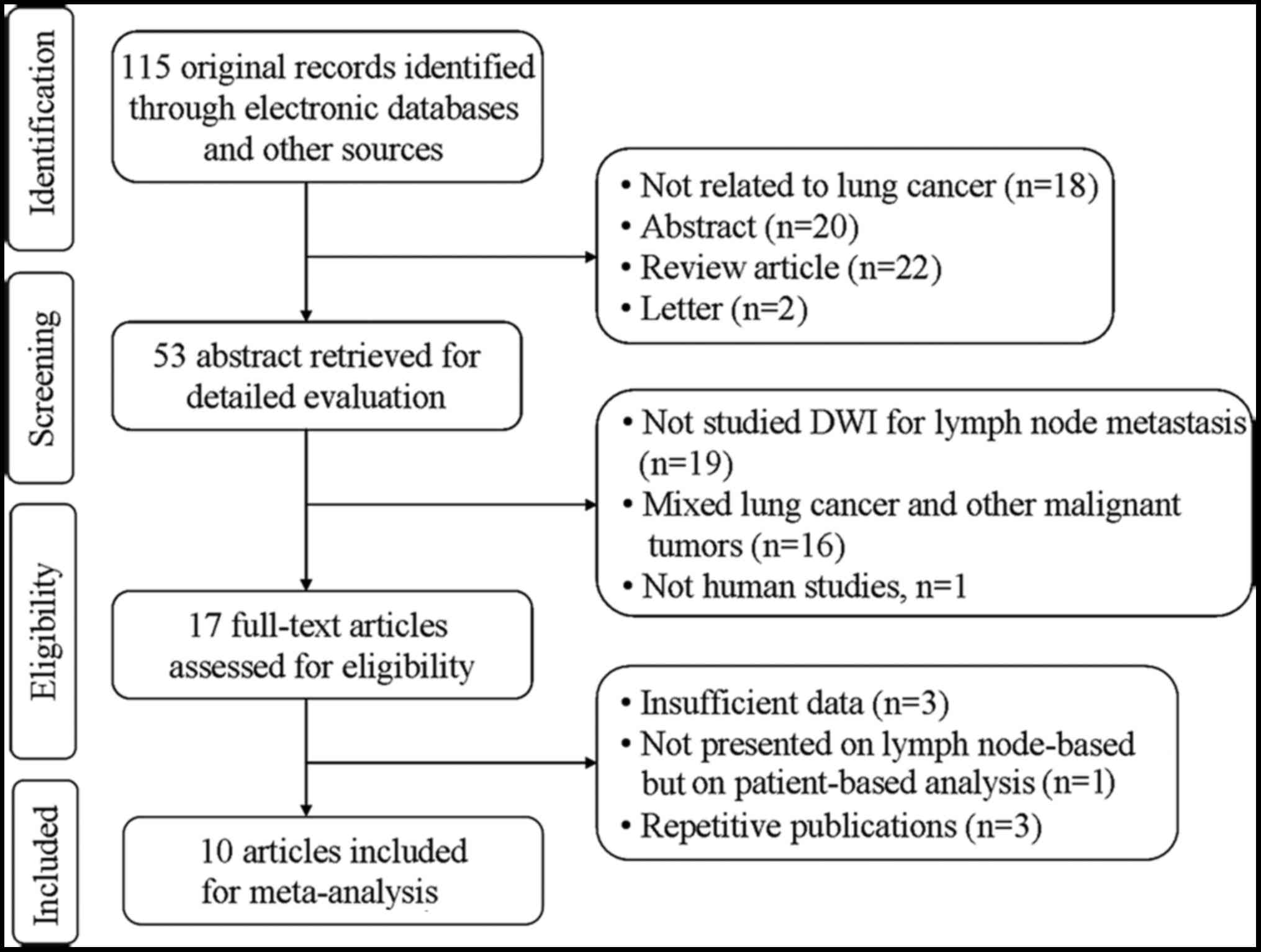
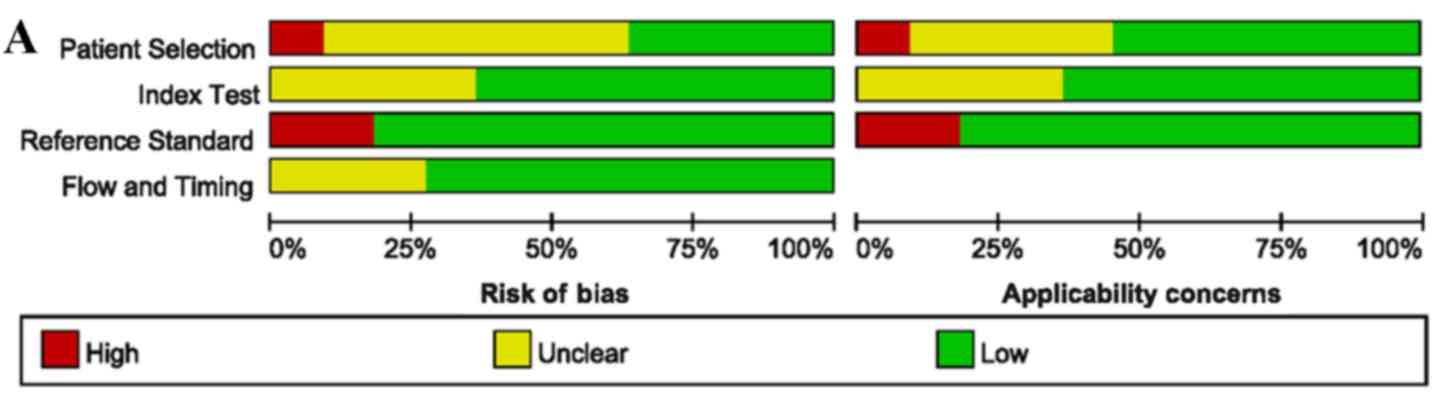
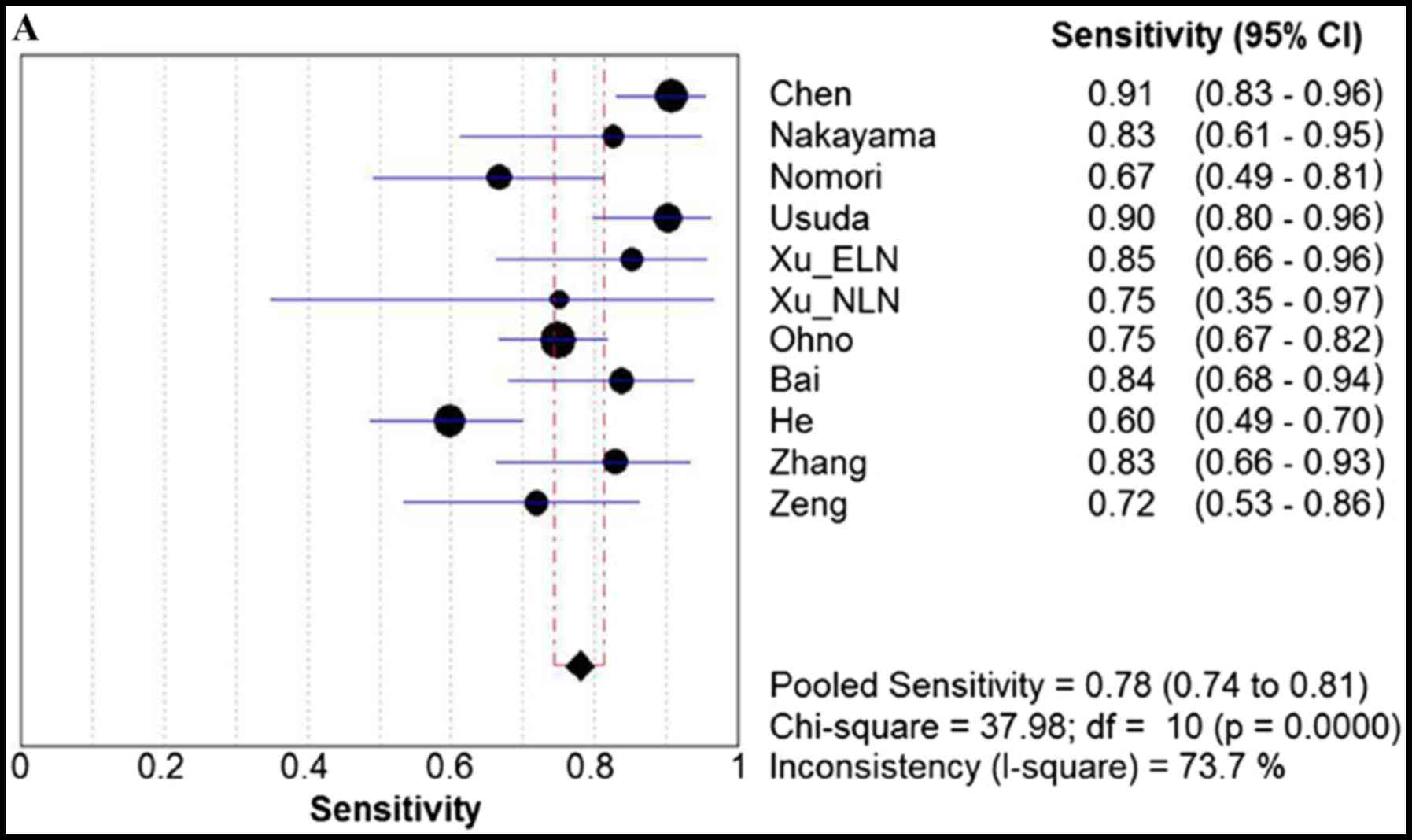
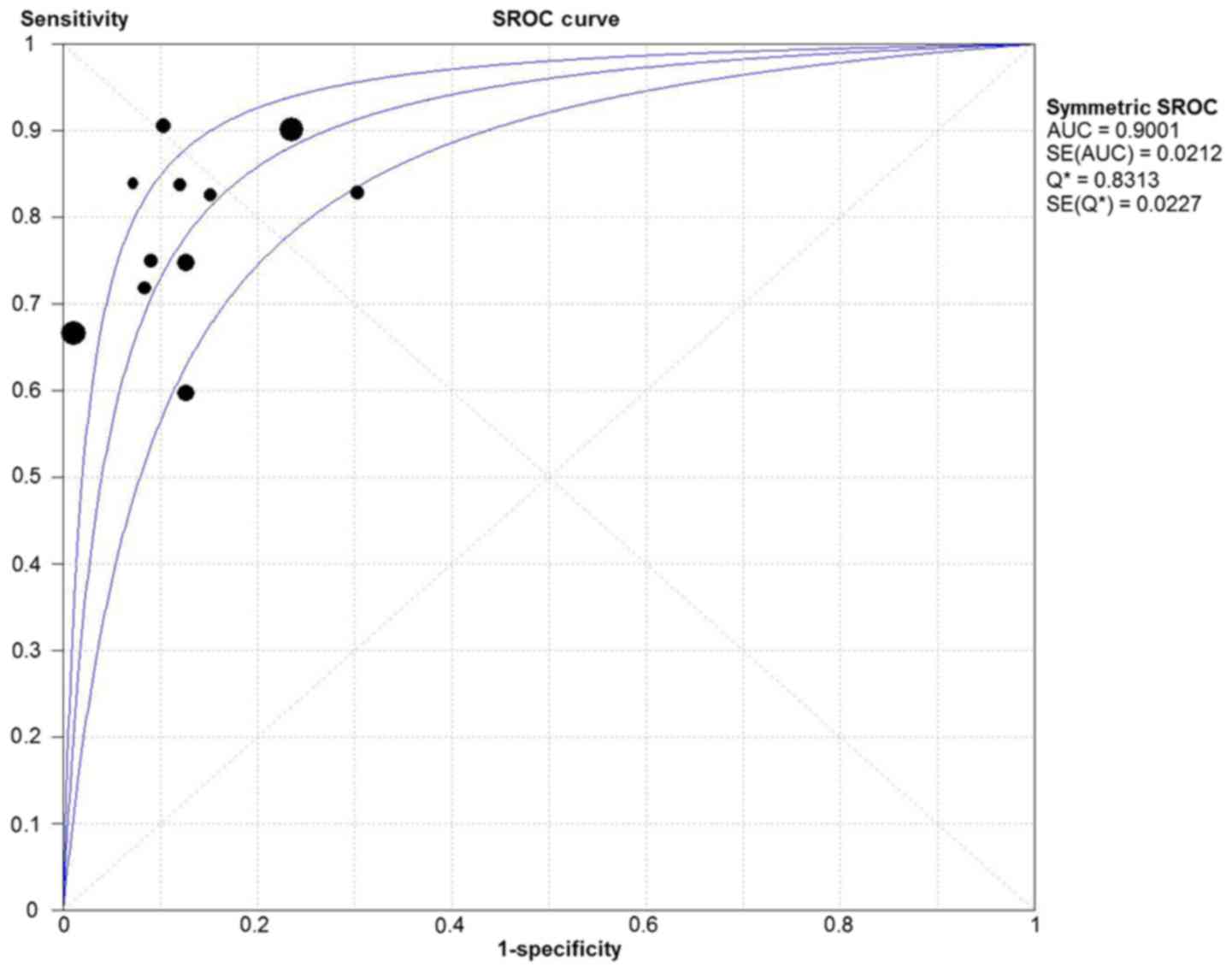
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kligerman S and Digumarthy S: Staging of
non-small cell lung cancer using integrated PET/CT. AJR Am J
Roentgenol. 193:1203–1211. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
De Wever W: Role of integrated PET/CT in
the staging of non-small cell lung cancer. JBR-BTR. 92:124–126.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pauls S, Schmidt SA, Juchems MS, Klass O,
Luster M, Reske SN, Brambs HJ and Feuerlein S: Diffusion-weighted
MR imaging in comparison to integrated [18F]-FDG PET/CT
for N-staging in patients with lung cancer. Eur J Radiol.
81:178–182. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim YN, Yi CA, Lee KS, Kwon OJ, Lee HY,
