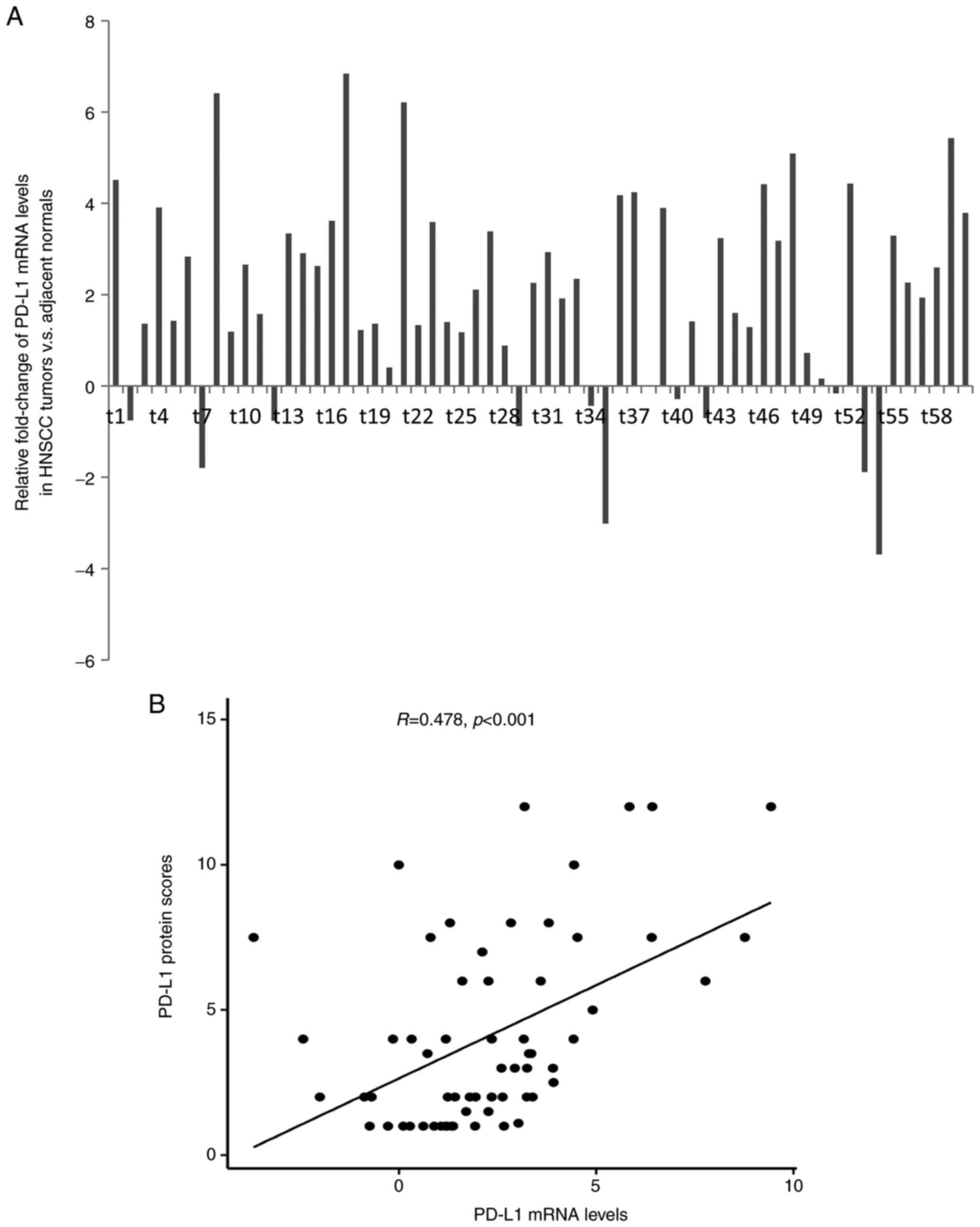
|
1
|
Argiris A, Karamouzis MV, Raben D and
Ferris RL: Head and neck cancer. Lancet. 371:1695–1709.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Johnson DE, Burtness B, Leemans CR, Lui
VWY, Bauman JE and Grandis JR: Head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 6(92)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Stein AP, Saha S, Kraninger JL, Swick AD,
Yu M, Lambert PF and Kimple RJ: Prevalence of human papillomavirus
in oropharyngeal cancer: A systematic review. Cancer J. 21:138–146.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang M, Zhao J, Zhang L, Wei F, Lian Y, Wu
Y, Gong Z, Zhang S, Zhou J, Cao K, et al: Role of tumor
microenvironment in tumorigenesis. J Cancer. 8:761–773.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
de Ruiter EJ, Ooft ML, Devriese LA and
Willems SM: The prognostic role of tumor infiltrating T-lymphocytes
in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Oncoimmunology.
