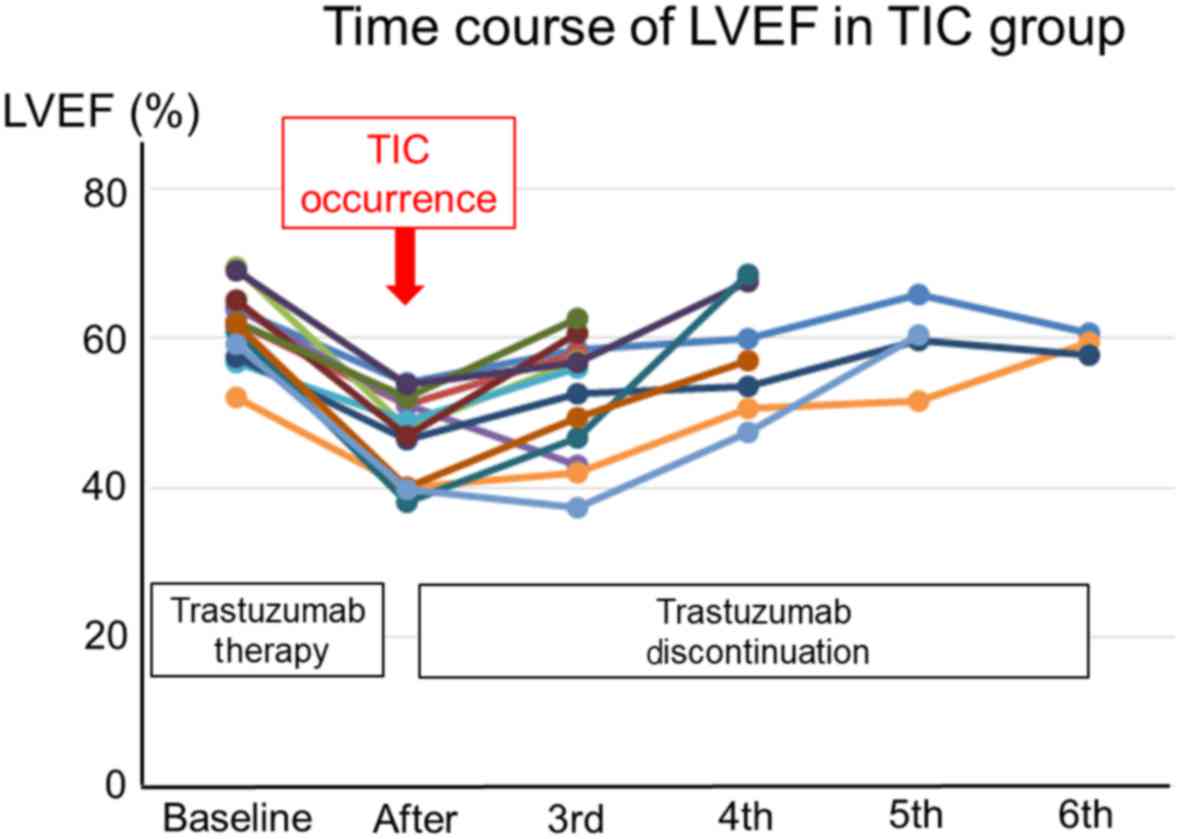
|
1
|
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB,
Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin.
66:271–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Santhosh S, Kumar P, Ramprasad V and
Chaudhuri A: Evolution of targeted therapies in cancer:
Opportunities and challenges in the clinic. Future Oncol.
11:279–293. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zamorano JL, Lancellotti P, Rodriguez
Muñoz D, Aboyans V, Asteggiano R, Galderisi M, Habib G, Lenihan DJ,
Lip GYH, Lyon AR, et al: Group ESCSD. 2016 esc position paper on
cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity developed under the
auspices of the esc committee for practice guidelines: The task
force for cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity of the
european society of cardiology (esc). Eur Heart J. 37:2768–2801.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lal H, Kolaja KL and Force T: Cancer
genetics and the cardiotoxicity of the therapeutics. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 61:267–274. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nikolai BC, Lanz RB, York B, Dasgupta S,
Mitsiades N, Creighton CJ, Tsimelzon A, Hilsenbeck SG, Lonard DM,
Smith CL and O'Malley BW: HER2 signaling drives DNA anabolism and
proliferation through SRC-3 phosphorylation and E2F1-regulated
genes. Cancer Res. 76:1463–1475. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hudis CA: Trastuzumab-mechanism of action
and use in clinical practice. N Engl J Med. 357:39–51. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pritchard KI, Shepherd LE, O'Malley FP,
Andrulis IL, Tu D, Bramwell VH and Levine MN: National Cancer
Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group: HER2 and responsiveness
of breast cancer to adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med.
354:2103–2111. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Perez EA, Romond EH, Suman VJ, Jeong JH,
Sledge G, Geyer CE Jr, Martino S, Rastogi P, Gralow J, Swain SM, et
al: Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for human epidermal
growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer: Planned joint
analysis of overall survival from NSABP B-31 and NCCTG N9831. J
Clin Oncol. 32:3744–3752. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Criscitiello C and Curigliano G: HER2
signaling pathway and trastuzumab cardiotoxicity. Future Oncol.
