|
1
|
Chen KW, Ou TM, Hsu CW, Horng CT, Lee CC,
Tsai YY, Tsai CC, Liou YS, Yang CC, Hsueh CW and Kuo WH: Current
systemic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A review of the
literature. World J Hepatol. 7:1412–1420. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cillo U, Vitale A, Grigoletto F, Farinati
F, Brolese A, Zanus G, Neri D, Boccagni P, Srsen N, D'Amico F, et
al: Prospective validation of the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer
staging system. J Hepatol. 44:723–731. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yi PS, Zhang M and Xu MQ: Management of
the middle hepatic vein in right lobe living donor liver
transplantation: A meta-analysis. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med
Sci. 35:600–605. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yi PS, Zhang M, Zhao JT and Xu MQ: Liver
resection for intermediate hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Hepatol. 8:607–615. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Montani F and Bianchi F: Circulating
cancer biomarkers: The macro-revolution of the micro-rna.
EBioMedicine. 5:4–6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chou CH, Chang NW, Shrestha S, Hsu SD, Lin
YL, Lee WH, Yang CD, Hong HC, Wei TY, Tu SJ, et al: miRTarBase
2016: Updates to the experimentally validated miRNA-target
interactions database. Nucleic Acids Res. 44(D1): D239–D247. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pfeffer SR, Yang CH and Pfeffer LM: The
role of mir-21 in cancer. Drug Dev Res. 76:270–277. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tomimaru Y, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Wada H,
Tomokuni A, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Takeda Y, Tanemura M,
Umeshita K, et al: MicroRNA-21 induces resistance to the
anti-tumour effect of interferon-α/5-fluorouracil in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 103:1617–1626. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tomimaru Y, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Wada H,
Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Tanemura M, Tomokuni A, Takemasa I,
Umeshita K, et al: Circulating microRNA-21 as a novel biomarker for
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 56:167–175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Karakatsanis A, Papaconstantinou I,
Gazouli M, Lyberopoulou A, Polymeneas G and Voros D: Expression of
microRNAs, miR-21, miR-31, miR-122, miR-145, miR-146a, miR-200c,
miR-221, miR-222, and miR-223 in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma or intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its prognostic
significance. Mol Carcinog. 52:297–303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Gao X, Wei F, Zhang X, Yu J, Zhao
H, Sun Q, Yan F, Yan C, Li H and Ren X: Diagnostic and prognostic
value of circulating miR-21 for cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Gene. 533:389–397. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yan SR, Liu ZJ, Yu S and Bao YX:
Investigation of the value of miR-21 in the diagnosis of early
stage HCC and its prognosis: A meta-analysis. Genet Mol Res.
14:11573–11586. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stang A: Critical evaluation of the
Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of
nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol.
25:603–605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lo CK, Mertz D and Loeb M:
Newcastle-Ottawa Scale: Comparing reviewers' to authors'
assessments. BMC Med Res Methodol. 14:452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett
S and Sydes MR: Practical methods for incorporating summary
time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials. 8:162007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou X, Wang X, Huang Z, Wang J, Zhu W,
Shu Y and Liu P: Prognostic value of miR-21 in various cancers: An
updating meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e1024132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Juskeviciute E, Dippold RP, Antony AN,
Swarup A, Vadigepalli R and Hoek JB: Inhibition of miR-21 rescues
liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in ethanol-fed rats.
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 311:G794–G806. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen X, Song M, Chen W,
Dimitrova-Shumkovska J, Zhao Y, Cao Y, Song Y, Yang W, Wang F,
Xiang Y and Yang C: Microrna-21 contributes to liver regeneration
by targeting pten. Med Sci Monit. 22:83–91. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hu S, Tao R, Wang S, Wang C, Zhao X, Zhao
H, Li L, Zhu S, He Y, Jiang X and Gao Y: MicroRNA-21 promotes cell
proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma partly by targeting
HEPN1. Tumour Biol. 36:5467–5472. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal
K, Jacob ST and Patel T: MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer.
