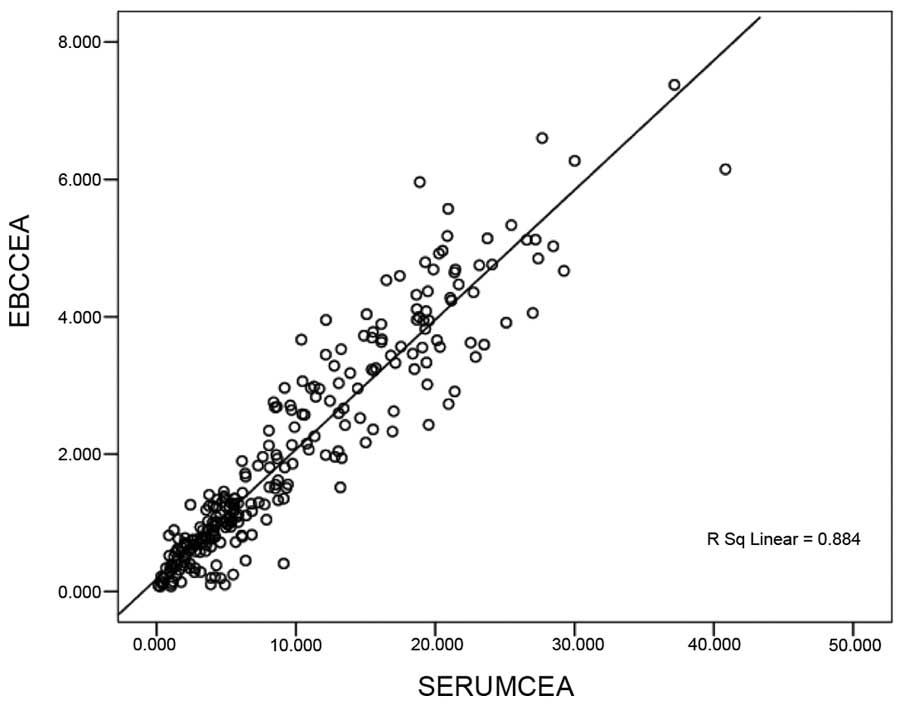
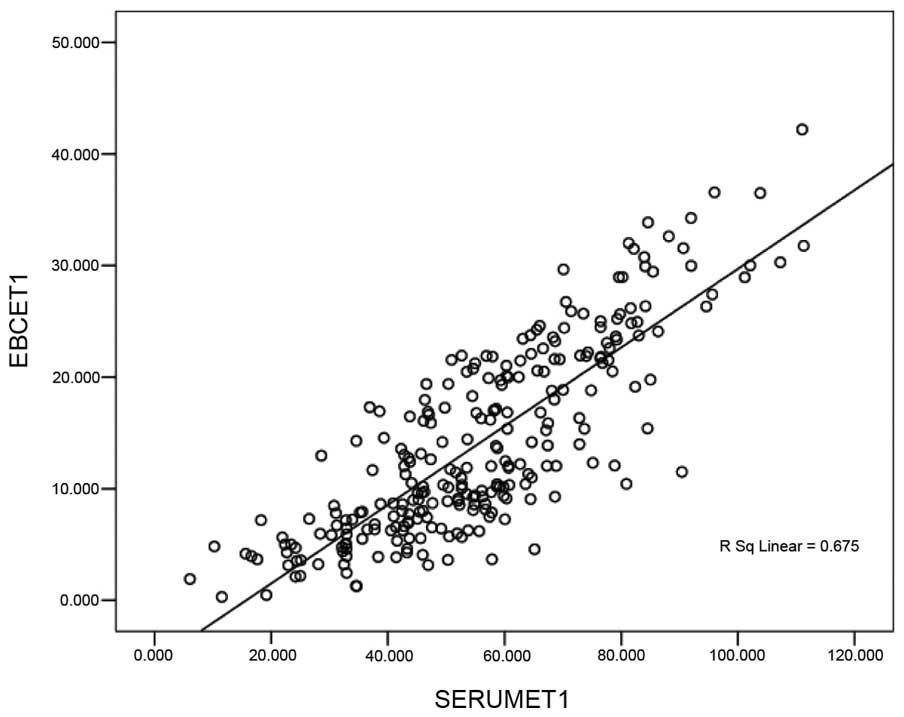
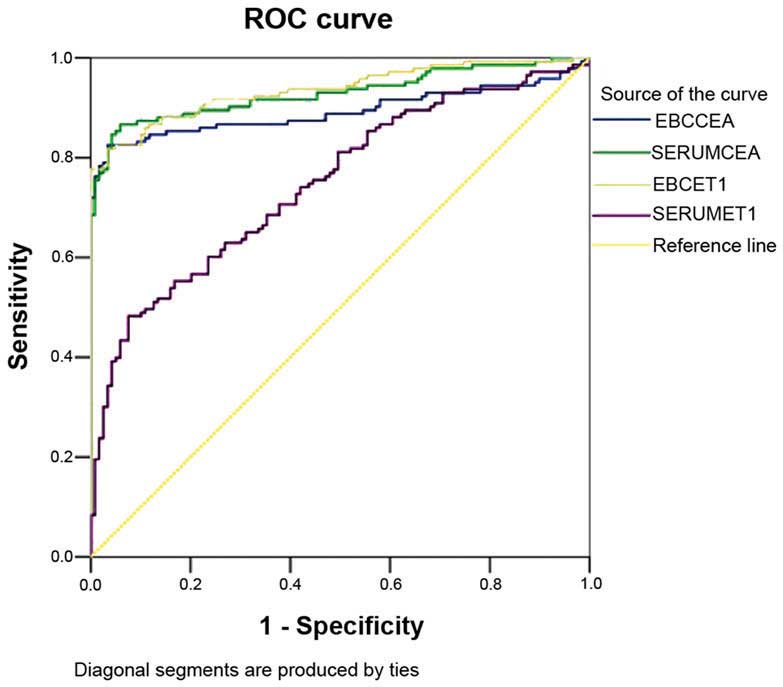
|
1
|
Eberini I, Gianazza E, Pastorino U and
Sirtori C: Assessment of individual lung cancer risk by the
proteomic analysis of exhaled breath condensate. Expert Opin Med
Diagn. 2:1309–1315. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pillai RN and Ramalingam SS: Advances in
the diagnosis and treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Mol
Cancer Ther. 13:557–564. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Padda SK, Burt BM, Trakul N and Wakelee
HA: Early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: Surgery, stereotactic
radiosurgery and individualized adjuvant therapy. Semin Oncol.
41:40–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dalaveris E, Kerenidi T,
Katsabeki-Katsafli A, Kiropoulos T, Tanou K, Gourgoulianis KI and
Kostikas K: VEGF, TNF-alpha and 8-isoprostane levels in exhaled
breath condensate and serum of patients with lung cancer. Lung
Cancer. 64:219–225. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ciebiada M, Górski P and Antczak A:
Eicosanoids in exhaled breath condensate and bronchoalveolar lavage
fluid of patients with primary lung cancer. Dis Markers.
32:329–335. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Antus B and Barta I: Exhaled breath
condensate pH in patients with lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
75:178–180. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chan HP, Lewis C and Thomas PS: Exhaled
breath analysis: Novel approach for early detection of lung cancer.
