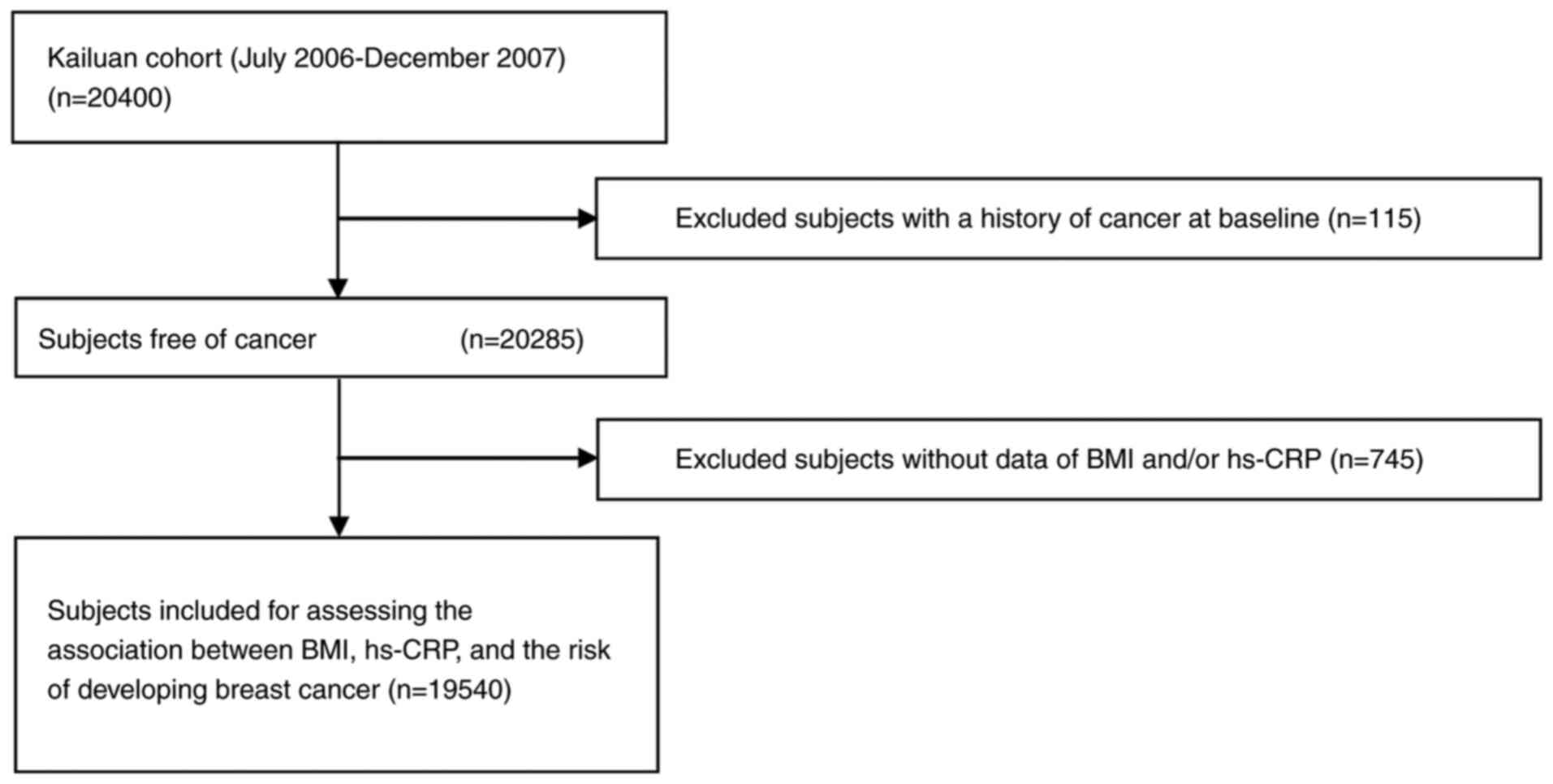
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Coignard J, Lush M, Beesley J, O'Mara TA,
Dennis J, Tyrer JP, Barnes DR, McGuffog L, Leslie G, Bolla MK, et
al: A case-only study to identify genetic modifiers of breast
cancer risk for BRCA1/BRCA2 mutation carriers. Nat Commun.
