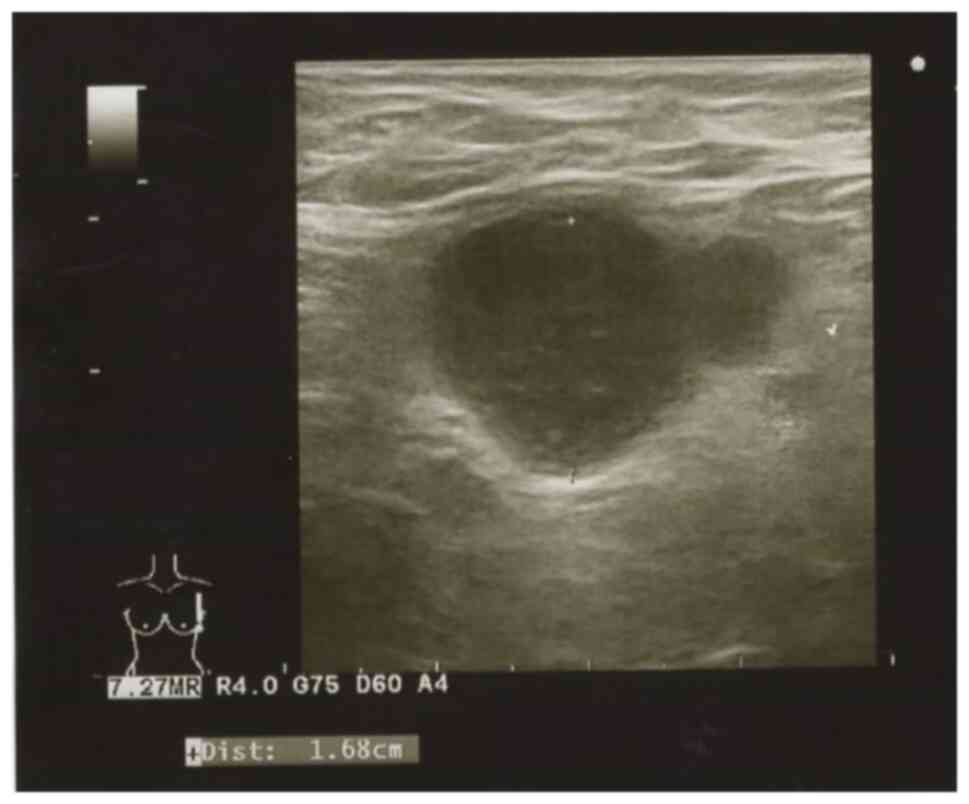
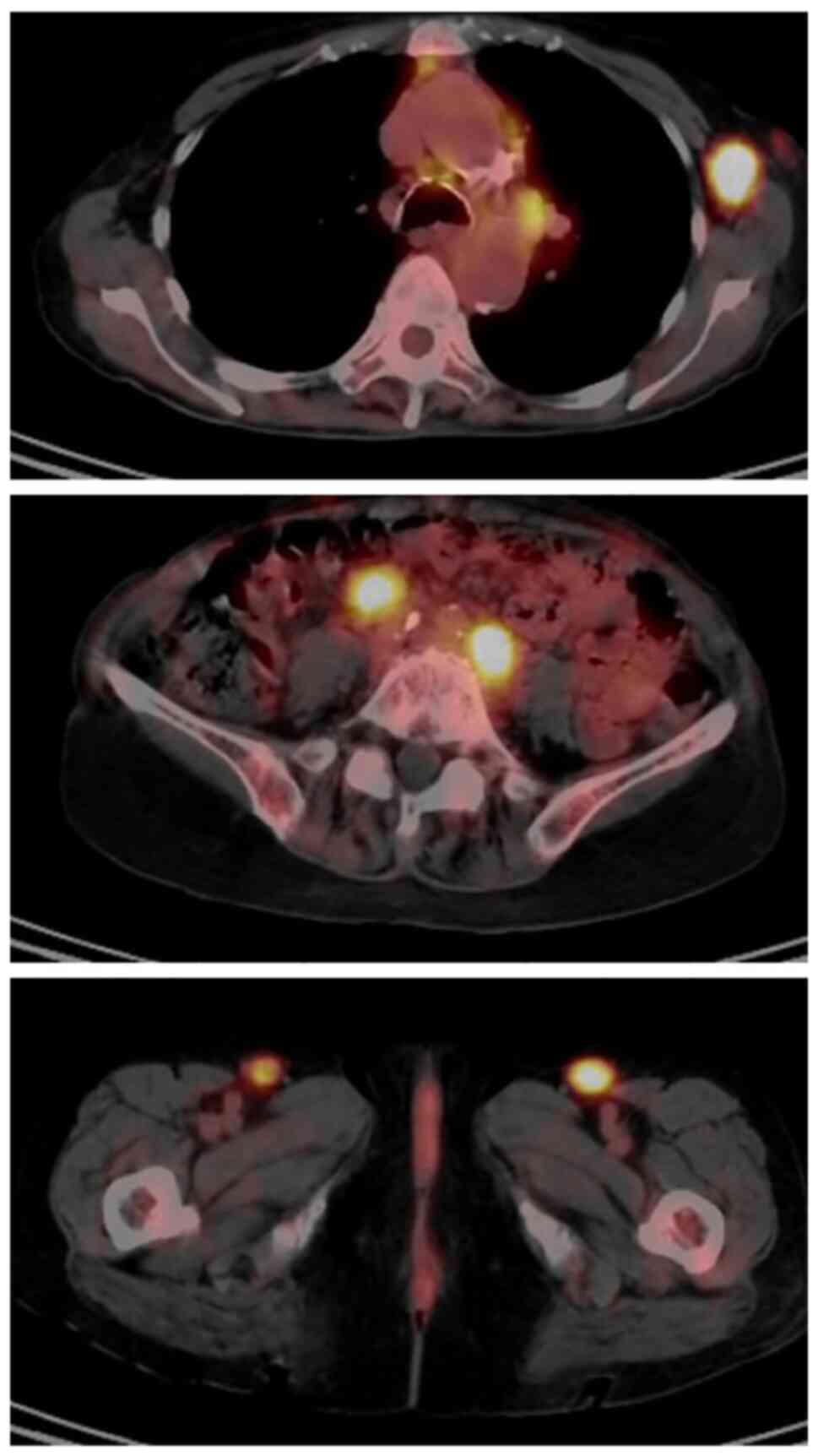
|
1
|
Roy SD, Stafford JA, Scally J and
Selvachandran SN: A rare case of breast carcinoma co-existing with
axillary mantle cell lymphoma. World J Surg Oncol.
1(27)2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Barranger E, Marpeau O, Uzan S and Antoine
M: Axillary sentinel node involvement by breast cancer coexisting
with B-cell follicular lymphoma in nonsentinel nodes. Breast J.
11:227–228. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cox J, Lunt L and Webb L: Synchronous
presentation of breast carcinoma and lymphoma in the axillary
nodes. Breast. 15:246–252. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Garg NK, Bagul NB, Rubin G and Shah EF:
Primary lymphoma of the breast involving both axillae with
bilateral breast carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol.
6(52)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cuff KE, Dettrick AJ and Chern B:
Synchronous breast cancer and lymphoma: A case series and a review
of the literature. J Clin Pathol. 63:555–557. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Laudenschlager MD, Tyler KL, Geis MC, Koch
MR and Graham DB: A rare case of synchronous invasive ductal
carcinoma of the breast and follicular lymphoma. S D Med.
63:123–125. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sordi E, Cagossi K, Lazzaretti MG,
Gusolfino D, Artioli F, Santacroce G, Brandi ML and Piscitelli P:
Rare case of male breast cancer and axillary lymphoma in the same
patient: An unique case report. Case Rep Med.
2011(940803)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Miles EF and Jacimore LL: Synchronous
bilateral breast carcinoma and axillary non-hodgkin lymphoma: A
case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Oncol Med.
2012(685919)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Arana S, Vasquez-Del-Aguila J,
Espinosa-Bravo M, Peg V and Rubio IT: Lymphatic mapping could not
be impaired in the presence of breast carcinoma and coexisting
small lymphocytic lymphoma. Am J Case Rep. 14:322–325.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tamaoki M, Nio Y, Tsuboi K, Nio M, Tamaoki
M and Maruyama R: A rare case of non-invasive ductal carcinoma of
the breast coexisting with follicular lymphoma: A case report with
a review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 7:1001–1006.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Woo EJ, Baugh AD and Ching K: Synchronous
presentation of invasive ductal carcinoma and mantle cell lymphoma:
A diagnostic challenge in menopausal patients. J Surg Case Rep.
