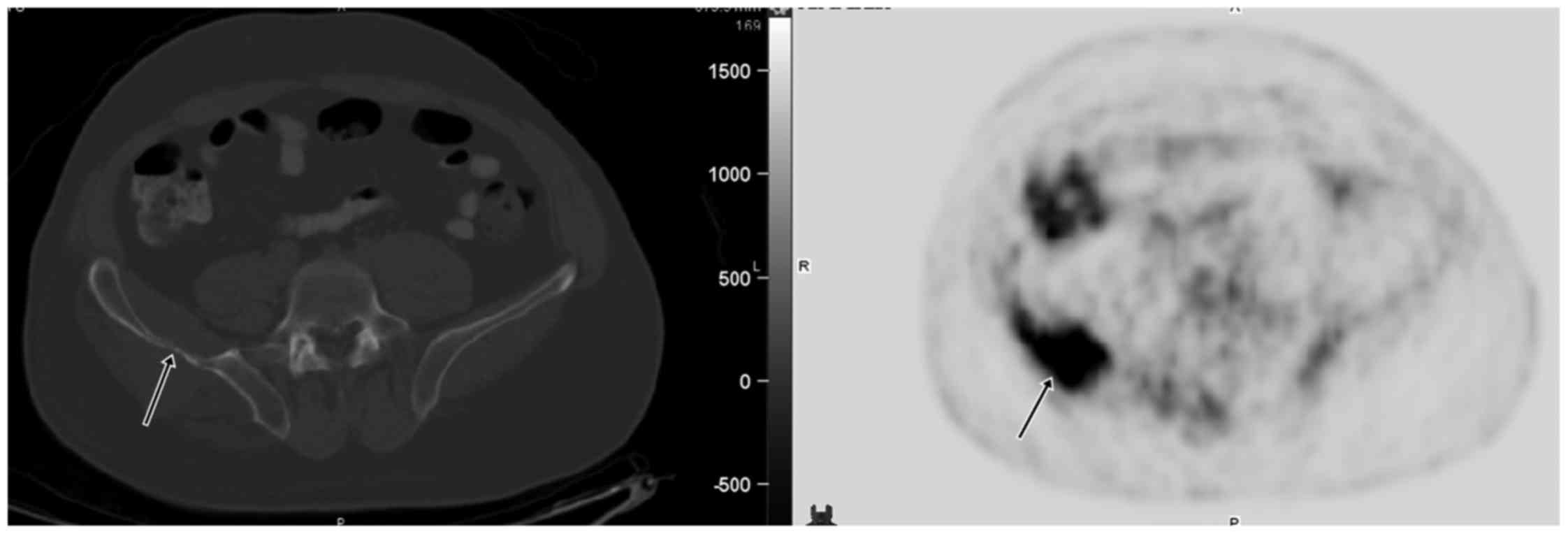
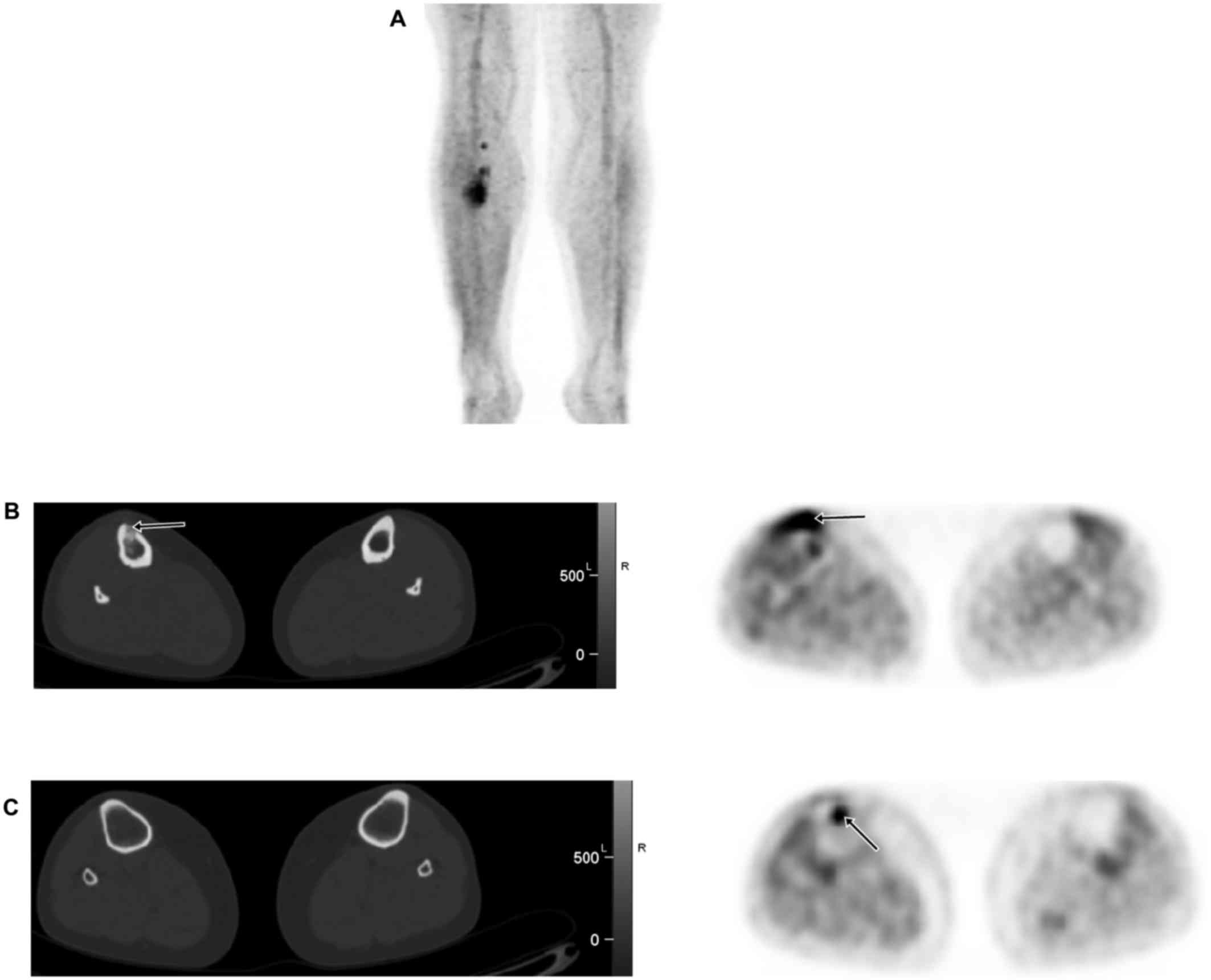
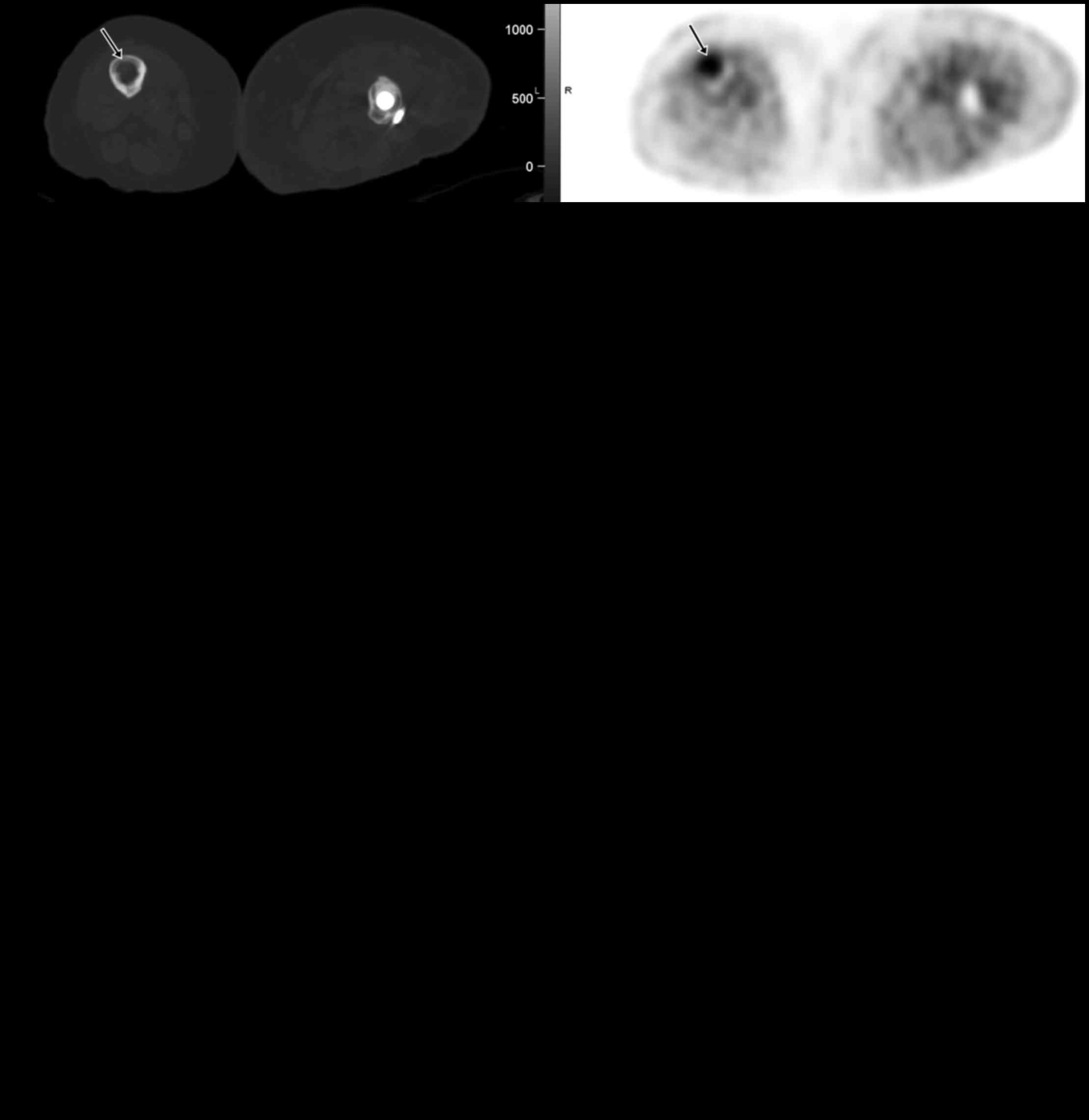
|
1
|
Stout AP and Murray MR:
Hemangiopericytoma: A vascular tumor featuring zimmermann's
pericytes. Ann Surg. 116:26–33. 1942. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Verbeke SL and Bovée JV: Primary vascular
tumors of bone: A spectrum of entities? Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
4:541–551. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fletcher CD: The evolving classification
of soft tissue tumours: An update based on the new who
classification. Histopathology. 48:3–12. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gengler C and Guillou L: Solitary fibrous
tumour and haemangiopericytoma: Evolution of a concept.
Histopathology. 48:63–74. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Espat NJ, Lewis JJ, Leung D, Woodruff JM,
Antonescu CR, Shia J and Brennan MF: Conventional
hemangiopericytoma: Modern analysis of outcome. Cancer.
