Introduction
Endometrial cancer (EC) is the most common and
frequently diagnosed gynecological malignancy in high- and
middle-income countries. Most patients with EC are diagnosed after
menopause; only 5% of EC cases occur before 40 years of age
(1). In Korea, the incidence of EC
has rapidly increased in recent years. In 2021, the
age-standardized incidence rate was 8.8 cases per 100,000 women,
and the number of newly diagnosed EC cases and deaths attributed to
EC were 3,749 and 429, respectively (2). This may be partly explained by the
rising prevalence of obesity, a well-established risk factor for
EC. The 2023 Obesity Fact Sheet of Korea reported that the overall
prevalence of obesity in 2021 was 38.4% (49.2% in men and 27.8% in
women). This increase is particularly pronounced in young adults
(3). Although early-onset EC
(EOEC; age at diagnosis <50 years) is relatively uncommon, its
incidence has been increasing in recent decades, possibly linked to
the rising obesity epidemic in younger women (4). In Korea, the incidence of EC between
1999 and 2017 increased most rapidly in young women aged ≤30 years
and 30-39 years (annual percentage change, 8.7 and 7.4%,
respectively) (5).
Iron deficiency anemia associated with heavy
menstrual bleeding (HMB) is prevalent among women of reproductive
age. Obese women are at risk of abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB),
and ~75-90% of patients with EC present with AUB. Patients often
present with atypical symptoms (6). The present case is an example of an
atypical presentation of EC in a woman who presented with ankle
fracture secondary to severe anemia. Although AUB can have serious
medical consequences, most women do not seek treatment for these
symptoms. Ankle fractures are relatively common orthopedic
injuries, with falls or trauma being the most common mechanism
(7). A total of 50% of the EC
cases occur in individuals with risk factors, such as obesity and
unopposed estrogen stimulation (8). In addition, a meta-analysis has
suggested an increased risk of EC among patients with hypertension
(9). Knowledge of the risk factors
for EC helps gynecologists to evaluate possible gynecological
malignancies. This case underscores the significance of recognizing
rare clinical presentations, such as ankle fracture secondary to
severe anemia in an obese woman with HMB, necessitating further
