|
1
|
Balamuth NJ and Womer RB: Ewing's sarcoma.
Lancet Oncol. 11:184–192. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gaspar N, Hawkins DS, Dirksen U, Lewis IJ,
Ferrari S, Le Deley MC, Kovar H, Grimer R, Whelan J, Claude L, et
al: Ewing sarcoma: Current management and future approaches through
collaboration. J Clin Oncol. 33:3036–3046. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lawlor ER and Thiele CJ: Epigenetic
changes in pediatric solid tumors: Promising new targets. Clin
Cancer Res. 18:2768–2779. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Riggi N, Knoechel B, Gillespie SM,
Rheinbay E, Boulay G, Suvà ML, Rossetti NE, Boonseng WE, Oksuz O,
Cook EB, et al: EWS-FLI1 utilizes divergent chromatin remodeling
mechanisms to directly activate or repress enhancer elements in
Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Cell. 26:668–681. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
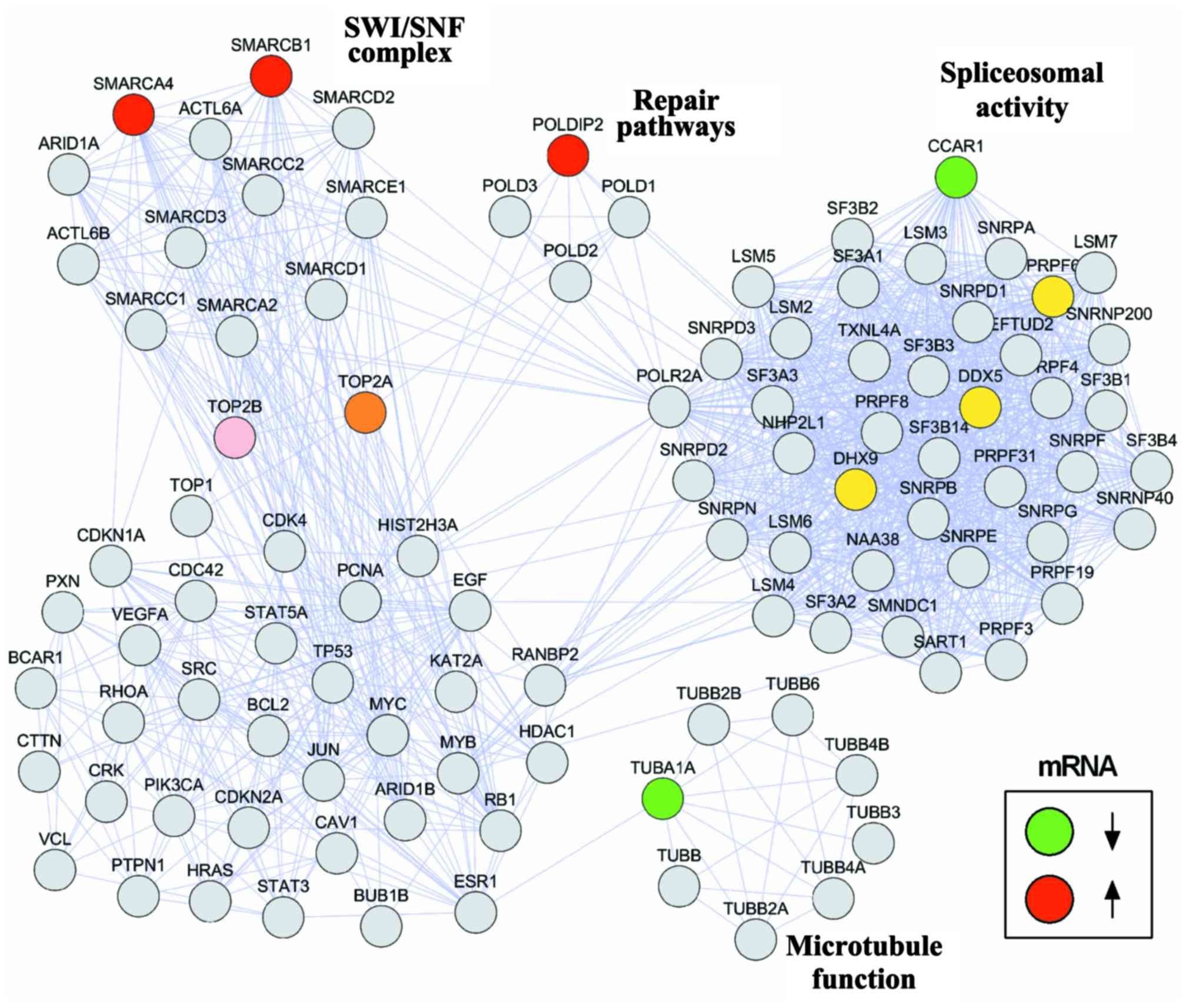
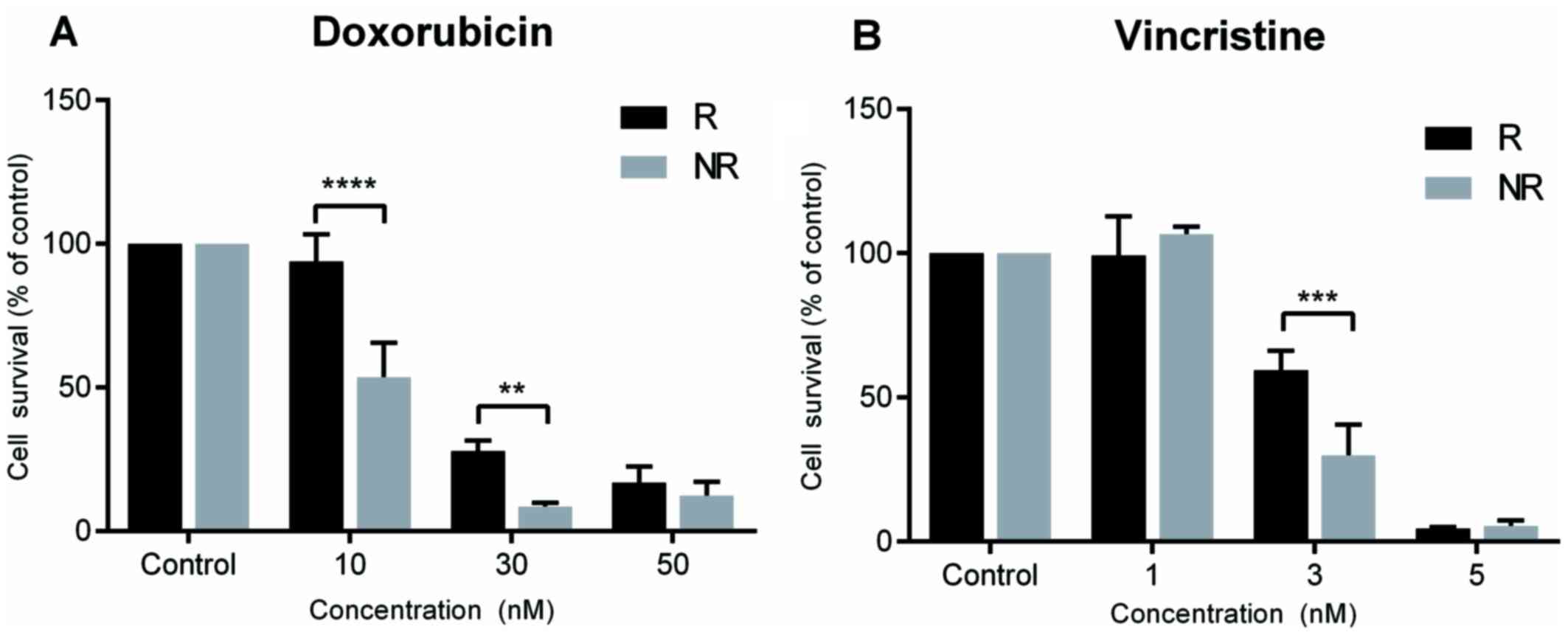
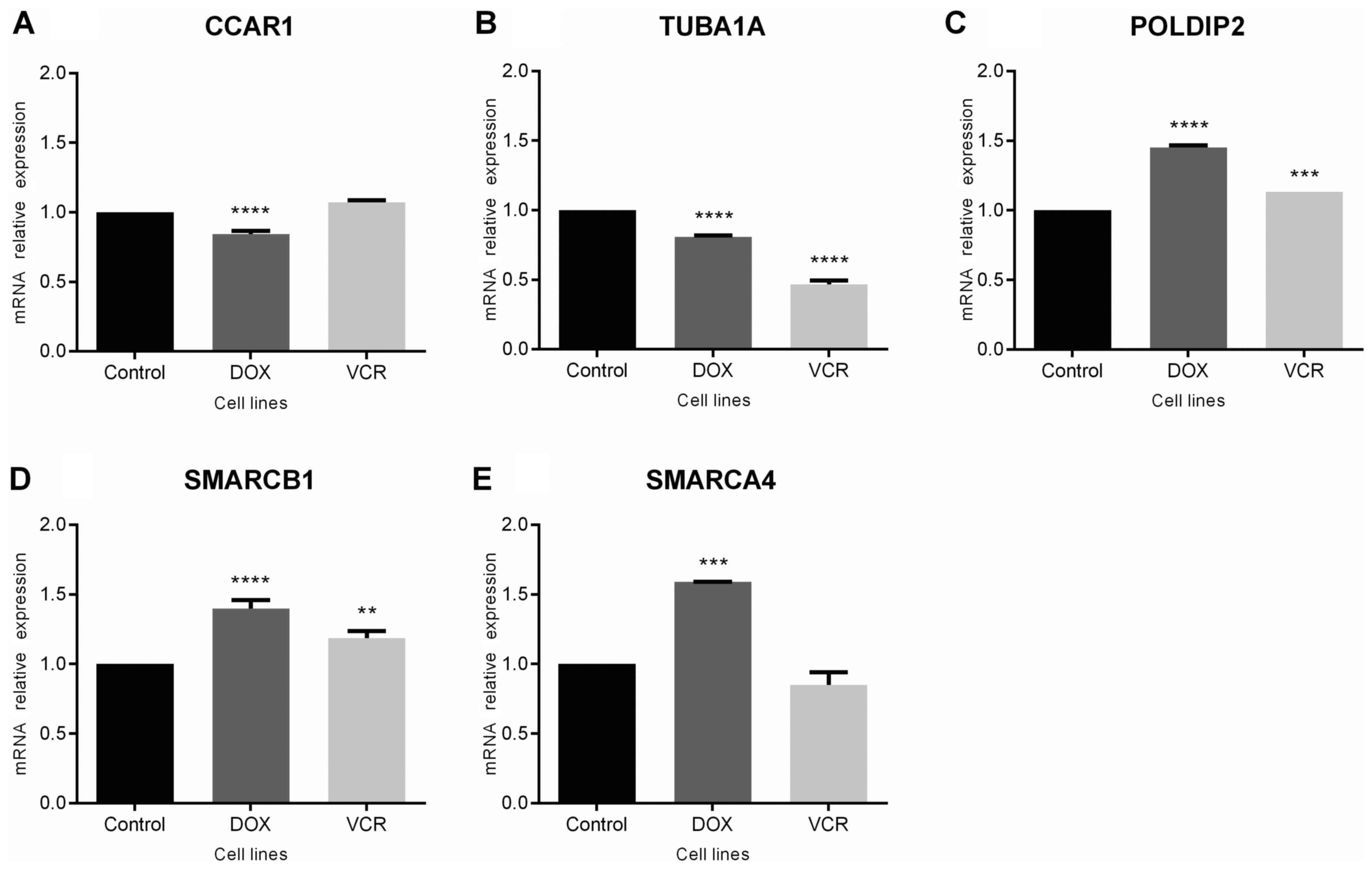
Sheffield NC, Pierron G, Klughammer J,
Datlinger P, Schönegger A, Schuster M, Hadler J, Surdez D,
Guillemot D, Lapouble E, et al: DNA methylation heterogeneity
defines a disease spectrum in Ewing sarcoma. Nat Med. 23:386–395.
