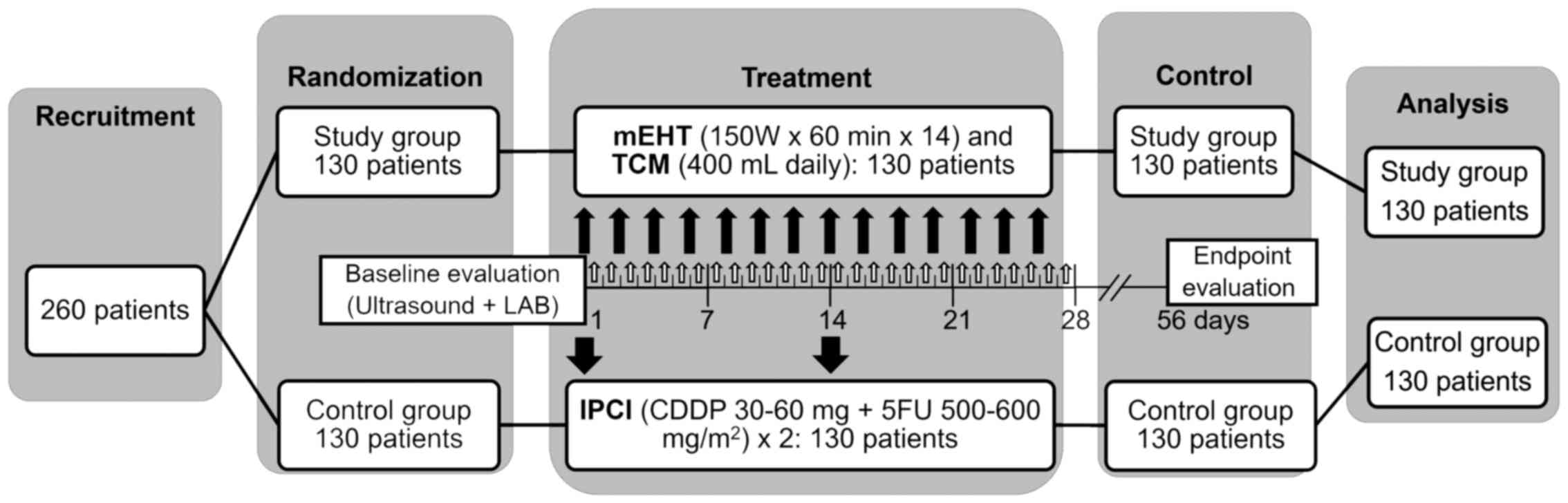
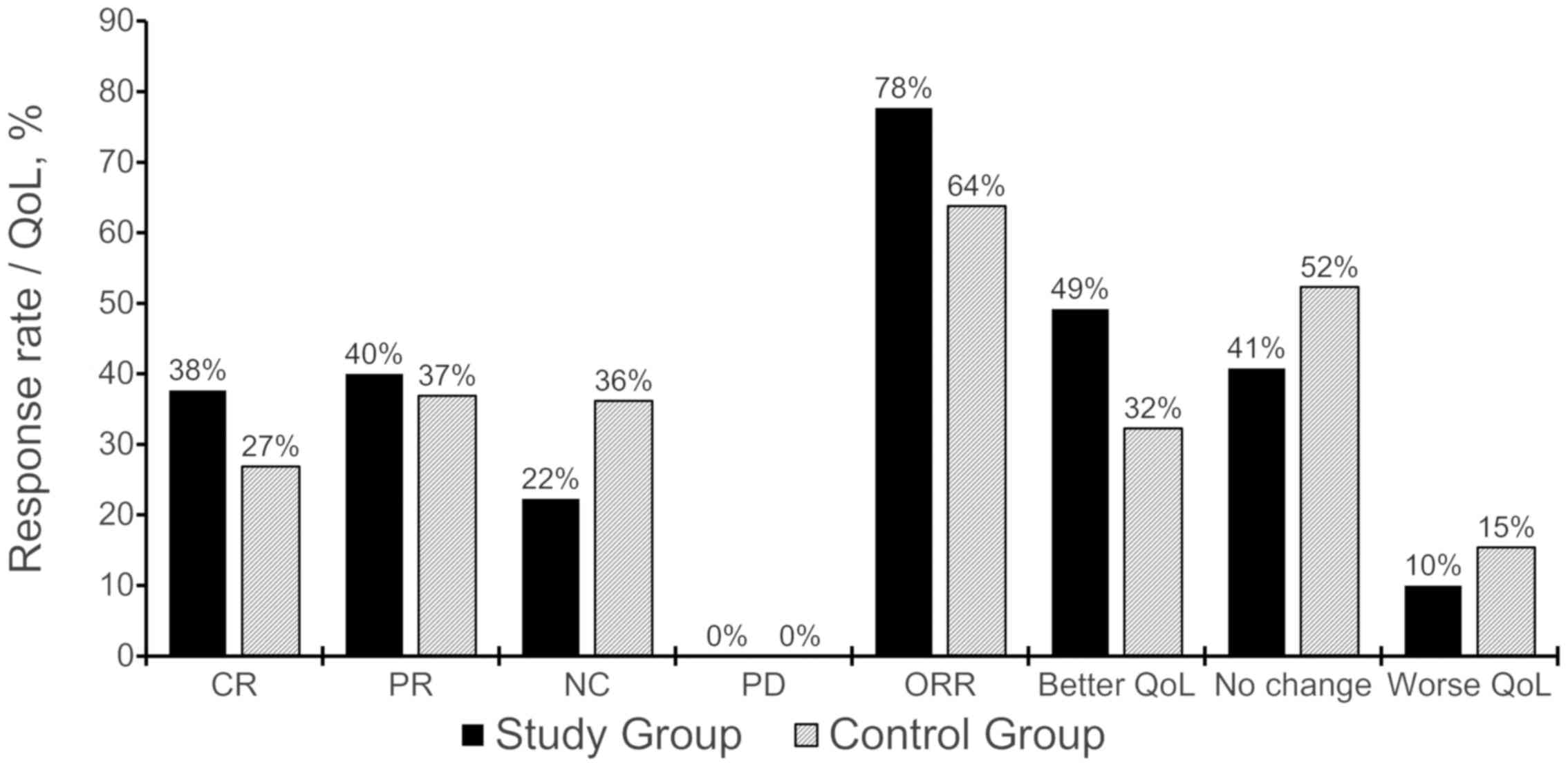
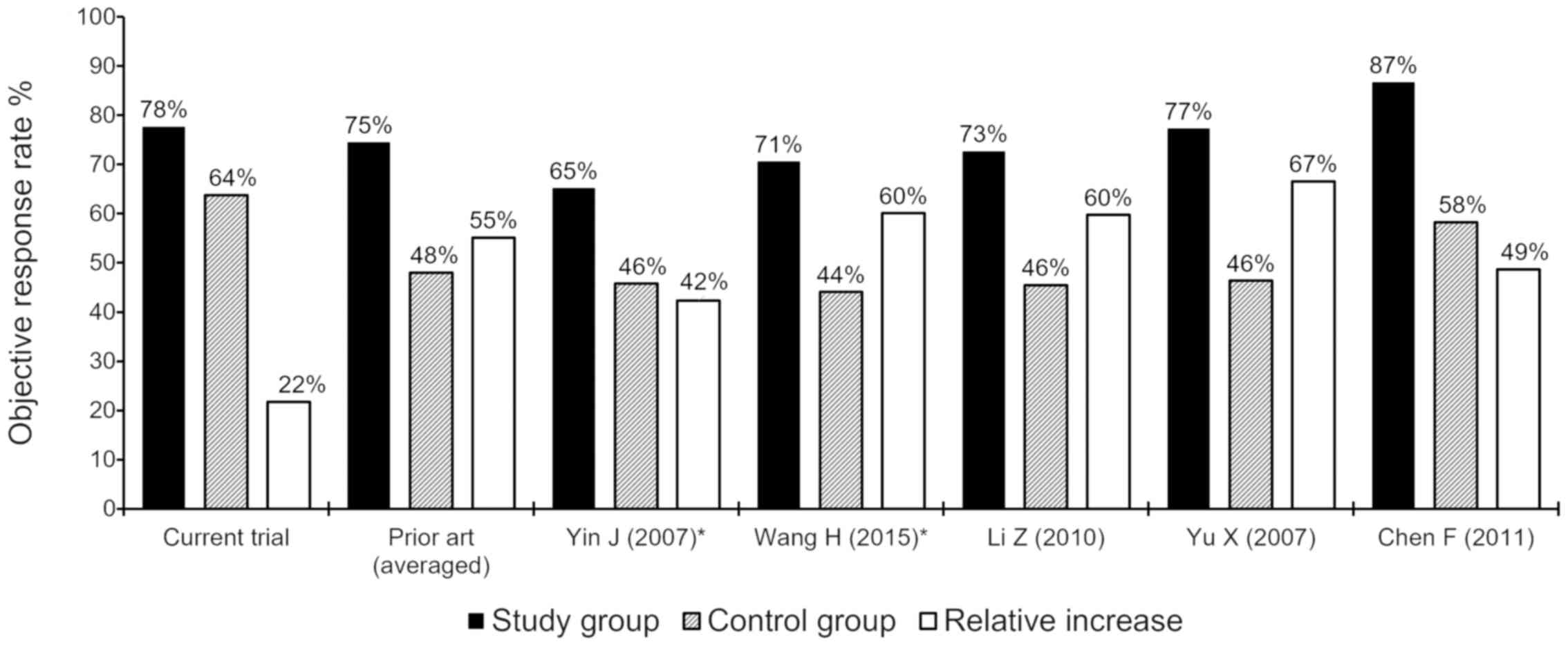
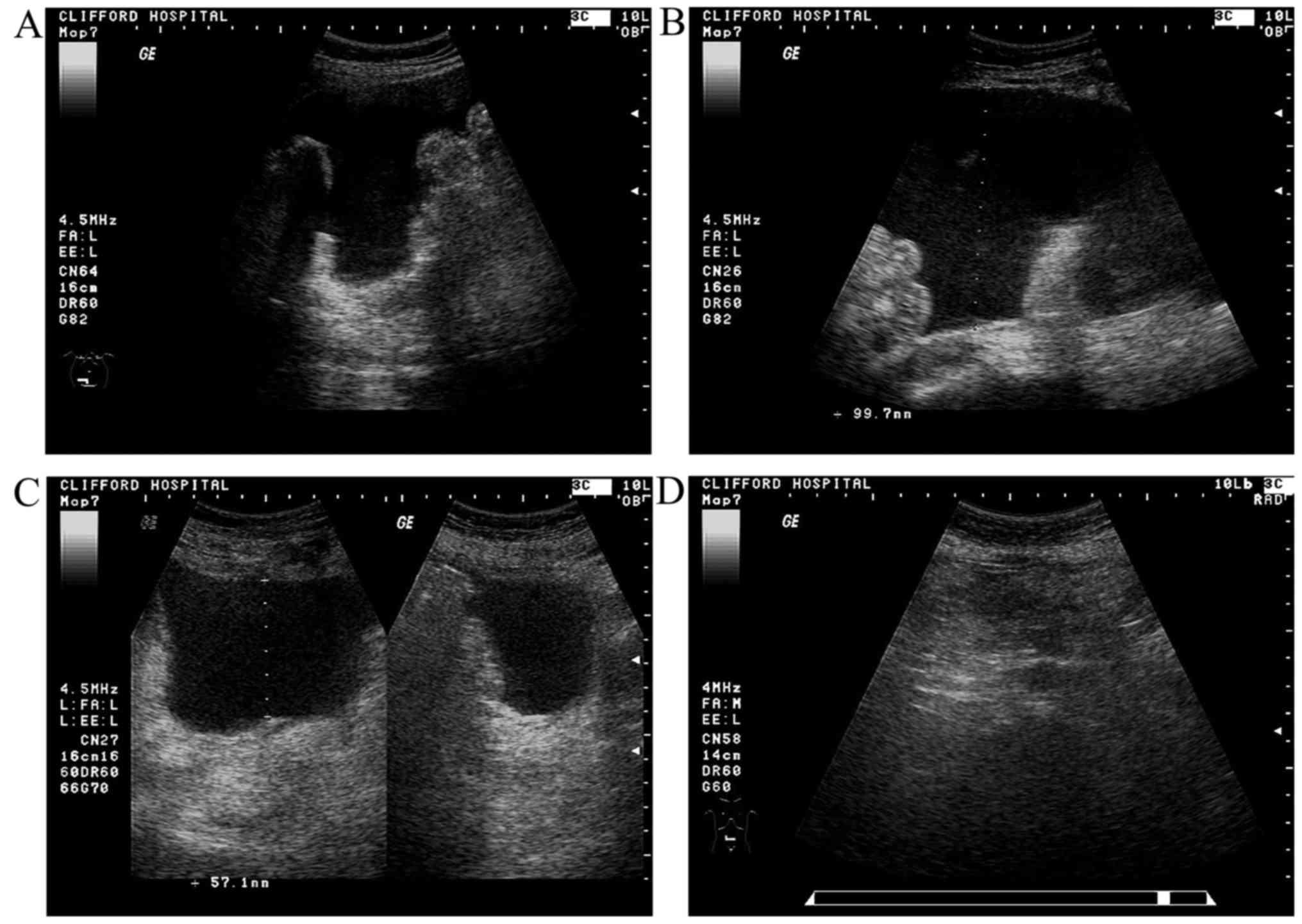
|
1
|
Ayantunde AA and Parsons SL: Pattern and
prognostic factors in patients with malignant ascites: A
retrospective study. Ann Oncol. 18:945–949. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sangisetty SL and Miner TJ: Malignant
ascites: A review of prognostic factors, pathophysiology and
