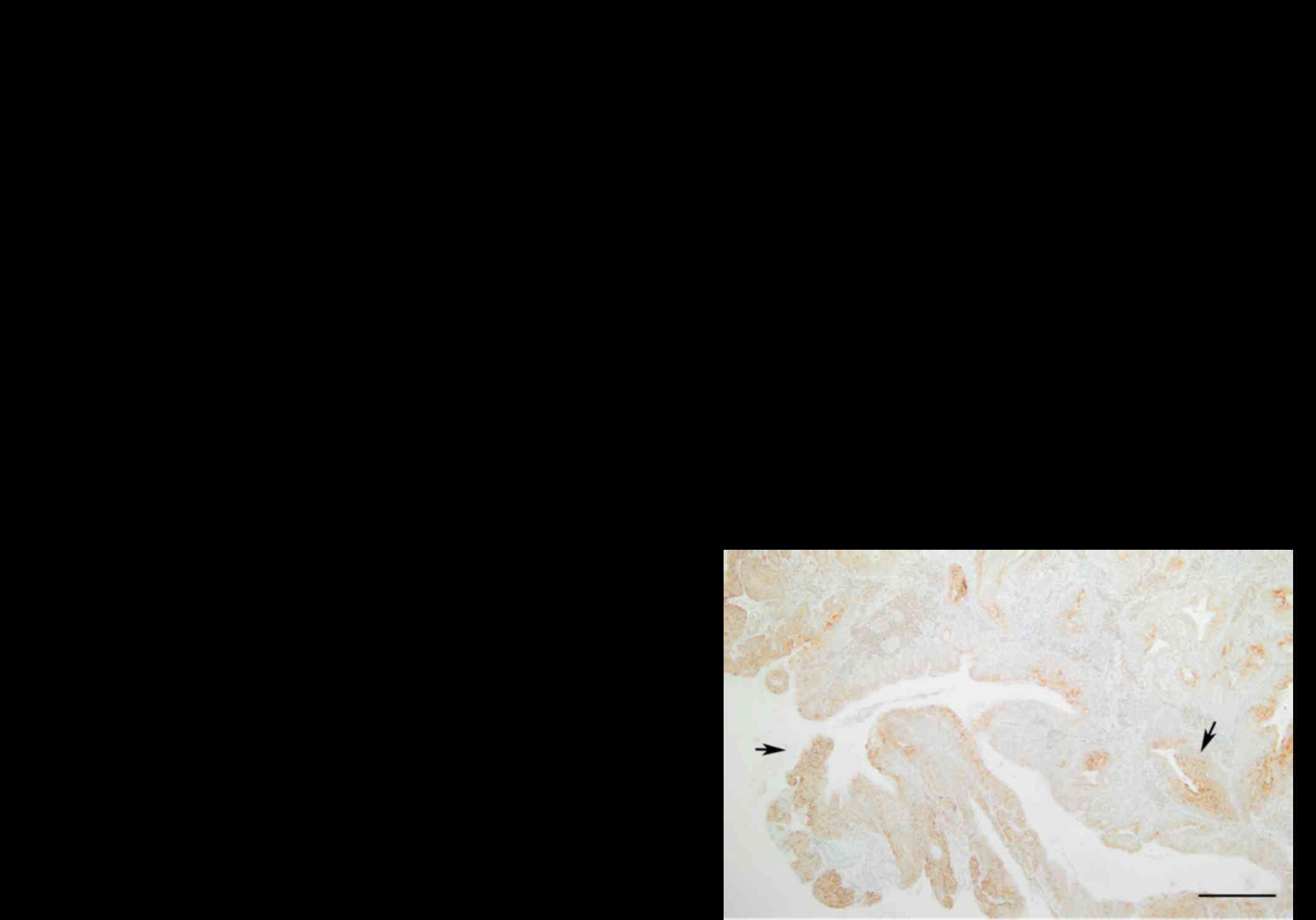
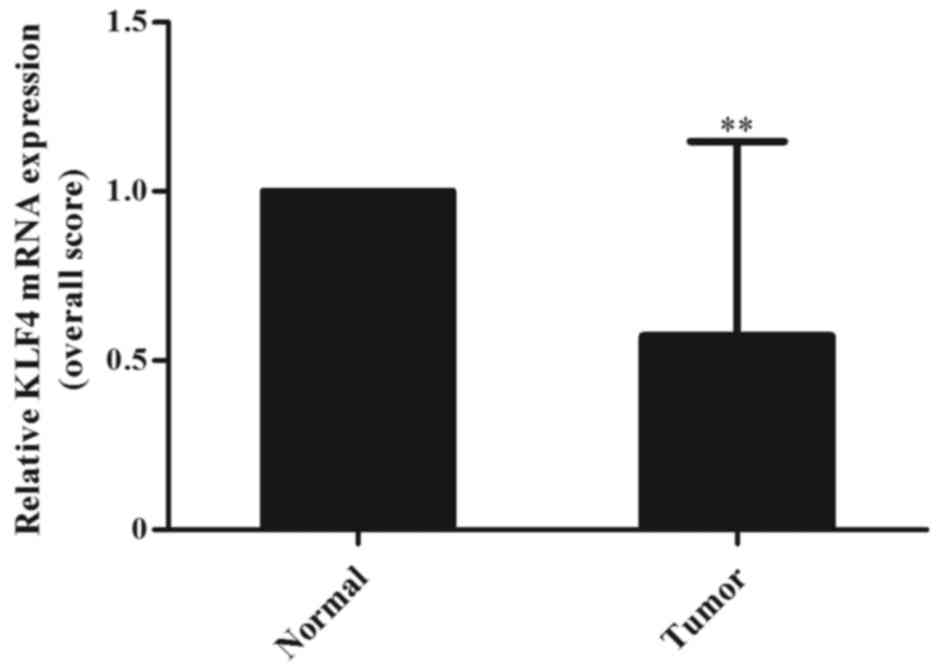
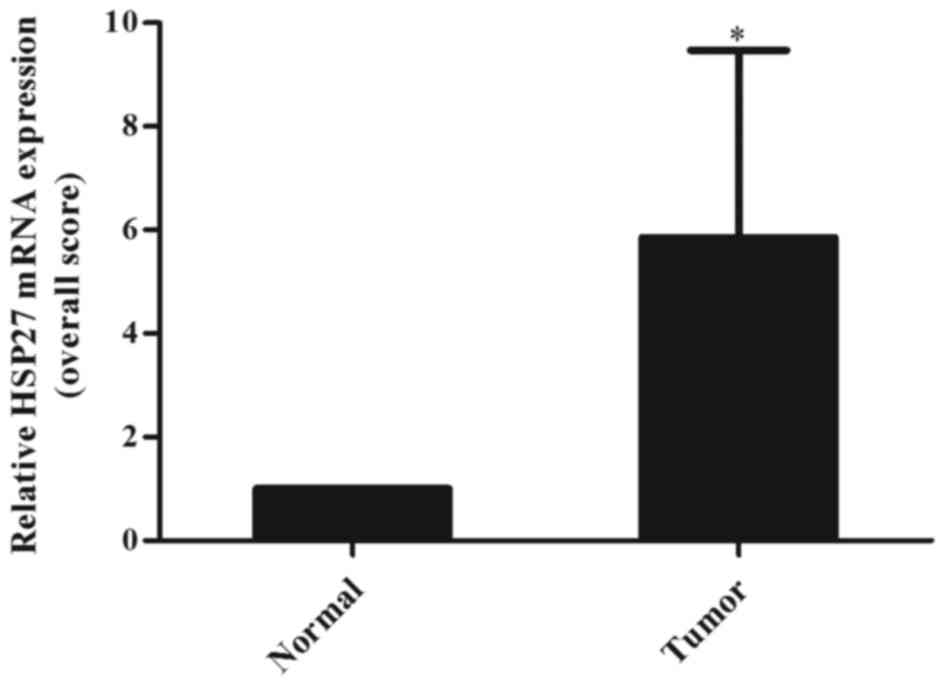
|
1
|
Santos TS, Estêvão R, Antunes L, Certal V,
Silva JC and Monteiro E: Clinical and histopathological prognostic
factors in locoregional advanced laryngeal cancer. J Laryngol Otol.
