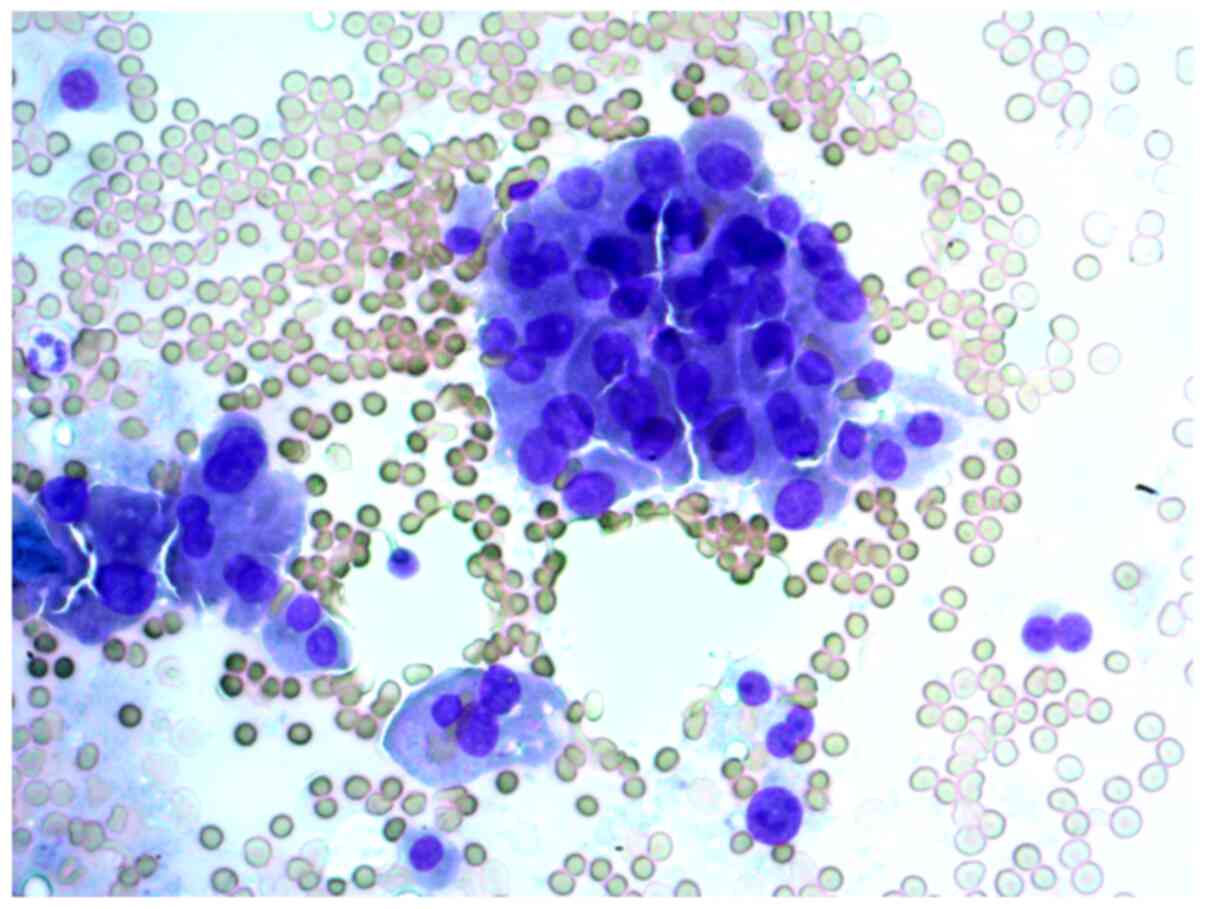
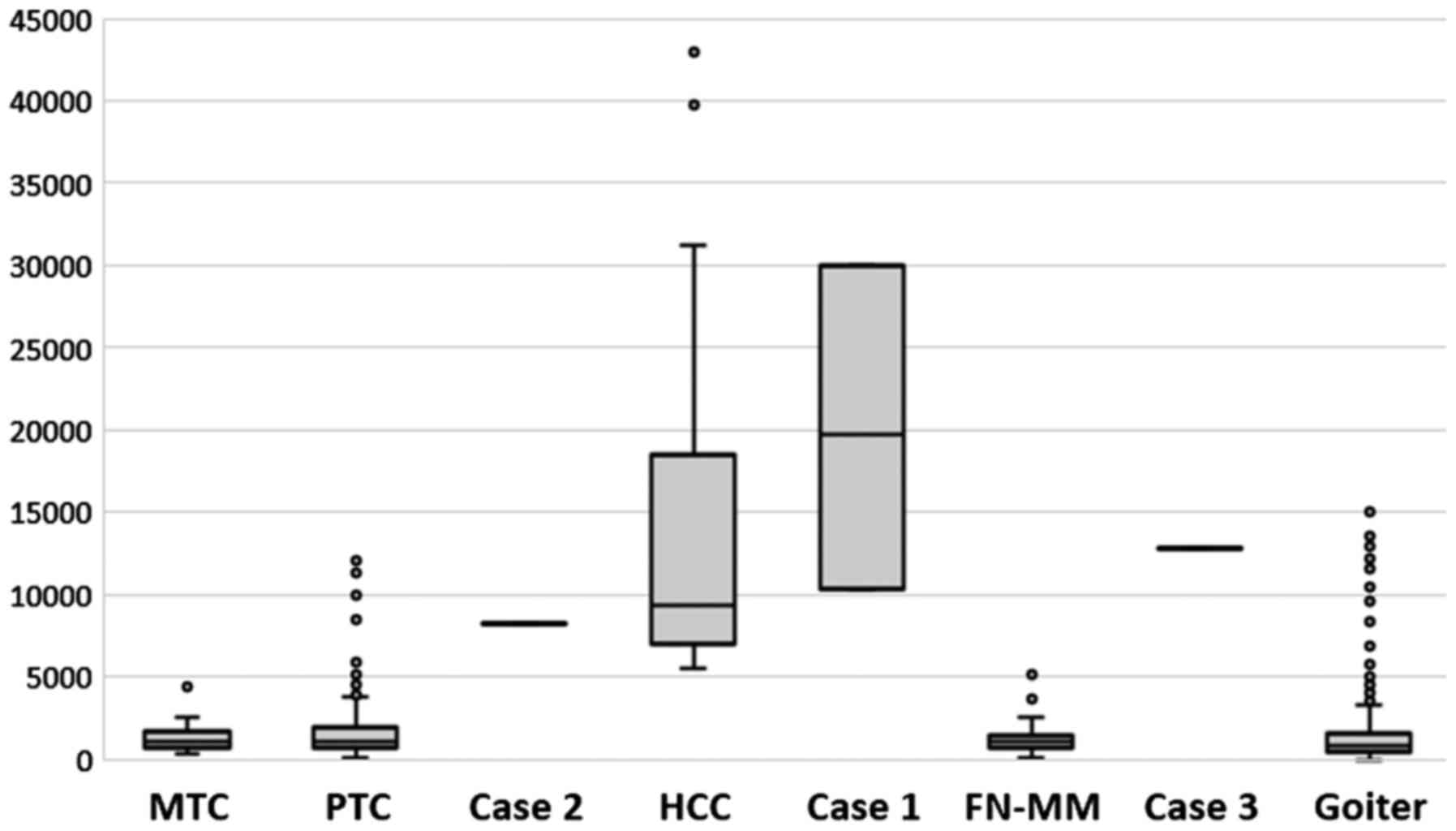
|
1
|
Ali SZ and Cibas ES (eds.): The Bethesda
System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology. Springer, New York, NY,
2018.
|
|
2
|
Baloch ZW, LiVolshi VA, Asa SL, Rosai J,
Merino MJ, Randolph G, Vielh P, DeMay RM, Sidawy MK and Frable WJ:
Diagnostic terminology and morphologic criteria for cytologic
diagnosis of thyroid lesions: A synopsis of the national cancer
institute thyroid fine-needle aspiration state of the science
conference. Diagn Cytopathol. 36:425–437. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Nguyen GK, Lee MW, Ginsberg J, Wragg T and
Bilodeau D: Fine-needle aspiration of the thyroid: An overview.
