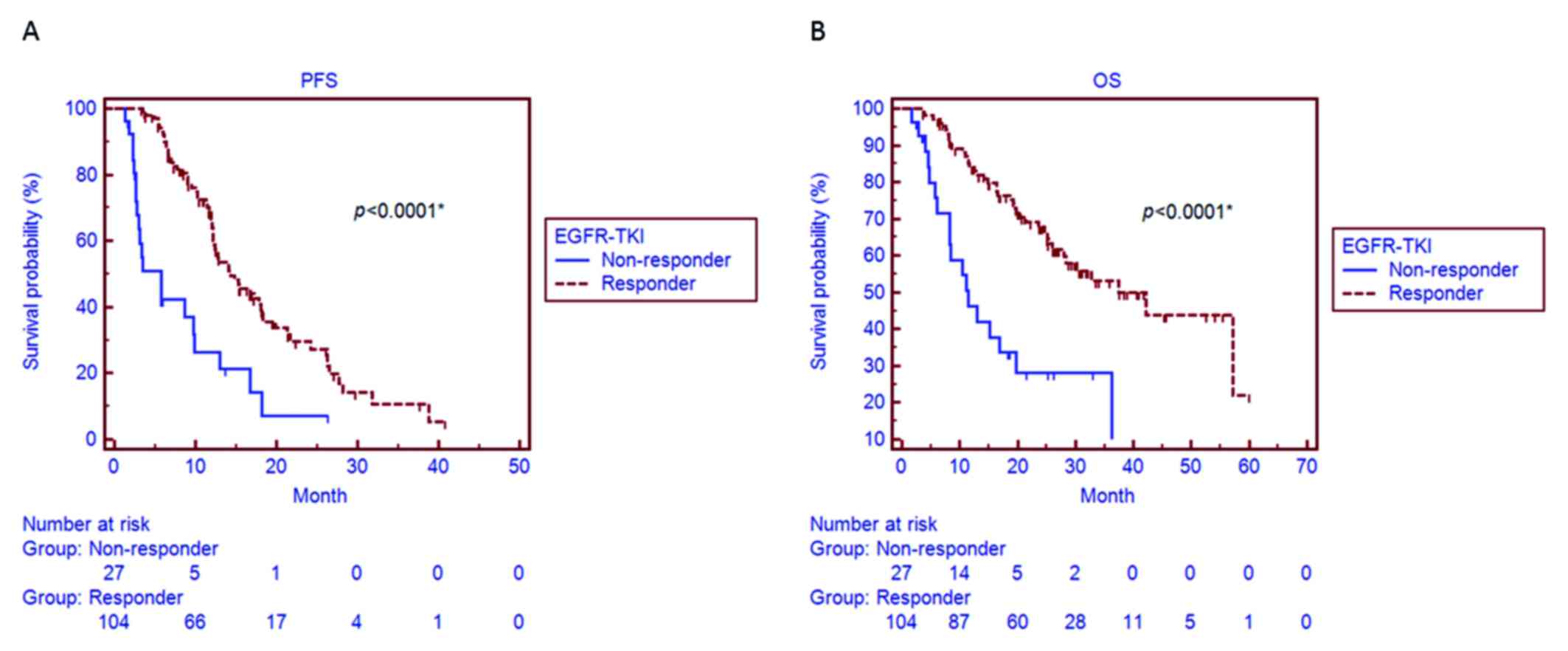
|
1
|
Breathnach OS, Freidlin B, Conley B, Green
MR, Johnson DH, Gandara DR, O'Connell M, Shepherd FA and Johnson
BE: Twenty-two years of phase III trials for patients with advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer: Sobering results. J Clin Oncol.
19:1734–1742. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goulart BH, Martins RG and Lynch TJ:
Twenty-two years of phase III trials for patients with advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer: Sobering results. J Clin Oncol.
19:40892001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP,
Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, Zhu J and Johnson DH; Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group, : Comparison of four chemotherapy
regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med.
346:92–98. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arteaga CL: Epidermal growth factor
receptor dependence in human tumors: More than just expression?
Oncologist. 7(Suppl 4): S31–S39. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R,
Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat
SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, et al: Activating mutations in the
epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of
non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med.
350:2129–2139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S,
Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, et
al: EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical
response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 304:1497–1500. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu CQ, da Cunha Santos G, Ding K,
Sakurada A, Cutz JC, Liu N, Zhang T, Marrano P, Whitehead M, Squire
JA, et al: Role of KRAS and EGFR as biomarkers of response to
erlotinib in National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials
Group Study BR.21. J Clin Oncol. 26:4268–4275. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang SF, Liu HP, Li LH, Ku YC, Fu YN,
Tsai HY, Chen YT, Lin YF, Chang WC, Kuo HP, et al: High frequency
of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations with complex patterns
in non-small cell lung cancers related to gefitinib responsiveness
in Taiwan. Clin Cancer Res. 10:8195–8203. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gazdar AF, Shigematsu H, Herz J and Minna
JD: Mutations and addiction to EGFR: The Achilles ‘heal’ of lung
cancers? Trends Mol Med. 10:481–486. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH,
Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, et
al: Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary
adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 361:947–957. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S,
Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, et
al: Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with
non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal
growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): An open label, randomised phase
3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 11:121–128. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ,
Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, et al: Erlotinib versus
chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced
EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL,
CTONG-0802): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study.