Lung Cancer. 63:164–168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mozzoni P, Banda I, Goldoni M, Corradi M,
Tiseo M, Acampa O, Balestra V, Ampollini L, Casalini A, Carbognani
P and Mutti A: Plasma and EBC microRNAs as early biomarkers of
non-small-cell lung cancer. Biomarkers. 18:679–686. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stathopoulos D, Loukides S and Syrigos K:
8-Isoprostane in exhaled breath condensate of patients with
non-small cell lung cancer: The effect of chemotherapy. Anticancer
Res. 34:5143–5145. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brussino L, Culla B, Bucca C, Giobbe R,
Boita M, Isaia G, Heffler E, Oliaro A, Filosso P and Rolla G:
Inflammatory cytokines and VEGF measured in exhaled breath
condensate are correlated with tumor mass in non-small cell lung
cancer. J Breath Res. 8:0271102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dassanayake DL, Muthunayake TM,
Senevirathna KH and Siribaddana A: Staging of lung cancer in a
tertiary care setting in Sri Lanka, using TNM 7th edition. A
comparison against TNM6. BMC Res Notes. 5:1432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fumagalli M, Ferrari F, Luisetti M, Stolk
J, Hiemstra PS, Capuano D, Viglio S, Fregonese L, Cerveri I, Corana
F, et al: Profiling the proteome of exhaled breath condensate in
healthy smokers and COPD patients by LC-MS/MS. Int J Mol Sci.
13:13894–13910. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu HC, Lu MC, Lin YC, Wu TC, Hsu JY, Jan
MS and Chen CM: Differences in IL-8 in serum and exhaled breath
condensate from patients with exacerbated COPD or asthma attacks. J
Formos Med Assoc. 113:908–914. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee AL, Button BM, Denehy L, Roberts S,
Bamford T, Mu FT, Mifsud N, Stirling R and Wilson JW: Exhaled
breath condensate pepsin: Potential noninvasive test for
gastroesophageal reflux in COPD and bronchiectasis. Respir Care.
60:244–250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Corhay JL, Moermans C, Henket M, Nguyen
Dang D, Duysinx B and Louis R: Increased of exhaled breath
condensate neutrophil chemotaxis in acute exacerbation of COPD.
Respir Res. 15:1152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stefanska J, Sarniak A, Wlodarczyk A,
Sokolowska M, Doniec Z, Bialasiewicz P, Nowak D and Pawliczak R:
Hydrogen peroxide and nitrite reduction in exhaled breath
condensate of COPD patients. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 25:343–348. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xiao P, Chen JR, Zhou F, Lu CX, Yang Q,
Tao GH, Tao YJ and Chen JL: Methylation of P16 in exhaled breath
condensate for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung
Cancer. 83:56–60. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gessner C, Kuhn H, Toepfer K,
Hammerschmidt S, Schauer J and Wirtz H: Detection of p53 gene
mutations in exhaled breath condensate of non-small cell lung
cancer patients. Lung Cancer. 43:215–222. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zou Y, Wang L, Zhao C, Hu Y, Xu S, Ying K,
Wang P and Chen X: CEA, SCC and NSE levels in exhaled breath
condensate-possible markers for early detection of lung cancer. J
Breath Res. 7:0471012013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Okamura K, Takayama K, Izumi M, Harada T,
Furuyama K and Nakanishi Y: Diagnostic value of CEA and CYFRA 21-1
tumor markers in primary lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 80:45–49. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cedrés S, Nuñez I, Longo M, Martinez P,
Checa E, Torrejón D and Felip E: Serum tumor markers CEA, CYFRA21-1
and CA-125 are associated with worse prognosis in advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Clin Lung Cancer. 12:172–179.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Grunnet M and Sorensen JB:
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) as tumor marker in lung cancer. Lung
Cancer. 76:138–143. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang WM, Zhou J and Ye QJ: Endothelin-1
enhances proliferation of lung cancer cells by increasing
intracellular free Ca2+. Life Sci. 82:764–771. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Carpagnano GE, Foschino-Barbaro MP, Resta
O, Gramiccioni E and Carpagnano F: Endothelin-1 is increased in the
breath condensate of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.
Oncology. 66:180–184. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Boldrini L, Gisfredi S, Ursino S, Lucchi
M, Melfi F, Mussi A, Basolo F and Fontanini G: Tumour necrosis
factor-alpha: Prognostic role and relationship with interleukin-8
and endothelin-1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Med.
17:887–892. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|