130:948–953. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marur S and Forastiere AA: Head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma: Update on epidemiology, diagnosis, and
treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 91:386–396. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ding B, Liu P, Liu W, Sun P and Wang CL:
Emerging roles of Krüppel-like factor 4 in cancer and cancer stem
cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:3629–3633. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Evans PM and Liu C: Roles of Krüpel-like
factor 4 in normal homeostasis, cancer and stem cells. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 40:554–564. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rowland BD and Peeper DS: KLF4, p21 and
context-dependent opposing forces in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:11–23. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao W, Hisamuddin IM, Nandan MO, Babbin
BA, Lamb NE and Yang VW: Identification of Krüppel-like factor 4 as
a potential tumor suppressor gene in colorectal cancer. Oncogene.
23:395–402. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wei D, Gong W, Kanai M, Schlunk C, Wang L,
Yao JC, Wu TT, Huang S and Xie K: Drastic down-regulation of
Krüppel-like factor 4 expression is critical in human gastric
cancer development and progression. Cancer Res. 65:2746–2754. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wei D, Kanai M, Huang S and Xie K:
Emerging role of KLF4 in human gastrointestinal cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 27:23–31. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu W, Hofstetter WL, Li H, Zhou Y, He Y,
Pataer A, Wang L, Xie K, Swisher SG and Fang B: Putative
tumor-suppressive function of Kruppel-like factor 4 in primary lung
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5688–5695. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pandya AY, Talley LI, Frost AR, Fitzgerald
TJ, Trivedi V, Chakravarthy M, Chhieng DC, Grizzle WE, Engler JA,
Krontiras H, et al: Nuclear localization of KLF4 is associated with
an aggressive phenotype in early-stage breast cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 10:2709–2719. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen CJ, Lin SE, Lin YM, Lin SH, Chen DR
and Chen CL: Association of expression of kruppel-like factor 4 and
kruppel-like factor 5 with the clinical manifestations of breast
cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 18:161–168. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rowland BD, Bernards R and Peeper DS: The
KLF4 tumour suppressor is a transcriptional repressor of p53 that
acts as a context-dependent oncogene. Nat Cell Biol. 7:1074–1082.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tai SK, Yang MH, Chang SY, Chang YC, Li
WY, Tsai TL, Wang YF, Chu PY and Hsieh SL: Persistent Krüppel-like
factor 4 expression predicts progression and poor prognosis of head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 102:895–902. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fadous-Khalifé MC, Aloulou N, Jalbout M,
Hadchity J, Aftimos G, Paris F and Hadchity E: Krüppel-like factor
4: A new potential biomarker of lung cancer. Mol Clin Oncol.
5:35–40. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zoubeidi A and Gleave M: Small heat shock
proteins in cancer therapy and prognosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
44:1646–1656. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lianos GD, Alexiou GA, Mangano A, Mangano
A, Rausei S, Boni L, Dionigi G and Roukos DH: The role of heat
shock proteins in cancer. Cancer Lett. 360:114–118. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kaigorodova EV and Bogatyuk MV: Heat shock
proteins as prognostic markers of cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
14:713–726. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sherman M and Multhoff G: Heat shock
proteins in cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1113:192–201. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ciocca DR, Arrigo AP and Calderwood SK:
Heat shock proteins and heat shock factor 1 in carcinogenesis and
tumor development: An update. Arch Toxicol. 87:19–48. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lo WY, Tsai MH, Tsai Y, Hua CH, Tsai FJ,
Huang SY, Tsai CH and Lai CC: Identification of over-expressed
proteins in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) patients by
clinical proteomic analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 376:101–107. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cordonnier T, Bishop JL, Shiota M, Nip KM,
Thaper D, Vahid S, Heroux D, Gleave M and Zoubeidi A: Hsp27
regulates EGF/β-catenin mediated epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 136:E496–E507. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shiota M, Bishop JL, Nip KM, Zardan A,
Takeuchi A, Cordonnier T, Beraldi E, Bazov J, Fazli L, Chi K, et
al: Hsp27 regulates epithelial mesenchymal transition, metastasis
and circulating tumor cells in prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
73:3109–3119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stope MB, Weiss M, Preuss M, Streitbörger
A, Ritter CA, Zimmermann U, Walther R and Burchardt M: Immediate
and transient phosphorylation of the heat shock protein 27
initiates chemoresistance in prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
32:2380–2386. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hansen RK, Parra I, Lemieux P, Oesterreich
S, Hilsenbeck SG and Fuqua SA: Hsp27 overexpression inhibits
doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 56:187–196. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hsu HS, Lin JH, Huang WC, Hsu TW, Su K,
Chiou SH, Tsai YT and Hung SC: Chemoresistance of lung cancer
stemlike cells depends on activation of Hsp27. Cancer.