6(e1356148)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Balermpas P, Michel Y, Wagenblast J, Seitz
O, Weiss C, Rödel F, Rödel C and Fokas E: Tumour-infiltrating
lymphocytes predict response to definitive chemoradiotherapy in
head and neck cancer. Br J Cancer. 110:501–509. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hendry S, Salgado R, Gevaert T, Russell
PA, John T, Thapa B, Christie M, van de Vijver K, Estrada MV,
Gonzalez-Ericsson PI, et al: Assessing tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes in solid tumors: A practical review for pathologists
and proposal for a standardized method from the International
Immunooncology Biomarkers Working Group: Part 1: Assessing the host
immune response, TILs in invasive breast carcinoma and ductal
carcinoma in situ, metastatic tumor deposits and areas for further
research. Adv Anat Pathol. 24:235–251. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T and Ono
M: Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 133:775–787.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nishimura T, Iwakabe K, Sekimoto M, Ohmi
Y, Yahata T, Nakui M, Sato T, Habu S, Tashiro H, Sato M and Ohta A:
Distinct role of antigen-specific T helper type 1 (Th1) and Th2
cells in tumor eradication in vivo. J Exp Med. 190:617–627.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Neisig A, Vangsted A, Zeuthen J and
Geisler C: Assembly of the T-cell antigen receptor. Participation
of the CD3 omega chain. J Immunol. 151:870–879. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang JY, Yan YY, Li JJ, Adhikari R and Fu
LW: PD-1/PD-L1 based combinational cancer therapy: Icing on the
cake. Front Pharmacol. 11(722)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rahimi Kalateh Shah Mohammad G,
Ghahremanloo A, Soltani A, Fathi E and Hashemy SI: Cytokines as
potential combination agents with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade for cancer
treatment. J Cell Physiol. 235:5449–5460. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang X, Yang X, Zhang C, Wang Y, Cheng T,
Duan L, Tong Z, Tan S, Zhang H, Saw PE, et al: Tumor cell-intrinsic
PD-1 receptor is a tumor suppressor and mediates resistance to PD-1
blockade therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:6640–6650.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sharpe AH and Pauken KE: The diverse
functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway. Nat Rev Immunol.
18:153–167. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H,
Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, et al:
Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential
mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 8:793–800. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Qiao XW, Jiang J, Pang X, Huang MC, Tang
YJ, Liang XH and Tang YL: The evolving landscape of PD-1/PD-L1
pathway in head and neck cancer. Front Immunol.
11(1721)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cramer JD, Burtness B and Ferris RL:
Immunotherapy for head and neck cancer: Recent advances and future
directions. Oral Oncol. 99(104460)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Burtness B, Zhang Y, Harrington KJ and
Rischin D: Further clinical interpretation and implications of
KEYNOTE-048 findings-Authors' reply. Lancet. 396:379–380.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Larbcharoensub N, Mahaprom K, Jiarpinitnun
C, Trachu N, Tubthong N, Pattaranutaporn P, Sirachainan E and
Ngamphaiboon N: Characterization of PD-L1 and PD-1 expression and
CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte in epstein-barr
virus-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol.