gynecologic evaluations. This report presents a case of EC detected
incidentally after an ankle fracture secondary to severe anemia in
a woman with HMB.
Case report
A 36-year-old, virgin woman, presented to the
emergency department of another institution with right ankle pain
due to a fall caused by dizziness and headache after menstruation.
The initial evaluation revealed swelling of the right ankle.
Initial radiography revealed a right ankle fracture without
dislocation. The patient was hypertensive, with a heart rate of 102
beats/min. Initial laboratory results showed a severely low
hemoglobin level (4.9 g/dl, reference range, 12.0-16.0 g/dl) and
hematocrit (16.6%, reference range 36.0-46.0%). She was treated
with packed red blood cells and iron infusion. Her weight and
height were 95.0 kg and 162 cm, respectively, and her body mass
index (BMI) was 36.2 kg/m2. She had a recent history of
menorrhagia and irregular cycles that lasted for two years. She had
never presented to a doctor because of her symptoms. The patient
was transferred to the Pusan National University Hospital (Busan,
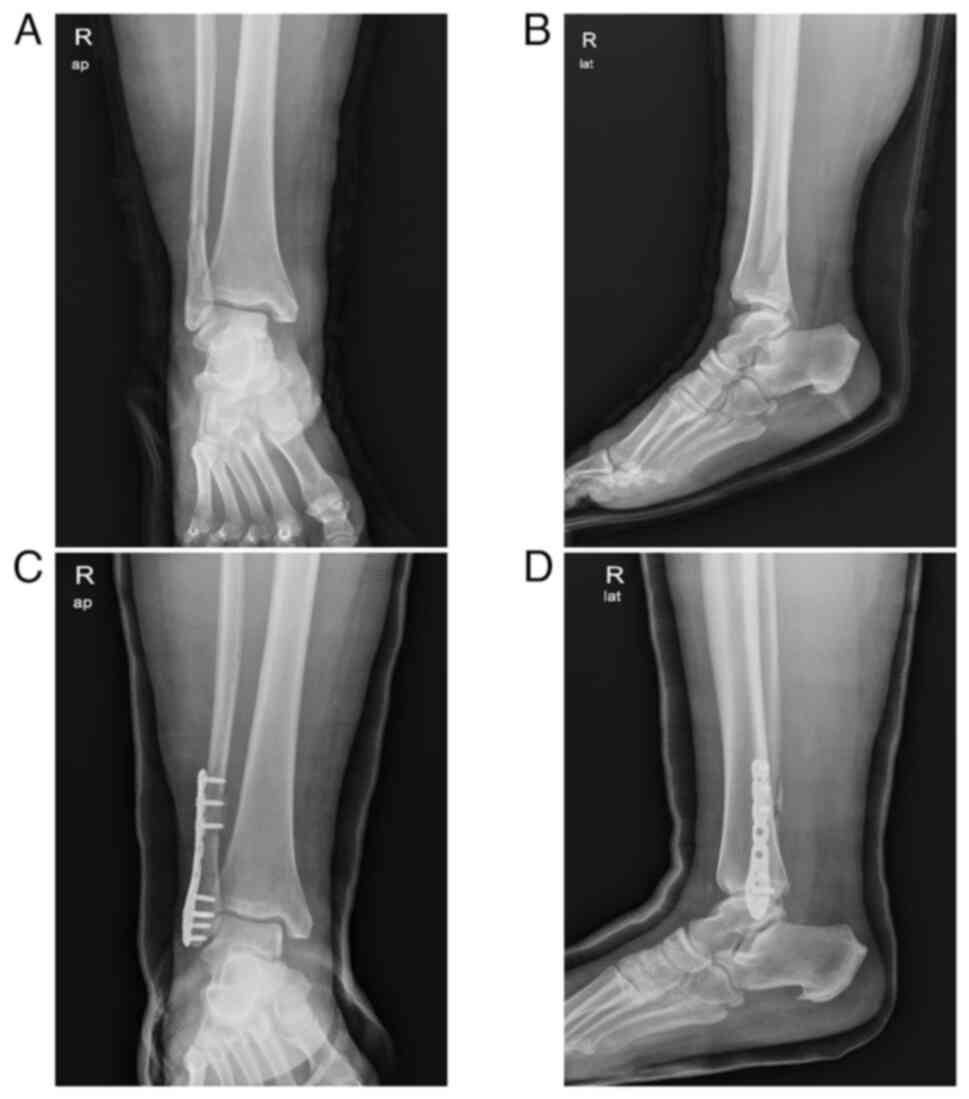
Korea) and evaluated by an orthopedic surgery team (Fig. 1). The decision was made to proceed
with the surgical intervention. During the evaluation, she was
referred to the gynecology oncology unit for further workup after a
computed tomography (CT) scan revealed a significant endometrial
mass suspected to be EC. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the
pelvis revealed a 6.7-cm-sized endometrial mass with restricted
diffusion, myometrial invasion of <1/2, and bilateral polycystic
ovaries. She had been receiving antihypertensive drugs for two
years but had recently stopped taking them because she experienced
hypotension caused by the drug. Her family history included
hypertension in her father and elder brother. Endometrial pipelle
sampling revealed FIGO grade 2 endometrioid adenocarcinoma.
Positron emission tomography-CT showed no evidence of
metastases.
Laboratory findings including fasting blood sugar,
HbA1c, C-reactive protein and CA125 levels, were unremarkable.
First, the patient underwent open reduction and internal fixation
involving screw fixation for a right ankle syndesmosis injury,
distal fibular fracture, and ankle posterior malleolar fracture.