12(1078)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Al Ajmi K, Lophatananon A, Mekli K, Ollier
W and Muir KR: Association of Nongenetic factors with breast cancer
risk in genetically predisposed groups of women in the UK Biobank
cohort. JAMA Netw Open. 3(e203760)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cohen SY, Stoll CR, Anandarajah A, Doering
M and Colditz GA: Modifiable risk factors in women at high risk of
breast cancer: A systematic review. Breast Cancer Res.
25(45)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Nelson HD, Zakher B, Cantor A, Fu R,
Griffin J, O'Meara ES, Buist DS, Kerlikowske K, van Ravesteyn NT,
Trentham-Dietz A, et al: Risk factors for breast cancer for women
aged 40 to 49 years: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann
Intern Med. 156:635–648. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
John EM, Phipps AI, Hines LM, Koo J,
Ingles SA, Baumgartner KB, Slattery ML and Wu AH: Menstrual and
reproductive characteristics and breast cancer risk by hormone
receptor status and ethnicity: The breast cancer Etiology in
minorities study. Int J Cancer. 147:1808–1822. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Safaei M, Sundararajan EA, Driss M,
Boulila W and Shapi'i A: A systematic literature review on obesity:
Understanding the causes & consequences of obesity and
reviewing various machine learning approaches used to predict
obesity. Comput Biol Med. 136(104754)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Laudisio D, Muscogiuri G, Barrea L,
Savastano S and Colao A: Obesity and breast cancer in premenopausal
women: Current evidence and future perspectives. Eur J Obstet
Gynecol Reprod Biol. 230:217–221. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Torres-de la Roche LA, Steljes I, Janni W,
Friedl TWP and De Wilde RL: The association between obesity and
premenopausal breast cancer according to intrinsic Subtypes-a
systematic review. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 80:601–610.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Neuhouser ML, Aragaki AK, Prentice RL,
Manson JE, Chlebowski R, Carty CL, Ochs-Balcom HM, Thomson CA, Caan
BJ, Tinker LF, et al: Overweight, obesity, and postmenopausal
invasive breast cancer risk: A secondary analysis of the Women's
Health initiative randomized clinical trials. JAMA Oncol.
1:611–621. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Park JW, Han K, Shin DW, Yeo Y, Chang JW,
Yoo JE, Jeong SM, Lee SK, Ryu JM and Park YM: Obesity and breast
cancer risk for pre- and postmenopausal women among over 6 million
Korean women. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 185:495–506. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chen MJ, Wu WY, Yen AM, Fann JC, Chen SL,
Chiu SY, Chen HH and Chiou ST: Body mass index and breast cancer:
Analysis of a nation-wide population-based prospective cohort study
on 1 393 985 Taiwanese women. Int J Obes (Lond). 40:524–530.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Slomski A: BMI not a good proxy for breast
cancer risk. JAMA. 321(735)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Iyengar NM, Gucalp A, Dannenberg AJ and
Hudis CA: Obesity and cancer mechanisms: Tumor microenvironment and
inflammation. J Clin Oncol. 34:4270–4276. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gabay C and Kushner I: Acute-phase
proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J
Med. 340:448–454. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Frydenberg H, Thune I, Lofterød T,
Mortensen ES, Eggen AE, Risberg T, Wist EA, Flote VG, Furberg AS,
Wilsgaard T, et al: Pre-diagnostic high-sensitive C-reactive
protein and breast cancer risk, recurrence, and survival. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 155:345–354. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang J, Lee IM, Tworoger SS, Buring JE,
Ridker PM, Rosner B and Hankinson SE: Plasma C-reactive protein and
risk of breast cancer in two prospective studies and a
meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 24:1199–1206.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Price TR, Friedenreich CM, Robson PJ, Li H
and Brenner DR: High-sensitivity C-reactive protein, hemoglobin A1c
and breast cancer risk: A nested case-control study from Alberta's
Tomorrow Project cohort. Cancer Causes Control. 31:1057–1068.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Dossus L, Jimenez-Corona A, Romieu I,
Boutron-Ruault MC, Boutten A, Dupré T, Fagherazzi G,
Clavel-Chapelon F and Mesrine S: C-reactive protein and
postmenopausal breast cancer risk: Results from the E3N cohort
study. Cancer Causes Control. 25:533–539. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li X, Chen H, Wang G, Feng X, Lyu Z, Wei
L, Wen Y, Chen S, Wu S, Hang D, et al: Metabolic syndrome
components and the risk of colorectal cancer: A Population-based
prospective study in Chinese men. Front Oncol.