Kim BT, Choi JY, Kim SW, Chung MP, Han J, et al: A proposal for
combined MRI and PET/CT interpretation criteria for preoperative
nodal staging in non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur Radiol.
22:1537–1546. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheran SK, Nielsen ND and Patz EF Jr:
False-negative findings for primary lung tumors on FDG positron
emission tomography: Staging and prognostic implications. AJR Am J
Roentgenol. 182:1129–1132. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shim SS, Lee KS, Kim BT, Choi JY, Chung MJ
and Lee EJ: Focal parenchymal lung lesions showing a potential of
false-positive and false-negative interpretations on integrated
PET/CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 186:639–648. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Usuda K, Zhao XT, Sagawa M, Aikawa H, Ueno
M, Tanaka M, Machida Y, Matoba M, Ueda Y and Sakuma T:
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) signal intensity and distribution
represent the amount of cancer cells and their distribution in
primary lung cancer. Clin Imaging. 37:265–272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ohba Y, Nomori H, Mori T, Ikeda K, Shibata
H, Kobayashi H, Shiraishi S and Katahira K: Is diffusion-weighted
magnetic resonance imaging superior to positron emission tomography
with fludeoxyglucose F 18 in imaging non-small cell lung cancer? J
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 138:439–445. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nomori H, Mori T, Ikeda K, Kawanaka K,
Shiraishi S, Katahira K and Yamashita Y: Diffusion-weighted
magnetic resonance imaging can be used in place of positron
emission tomography for N staging of non-small cell lung cancer
with fewer false-positive results. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
135:816–822. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nomori H, Cong Y, Abe M, Sugimura H and
Kato Y: Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in
preoperative assessment of non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 149:991–996. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Koyama H, Ohno Y, Nishio M, Takenaka D,
Yoshikawa T, Matsumoto S, Seki S, Maniwa Y, Ito T, Nishimura Y and
Sugimura K: Diffusion-weighted imaging vs STIR turbo SE imaging:
Capability for quantitative differentiation of small-cell lung
cancer from non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Radiol.