The postoperative follow-up showed successful healing and
functional recovery (Fig. 1). A
total of 4 weeks later, robot-assisted total hysterectomy,
bilateral salpingectomy and sentinel lymph node sampling were
performed. Final pathology revealed stage 1B, grade 2 endometroid
adenocarcinoma with substantial lymphovascular space invasion
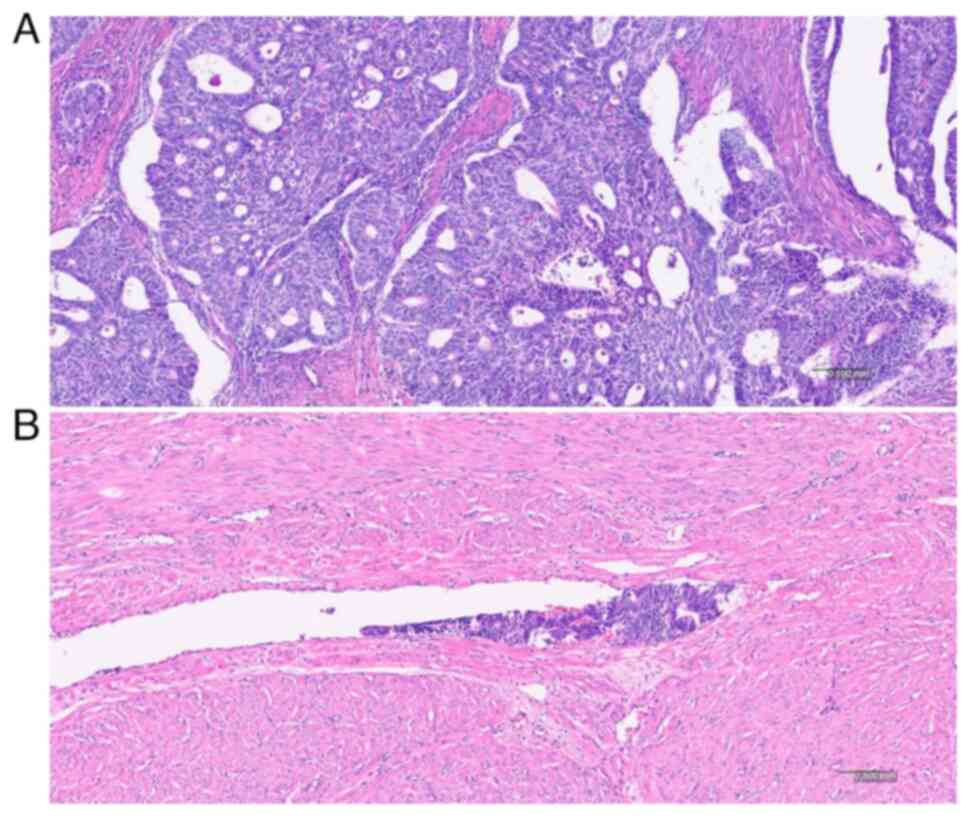
(LVSI) (Fig. 2). Regional lymph
node involvement was not identified. The peritoneal fluid cytology
was negative for malignant cells. Immunohistochemistry staining
revealed p53 (-), MLH1 (+), PMS2 (+), MSH-2 (+) and MSH-6 (+). The
patient received 50.4 Gy external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) to the
whole pelvis. Chest and abdominopelvic imaging (CT or MRI) were
checked every 6 months. The 26-month postoperative follow-up showed
that the patient was disease-free. The present study was reviewed
and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Pusan National
University Hospital (approval no. 2404-017-138; Busan, Korea).
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for
publication of data of her medical case and associated images.
Discussion
Obesity and obesity-related diseases present a major
global health challenge associated with several major chronic
illnesses, including diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease and
several common cancers (10). A
total of ~4-8% of all cancers are attributed to obesity (11). The rising incidence of EC is
largely attributable to rising rates of obesity in developed
countries. The underlying mechanisms of obesity-associated cancer
are complex and incompletely understood. Endoplasmic reticulum
stress, macrophage infiltration and polarization, hypoxia-induced
inflammatory signaling, direct immune system activation, and free
fatty acid-Toll-like receptor signaling have been suggested as the
causative factors (12).
