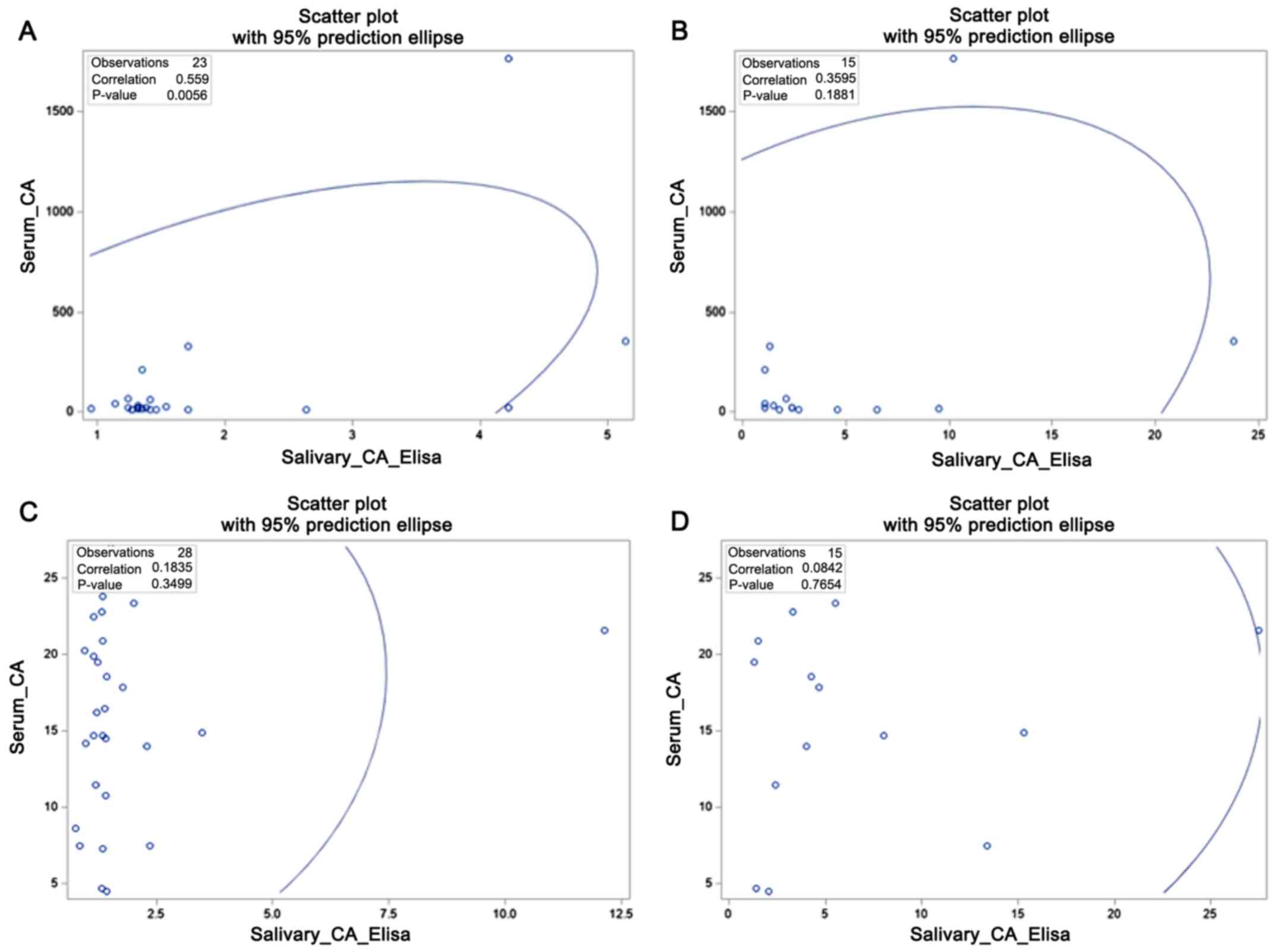
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:94–424. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Narod SA, Iqbal J and Miller AB: Why have
breast cancer mortality rates declined? J Cancer Policy. 5:8–17.
2015.
|
|
3
|
Arellano M, Jiang J, Zhou X, Zhang L, Ye
H, Wong DT and Hu S: Current advances in identification of cancer
biomarkers in Saliva. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 1:296–303.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Giuliano AE, Connolly JL, Edge SB,
Mittendorf EA, Rugo HS, Solin LJ, Weaver DL, Winchester DJ and
Hortobagyi GN: Breast cancer-major changes in the American joint
committee on cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer
J Clin. 67:290–303. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Berg WA, Gutierrez L, NessAiver MS, Carter
WB, Bhargavan M, Lewis RS and Ioffe OB: Diagnostic accuracy of
mammography, clinical examination, US, and MR imaging in
preoperative assessment of breast cancer. Radiology. 233:830–849.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang YJ, Wei L, Li J, Zheng YQ and Li XR:
Status quo and development trend of breast biopsy technology. Gland
Surg. 2:15–24. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hollingsworth MA and Swanson BJ: Mucins in
cancer: Protection and control of the cell surface. Nat Rev Cancer.