117:1516–1528. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ciocca DR and Calderwood SK: Heat shock
proteins in cancer: Diagnostic, prognostic, predictive, and
treatment implications. Cell Stress Chaperones. 10:86–103. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hadchity E, Aloy MT, Paulin C, Armandy E,
Watkin E, Rousson R, Gleave M, Chapet O and Rodriguez-Lafrasse C:
Heat shock protein 27 as a new therapeutic target for radiation
sensitization of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Ther.
17:1387–1394. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Aloy MT, Hadchity E, Bionda C, Diaz-Latoud
C, Claude L, Rousson R, Arrigo AP and Rodriguez-Lafrasse C:
Protective role of Hsp27 protein against gamma radiation-induced
apoptosis and radiosensitization effects of Hsp27 gene silencing in
different human tumor cells. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
70:543–553. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lelj-Garolla B, Kumano M, Beraldi E, Nappi
L, Rocchi P, Ionescu DN, Fazli L, Zoubeidi A and Gleave ME: Hsp27
inhibition with OGX-427 sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells
to erlotinib and chemotherapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:1107–1116. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chi KN, Yu EY, Jacobs C, Bazov J,
Kollmannsberger C, Higano CS, Mukherjee SD, Gleave ME, Stewart PS
and Hotte SJ: A phase I dose-escalation study of apatorsen
(OGX-427), an antisense inhibitor targeting heat shock protein 27
(Hsp27), in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer and
other advanced cancers. Ann Oncol. 27:1116–1122. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kaigorodova EV, Zavyalova MV, Bychkov VA,
Perelmuter VM and Choynzonov EL: Functional state of the Hsp27
chaperone as a molecular marker of an unfavorable course of larynx
cancer. Cancer Biomark. 17:145–153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu X, Zhao M and Shi Y: Expression of heat
shock proteins in laryngeal carcinoma. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za
Zhi. 33:232–234. 1998.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ghaleb AM and Yang VW: Krüppel-like factor
4 (KLF4): What we currently know. Gene. 611:27–37. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu J, Liu T, Rios Z, Mei Q, Lin X and Cao
S: Heat Shock Proteins and Cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
38:226–256. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ohnishi S, Ohnami S, Laub F, Aoki K,
Suzuki K, Kanai Y, Haga K, Asaka M, Ramirez F and Yoshida T:
Downregulation and growth inhibitory effect of epithelial-type
Krüppel-like transcription factor KLF4, but not KLF5, in bladder
cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 308:251–256. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang N, Liu ZH, Ding F, Wang XQ, Zhou CN
and Wu M: Down-regulation of gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor
expression in esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 8:966–970.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang Z, Wang Z, Liu X, Shi M, Chen G,
Zhang B, Li Z and Song L: Correlation of KLF4 and SPARC expression
with the clinical characteristics of non-small cell lung cancer.
Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 15:720–724. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yoshihama R, Yamaguchi K, Imajyo I, Mine
M, Hiyake N, Akimoto N, Kobayashi Y, Chigita S, Kumamaru W,
Kiyoshima T, et al: Expression levels of SOX2, KLF4 and brachyury
transcription factors are associated with metastasis and poor
prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
11:1435–1446. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Acunzo J, Andrieu C, Baylot V, So A and
Rocchi P: Hsp27 as a therapeutic target in cancers. Curr Drug
Targets. 15:423–431. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Friedman MJ, Li S and Li XJ: Activation of
gene transcription by heat shock protein 27 may contribute to its
neuronal protection. J Biol Chem. 284:27944–27951. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Deaton RA, Gan Q and Owens GK:
Sp1-dependent activation of KLF4 is required for PDGF-BB-induced
phenotypic modulation of smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 296:H1027–H1037. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang JP, Zhang H, Wang HB, Li YX, Liu GH,
Xing S, Li MZ and Zeng MS: Down-regulation of Sp1 suppresses cell
proliferation, clonogenicity and the expressions of stem cell
markers in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Transl Med. 12:2222014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|