9:179–181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Negro A, Brar BK and Lee KF: Essential
roles of Her2/erbB2 in cardiac development and function. Recent
Prog Horm Res. 59:1–12. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bloom MW, Hamo CE, Cardinale D, Ky B,
Nohria A, Baer L, Skopicki H, Lenihan DJ, Gheorghiade M, Lyon AR
and Butler J: Cancer therapy-related cardiac dysfunction and heart
failure: Part 1: Definitions, pathophysiology, risk factors and
imaging. Circ Heart Fail. 9:e0026612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ezaz G, Long JB, Gross CP and Chen J: Risk
prediction model for heart failure and cardiomyopathy after
adjuvant trastuzumab therapy for breast cancer. J Am Heart Assoc.
3:e0004722014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Goldhirsch A, Gelber RD, Piccart-Gebhart
MJ, de Azambuja E, Procter M, Suter TM, Jackisch C, Cameron D,
Weber HA, Heinzmann D, et al: 2 years versus 1 year of adjuvant
trastuzumab for HER2-positive breast cancer (HERA): An open-label,
randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 382:1021–1028. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
McKee PA, Castelli WP, McNamara PM and
Kannel WB: The natural history of congestive heart failure: The
framingham study. N Engl J Med. 285:1441–1446. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Seidman A, Hudis C, Pierri MK, Shak S,
Paton V, Ashby M, Murphy M, Stewart SJ and Keefe D: Cardiac
dysfunction in the trastuzumab clinical trials experience. J Clin
Oncol. 20:1215–1221. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brown SA, Sandhu N and Herrmann J: Systems
biology approaches to adverse drug effects: The example of
cardio-oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 12:718–731. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guglin M, Cutro R and Mishkin JD:
Trastuzumab-induced cardiomyopathy. J Card Fail. 14:437–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bowles EJ, Wellman R, Feigelson HS,
Onitilo AA, Freedman AN, Delate T, Allen LA, Nekhlyudov L, Goddard
KA, Davis RL, et al: Risk of heart failure in breast cancer
patients after anthracycline and trastuzumab treatment: A
retrospective cohort study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 104:1293–1305.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Smith LA, Cornelius VR, Plummer CJ, Levitt
G, Verrill M, Canney P and Jones A: Cardiotoxicity of anthracycline
agents for the treatment of cancer: Systematic review and
meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMC Cancer.
10:3372010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Russell SD, Blackwell KL, Lawrence J,
Pippen JE Jr, Roe MT, Wood F, Paton V, Holmgren E and Mahaffey KW:
Independent adjudication of symptomatic heart failure with the use
of doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by trastuzumab
adjuvant therapy: A combined review of cardiac data from the
National Surgical Adjuvant breast and Bowel Project B-31 and the
North Central Cancer Treatment Group N9831 clinical trials. J Clin
Oncol. 28:3416–3421. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu AF, Yadav NU, Eaton AA, Lung BY, Thaler
HT, Liu JE, Hudis CA, Dang CT and Steingart RM: Continuous
trastuzumab therapy in breast cancer patients with asymptomatic
left ventricular dysfunction. Oncologist. 20:1105–1110. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Martin M, Esteva FJ, Alba E, Khandheria B,
Pérez-Isla L, García-Sáenz JA, Márquez A, Sengupta P and Zamorano
J: Minimizing cardiotoxicity while optimizing treatment efficacy
with trastuzumab: Review and expert recommendations. Oncologist.
14:1–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hensley ML, Schuchter LM, Lindley C,
Meropol NJ, Cohen GI, Broder G, Gradishar WJ, Green DM, Langdon RJ
Jr, Mitchell RB, et al: American society of clinical oncology
clinical practice guidelines for the use of chemotherapy and
radiotherapy protectants. J Clin Oncol. 17:3333–3355. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hering D, Faber L and Horstkotte D:
Echocardiographic features of radiation-associated valvular
disease. Am J Cardiol. 92:226–230. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tassan-Mangina S, Codorean D, Metivier M,
Costa B, Himberlin C, Jouannaud C, Blaise AM, Elaerts J and
Nazeyrollas P: Tissue doppler imaging and conventional
echocardiography after anthracycline treatment in adults: Early and
late alterations of left ventricular function during a prospective
study. Eur J Echocardiogr. 7:141–146. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Oreto L, Todaro MC, Umland MM, Kramer C,
Qamar R, Carerj S, Khandheria BK and Paterick TE: Use of
echocardiography to evaluate the cardiac effects of therapies used
in cancer treatment: What do we know? J Am Soc Echocardiogr.
25:1141–1152. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ferté C, Massard C, Cohen A, Soria JC and
Ederhy S: Trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity: Is it time for
troponin for all patients? Am J Clin Oncol. 35:183–184. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cardinale D, Colombo A, Torrisi R, Sandri
MT, Civelli M, Salvatici M, Lamantia G, Colombo N, Cortinovis S,
Dessanai MA, et al: Trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity: Clinical
and prognostic implications of troponin i evaluation. J Clin Oncol.
28:3910–3916. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|