4:45–60. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nath S and Mukherjee P: MUC1: A
multifaceted oncoprotein with a key role in cancer progression.
Trends Mol Med. 20:332–342. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Duffy MJ, Shering S, Sherry F, McDermott E
and O'Higgins N: CA 15-3: A prognostic marker in breast cancer. Int
J Biol Markers. 15:330–333. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Harris LN, Ismaila N, McShane LM, Andre F,
Collyar DE, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hammond EH, Kuderer NM, Liu MC,
Mennel RG, et al: Use of biomarkers to guide decisions on adjuvant
systemic therapy for women with early-stage invasive breast cancer:
American society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline.
J Clin Oncol. 34:1134–1150. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Punyadeera C and Slowey PD: Saliva as an
emerging biofluid for clinical diagnosis and applications of
MEMS/NEMS in salivary diagnostics. Nanobiomat Clin Dent, pp453-473,
2012.
|
|
12
|
Schafer CA, Schafer JJ, Yakob M, Lima P,
Camargo P and Wong DT: Saliva diagnostics: Utilizing oral fluids to
determine health status. Monogr Oral Sci. 24:88–98. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bigler LR, Streckfus CF, Copeland L, Burns
R, Dai X, Kuhn M, Martin P and Bigler SA: The potential use of
saliva to detect recurrence of disease in women with breast
carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 31:421–431. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li P, Ye H, Liu J, Jin H, Lin Y, Yan S, Yu
Y, Gao L, Xu F and Zhang Z: Evaluation of a newly developed
quantitative determination kit for tumor marker CA15-3 with
chemiluminescent assay. J Clin Lab Anal 32, 2018.
|
|
15
|
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz AG,
Balch CM, Haller DG and Morrow M (eds): AJCC Cancer Staging Manual.
7th edition, Sringer, 2017. https://cancerstaging.org/Pages/default.aspx.
|
|
16
|
Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber
RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B and Senn HJ: Panel members.
Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer:
Highlights of the St Gallen international expert consensus on the
primary therapy of early breast cancer 2013. Ann Oncol.
24:2206–2223. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Victer TN, Dos Santos CS, Báo SN and
Sampaio TL: Deceased tissue donor serology and molecular testing
for HIV, hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses: A lack of cadaveric
validated tests. Cell Tissue Bank. 17:543–553. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Streckfus CF, Bigler L, Edwards C,
Guajardo-Streckfus C and Bigler SA: Using saliva secretions to
model disease progression. Adv Saliva Diagn, pp187-198, 2015.
|
|
19
|
Atoum M, Nimer N, Abdeldayem S and Nasr H:
Relationships among serum CA15-3 tumor marker, TNM staging, and
estrogen and progesterone receptor expression in benign and
malignant breast lesions. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev. 13:857–860.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Park S, Ahn HK, Park LC, Hwang DW, Ji JH,
Maeng CH, Cho SH, Lee JY, Park KT, Ahn JS, et al: Implications of
different CA 15-3 levels according to breast cancer subtype at
initial diagnosis of recurrent or metastatic breast cancer.
Oncology. 82:180–187. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Horm TM and Schroeder JA: MUC1 and
metastatic cancer: Expression, function and therapeutic targeting.
Cell Adhes Migr. 7:187–198. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Harris L, Fritsche H, Mennel R, Norton L,
Ravdin P, Taube S, Somerfield MR, Hayes DF and Bast RC Jr: American
Society of Clinical Oncology. American society of clinical oncology
2007 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in
breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 25:5287–5312. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Emens LA and Davidson NE: The follow-up of
breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 30:338–348. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Agha-Hosseini F, Mirzaii-Dizgah I, Rahimi
A and Seilanian-Toosi M: Correlation of serum and salivary CA125
levels in patients with breast cancer. J Contemp Dent Pract.
10:E001–E008. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kaczor-Urbanowicz KE, Martin
Carreras-Presas C, Aro K, Tu M, Garcia-Godoy F and Wong DT: Saliva
diagnostics-current views and directions. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
242:459–472. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Dawes C and Wong DTW: Role of saliva and
salivary diagnostics in the advancement of oral health. J Dent Res.
98:133–141. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Meghnani V, Mohammed N, Giauque C, Nahire
R and David T: Performance characterization and validation of
saliva as an alternative specimen source for detecting hereditary
breast cancer mutations by next generation sequencing. Int J
Genomics. 2016(2059041)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Cascella R, Stocchi L, Strafella C,
Mezzaroma I, Mannazzu M, Vullo V, Montella F, Parruti G, Borgiani
P, Sangiuolo F, et al: Comparative analysis between saliva and
buccal swabs as source of DNA: Lesson from HLA-B*57:01 testing.
Pharmacogenomics. 16:1039–1046. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|