22(rjv153)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Brice P, Bastion Y, Lepage E, Brousse N,
Haïoun C, Moreau P, Straetmans N, Tilly H, Tabah I and
Solal-Céligny P: Comparison in low-tumor-burden follicular
lymphomas between an initial no-treatment policy, prednimustine, or
interferon alfa: A randomized study from the Groupe d'Etude des
Lymphomes Folliculaires. Groupe d'Etude des Lymphomes de l'Adulte.
J Clin Oncol. 15:1110–1117. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Solal-Céligny P, Lepage E, Brousse N,
Tendler CL, Brice P, Haïoun C, Gabarre J, Pignon B, Tertian G,
Bouabdallah R, et al: Doxorubicin-containing regimen with or
without interferon alfa-2b for advanced follicular lymphomas: Final
analysis of survival and toxicity in the Groupe d'Etude des
Lymphomes Folliculaires 86 trial. J Clin Oncol. 16:2332–2338.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sebban C, Mounier N, Brousse N, Belanger
C, Brice P, Haioun C, Tilly H, Feugier P, Bouabdallah R, Doyen C,
et al: Standard chemotherapy with interferon compared with CHOP
followed by high-dose therapy with autologous stem cell
transplantation in untreated patients with advanced follicular
lymphoma: The GELF-94 randomized study from the Groupe d'Etude des
Lymphomes de l'Adulte (GELA). Blood. 108:2540–2544. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Park S, Koo JS, Kim GM, Sohn J, Kim SI,
Cho YU, Park BW, Park VY, Yoon JH, Moon HJ, et al: Feasibility of
charcoal tattooing of cytology-proven metastatic axillary lymph
node at diagnosis and sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant
chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. Cancer Res Treat.
50:801–812. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gentilini O and Veronesi U: Abandoning
sentinel lymph node biopsy in early breast cancer? A new trial in
progress at the European institute of oncology of Milan (SOUND:
Sentinel node vs. observation after axillary UltraSouND). Breast.
21:678–681. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cyr AE, Tucker N, Ademuyiwa F,
Margenthaler JA, Aft RL, Eberlein TJ, Appleton CM, Zoberi I, Thomas
MA, Gao F and Gillanders WE: Successful completion of the pilot
phase of a randomized controlled trial comparing sentinel lymph
node biopsy to no further axillary staging in patients with
clinical T1-T2 N0 breast cancer and normal axillary ultrasound. J
Am Coll Surg. 223:399–407. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nguyen BM, Halprin C, Olimpiadi Y, Traum
P, Yeh JJ and Dauphine C: Core needle biopsy is a safe and accurate
initial diagnostic procedure for suspected lymphoma. Am J Surg.
208:1003–1008. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zinzani PL, Colecchia A, Festi D,
Magagnoli M, Larocca A, Ascani S, Bendandi M, Orcioni GF,
Gherlinzoni F, Albertini P, et al: Ultrasound-guided core-needle
biopsy is effective in the initial diagnosis of lymphoma patients.
Haematologica. 83:989–992. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nakamura R, Yamamoto N, Miyaki T, Itami M,
Shina N and Ohtsuka M: Impact of sentinel lymph node biopsy by
ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy for patients with suspicious
node positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 25:86–93.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bhandari A, Xia E, Wang Y, Sindan N, Kc R,
Guan Y, Lin YL, Wang X, Zhang X and Wang O: Impact of sentinel
lymph node biopsy in newly diagnosed invasive breast cancer
patients with suspicious node: A comparative accuracy survey of
fine-needle aspiration biopsy versus core-needle biopsy. Am J
Transl Res. 10:1860–1873. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sandrucci S and Mussa A: Sentinel lymph
node biopsy and axillary staging of T1-T2 N0 breast cancer: A
multicenter study. Semin Surg Oncol. 15:278–283. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gulec SA, Moffat FL, Carroll RG and Krag
DN: Gamma probe guided sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer. Q J
Nucl Med. 41:251–261. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sener SF, Winchester DJ, Brinkmann E,
Winchester DP, Alwawi E, Nickolov A, Perlman RM, Bilimoria M,
Barrera E and Bentrem DJ: Failure of sentinel lymph node mapping in
patients with breast cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 198:732–736.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kramer EL: Lymphoscintigraphy:
Radiopharmaceutical selection and methods. Int J Rad Appl Instrum
B. 17:57–63. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Albertini JJ, Lyman GH, Cox C, Yeatman T,
Balducci L, Ku N, Shivers S, Berman C, Wells K, Rapaport D, et al:
Lymphatic mapping and sentinel node biopsy in the patient with
breast cancer. JAMA. 276:1818–1822. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Veronesi U, Paganelli G, Galimberti V,
Viale G, Zurrida S, Bedoni M, Costa A, de Cicco C, Geraghty JG,
Luini A, et al: Sentinel-node biopsy to avoid axillary dissection
in breast cancer with clinically negative lymph-nodes. Lancet.
