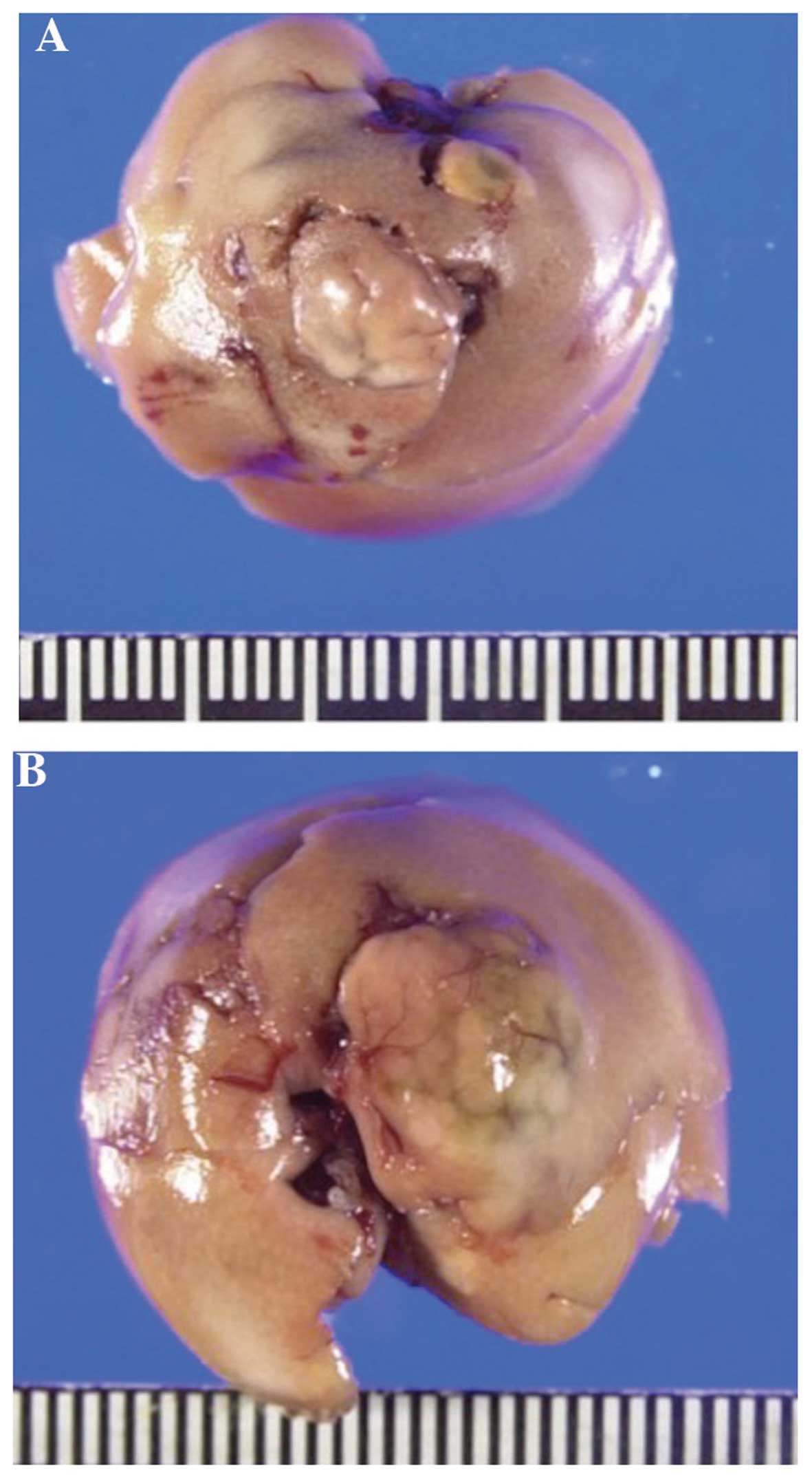
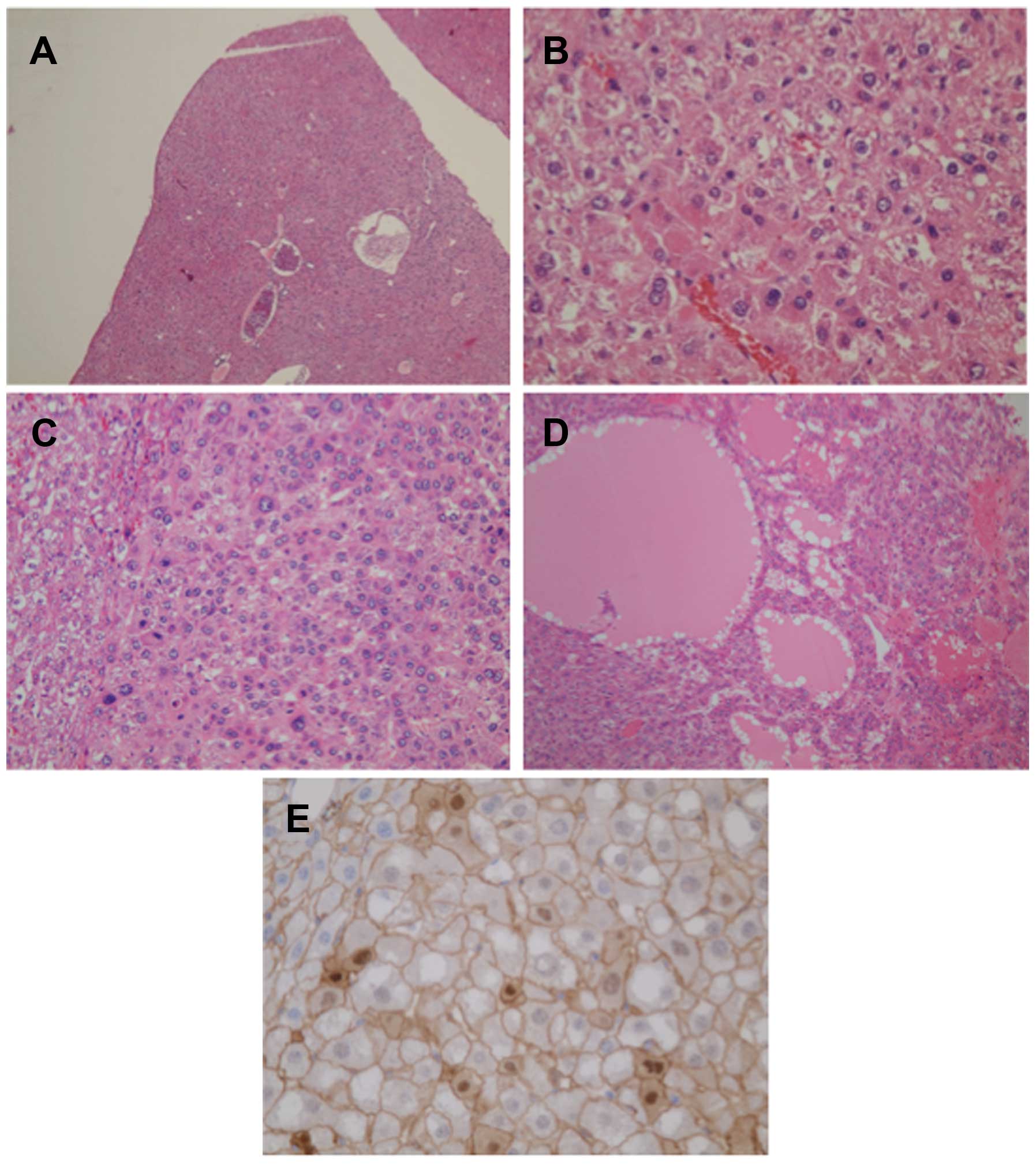
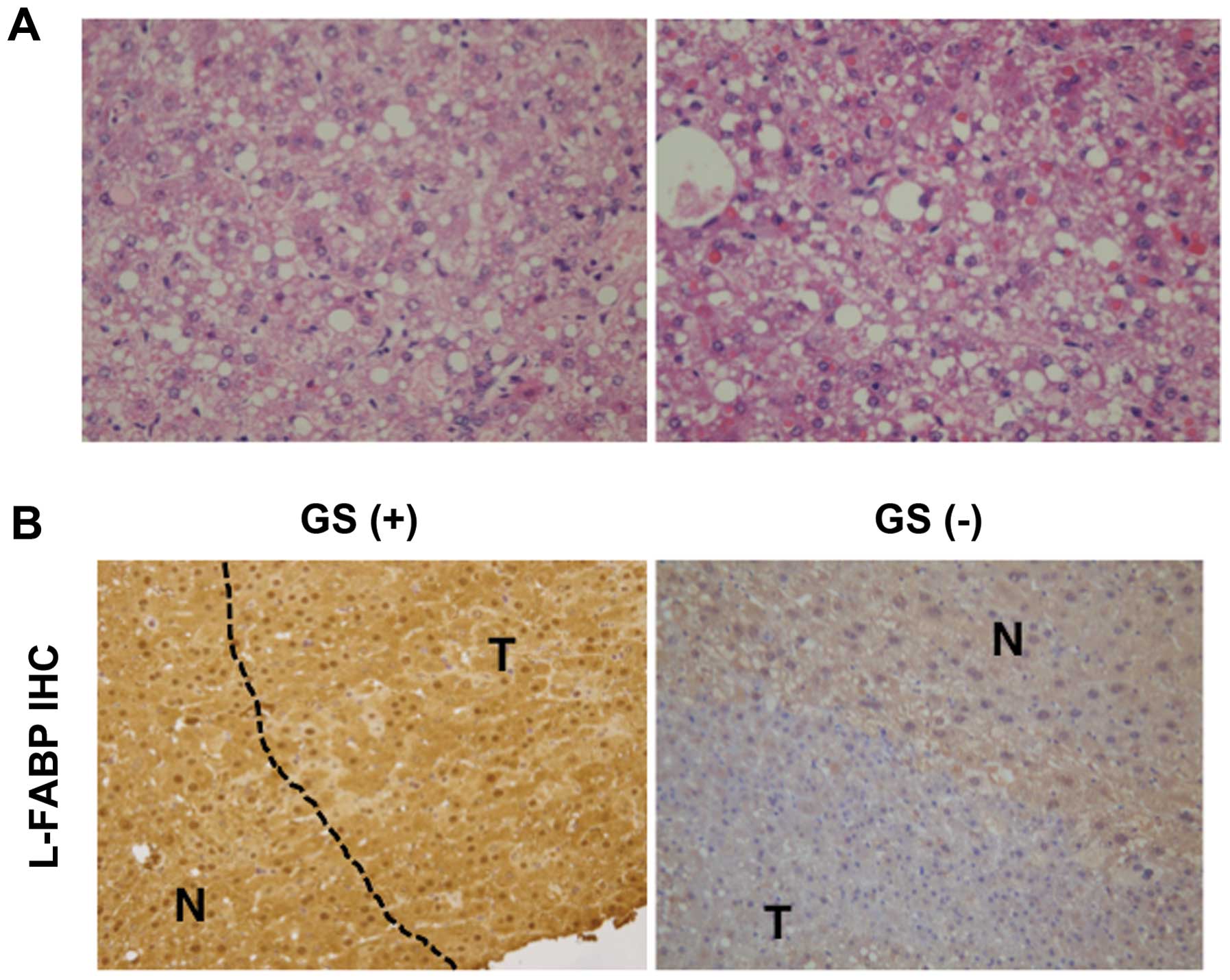
|
1
|
Miura T, Suzuki W, Ishihara E, Arai I,
Ishida H, Seino Y and Tanigawa K: Impairment of insulin-stimulated
GLUT4 translocation in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue in the
Tsumura Suzuki obese diabetic mouse: A new genetic animal model of
type 2 diabetes. Eur J Endocrinol. 145:785–790. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Suzuki W, Iizuka S, Tabuchi M, Funo S,
Yanagisawa T, Kimura M, Sato T, Endo T and Kawamura H: A new mouse
model of spontaneous diabetes derived from ddY strain. Exp Anim.
48:181–189. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Takahashi A, Tabuchi M, Suzuki W, Iizuka
S, Nagata M, Ikeya Y, Takeda S, Shimada T and Aburada M: Insulin
resistance and low sympathetic nerve activity in the Tsumura Suzuki
obese diabetic mouse: A new model of spontaneous type 2 diabetes
mellitus and obesity. Metabolism. 55:1664–1669. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nishida T, Tsuneyama K, Fujimoto M, Nomoto
K, Hayashi S, Miwa S, Nakajima T, Nakanishi Y, Sasaki Y, Suzuki W,
et al: Spontaneous onset of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and
hepatocellular carcinoma in a mouse model of metabolic syndrome.