2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Womer RB, West DC, Krailo MD, Dickman PS,
Pawel BR, Grier HE, Marcus K, Sailer S, Healey JH, Dormans JP, et
al: Randomized controlled trial of interval-compressed chemotherapy
for the treatment of localized Ewing sarcoma: A report from the
Children's Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 30:4148–4154. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Grier HE, Krailo MD, Tarbell NJ, Link MP,
Fryer CJ, Pritchard DJ, Gebhardt MC, Dickman PS, Perlman EJ, Meyers
PA, et al: Addition of ifosfamide and etoposide to standard
chemotherapy for Ewing's sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal
tumor of bone. N Engl J Med. 348:694–701. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ahmed AA, Zia H and Wagner L: Therapy
resistance mechanisms in Ewing's sarcoma family tumors. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 73:657–663. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Heinen TE, Dos Santos RP, da Rocha A, Dos
Santos MP, Lopez PL, Filho Silva MA, Souza BK, Rivero LF, Becker
RG, Gregianin LJ, et al: Trk inhibition reduces cell proliferation
and potentiates the effects of chemotherapeutic agents in Ewing
sarcoma. Oncotarget. 7:34860–34880. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Anderson PM, Bielack SS, Gorlick RG,
Skubitz K, Daw NC, Herzog CE, Monge OR, Lassaletta A, Boldrini E,
Pápai Z, et al: A phase II study of clinical activity of SCH 717454
(robatumumab) in patients with relapsed osteosarcoma and Ewing
sarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 63:1761–1770. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wagner LM, Fouladi M, Ahmed A, Krailo MD,
Weigel B, DuBois SG, Doyle LA, Chen H and Blaney SM: Phase II study
of cixutumumab in combination with temsirolimus in pediatric
patients and young adults with recurrent or refractory sarcoma: A
report from the Children's Oncology Group. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
62:440–444. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pang B, Qiao X, Janssen L, Velds A,
Groothuis T, Kerkhoven R, Nieuwland M, Ovaa H, Rottenberg S, van
Tellingen O, et al: Drug-induced histone eviction from open
chromatin contributes to the chemotherapeutic effects of
doxorubicin. Nat Commun. 4:19082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang F, Teves SS, Kemp CJ and Henikoff S:
Doxorubicin, DNA torsion, and chromatin dynamics. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1845:84–89. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cox J and Weinman S: Mechanisms of
doxorubicin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat Oncol.
3:57–59. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kavallaris M: Microtubules and resistance
to tubulin-binding agents. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:194–204. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mohammadgholi A, Rabbani-Chadegani A and
Fallah S: Mechanism of the interaction of plant alkaloid
vincristine with DNA and chromatin: Spectroscopic study. DNA Cell
Biol. 32:228–235. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Skladanowski A, Côme MG, Sabisz M,
Escargueil AE and Larsen AK: Down-regulation of DNA topoisomerase
IIalpha leads to prolonged cell cycle transit in G2 and early M
phases and increased survival to microtubule-interacting agents.
