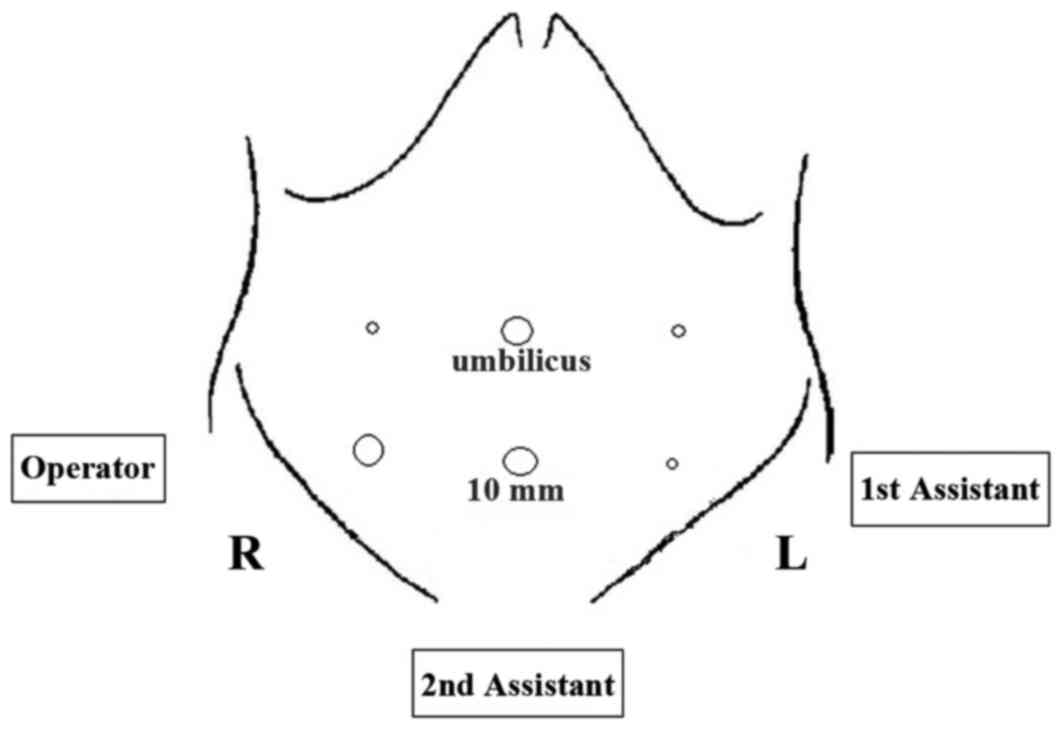
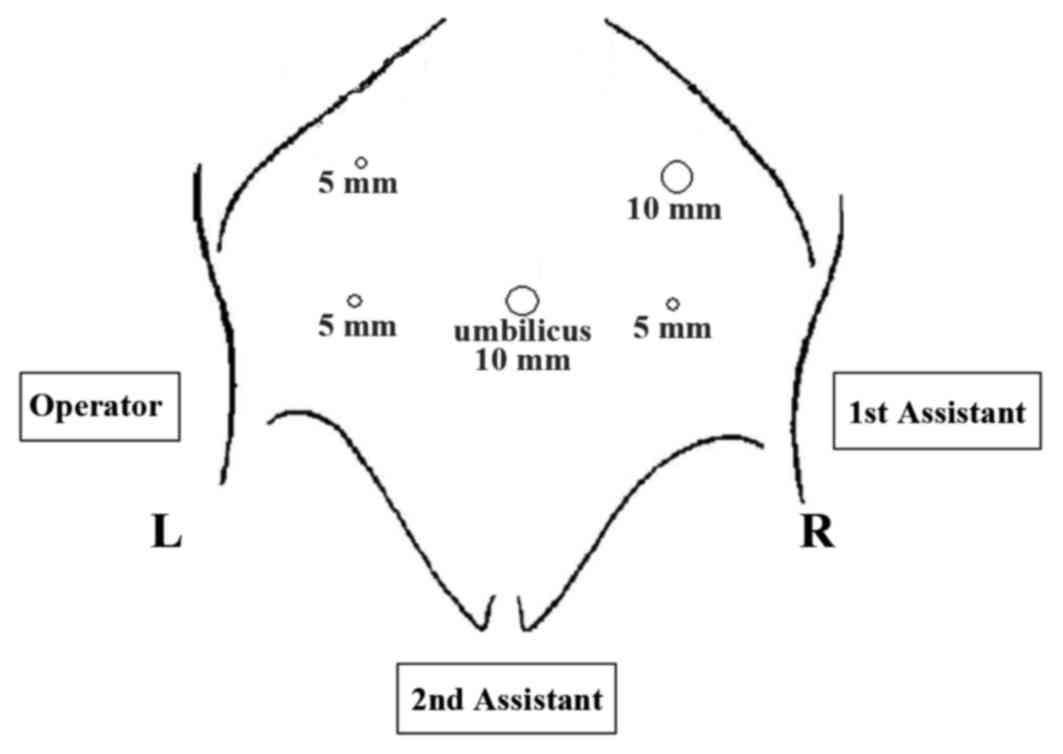
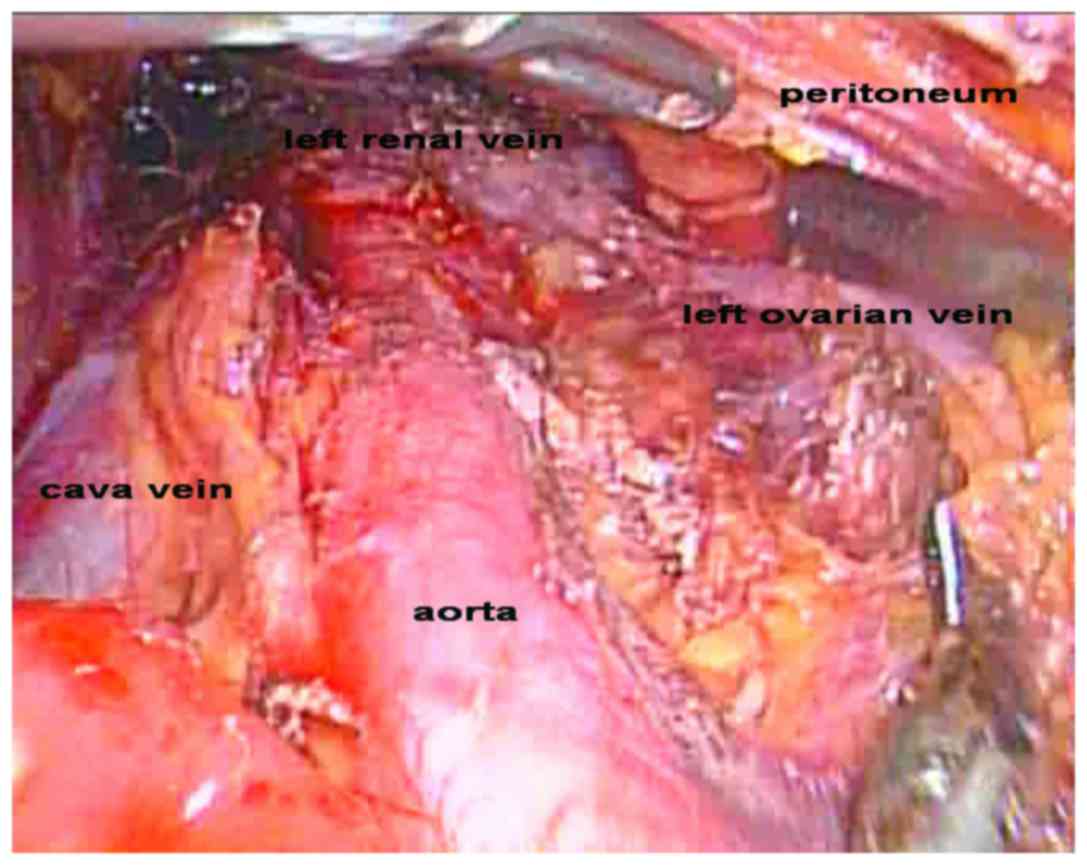
Article
Laparoscopic local extraperitoneal para-aortic lymphadenectomy: Description of a novel technique
- Authors:
- Xuyin Zhang
- Jingxin Ding
- Keqin Hua
-
View Affiliations / Copyright
Affiliations:
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200090, P.R. China
-
Pages:
377-380
|
Published online on:
January 20, 2017
https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2017.1136
- Expand metrics +
Metrics:
Total
Views: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
Metrics:
Total PDF Downloads: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
This article is mentioned in:
Abstract
The aim of the present study was to introduce and describe a novel technique, which has been termed ‘laparoscopic local extraperitoneal para-aortic lymphadenectomy’, and to evaluate its feasibility and safety. In this retrospective case study, a series of 21 patients were selected who underwent laparoscopic local extraperitoneal para‑aortic lymphadenectomy for gynecological malignancies between March and August 2014 at the Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, China. All the surgical procedures were performed by the same operational team. Patients' data were collected retrospectively, and the characteristics included patient age, body mass index (BMI), tumor stage, tumor