9(1047)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu T, Song C, Zhang Y, Siyin ST, Zhang Q,
Song M, Cao L and Shi H: Hepatitis B virus infection and the risk
of gastrointestinal cancers among Chinese population: A prospective
cohort study. Int J Cancer. 150:1018–1028. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhou BF: Cooperative Meta-Analysis Group
of the Working Group on Obesity in China. Predictive values of body
mass index and waist circumference for risk factors of certain
related diseases in Chinese adults-study on optimal cut-off points
of body mass index and waist circumference in Chinese adults.
Biomed Environ Sci. 15:83–96. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pearson TA, Mensah GA, Alexander RW,
Anderson JL, Cannon RO III, Criqui M, Fadl YY, Fortmann SP, Hong Y,
Myers GL, et al: Markers of inflammation and cardiovascular
disease: Application to clinical and public health practice: A
statement for healthcare professionals from the centers for disease
control and prevention and the American Heart Association.
Circulation. 107:499–511. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Utter GH, Atolagbe OO and Cooke DT: The
use of the international classification of diseases, tenth
revision, clinical modification and procedure classification system
in clinical and health services research: The devil is in the
details. JAMA Surg. 154:1089–1090. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang X, Li L, Gao J, Liu J, Guo M, Liu L,
Wang W, Wang J, Xing Z, Yu Z and Wang X: The association between
body size and breast cancer in Han Women in Northern and Eastern
China. Oncologist. 21:1362–1368. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Guo L, Liu S, Zhang S, Chen Q, Zhang M,
Quan P, Lu J and Sun X: C-reactive protein and risk of breast
cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep.
5(10508)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Renehan AG, Zwahlen M and Egger M:
Adiposity and cancer risk: New mechanistic insights from
epidemiology. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:484–498. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Crespi E, Bottai G and Santarpia L: Role
of inflammation in obesity-related breast cancer. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 31:114–122. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Irahara N, Miyoshi Y, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y
and Noguchi S: Quantitative analysis of aromatase mRNA expression
derived from various promoters (I.4, I.3, PII and I.7) and its
association with expression of TNF-alpha, IL-6 and COX-2 mRNAs in
human breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 118:1915–1921. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wagner M, Samdal Steinskog ES and Wiig H:
Adipose tissue macrophages: The inflammatory link between obesity
and cancer? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 19:527–538. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gilbert CA and Slingerland JM: Cytokines,
obesity, and cancer: New insights on mechanisms linking obesity to
cancer risk and progression. Annu Rev Med. 64:45–57.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Iyengar NM, Zhou XK, Gucalp A, Morris PG,
Howe LR, Giri DD, Morrow M, Wang H, Pollak M, Jones LW, et al:
Systemic correlates of white adipose tissue inflammation in
early-stage breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 22:2283–2289.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|