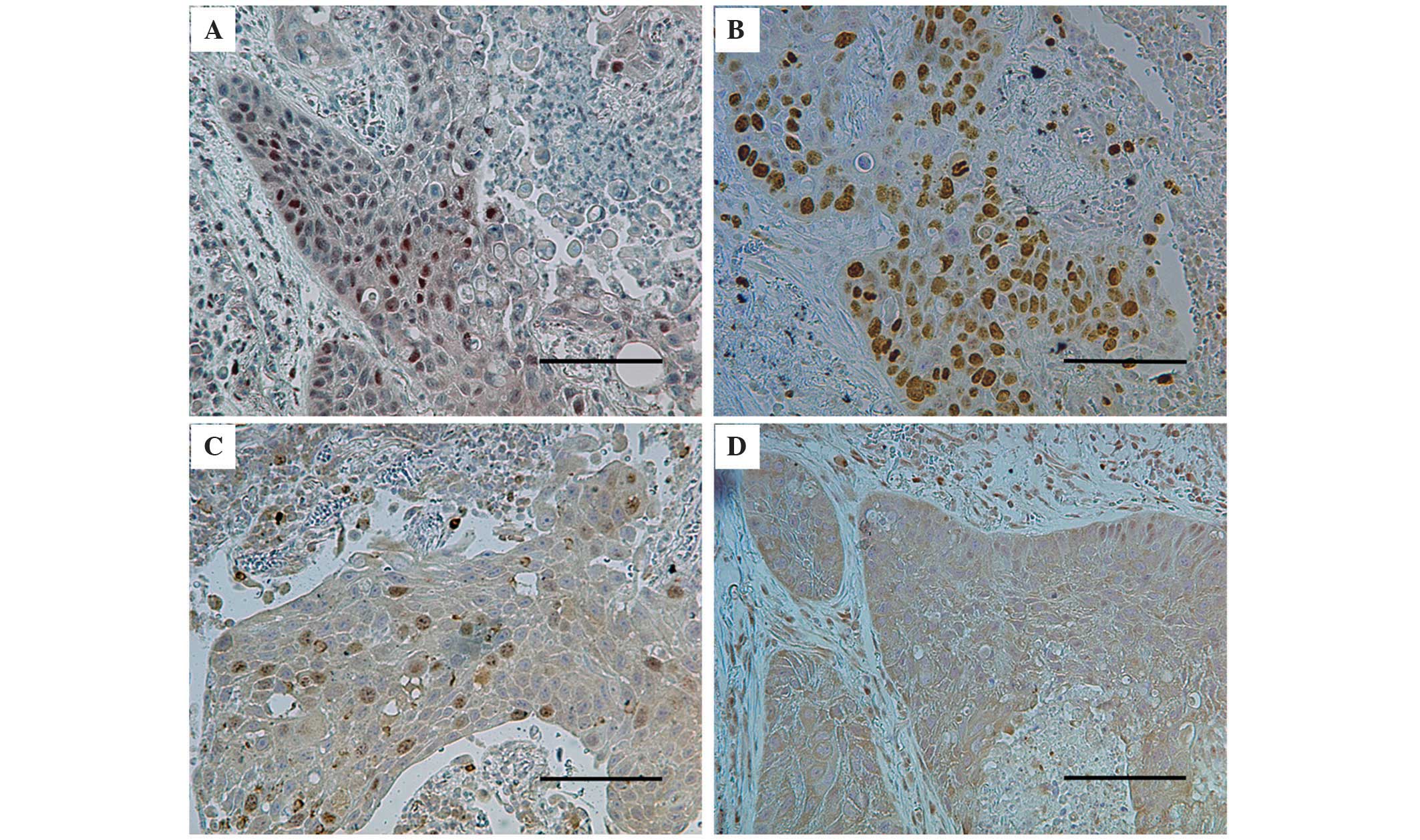
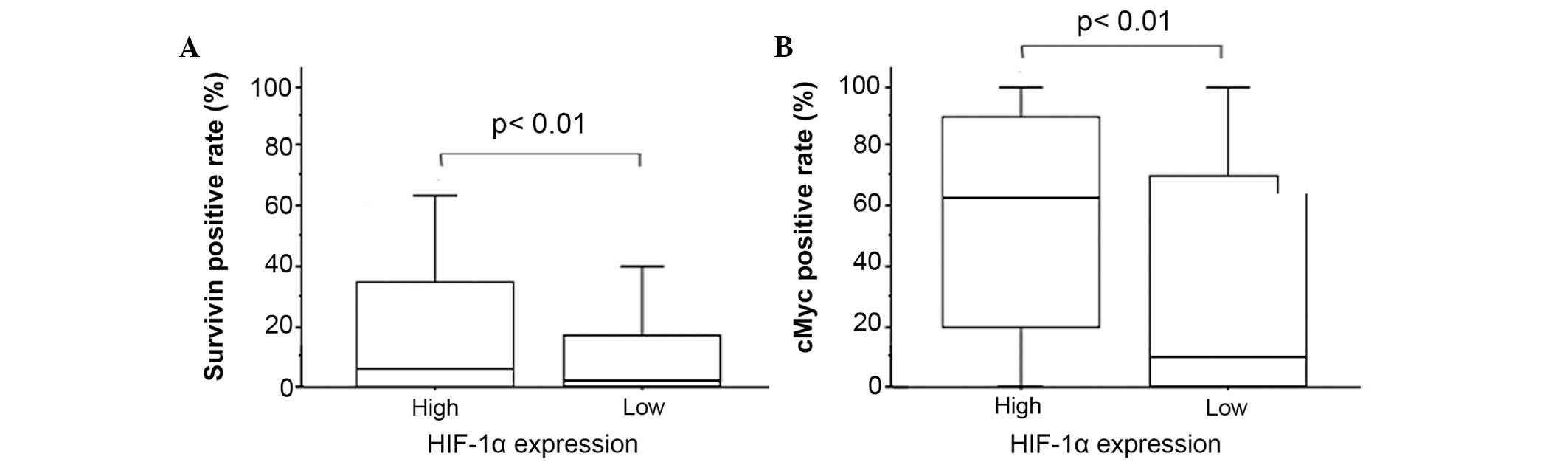
|
1
|
Semenza GL: Expression of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1: Mechanisms and consequences. Biochem
Pharmacol. 59:47–53. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Semenza GL: Targeting HIF-1 for cancer
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:721–732. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thrash-Bingham CA and Tartof KD: aHIF: A
natural antisense transcript overexpressed in human renal cancer
and during hypoxia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 91:143–151. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Harada H, Itasaka S, Kizaka-Kondoh S,
Shibuya K, Morinibu A, Shinomiya K and Hiraoka M: The Akt/mTOR
pathway assures the synthesis of HIF-1alpha protein in a glucose-
and reoxygenation-dependent manner in irradiated tumors. J Biol
Chem. 284:5332–5342. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kaelin WG Jr: The won Hippel-Lindau tumor
suppressor protein: O2 sensing and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:865–873. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Simon F, Bockhorn M, Praha C, Baba HA,
Broelsch CE, Frilling A and Weber F: Deregulation of HIF1-alpha and
hypoxia-regulated pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma and
corresponding non-malignant liver tissue-influence of a modulated
host stroma on the prognosis of HCC. Langenbecks Arch Surg.
