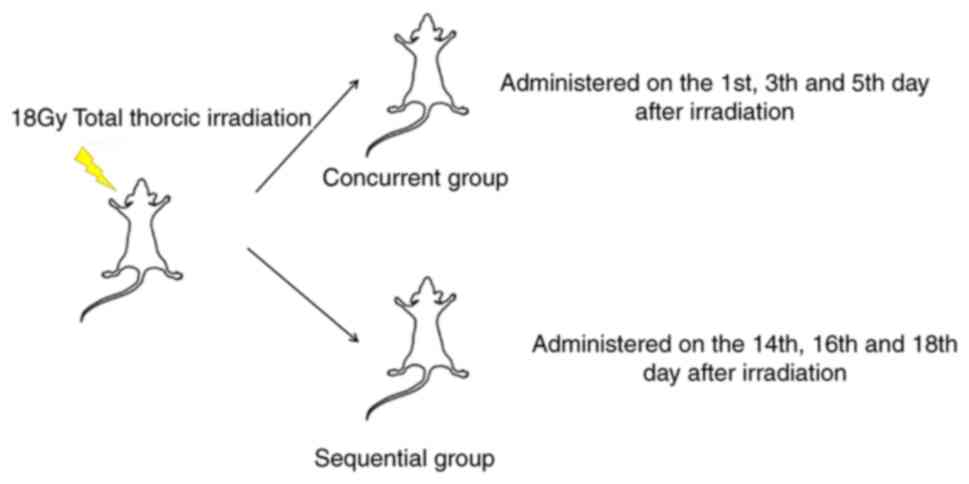
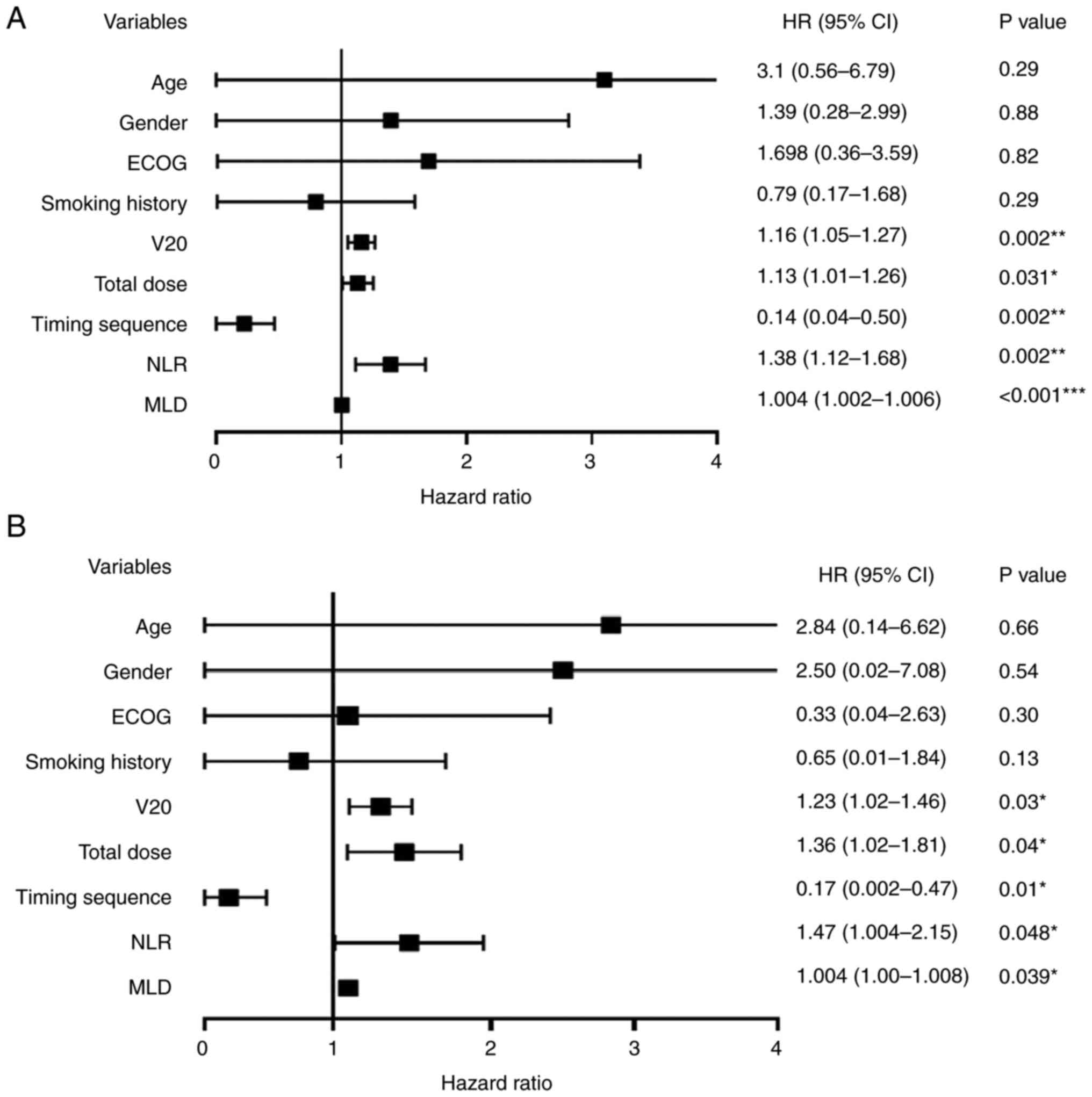
|
1
|
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR,
Steins M, Ready NE, Chow LQ, Vokes EE, Felip E, Holgado E, et al:
Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 373:1627–1639. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shitara K, Özgüroğlu M, Bang YJ, Di
Bartolomeo M, Mandalà M, Ryu MH, Fornaro L, Olesiński T, Caglevic
C, Chung HC, et al: Pembrolizumab versus paclitaxel for previously
treated, advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer
(KEYNOTE-061): A randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial.