Cytojournal. 2(12)2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lloyd RV, Osamura RY, Klöppel G and Rosai
J (eds): WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs. IARC,
Lyon, 2017.
|
|
5
|
Montone KT, Baloch ZW and LiVolsi VA: The
thyroid Hürthle (oncocytic) cell and its associated pathologic
conditions: A surgical pathology and cytopathology review. Arch
Pathol Lab Med. 132:1241–1250. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Nikiforov YE, Biddinger PW, Thompson LDR
and Nikiforova MN (eds): Diagnostic Pathology and Molecular
Genetics of the Thyroid. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,
Piladelphia, PA, 2009.
|
|
7
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang J, Chen J and Sen S: MicroRNA as
biomarkers and diagnostics. J Cell Physiol. 231:25–30.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nikiforova MN, Tseng GC, Steward D, Diorio
D and Nikiforov YE: MicroRNA expression profiling of thyroid
tumors: Biological significance and diagnostic utility. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 93:1600–1608. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network.
Integrated genomic characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Cell. 159:676–690. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pallante P, Battista S, Pierantoni GM and
Fusco A: Deregulation of microRNA expression in thyroid neoplasias.
Nat Rev Endocrinol. 10:88–101. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Swierniak M, Wojcicka A, Czetwertynska M,
Stachlewska E, Maciag M, Wiechno W, Gornicka B, Bogdanska M,
Koperski L, de la Chapelle A and Jazdzewski K: In-depth
characterization of the microRNA transcriptome in normal thyroid
and papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
98:E1401–E1409. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Titov SE, Ivanov MK, Demenkov PS, Katanyan
GA, Kozorezova ES, Malek AV, Veryaskina YA and Zhimulev IF:
Combined quantitation of HMGA2 mRNA, microRNAs, and
mitochondrial-DNA content enables the identification and typing of
thyroid tumors in fine-needle aspiration smears. BMC Cancer.
19(1010)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Titov S, Demenkov PS, Lukyanov SA,
Sergiyko SV, Katanyan GA, Veryaskina YA and Ivanov MK: Preoperative
detection of malignancy in fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC)
smears with indeterminate cytology (Bethesda III, IV) by a combined
molecular classifier. J Clin Pathol. 73:722–727. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee
DH, Nguyen JT, Barbisin M, Xu NL, Mahuvakar VR, Andersen MR, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33(e179)2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Titov SE, Ivanov MK, Karpinskaya EV,
Tsivlikova EV, Shevchenko SP, Veryaskina YA, Akhmerova LG, Poloz
TL, Klimova OA, Gulyaeva LF, et al: miRNA profiling, detection of
BRAF V600E mutation and RET-PTC1 translocation in patients from
Novosibirsk oblast (Russia) with different types of thyroid tumors.
BMC Cancer. 16(201)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cannon J: The Significance of Hürthle
Cells in Thyroid Disease. Oncologist. 16:1380–1387. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Valenta LJ, Michel-Bechet M, Warshaw JB
and Maloof F: Human thyroid tumors composed of mitochondrion-rich
cells: Electron microscopic and biochemical findings. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 39:719–733. 1974.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sobrinho-Simoes M, Asa SL, Kroll TG,
Nikiforov YE, DeLellis RA, Farid P, Kitamura Y, Noguchi S, Eng C,
Harach HR, et al: Follicular carcinoma. In: World Health
Organization Classification of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics of
Tumours of Endocrine Organs. deLellis RA, Lloyd RV, Heitz PU and
Eng C (eds). IARC Press, Lyon, pp 67-72, 2004.
|
|
21
|
Máximo V, Lima J, Prazeres H, Soares P and
Sobrinho-Simões M: The biology and the genetics of Hurthle cell
tumors of the thyroid. Endocr Relat Cancer. 19:R131–R147.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Patel KN, Angell TE, Babiarz J, Barth NM,
Blevins T, Duh QY, Ghossein RA, Harrell RM, Huang J, Kennedy GC, et
al: Performance of a genomic sequencing classifier for the
preoperative diagnosis of cytologically indeterminate thyroid
nodules. JAMA Surg. 153:817–824. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|