Lancet Oncol. 12:735–742. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu YL, Zhou C, Hu CP, Feng J, Lu S, Huang
Y, Li W, Hou M, Shi JH, Lee KY, et al: Afatinib versus cisplatin
plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations
(LUX-Lung 6): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 15:213–222. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vallée A, Le Loupp AG and Denis MG:
Efficiency of the Therascreen® RGQ PCR kit for the
detection of EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung carcinomas. Clin
Chim Acta. 429:8–11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim GW, Song JS, Choi CM, Rho JK, Kim SY,
Jang SJ, Park YS, Chun SM, Kim WS, Lee JS, et al: Multiple
resistant factors in lung cancer with primary resistance to EGFR-TK
inhibitors confer poor survival. Lung cancer. 88:139–146. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cha YK, Lee HY, Ahn MJ, Choi YL, Lee JH,
Park K and Lee KS: Survival outcome assessed according to tumor
burden and progression patterns in patients with epidermal growth
factor receptor mutant lung adenocarcinoma undergoing epidermal
growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Clin Lung
Cancer. 16:228–236. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Riely GJ, Pao W, Pham D, Li AR, Rizvi N,
Venkatraman ES, Zakowski MF, Kris MG, Ladanyi M and Miller VA:
Clinical course of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and
epidermal growth factor receptor exon 19 and exon 21 mutations
treated with gefitinib or erlotinib. Clin Cancer Res. 12:839–844.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rosell R, Moran T, Queralt C, Porta R,
Cardenal F, Camps C, Majem M, Lopez-Vivanco G, Isla D, Provencio M,
et al: Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 361:958–967. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jackman DM, Miller VA, Cioffredi LA, Yeap
BY, Jänne PA, Riely GJ, Ruiz MG, Giaccone G, Sequist LV and Johnson
BE: Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor and KRAS mutations
on clinical outcomes in previously untreated non-small cell lung
cancer patients: Results of an online tumor registry of clinical
trials. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5267–5273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu JQ, Zhong WZ, Zhang GC, Li R, Zhang
XC, Guo AL, Zhang YF, An SJ, Mok TS and Wu YL: Better survival with
EGFR exon 19 than exon 21 mutations in gefitinib-treated non-small
cell lung cancer patients is due to differential inhibition of
downstream signals. Cancer Lett. 265:307–317. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bury T, Barreto A, Daenen F, Barthelemy N,
Ghaye B and Rigo P: Fluorine-18 deoxyglucose positron emission
tomography for the detection of bone metastases in patients with
non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Nucl Med. 25:1244–1247. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hong SH, Kim YS, Lee JE, Kim IH, Kim SJ,
Han D, Yoo Ie R, Chung YG, Kim YH, Lee KY and Kang JH: Clinical
characteristics and continued epidermal growth factor receptor
tyrosine kinase inhibitor administration in EGFR-mutated non-small
cell lung cancer with skeletal metastasis. Cancer Res Treat.
48:1110–1119. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim MH, Kim HR, Cho BC, Bae MK, Kim EY,
Lee CY, Lee JS, Kang DR and Kim JH: Impact of cigarette smoking on
response to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase
inhibitors in lung adenocarcinoma with activating EGFR mutations.
Lung cancer. 84:196–202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takeda M, Okamoto I, Fujita Y, Arao T, Ito
H, Fukuoka M, Nishio K and Nakagawa K: De novo resistance to
epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR
mutation-positive patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J
Thorac Oncol. 5:399–400. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ludovini V, Bianconi F, Pistola L, Chiari
R, Minotti V, Colella R, Giuffrida D, Tofanetti FR, Siggillino A,
Flacco A, et al: Phosphoinositide-3-kinase catalytic alpha and KRAS
mutations are important predictors of resistance to therapy with
epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in
patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol.
6:707–715. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cappuzzo F, Jänne PA, Skokan M,
Finocchiaro G, Rossi E, Ligorio C, Zucali PA, Terracciano L, Toschi
L, Roncalli M, et al: MET increased gene copy number and primary
resistance to gefitinib therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer
patients. Ann Oncol. 20:298–304. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tanaka A, Sueoka-Aragane N, Nakamura T,
Takeda Y, Mitsuoka M, Yamasaki F, Hayashi S, Sueoka E and Kimura S:
Co-existence of positive MET FISH status with EGFR mutations
signifies poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Lung
cancer. 75:89–94. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ying HQ, Chen J, He BS, Pan YQ, Wang F,
Deng QW, Sun HL, Liu X and Wang SK: The effect of BIM deletion
polymorphism on intrinsic resistance and clinical outcome of cancer
patient with kinase inhibitor therapy. Sci Rep. 5:113482015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee JY, Ku BM, Lim SH, Lee MY, Kim H, Kim
M, Kim S, Jung HA, Sun JM, Ahn JS, et al: The BIM deletion
polymorphism and its clinical implication in patients with
EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer treated with EGFR tyrosine
kinase inhibitors. J Thorac Oncol. 10:903–909. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sos ML, Koker M, Weir BA, Heynck S,
Rabinovsky R, Zander T, Seeger JM, Weiss J, Fischer F, Frommolt P,
et al: PTEN loss contributes to erlotinib resistance in EGFR-mutant
lung cancer by activation of Akt and EGFR. Cancer Res.
69:3256–3261. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee Y, Lee GK, Hwang JA, Yun T, Kim HT and
Lee JS: Clinical likelihood of sporadic primary EGFR T790M mutation
in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 16:46–50. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|