Lancet. 392:123–133. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ikeda S, Goodman AM, Cohen PR, Jensen TJ,
Ellison CK, Frampton G, Miller V, Patel SP and Kurzrock R:
Metastatic basal cell carcinoma with amplification of PD-L1:
Exceptional response to anti-PD1 therapy. NPJ Genom Med.
1(16037)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sharabi AB, Nirschl CJ, Kochel CM, Nirschl
TR, Francica BJ, Velarde E, Deweese TL and Drake CG: Stereotactic
radiation therapy augments antigen-specific PD-1-Mediated antitumor
immune responses via cross-presentation of tumor antigen. Cancer
Immunol Res. 3:345–355. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Deng L, Liang H, Burnette B, Beckett M,
Darga T, Weichselbaum RR and Fu YX: Irradiation and anti-PD-L1
treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice. J
Clin Invest. 124:687–695. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Shaverdian N, Lisberg AE, Bornazyan K,
Veruttipong D, Goldman JW, Formenti SC, Garon EB and Lee P:
Previous radiotherapy and the clinical activity and toxicity of
pembrolizumab in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: A
secondary analysis of the KEYNOTE-001 phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol.
18:895–903. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Theelen WSME, Peulen HMU, Lalezari F, van
der Noort V, de Vries JF, Aerts JGJV, Dumoulin DW, Bahce I,
Niemeijer AN, de Langen AJ, et al: Effect of pembrolizumab after
stereotactic body radiotherapy vs pembrolizumab alone on tumor
response in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer:
Results of the PEMBRO-RT phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA
Oncol. 5:1276–1282. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lee H, Kim I, Kang BH and Um SJ:
Prognostic value of serial neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
measurements in hospitalized community-acquired pneumonia. PLoS
One. 16(e0250067)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liu J, Liu J and Zou Y: Relationship
between neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and short-term prognosis in the
chronic obstructive pulmonary patients with acute exacerbation.
Biosci Rep. 39(BSR20190675)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu J, Liu Y, Xiang P, Pu L, Xiong H, Li
C, Zhang M, Tan J, Xu Y, Song R, et al: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte
ratio predicts critical illness patients with 2019 coronavirus
disease in the early stage. J Transl Med. 18(206)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lee YH, Choi HS, Jeong H, Kang KM, Song
JH, Lee WS, Lee GW, Song HN, Kim HG, Kang MH, et al:
Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and a dosimetric factor for predicting
symptomatic radiation pneumonitis in non-small-cell lung cancer
patients treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Clin Respir J.
12:1264–1273. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lin X, Deng H, Yang Y, Wu J, Qiu G, Li S,
Xie X, Liu M, Xie Z, Qin Y, et al: Peripheral blood biomarkers for
early diagnosis, severity, and prognosis of checkpoint
inhibitor-related pneumonitis in patients with lung cancer. Front
Oncol. 11(698832)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, Vicente
D, Murakami S, Hui R, Kurata T, Chiappori A, Lee KH, de Wit M, et
al: Overall survival with durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in
stage III NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 379:2342–2350. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Peters S, Felip E, Dafni U, Belka C,
Guckenberger M, Irigoyen A, Nadal E, Becker A, Vees H, Pless M, et
al: Safety evaluation of nivolumab added concurrently to
radiotherapy in a standard first line chemo-radiotherapy regimen in
stage III non-small cell lung cancer-The ETOP NICOLAS trial. Lung
Cancer. 133:83–87. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jabbour SK, Lee KH, Frost N, Breder V,
Kowalski DM, Pollock T, Levchenko E, Reguart N, Martinez-Marti A,
Houghton B, et al: Pembrolizumab plus concurrent chemoradiation
therapy in patients with unresectable, locally advanced, stage III
non-small cell lung cancer: The phase 2 KEYNOTE-799 nonrandomized
trial. JAMA Oncol. 7:1–9. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gao J, Peng S, Shan X, Deng G, Shen L, Sun
J, Jiang C, Yang X, Chang Z, Sun X, et al: Inhibition of AIM2
inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis by Andrographolide contributes to
amelioration of radiation-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis.