grade, blood loss, operative time (laparoscopic local extraperitoneal para‑aortic lymphadenectomy), length of hospital stay, intraoperative and postoperative complications, pathology, lymph node count and lymph node status. A total of 21 patients underwent laparoscopic local extraperitoneal para‑aortic lymphadenectomy. The median patient age was 52 years (range, 45‑71 years); the median BMI was 24.8 kg/m2 (range, 22.2‑32.4 kg/m2); the median operating time for the para‑aortic lymphadenectomy was 70 min (range, 58‑95 min); and the median estimated blood loss of the total surgery was 200 ml (range, 100‑600 ml). No patient required a blood transfusion during the operation. The median length of hospital stay was 7 days (range, 5‑9 days), and the median number of para‑aortic lymph nodes was measured as 12 (range, 7‑17). Postoperative complications included one patient with chylous ascites, who responded to conservative management with intravenous somatostatin. In conclusion, the present study has demonstrated that laparoscopic local extraperitoneal para‑aortic lymphadenectomy, which avoids interference of the bowels during surgery, is safe and practical.
View References
|
1
|
Vasilev SA and McGonigle KF:
Extraperitoneal laparoscopic para-aortic lymph node dissection.
Gynecol Oncol. 61:315–320. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Iacoponi S, De Santiago J, Diestro MD,
Hernandez A and Zapardiel I: Single-port laparoscopic
extraperitoneal para-aortic lymphadenectomy. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
23:1712–1716. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pakish J, Soliman PT, Frumovitz M, Westin
SN, Schmeler KM, Reis RD, Munsell MF and Ramirez PT: A comparison
of extraperitoneal versus transperitoneal laparoscopic or robotic
para-aortic lymphadenectomy for staging ofendometrial carcinoma.
Gynecol Oncol. 132:366–371. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Escobar PF, Fader AN, Rasool N and
Espalliat LR: Single-port laparoscopic pelvic and para-aortic lymph
node sampling or lymphadenectomy: Development of a technique and
instrumentation. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 20:1268–1273. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kavallaris A, Kalogiannidis I, Chalvatzas
N, Hornemann A, Bohlmann MK and Diedrich K: Standardized technique
of laparoscopic pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy in
gynecologic cancer optimizes the perioperative outcomes. Arch
Gynecol Obstet. 283:1373–1380. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gouy S, Uzan C, Scherier S, Gauthier T,
Bentivegna E, Kane A, Morice P and Marchal F: Single-port
laparoscopy and extraperitoneal para-aortic lymphadenectomy for
locally advanced cervical cancer: Assessment after 52 consecutive
patients. Surg Endosc. 28:249–256. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|