Up to 1/3 of women of reproductive age experience
HMB. Iron deficiency anemia associated with HMB is a common problem
that remains underdiagnosed and undertreated, and the consequences
of anemia are beyond the scope of gynecology. Common symptoms
include fatigue, weakness, irritability, poor concentration,
shortness of breath, headache, hair loss, brittle nails, cold
intolerance and restless legs syndrome. EC is mainly diagnosed at
an early stage confined to the uterus, and women must seek medical
attention for early symptoms, such as AUB. HMB is frequently
underreported, and a relevant number of women are unaware of the
condition because 46% have never consulted a doctor for HMB
symptoms (13). HMB is a clinical
entity with different underlying structural and non-structural
causes. Some causes of HMB are endometrial precursors to cancer
(14). EC presents primarily with
gynecological symptoms, but the patient of the present case report
visited the hospital due to orthopedic problems despite having
troublesome gynecologic complaints such as HMB, dizziness and
headache after menstruation, necessitating treatment. Numerous
women of reproductive age may not perceive AUB as a significant
health concern and frequently normalize its symptoms. The presence
of menorrhagia and anemia in high-risk populations requires further
investigation to ensure that pathology is not missed. A
comprehensive history should be received and additional
investigations ordered. Increasing BMI levels are directly
correlated with a proportional increase in EC risk, underscoring
the potential significance of weight management interventions in EC
prevention strategies. Preventative approaches such as intrauterine
device with progestogen (for example Mirena) may help reduce
disease burden in those identified at higher risk. In addition,
interventions directed at weight reduction are an important
component of the survivorship care of overweight patients with
cancer. Lifestyle interventions that include diet, exercise and
behavior therapy are the primary elements of weight reducing
strategies (11). She was found to
be severely anemic, with a hemoglobin level of 4.9 g/dl. She may
have been reluctant to visit the gynecological clinic because she
had no coital history and did not know what gynecological
conditions could cause her risk factors.
Several risk factors for EC have been established,
including excess body weight (BMI >30 kg/m²), polycystic ovarian
syndrome (PCOS), nulliparity, early menarche, late menopause, low
physical activity, diabetes mellitus and the use of unopposed
hormone replacement therapy (9).
These conditions are considered to contribute to unopposed estrogen
exposure. As in this case, EC should be suspected in a patient with
severe anemia and HMB, particularly if she has risk factors for EC
such as obesity, hypertension and irregular cycles due to PCOS.
The global burden of obesity is well represented in
World Health Organization data. In 2016, ~13% of the global adult
population was obese, with a higher prevalence among women (15%)
than among men (11%) (15).
Regarding the Korean population in 2021, data suggest a 38.45%
obesity prevalence in adults (49.2% in men and 27.8% in women)
(3). An excess BMI is a risk
factor for several major types of cancer, including breast
(postmenopausal), endometrial, colorectal and kidney (11). Korean data show that women with
metabolic syndrome, especially premenopausal women with abdominal
obesity, are at high risk of developing EC (5).
The role of obesity in the etiology and
carcinogenesis of EC has been reviewed (12). Increasing BMI is directly
correlated with a proportional increase in the risk of EC. Obesity
causes chronic inflammation through a multifactorial process, and
this chronic inflammatory state contributes to the development of
various obesity-associated comorbidities such as EC.
PCOS is the most common endocrine disorder in women
of reproductive-age. This disorder is associated with chronic
anovulation and unopposed estrogen exposure, which can lead to EC.
Additionally, higher insulin levels in women with PCOS can increase
the risk of developing EC. The risk of EC is 2-6-fold higher in
women with PCOS (16). The
association between PCOS and EC is complex and multi-faceted.
However, the association between PCOS and EC remains inconclusive.
It has been previously reported that women with obesity are at risk
of AUB and PCOS caused by insulin resistance and elevated unopposed
estrogens, increasing the risk of EC (17). Others have reported that the risk
may be due to age or endometrial thickness rather than a direct
effect of PCOS on the development of the disease (16). Routine screening for EC in PCOS is
not indicated, despite the recommendation that women with PCOS are
at risk of EC and should be monitored closely. The risk factors for
EC include obesity, long-term use of unopposed estrogen, family
history of EC, prolonged amenorrhea and AUB. In this case,
bilateral polycystic ovaries were observed on MRI, but the patient
was unaware of this because she had never visited the hospital
before.