395:395–405. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Giles RH, Lolkema MP, Snijckers CM,
Belderbos M, van der Groep P, Mans DA, van Beest M, van Noort M,
Goldschmeding R, van Diest PJ, et al: Interplay between
VHL/HIF1alpha and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways during colorectal
tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 25:3065–3070. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim SJ, Rabbani ZN, Dewhirst MW,
Vujaskovic Z, Vollmer RT, Schreiber EG, Oosterwijk E and Kelley MJ:
Expression of HIF-1alpha, CA IX, VEGF, and MMP-9 in surgically
resected non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 49:325–335. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Volm M and Koomägi R: Hypoxia-inducible
factor (HIF-1) and its relationship to apoptosis and proliferation
in lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 20:1527–1533. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST and Giles
FJ: Survivin: Key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel
target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5000–5005.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu N, Sun Y, Zhao N and Chen L: Role of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and survivin in oxygen-induced
retinopathy in mice. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:6814–6819.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu XY, Fu ZX and Wang XH: Effect of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α on survivin in colorectal cancer. Mol
Med Rep. 3:409–415. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen XQ, Zhao CL and Li W: Effect of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha on transcription of survivin in
non-small cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:292009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shinohara ET, Gonzalez A, Massion PP, Chen
H, Li M, Freyer AS, Olson SJ, Andersen JJ, Shyr Y, Carbone DP, et
al: Nuclear survivin predicts recurrence and poor survival in
patients with resected nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer.
103:1685–1692. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brennan DJ, Rexhepaj E, O'Brien SL,
McSherry E, O'Connor DP, Fagan A, Culhane AC, Higgins DG, Jirstrom
K, Millikan RC, et al: Altered cytoplasmic-to-nuclear ratio of
surivin is a prognostic indicator in breast cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:2681–2689. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Koshiji M, Kageyama Y, Pete EA, Horikawa
I, Barret JC and Huang LE: HIF-1alpha induces cell cycle arrest by
functionally counteracting Myc. EMBO J. 23:1949–1956. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pelengaris S, Khan M and Evan G: c-Myc:
More than just a matter of life and death. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:764–776. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dang CV, Resar LM, Emison E, Kim S, Li Q,
Prescott JE, Wonsey D and Zeller K: Function of the c-Myc oncogenec
transcription factor. Exp Cell Res. 253:63–77. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, Giroux
DJ, Groome PA, Rami-Porta R, Postmus PE, Rusch V and Sobin L:
International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer
International Staging Committee; Participating Institutions: The
IASLC lung cancer staging project: Proposals for the revision of
the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the
TNM classification of malignant tumors. J Thorac Oncol. 2:706–714.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Karetsi E, Ioannou MG, Kerenidi T, Minas
M, Molyvdas PA, Gourgoulianis KL and Paraskeva E: Differential
expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in non-small cell lung
cancer and small cell lung cancer. Clinics (Sao Paulo).
67:1373–1378. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kobayashi M, Hyang CL, Sonobe M, Kikuchi
R, Ishikawa M, Kitamura J, Miyahara R, Menju T, Iwakiri S, Itoi K,
et al: Intratumoral Wnt2B expression affects tumor proliferation
and survival in malignant pleural mesothelioma patients. Exp Ther
Med. 3:952–958. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dang CV, Kim JW, Gao P and Yustein J: The
interplay between MYC and HIF in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:51–56.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang LE: Carrot and stick: HIF-alpha
engages c-Myc in hypoxic adaptation. Cell Death Differ. 15:672–677.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Semenza GL: Evaluation of HIF-1 inhibitors
as anticancer agents. Drug Discov Today. 12:853–859. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fujita M, Yasuda M, Kitatani K, Miyazawa
M, Hirabayashi K, Takekoshi S, Iida T, Hirasawa T, Murakami M,
Mikami M, et al: An up-to-date anti-cancer treatment strategy
focusing on HIF-1alpha suppression: Its application for refractory
ovarian cancer. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 40:139–142. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|