therapeutic measures. World J Gastrointest Surg. 4:87–95. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Roussakow S: Critical analysis of
electromagnetic hyperthermia randomized trials: Dubious effect and
multiple biases. Conference Papers in Medicine 2013. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Roussakow S: The history of hyperthermia
rise and decline. Conference Papers in Medicine 2013. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
The American Cancer Society: Hyperthermia
to Treat Cancer. http://www.cancer.org/treatment/treatmentsandsideeffects/treatmenttypes/hyperthermiaAccessed.
February 16–2017.
|
|
6
|
Ma Shenglin: Research progress of
thermo-chemo-therapy. Mod Pract Med. 16:256–258. 2004.
|
|
7
|
Szasz A, Szasz N and Szasz O: Oncothermia:
Principles and Practices. New York: Springer, NY; pp. 5652011
|
|
8
|
Andocs G, Renner H, Balogh L, Fonyad L,
Jakab C and Szasz A: Strong synergy of heat and modulated
electromagnetic field in tumor cell killing. Strahlenther Onkol.
185:120–126. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pang CLK: Clinical research on integrative
treatment of colon carcinoma with oncothermia and clifford TCM
immune Booster. Oncothermia J. 5:24–41. 2012.
|
|
10
|
Ling Y: Traditional Chinese medicine in
the treatment of symptoms in patients with advanced cancer. Ann
Palliat Med. 2:141–152. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Veith I (translator): The Yellow Emperor's
Classic of Internal Medicine. (1972)Revised paperback edition.