349:1864–1867. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, Davies C,
Elphinstone P, Evans V, Godwin J, Gray R, Hicks C, James S, et al:
Early breast cancer Trialists' Collaborative group (EBCTCG):
Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery
for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival:
An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 366:2087–2106.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Fortunato L, Santoni M, Drago S, Gucciardo
G, Farina M, Cesarini C, Cabassi A, Tirelli C, Terribile D, Grassi
GB, et al: Sentinel lymph node biopsy in women with pT1a or
‘microinvasive’ breast cancer. Breast. 17:395–400. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Barone JE, Tucker JB, Perez JM, Odom SR
and Ghevariya V: Evidence-based medicine applied to sentinel lymph
node biopsy in patients with breast cancer: Am. Surg. 71:66–70.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim KH, Son EJ, Kim EK, Ko KH, Kang H and
Oh KK: Safety and efficiency of the ultrasound-guided large needle
core biopsy of axilla lymph nodes. Yonsei Med J. 49:249–254.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Brennan ME and Houssami N: Evaluation of
the evidence on staging imaging for detection of asymptomatic
distant metastases in newly diagnosed breast cancer. Breast.
21:112–123. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kawada N, Uehara H, Hosoki T, Takami M,
Shiroeda H, Arisawa T and Tomita Y: Usefulness of dual-phase
18F-FDG PET/CT for diagnosing small pancreatic tumors. Pancreas.
44:655–659. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Pugliese N, Perna MD, Cozzolino I, Ciancia
G, Pettinato G, Zeppa P, Varone V, Masone S, Cerchione C, Pepa RD,
et al: Randomized comparison of power doppler
ultrasonography-guided core-needle biopsy with open surgical biopsy
for the characterization of lymphadenopathies in patients with
suspected lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 96:627–637. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Nakamura R, Hayama S, Sonoda I, Miyaki T,
Itami M and Yamamoto N: Clinical impact of the biology of
synchronous axillary lymph node metastases in primary breast cancer
on preoperative treatment strategy. J Surg Oncol. 123:1513–1520.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tilly H, Vitolo U, Walewski J, da Silva
MG, Shpilberg O, André M, Pfreundschuh M and Dreyling M: ESMO
guidelines working group. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL):
ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and
follow-up. Ann Oncol. 23 (Suppl 7):vii78–vii82. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chatani S, Hasegawa T, Kato S, Murata S,
Sato Y, Yamaura H, Yamamoto K, Yatabe Y and Inaba Y: Image-guided
core needle biopsy in the diagnosis of malignant lymphoma:
Comparison with surgical excision biopsy. Eur J Radiol.
127(108990)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hu Q, Naushad H, Xie Q, Al-Howaidi I, Wang
M and Fu K: Needle-core biopsy in the pathologic diagnosis of
malignant lymphoma showing high reproducibility among pathologists.
Am J Clin Pathol. 140:238–247. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lachar WA, Shahab I and Saad AJ: Accuracy
and cost-effectiveness of core needle biopsy in the evaluation of
suspected lymphoma: A study of 101 cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
131:1033–1039. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ardeshna KM, Qian W, Smith P, Braganca N,
Lowry L, Patrick P, Warden J, Stevens L, Pocock CF, Miall F, et al:
Rituximab versus a watch-and-wait approach in patients with
advanced-stage, asymptomatic, non-bulky follicular lymphoma: An
open-label randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 15:424–435.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Feu J, Tresserra F, Fábregas R, Navarro B,
Grases PJ, Suris JC, Fernández-Cíd A and Alegret X: Metastatic
breast carcinoma in axillary lymph nodes: In vitro US detection.
Radiology. 205:831–835. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Vassallo P, Wernecke K, Roos N and Peters
PE: Differentiation of benign from malignant superficial
lymphadenopathy: The role of high-resolution US. Radiology.
183:215–220. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Abe H, Schmidt RA, Sennett CA, Shimauchi A
and Newstead GM: US-guided core needle biopsy of axillary lymph
nodes in patients with breast cancer: Why and how to do it.
Radiographics. 27 (Suppl 1):S91–S99. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|