Cell Death Dis. 10(957)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mikawa K, Nishina K, Takao Y and Obara H:
ONO-1714, a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, attenuates
endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rabbits. Anesth Analg.
97:1751–1755. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dave MN, Silva JE, Eliçabe RJ, Jeréz MB,
Filippa VP, Gorlino CV, Autenrieth S, Autenrieth IB and Di Genaro
MS: Yersinia enterocolitica YopH-Deficient strain activates
neutrophil recruitment to Peyer's patches and promotes clearance of
the virulent strain. Infect Immun. 84:3172–3181. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Loken MR, Brosnan JM, Bach BA and Ault KA:
Establishing optimal lymphocyte gates for immunophenotyping by flow
cytometry. Cytometry. 11:453–459. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Herrera FG, Bourhis J and Coukos G:
Radiotherapy combination opportunities leveraging immunity for the
next oncology practice. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:65–85. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Suzuki Y, Mimura K, Yoshimoto Y, Watanabe
M, Ohkubo Y, Izawa S, Murata K, Fujii H, Nakano T and Kono K:
Immunogenic tumor cell death induced by chemoradiotherapy in
patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res.
72:3967–3976. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ma JL, Jin L, Li YD, He CC, Guo XJ, Liu R,
Yang YY and Han SX: The intensity of radiotherapy-elicited immune
response is associated with esophageal cancer clearance. J Immunol
Res. 2014(794249)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Segawa Y, Takigawa N, Kataoka M, Takata I,
Fujimoto N and Ueoka H: Risk factors for development of radiation
pneumonitis following radiation therapy with or without
chemotherapy for lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
39:91–98. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kong FM, Hayman JA, Griffith KA,
Kalemkerian GP, Arenberg D, Lyons S, Turrisi A, Lichter A, Fraass
B, Eisbruch A, et al: Final toxicity results of a radiation-dose
escalation study in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer
(NSCLC): Predictors for radiation pneumonitis and fibrosis. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 65:1075–1086. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cadranel J, Canellas A, Matton L, Darrason
M, Parrot A, Naccache JM, Lavolé A, Ruppert AM and Fallet V:
Pulmonary complications of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients
with nonsmall cell lung cancer. Eur Respir Rev.
28(190058)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Klein D, Steens J, Wiesemann A, Schulz F,
Kaschani F, Röck K, Yamaguchi M, Wirsdörfer F, Kaiser M, Fischer
JW, et al: Mesenchymal stem cell therapy protects lungs from
radiation-induced endothelial cell loss by restoring superoxide
dismutase 1 expression. Antioxid Redox Signal. 26:563–582.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Azzam EI, Jay-Gerin JP and Pain D:
Ionizing radiation-induced metabolic oxidative stress and prolonged
cell injury. Cancer Lett. 327:48–60. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Abratt RP, Morgan GW, Silvestri G and
Willcox P: Pulmonary complications of radiation therapy. Clin Chest
Med. 25:167–177. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhai X, Zhang J, Tian Y, Li J, Jing W, Guo
H and Zhu H: The mechanism and risk factors for immune checkpoint
inhibitor pneumonitis in non-small cell lung cancer patients.
Cancer Biol Med. 17:599–611. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sheng L, Cui X, Cheng L, Chen Y and Du X:
Risk factors of grade ≥ 2 radiation pneumonitis after gemcitabine
induction chemotherapy for patients with non-small cell lung
cancer. Radiat Oncol. 14(229)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yuan C, Pan Y and Ning Y: Predictive Value
of IL-6 Combined with NLR in inflammation and cancer. Cancer
Invest. 39:489–504. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cheng H, Luo G, Lu Y, Jin K, Guo M, Xu J,
Long J, Liu L, Yu X and Liu C: The combination of systemic
inflammation-based marker NLR and circulating regulatory T cells
predicts the prognosis of resectable pancreatic cancer patients.
Pancreatology. 16:1080–1084. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mundama M, Van Cauter M, Detrembleur C,
Cornu O, Dubuc JE and Yombi JC: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
(NLR) distribution shows an advantage compared to C-reactive
protein (CRP) for the early inflammation monitoring after total hip
arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Belg. 86:405–411. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang Z, Fu Z, Huang W and Huang K:
Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in sepsis: A
meta-analysis. Am J Emerg Med. 38:641–647. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Buonacera A, Stancanelli B, Colaci M and
Malatino L: Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio: An emerging marker of
the relationships between the immune system and diseases. Int J Mol
Sci. 23(3636)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|