87:201303072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen W, Jian W, Li HT, Li C, Zhang YK, Xie
B, Zhou DQ, Dai YM, Lin Y, Lu M, et al: Whole-body
diffusion-weighted imaging vs. FDG-PET for the detection of
non-small-cell lung cancer. How do they measure up? Magn Reson
Imaging. 28:613–620. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu L, Tian J, Liu Y and Li C: Accuracy of
diffusion-weighted (DW) MRI with background signal suppression
(MR-DWIBS) in diagnosis of mediastinal lymph node metastasis of
nonsmall-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Magn Reson Imaging.
40:200–205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He W, Xu JP, Zhou XH, et al: Comparison of
CT and DWI in preoperative evaluation of chest lymph node status in
lung cancer. Journal of Clinical Radiology. 32:802–806. 2013.(In
Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Zhang X, Xing W and Chen J: Application of
DWI in differential diagnosis of lymph nodes in patients with lung
cancer. Chin Comput Med Imag. 19:213–216. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Usuda K, Sagawa M, Motono N, Ueno M,
Tanaka M, Machida Y, Matoba M, Kuginuki Y, Taniguchi M, Ueda Y and
Sakuma T: Advantages of diffusion-weighted imaging over positron
emission tomography-computed tomography in assessment of hilar and
mediastinal lymph node in lung cancer. Ann Surg Oncol.
20:1676–1683. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ohno Y, Koyama H, Yoshikawa T, Nishio M,
Aoyama N, Onishi Y, Takenaka D, Matsumoto S, Maniwa Y and Nishio W:
N stage disease in patients with non-small cell lung cancer:
Efficacy of quantitative and qualitative assessment with STIR turbo
spin-echo imaging, diffusion-weighted MR imaging, and
fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT. Radiology. 261:605–615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nakayama J, Miyasaka K, Omatsu T, Onodera
Y, Terae S, Matsuno Y, Cho Y, Hida Y, Kaga K and Shirato H:
Metastases in mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes in patients with
non-small cell lung cancer: Quantitative assessment with
diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and apparent
diffusion coefficient. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 34:1–8. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bai CG, Zhang XM and Qiao W: Application
of apparent diffusion coefficient in evaluating lymphatic
metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. Jiangsu Med J.
39:2977–2979. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Zeng Z, Liao Q, Cai J and Liu A:
Diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient
values in the differential diagnosis of hilar and mediastinal lymph
nodes of non-small cell lung cancer. Chinese Journal of Clinical
Oncology. 39:706–710. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Wu LM, Xu JR, Gu HY, Hua J, Chen J, Zhang
W, Haacke EM and Hu J: Preoperative mediastinal and hilar nodal
staging with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and
fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography
in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: Which is better? J
Surg Res. 178:304–314. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou M, Lu B, Lv G, Tang Q, Zhu J, Li J
and Shi K: Differential diagnosis between metastatic and
non-metastatic lymph nodes using DW-MRI: A meta-analysis of
diagnostic accuracy studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
141:1119–1130. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME,
Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, Leeflang MM, Sterne JA and Bossuyt
PM: QUADAS-2 Group: QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality
assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med.
155:529–536. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Higgins JP and Thompson SG: Quantifying
heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–1558. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen LH, Zhang J, Bao J, Zhang L, Hu X,
Xia Y and Wang J: Meta-analysis of diffusion-weighted MRI in the
differential diagnosis of lung lesions. J Magn Reson Imaging.