Mol Pharmacol. 68:625–634. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang Y, Yang SH and Guo XL: New insights
into Vinca alkaloids resistance mechanism and circumvention in lung
cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 96:659–666. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Flores DG, de Farias CB, Leites J, de
Oliveira MS, Lima RC, Tamajusuku AS, Di Leone LP, Meurer L,
Brunetto AL, Schwartsmann G, et al: Gastrin-releasing peptide
receptors regulate proliferation of C6 Glioma cells through a
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent mechanism. Curr Neurovasc
Res. 5:99–105. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huzil JT, Chen K, Kurgan L and Tuszynski
JA: The roles of beta-tubulin mutations and isotype expression in
acquired drug resistance. Cancer Inform. 3:159–181. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Villeneuve DJ, Hembruff SL, Veitch Z,
Cecchetto M, Dew WA and Parissenti AM: cDNA microarray analysis of
isogenic paclitaxel- and doxorubicin-resistant breast tumor cell
lines reveals distinct drug-specific genetic signatures of
resistance. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 96:17–39. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guilliam TA, Bailey LJ, Brissett NC and
Doherty AJ: PolDIP2 interacts with human PrimPol and enhances its
DNA polymerase activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:3317–3329. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maga G, Crespan E, Markkanen E, Imhof R,
Furrer A, Villani G, Hübscher U and van Loon B: DNA polymerase
δ-interacting protein 2 is a processivity factor for DNA polymerase
λ during 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine bypass. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:18850–18855. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brown DI, Lassègue B, Lee M, Zafari R,
Long JS, Saavedra HI and Griendling KK: Poldip2 knockout results in
perinatal lethality, reduced cellular growth and increased
autophagy of mouse embryonic fibroblasts. PLoS One. 9:e966572014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sutliff RL, Hilenski LL, Amanso AM,
Parastatidis I, Dikalova AE, Hansen L, Datla SR, Long JS, El-Ali
AM, Joseph G, et al: Polymerase delta interacting protein 2
sustains vascular structure and function. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 33:2154–2161. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wijdeven RH, Pang B, van der Zanden SY,
Qiao X, Blomen V, Hoogstraat M, Lips EH, Janssen L, Wessels L,
Brummelkamp TR, et al: Genome-wide identification and
characterization of novel factors conferring resistance to
topoisomerase II poisons in cancer. Cancer Res. 75:4176–4187. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dubey R, Lebensohn AM, Bahrami-Nejad Z,
Marceau C, Champion M, Gevaert O, Sikic BI, Carette JE and Rohatgi
R: Chromatin-remodeling complex SWI/SNF controls multidrug
resistance by transcriptionally regulating the drug efflux pump
ABCB1. Cancer Res. 76:5810–5821. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jahromi MS, Putnam AR, Druzgal C, Wright
J, Spraker-Perlman H, Kinsey M, Zhou H, Boucher KM, Randall RL,
Jones KB, et al: Molecular inversion probe analysis detects novel
copy number alterations in Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Genet.
205:391–404. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chang TS, Wei KL, Lu CK, Chen YH, Cheng
YT, Tung SY, Wu CS and Chiang MK: Inhibition of CCAR1, a
coactivator of beta-catenin, suppresses the proliferation and
migration of gastric cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E4602017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ha SY, Kim JH, Yang JW, Kim J, Kim B and
Park CK: The overexpression of CCAR1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
associates with poor prognosis. Cancer Res Treat. 48:1065–1073.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim JH, Yang CK, Heo K, Roeder RG, An W
and Stallcup MR: CCAR1, a key regulator of mediator complex
recruitment to nuclear receptor transcription complexes. Mol Cell.
31:510–519. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Seo WY, Jeong BC, Yu EJ, Kim HJ, Kim SH,
Lim JE, Kwon GY, Lee HM and Kim JH: CCAR1 promotes chromatin
loading of androgen receptor (AR) transcription complex by
stabilizing the association between AR and GATA2. Nucleic Acids
Res. 41:8526–8536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Selvanathan SP, Graham GT, Erkizan HV,
Dirksen U, Natarajan TG, Dakic A, Yu S, Liu X, Paulsen MT, Ljungman
ME, et al: Oncogenic fusion protein EWS-FLI1 is a network hub that
regulates alternative splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:E1307–E1316. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|