Gastroenterology. 133:647–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bao L, Yan Y, Xu C, Ji W, Shen S, Xu G,
Zeng Y, Sun B, Qian H, Chen L, et al: MicroRNA-21 suppresses PTEN
and hSulf-1 expression and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma
progression through AKT/ERK pathways. Cancer Lett. 337:226–236.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
He C, Dong X, Zhai B, Jiang X, Dong D, Li
B, Jiang H, Xu S and Sun X: MiR-21 mediates sorafenib resistance of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting autophagy via the
PTEN/Akt pathway. Oncotarget. 6:28867–28881. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu Q, Wang Z, Hu Y, Li J, Li X, Zhou L
and Huang Y: miR-21 promotes migration and invasion by the
miR-21-PDCD4-AP-1 feedback loop in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncol Rep. 27:1660–1668. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qiu X, Dong S, Qiao F, Lu S, Song Y, Lao
Y, Li Y, Zeng T, Hu J, Zhang L, et al: HBx-mediated miR-21
upregulation represses tumor-suppressor function of PDCD4 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 32:3296–3305. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang X, Zhang J, Zhou L, Lu P, Zheng ZG,
Sun W, Wang JL, Yang XS, Li XL, Xia N, et al: Significance of serum
microRNA-21 in diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC):
Clinical analyses of patients and an HCC rat model. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:1466–1478. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
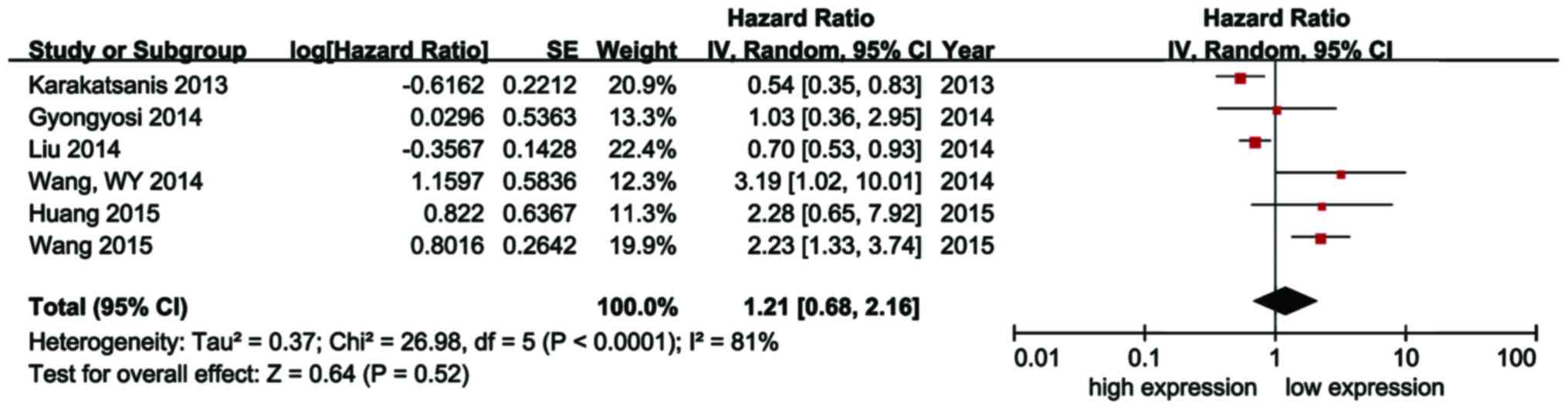
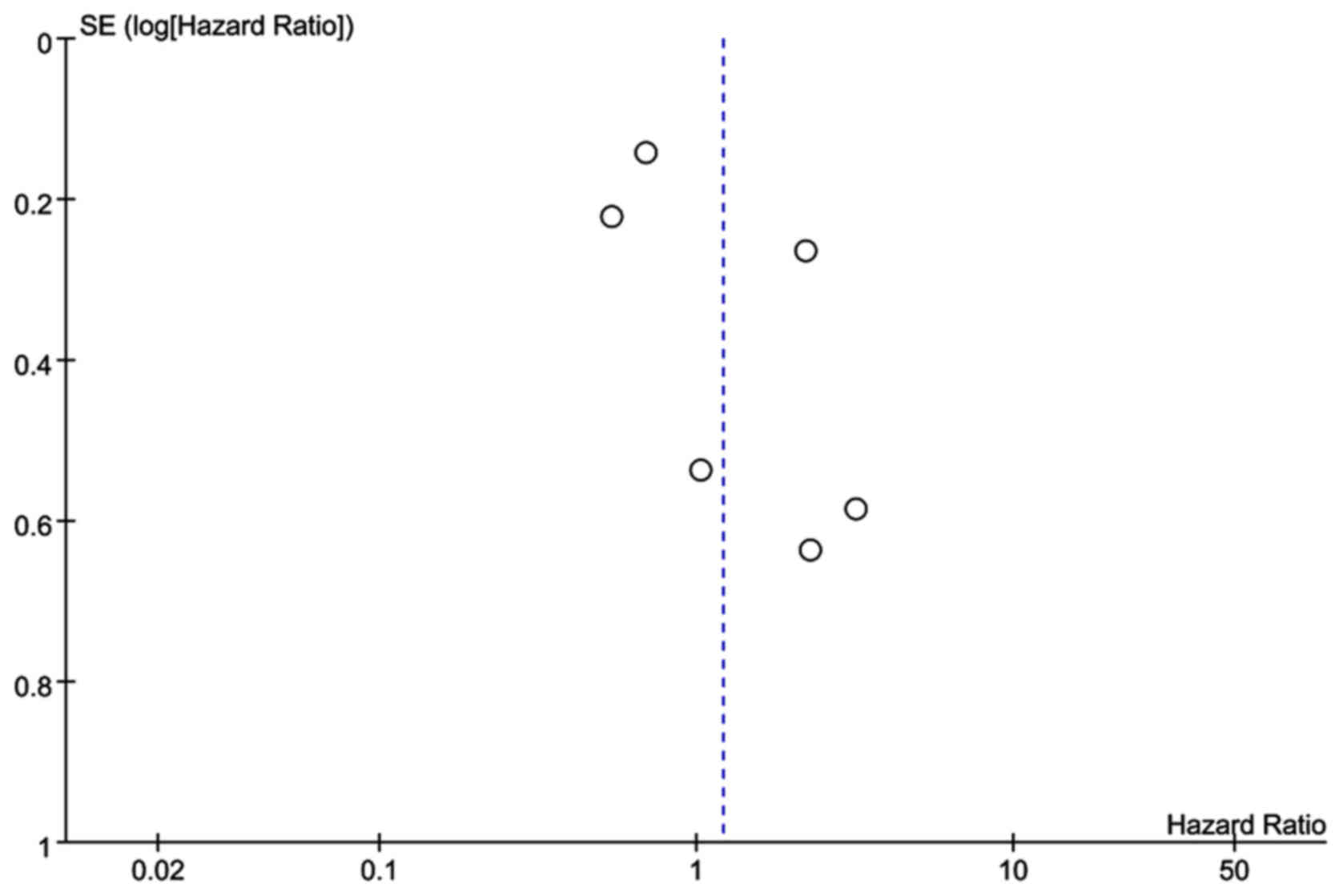
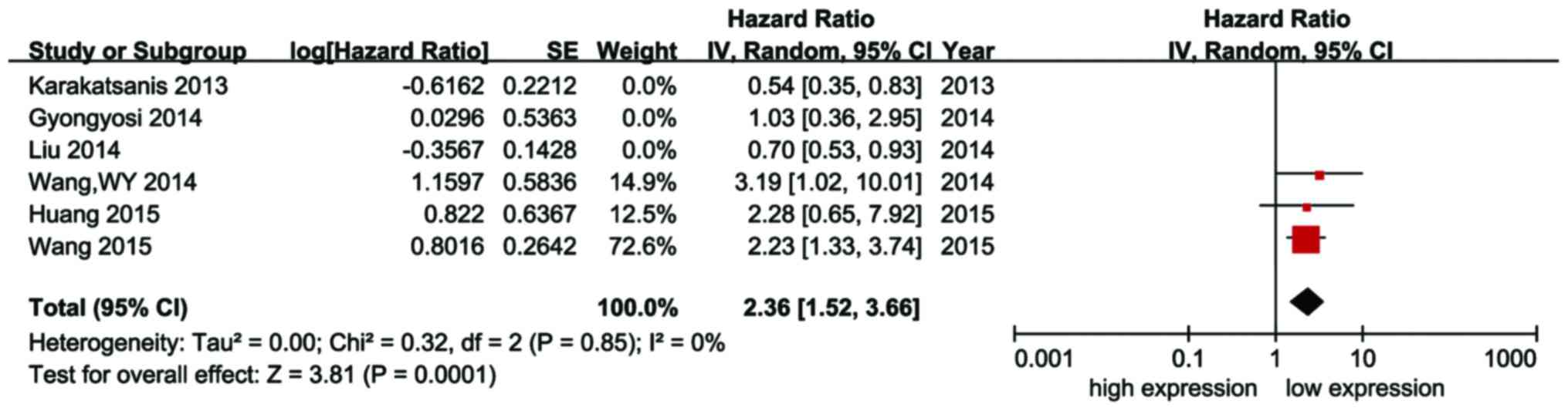
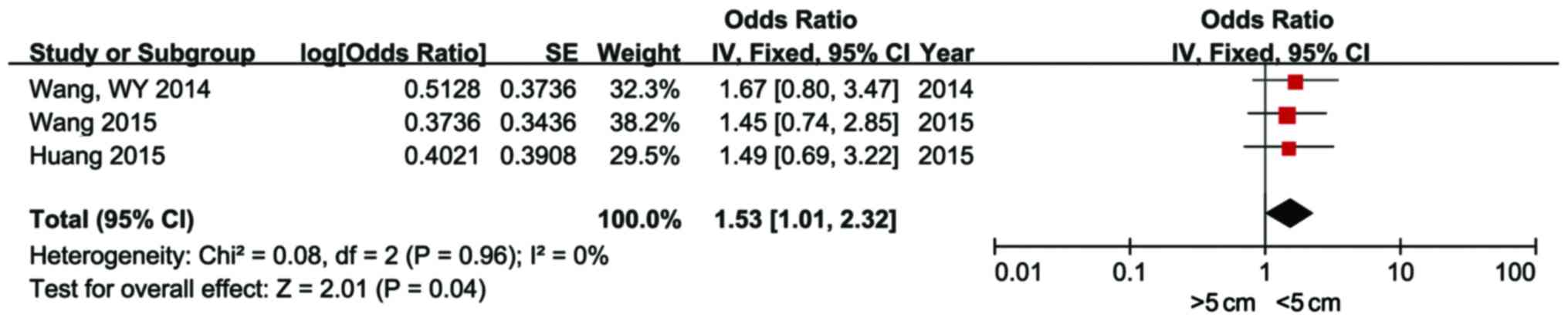
26
|
Huang CS, Yu W, Cui H, Wang YJ, Zhang L,
Han F and Huang T: Increased expression of miR-21 predicts poor
prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:7234–7238. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang WY, Zhang HF, Wang L, Ma YP, Gao F,
Zhang SJ and Wang LC: miR-21 expression predicts prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol.
38:715–719. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang H, Hou L, Li A, Duan Y, Gao H and
Song X: Expression of serum exosomal microRNA-21 in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Res Int.
2014:8648942014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu M, Liu J, Wang L, Wu H, Zhou C, Zhu H,
Xu N and Xie Y: Association of serum microRNA expression in
hepatocellular carcinomas treated with transarterial
chemoembolization and patient survival. PLoS One. 9:e1093472014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gyöngyösi B, Végh É, Járay B, Székely E,
Fassan M, Bodoky G, Schaff Z and Kiss A: Pretreatment microrna
level and outcome in sorafenib-treated hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Histochem Cytochem. 62:547–555. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|