University of California Press; Berkeley, LA: pp. 912002
|
|
12
|
Zheng Y and Gao F: The recognition of TCM
on seroperitoneum of hepatic cirrhosis. J Trad Chinese Med.
5:832008.
|
|
13
|
Zhou D: Oncology of TCM. Guangzhou:
Guangdong High Education Publishing House; pp. 902007
|
|
14
|
Chen F: Clinical research of out-of-body
high frequency hyperthermia in combination with TCM treating
malignant pleural fluid and ascites. J Practical Traditional
Chinese Med. 27:686–687. 2011.
|
|
15
|
Zhou L and Zhang S: Clinical observation
of adjusted Wu Ling Decoction treating 70 patients with malignant
ascites. J Practical Chinese Intern Med. 24:7–711. 2010.
|
|
16
|
Huang X: Observation of Shen Zhu Decoction
in combination with endogeny hyperthermia treating 69 patients with
malignant ascites. J Practical Chinese Intern Med. 20:3882006.
|
|
17
|
Gong S: Observation of the therapeutic
effect of microwave hyperthermia in combination with No2.3
Readjusted Decoction treating malignant pleural fluid and ascites.
J Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Med. 27:643–644.
2011.
|
|
18
|
Ji Sheng Fang: (8 juan/(Song) Yan Yonghe
zhuan). (In Chinese). Taibei: Taiwan shang wu yin shu guan; pp.
1491975
|
|
19
|
Becker G, Galandi D and Blum HE: Malignant
ascites: Systematic review and guideline for treatment. Europ J
Cancer. 42:589–597. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Matharu G, Tucker O and Alderson D:
Systematic review of intraperitoneal chemotherapy for gastric
cancer. Br J Surg. 98:1225–1235. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
McRee AJ and O'Neil BH: The role of HIPEC
in gastrointestinal malignancies: Controversies and conclusions.
Oncology (Williston Park). 29:523–524, C3. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Verhulst J: Effects of bevacizumab and
hyperthermia in a rodent model of hyperthermic intraperitoneal
chemotherapy (HIPEC). Int J Hyperthermia. 29:62–70. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zeamari S, Floot B, van der Vange N and
Stewart FA: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of cisplatin
after intraoperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemoperfusion
(HIPEC). Anticancer Res. 23:1643–1648. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sørensen O, Andersen AM, Kristian A,
Giercksky KE and Flatmark K: Impact of hyperthermia on
pharmacokinetics of intraperitoneal mitomycin C in rats
investigated by microdialysis. J Surg Oncol. 109:521–526. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kroon HM and Thompson JF: Isolated limb
infusion: A review. J Surg Oncol. 100:169–177. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Di Miceli D, Alfieri S, Caprino P, Menghi
R, Quero G, Cina C, Pericoli Ridolfini M and Doglietto GB:
Complications related to hyperthermia during hypertermic
intraoperative intraperitoneal chemiotherapy (HIPEC) treatment. Do
they exist? Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 16:737–142. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jafari MD, Halabi WJ, Stamos MJ, Nguyen
VQ, Carmichael JC, Mills SD and Pigazzi A: Surgical outcomes of
hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy: Analysis of the american
college of surgeons national surgical quality improvement program.
JAMA Surg. 149:170–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhenxia Z, Ziwei L and Ran J: Abdominal
indwelling catheter drainage combined with intracavitary perfusion
chemotherapy for patients with malignant seroperitoneum. J Huaihai
Med. 26:306–528. 2008.
|
|
29
|
Chongqi W, Chiping W and Yuying S: The
clinical value of 5-FU combined with cisplatin for hyperthermic
intraperitoneal chemoinfusion in treating cancerous ascites. Chin J
Med Drug Appl. 2:9–10. 2008.
|
|
30
|
de Kock I, Mirhosseini M, Lau F, Thai V,
Downing M, Quan H, Lesperance M and Yang J: Conversion of karnofsky
performance status (KPS) and Eastern cooperative oncology group
performance status (ECOG) to palliative performance scale (PPS),
and the interchangeability of PPS and KPS in prognostic tool. J
Palliat Care. 29:163–169. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ovarian cancer including fallopian tube
cancer and primary peritoneal carcinoma. NCCN Clinical Practice
Guidelines in Oncology. Ver. 3.2014. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.aspAccessed.