Lab Invest. 93:230–241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ono M, Okamoto N and Saibara T: The latest
idea in NAFLD/NASH pathogenesis. Clin J Gastroenterol. 3:263–270.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bhala N, Jouness RI and Bugianesi E:
Epidemiology and natural history of patients with NAFLD. Curr Pharm
Des. 19:5169–5176. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ratziu V, Bonyhay L, Di Martino V,
Charlotte F, Cavallaro L, Sayegh-Tainturier MH, Giral P, Grimaldi
A, Opolon P and Poynard T: Survival, liver failure and
hepatocellular carcinoma in obesity-related cryptogenic cirrhosis.
Hepatology. 35:1485–1493. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tremosini S, Forner A, Boix L, Vilana R,
Bianchi L, Reig M, Rimola J, Rodríguez-Lope C, Ayuso C, Solé M and
Bruix J: Prospective validation of an immunohistochemical panel
(glypican 3, heat shock protein 70 and glutamine synthetase) in
liver biopsies for diagnosis of very early hepatocellular
carcinoma. Gut. 61:1481–1487. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bellamy CO, Maxwell RS, Prost S, Azodo IA,
Powell JJ and Manning JR: The value of immunophenotyping
hepatocellular adenomas: Consecutive resections at one UK centre.
Histopathology. 62:431–445. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Webb JT and Brown GW Jr: Glutamine
synthetase: Assimilatory role in livers as related to urea
retention in marine chondrichthyes. Science. 208:293–295. 1980.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zeng G, Apte U, Cieply B, Singh S and
Monga SP: siRNA-mediated beta-catenin knockdown in human hepatoma
cells results in decreased growth and survival. Neoplasia.
9:951–959. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lachenmayer A, Alsinet C, Savic R,
Cabellos L, Toffanin S, Hoshida Y, Villanueva A, Minguez B, Newell
P, Tsai HW, et al: Wnt-pathway activation in two molecular classes
of hepatocellular carcinoma and experimental modulation by
sorafenib. Clin Cancer Res. 18:4997–5007. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Duan XY, Zhang L, Fan JG and Qiao L: NAFLD
leads to liver cancer: Do we have sufficient evidence? Cancer Lett.
345:230–234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nakanishi Y, Tsuneyama K, Nomoto K, et al:
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma in
galectin-3 knockout mice. Hepatology Research. 38:1241–1251.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zucmann-Rossi J, Jeannot E, Nhieu JT,
Scoazec JY, Guettier C, Rebouissou S, Bacq Y, Leteurtre E, Paradis
V, Michalak S, et al: Genotype-phenotype correlation in
hepatocellular carcinoma: New classification and relationship with
HCC. Hepatology. 43:515–524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zucmann-Rossi J, Benhamouche S, Godard C,
Boyault S, Grimber G, Balabaud C, Cunha AS, Bioulac-Sage P and
Perret C: Differential effects of inactivated Axin1 and activated
beta-catenin mutations in human hepatocellular carcinomas.
Oncogene. 26:774–780. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bioulac-Sage P, Blanc JF, Rebouissou S,
Balabaud C and Zucmann-Rossi J: Genotype phenotype classification
of hepatocellular adenoma. World J Gastroenterol. 13:2649–2654.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Akiyama TE, Ward JM and Gonzalez FJ:
Regulation of the liver fatty acid-binding protein gene by
hepatocyte nuclear factor 1alpha (HNF1alpha). Alterations in fatty
acid homeostasis in HNF1alpha-deficient mice. J Biol Chem.
275:27117–27122. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Atshaves BP, Martin GG, Hostetler HA,
McIntosh AL, Kier AB and Schroeder F: Liver fatty acid-binding
protein and obesity. J Nutr Biochem. 21:1015–1032. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Inoue M, Takahashi Y, Fujii T, Kitagawa M
and Fukusato T: Significance of downregulation of liver fatty
acid-binding protein in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:17541–17551. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Alpini G, Elias I, Glaser SS, Rodgers RE,
Phinizy JL, Robertson WE, Francis H, Lasater J, Richards M and
LeSage GD: Gamma-Interferon inhibits secretin-induced choleresis
and cholangiocyte proliferation in a murine model of cirrhosis. J
Hepatol. 27:371–380. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|