95:1746–1751. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Combs SE, Thilmann C, Debus J and
Schulz-Ertner D: Precision radiotherapy for hemangiopericytomas of
the central nervous system. Cancer. 104:2457–2465. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Unni KK, Ivins JC, Beabout JW and Dahlin
DC: Hemangioma, hemangiopericytoma and hemangioendothelioma
(angiosarcoma) of bone. Cancer. 27:1403–1414. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu J, Cao L, Liu L, Guo S, Tai H and Chen
Z: Primary epidural hemangiopericytoma in the sacrum: A rare case
and literature review. Tumour Biol. 35:11655–11658. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang P, Hu J and Zhou D:
Hemangiopericytoma of the cervicothoracic spine: A case report and
literature review. Turk Neurosurg. 24:948–953. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lian YW, Yao MS, Hsieh SC, Lao WT, Fang CL
and Chan WP: MRI of hemangiopericytoma in the sacrum. Skeletal
Radiol. 33:485–487. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dürr HR, Nerlich A, Lienemann A, Müller PE
and Refior HJ: Malignant hemangiopericytoma of the bone.
Langenbecks Arch Surg. 385:207–212. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sahin-Akyar G, Fitöz S, Akpolat I, Sağlik
Y and Erekul S: Primary hemangiopericytoma of bone located in the
tibia. Skeletal Radiol. 26:47–50. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin YJ, Tu YK, Lin SM and Shun CT: Primary
hemangiopericytoma in the axis bone: Case report and review of
literature. Neurosurgery. 39:397–399. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang JS, Gold RH, Mirra JM and Eckardt J:
Hemangiopericytoma of bone. Cancer. 62:848–859. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jain AS, Shelley S, Muthukrishnan I, Kalal
S, Amalachandran J and Chandran S: Diagnostic importance of
contrast enhanced (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission
computed tomography in patients with tumor induced osteomalacia:
Our experience. Indian J Nucl Med. 31:14–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee SJ, Kim ST, Park SH, Choi YL, Park JB,
Kim SJ and Lee J: Successful use of pazopanib for treatment of
refractory metastatic hemangiopericytoma. Clin Sarcoma Res.
4:132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aras M, Dede F, Ones T, Atasoy BM, Inanir
S, Erdil TY and Turoglu HT: F-18 FDG PET/CT findings of primary
sinonasal hemangiopericytoma: Rare location in a young adult
patient. Clin Nucl Med. 36:473–474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ito S, Yokoyama J, Yoshimoto H, Yazawa M,
Kazuo K, Hanaguri M, Ohba S, Fujimaki M and Ikeda K: Usefulness of
choline-PET for the detection of residual hemangiopericytoma in the
skull base: Comparison with FDG-PET. Head Face Med. 8:32012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hung TJ, Macdonald W, Muir T, Celliers L
and Al-Ogaili Z: 68Ga DOTATATE PET/CT of Non-FDG-Avid pulmonary
metastatic hemangiopericytoma. Clin Nucl Med. 41:779–780. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Khadgawat R, Singh Y, Kansara S, Tandon N,
Bal C, Seith A and Kotwal P: PET/CT localisation of a scapular
haemangiopericytoma with tumour-induced osteomalacia. Singapore Med
J. 50:e55–e57. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Verbeke SL, Fletcher CD, Alberghini M,
Daugaard S, Flanagan AM, Parratt T, Kroon HM, Hogendoorn PC and
Bovée JV: A reappraisal of hemangiopericytoma of bone; analysis of
cases reclassified as synovial sarcoma and solitary fibrous tumor
of bone. Am J Surg Pathol. 34:777–783. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fuentealba C, Pinto D, Ballesteros F,
Pacheco D, Boettiger O, Soto N, Fernandez W, Gabler F, Gonzales G
and Reginato AJ: Oncogenic hypophosphatemic osteomalacia associated
with a nasal hemangiopericytoma. J Clin Rheumatol. 9:373–379. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chung J and Henry RR: Mechanisms of
tumor-induced hypoglycemia with intraabdominal hemangiopericytoma.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 81:919–925. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|