February 16–2017.
|
|
32
|
Zhou Daihan: TCM Oncology. Guangdong High
Education Press; 1. 2007, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Sun Yan: Medical Oncology. Beijing:
People's Medical Publishing House; pp. 648–649. 2001
|
|
34
|
Hawker GA, Mian S, Kendzerska T and French
M: Measures of adult pain: Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain),
Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS Pain), McGill Pain Questionnaire
(MPQ), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Chronic Pain
Grade Scale (CPGS), Short Form-36 Bodily Pain Scale (SF-36 BPS),
and Measure of Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain
(ICOAP). Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 63:(Suppl 11). S240–S252.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse
Events (CTCAE) (v4.03: June 14, 2010) U.S. Department of Health and
Human ServicesNational Institutes of Health. National Cancer
Institute;
|
|
36
|
Moher D, Hopewell S, Schulz KF, Montori V,
Gøtzsche PC, Devereaux PJ, Elbourne D, Egger M and Altman DG:
CONSORT: CONSORT 2010 Explanation and Elaboration: Updated
guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Int J
Surg. 10:28–55. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Z, Zhang L and Li L: Treatment of
malignant ascites with hyperthermic perfusion chemotherapy and
high-frequency hyperthermia. Med J West China. 22:517–521.
2010.
|
|
38
|
Yu X, Li X, Zhou J, et al: The clinical
study of intraperitoneal chemotherapy combined with whole body
hyperthermia by using microwave on abdomen for treating malignant
peritoneal effusion. J Clin Intern Med. 24:253–255. 2007.
|
|
39
|
Yin J, Dai P and Xie Z: Clinical study of
chemotherapeutic hyperthermia intraperitoneal perfusion combined
with high frequency hyperthermia for the treatment of malignant
ascites. Med J Wuhan University. 28:248–250. 2007.
|
|
40
|
Wang H, Liu P, Wang Y, et al: Effects
observation of treating malignant ascites with in vitro
radiofrequency thermotherapy combined intraperitoneal perfusion
chemotherapy. China Clinicians. 43:31–32. 2015.
|
|
41
|
Meggyeshazi N, Andocs G, Balogh L, Balla
P, Kiszner G, Teleki I, Jeney A and Krenacs T: DNA fragmentation
and caspase-independent programmed cell death by modulated
electrohyperthermia. Strahlenther Onkol. 190:815–822. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Andocs G, Meggyeshazi N, Balogh L, Spisak
S, Maros ME, Balla P, Kiszner G, Teleki I, Kovago C and Krenacs T:
Upregulation of heat shock proteins and the promotion of
damage-associated molecular pattern signals in a colorectal cancer
model by modulated electrohyperthermia. Cell Stress Chaperones.
20:37–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tsang YW, Huang CC, Yang KL, Chi MS,
Chiang HC, Wang YS, Andocs G, Szasz A, Li WT and Chi KH: Improving
immunological tumor microenvironment using electro-hyperthermia
followed by dendritic cell immunotherapy. BMC Cancer. 15:7082015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Akutsu Y, Tamura Y, Murakami K, et al: Can
modulated electro-hyperthermia (mEHT) elicit immune reaction? -From
basic and clinical research. Therm Med. 30:62(WS1WS1-3). 2014.
|
|
45
|
Sugarbaker H: Technical Handbook for the
Integration of Cytoreductive Surgery and Perioperative
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy into the Surgical Management of
Gastrointestinal and Gynecologic Malignancy. 4th. Ludann Company;
Grand Rapids, MI: pp. 672005
|