41:1204–1210. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Badoual C, Hans S, Merillon N, Van Ryswick
C, Ravel P, Benhamouda N, Levionnois E, Nizard M, Si-Mohamed A,
Besnier N, et al: PD-1-expressing tumor-infiltrating T cells are a
favorable prognostic biomarker in HPV-associated head and neck
cancer. Cancer Res. 73:128–138. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cho YA, Yoon HJ, Lee JI, Hong SP and Hong
SD: Relationship between the expressions of PD-L1 and
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Oral Oncol. 47:1148–1153. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Upadhaya S, Neftelino ST, Hodge JP, Oliva
C, Campbell JR and Yu JX: Combinations take centre stage in
PD1/PDL1 inhibitor clinical trials. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
20:168–169. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Maibach F, Sadozai H, Seyed Jafari SM,
Hunger RE and Schenk M: Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and their
prognostic value in cutaneous melanoma. Front Immunol.
11(2105)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Canning M, Guo G, Yu M, Myint C, Groves
MW, Byrd JK and Cui Y: Heterogeneity of the head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma immune landscape and its impact on immunotherapy.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 7(52)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Spector ME, Bellile E, Amlani L, Zarins K,
Smith J, Brenner JC, Rozek L, Nguyen A, Thomas D, McHugh JB, et al:
Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
145:1012–1019. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
van Kempen PM, Noorlag R, Swartz JE,
Bovenschen N, Braunius WW, Vermeulen JF, Van Cann EM, Grolman W and
Willems SM: Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas differentially
express granzyme inhibitors. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 65:575–585.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang D, He W, Wu C, Tan Y, He Y, Xu B,
Chen L, Li Q and Jiang J: Scoring system for tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes and its prognostic value for gastric cancer. Front
Immunol. 10(71)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Höing B, Kanaan O, Altenhoff P, Petri R,
Thangavelu K, Schlüter A, Lang S, Bankfalvi A and Brandau S:
Stromal versus tumoral inflammation differentially contribute to
metastasis and poor survival in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 9:8415–8426. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Barnes TA and Amir E: HYPE or HOPE: The
prognostic value of infiltrating immune cells in cancer. Br J
Cancer. 117:451–460. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Schüler T, Qin Z, Ibe S, Noben-Trauth N
and Blankenstein T: T helper cell type 1-associated and cytotoxic T
lymphocyte-mediated tumor immunity is impaired in interleukin
4-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 189:803–810. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Martin-Orozco N, Muranski P, Chung Y, Yang
XO, Yamazaki T, Lu S, Hwu P, Restifo NP, Overwijk WW and Dong C: T
helper 17 cells promote cytotoxic T cell activation in tumor
immunity. Immunity. 31:787–798. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Quezada SA, Peggs KS, Curran MA and
Allison JP: CTLA4 blockade and GM-CSF combination immunotherapy
alters the intratumor balance of effector and regulatory T cells. J
Clin Invest. 116:1935–1945. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Nguyen N, Bellile E, Thomas D, McHugh J,
Rozek L, Virani S, Peterson L, Carey TE, Walline H, Moyer J, et al:
Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and survival in patients with head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 38:1074–1084.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Schneider S, Kadletz L, Wiebringhaus R,
Kenner L, Selzer E, Füreder T, Rajky O, Berghoff AS, Preusser M and
Heiduschka G: PD-1 and PD-L1 expression in HNSCC primary cancer and
related lymph node metastasis-impact on clinical outcome.
Histopathology. 73:573–584. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yang WF, Wong MCM, Thomson PJ, Li KY and
Su YX: The prognostic role of PD-L1 expression for survival in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 86:81–90. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Marin-Acevedo JA, Kimbrough EO and Lou Y:
Next generation of immune checkpoint inhibitors and beyond. J
Hematol Oncol. 14(45)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|