37:1351–1358. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Arends LR, Hamza TH, van Houwelingen JC,
Heijenbrok-Kal MH, Hunink MG and Stijnen T: Bivariate random
effects meta-analysis of ROC curves. Med Decis Making. 28:621–638.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zamora J, Abraira V, Muriel A, Khan K and
Coomarasamy A: Meta-DiSc: A software for meta-analysis of test
accuracy data. BMC Med Res Methodol. 6:312006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Song F, Khan KS, Dinnes J and Sutton AJ:
Asymmetric funnel plots and publication bias in meta-analyses of
diagnostic accuracy. Int J Epidemiol. 31:88–95. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Herneth AM, Mayerhoefer M, Schernthaner R,
Ba-Ssalamah A, Czerny Ch and Fruehwald-Pallamar J: Diffusion
weighted imaging: Lymph nodes. Eur J Radiol. 76:398–406. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Harders SW, Madsen HH, Hjorthaug K,
Arveschoug AK, Rasmussen TR, Meldgaard P, Hoejbjerg JA, Pilegaard
HK, Hager H, Rehling M and Rasmussen F: Mediastinal staging in
non-small-cell lung carcinoma: Computed tomography versus
F-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography and computed
tomography. Cancer Imaging. 14:232014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Al-Sarraf N, Gately K, Lucey J, Wilson L,
McGovern E and Young V: Lymph node staging by means of positron
emission tomography is less accurate in non-small cell lung cancer
patients with enlarged lymph nodes: Analysis of 1,145 lymph nodes.
Lung Cancer. 60:62–68. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu LM, Xu JR, Hua J, Gu HY, Chen J, Haacke
EM and Hu J: Can diffusion-weighted imaging be used as a reliable
sequence in the detection of malignant pulmonary nodules and
masses? Magn Reson Imaging. 31:235–246. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Harbord RM, Deeks JJ, Egger M, Whiting P
and Sterne JA: A unification of models for meta-analysis of
diagnostic accuracy studies. Biostatistics. 8:239–251. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rutter CM and Gatsonis CA: A hierarchical
regression approach to meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy
evaluations. Stat Med. 20:2865–2884. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Glas AS, Lijmer JG, Prins MH, Bonsel GJ
and Bossuyt PM: The diagnostic odds ratio: A single indicator of
test performance. J Clin Epidemiol. 56:1129–1135. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Deeks JJ and Altman DG: Diagnostic tests
4: Likelihood ratios. BMJ. 329:168–169. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cronin P, Dwamena BA, Kelly AM, Bernstein
SJ and Carlos RC: Solitary pulmonary nodules and masses: A
meta-analysis of the diagnostic utility of alternative imaging
tests. Eur Radiol. 18:1840–1856. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Naaktgeboren CA, van Enst WA, Ochodo EA,
de Groot JA, Hooft L, Leeflang MM, Bossuyt PM, Moons KG and Reitsma
JB: Systematic overview finds variation in approaches to
investigating and reporting on sources of heterogeneity in
systematic reviews of diagnostic studies. J Clin Epidemiol.
67:1200–1209. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lijmer JG, Bossuyt PM and Heisterkamp SH:
Exploring sources of heterogeneity in systematic reviews of
diagnostic tests. Stat Med. 21:1525–1537. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Matoba M, Tonami H, Kondou T, Yokota H,
Higashi K, Toga H and Sakuma T: Lung carcinoma: Diffusion-weighted
MR imaging-preliminary evaluation with apparent diffusion
coefficient. Radiology. 243:570–577. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu HD, Liu Y, Yu TL and Ye N: Usefulness
of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the evaluation of pulmonary
lesions. Eur Radiol. 20:807–815. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jezzard P, Barnett AS and Pierpaoli C:
Characterization of and correction for eddy current artifacts in
echo planar diffusion imaging. Magn Reson Med. 39:801–812. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bastin ME: Correction of eddy
current-induced artefacts in diffusion tensor imaging using
iterative cross-correlation. Magn Reson Imaging. 17:1011–1024.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|