The prevalence of hypertension, another component of
metabolic syndrome, is also increasing, and emerging evidence
suggests that it may be associated with the development of certain
cancers, mainly through inflammatory, hormonal and metabolic
pathways (18). However, the role
of hypertension as an independent risk factor for EC remains
unclear. Obesity and diabetes are important risk factors of
hypertension and EC. Therefore, it is unclear whether these factors
confounded the association between hypertension and EC because
certain studies did not adjust for BMI or diabetes (9). A recent study reported that
hypertension was associated with a 14% increased risk of EC,
independent of known risk factors, such as BMI, diabetes and
reproductive factors (19). A
previous systematic review and meta-analysis suggested that women
with hypertension might have a 61% increase in the relative risk of
developing EC (9). The
inconsistencies in the risk among studies may be explained by the
fact that the meta-analysis included effect estimates from studies
that did not adjust for all known risk factors for EC, particularly
BMI. In the present case, the patient was known to have
hypertension under treatment, with no other comorbidities. Her
family history included hypertension in her father and elder
brother. In this case, obesity (BMI, 36.2 kg/m2)
contributed most significantly to the EC, with some contribution
from PCOS and hypertension.
EC has disproportionately increased in adults aged
≤50 years and has become a major public health problem (20). The faster increase in EOEC was
possibly linked to the rising obesity epidemic in younger women and
also coincides with the observations of broader increases in cancer
among younger adults (21,22). Fertility-sparing treatment for
carefully selected patients with low-stage EC is a possible
therapeutic option for premenopausal women desiring to preserve
fertility. There is insufficient experience to support the
recommendation of fertility-sparing therapy for higher-grade tumors
(grade 2-3) (23). In the present
case, the disease was stage 1B, grade 2 endometroid adenocarcinoma
with lymphovascular space invasion. No fertility-sparing management
was performed. Instead, total hysterectomy, bilateral salpingectomy
and sentinel lymph node sampling were performed, and postoperative
radiation was administered.
EC can present in an atypical fashion with
non-gynecologic symptoms, such as angina and pancytopenia (6), singular bone metastasis (24), or solitary adrenal metastases
(25). Therefore, receiving
careful history is needed not only for gynecological symptoms but
also for non-gynecologic symptoms. EC is an important differential
condition in obese patients with AUB. In addition, endometrial
sampling should be considered in individuals <45 years of age
with AUB if there are other risk factors for EC, as well as in any
patient with a BMI >30 or persistent AUB (6).
Lifetime incidence of EC among the risk factors as
in the present case, class 2 obesity (BMI ≥35 and <40
kg/m2), premenopausal PCOS and premenopausal AUB is 9, 4
and 0.3%, respectively. In this premenopausal period, the low
incidence of EC entails frequent diagnostic delays. EC should be
considered in premenopausal women with AUB, particularly those with
obesity, PCOS, a strong family history or other risk factors
(26). EC is overwhelmingly a
disease of postmenopausal women, with >90% occurring in women
>50 years old; however, increasing rates of obesity may lead to
a rise in the proportion of premenopausal cases. Early screening
for EC in obese women with AUB or other risk factors could detect
the disease in the pre-invasive or early stage (before developing
myometrial invasion), which would improve cure rates, reduce the
morbidity associated with aggressive treatment and offer
fertility-sparing management options for younger women (27).
There has been marked discussion over the adjuvant
treatment of this high-intermediate risk group of patients which
includes those with stage IA and IB disease with substantial LVSI
(such as the present case), stage IB G3 and stage II G1 disease
with substantial LVSI and stage II G2-G3 (dMMR or NSMP) disease: i)
Adjuvant EBRT is recommended in NCCN and ESMO guidelines; ii)
Adding (concomitant and/or sequential) chemotherapy to EBRT could
be considered, especially for G3 and/or substantial LVSI. The high
incidence of short- and long-term side-effects associated with the
addition of chemotherapy to EBRT, whilst conferring minimal
benefit, needed to be discussed with these patients; iii) Despite
evidence of a benefit from adjuvant treatment, its omission is an
option, when close follow-up can be ensured, following shared
decision making with the patient (28).
Surveillance can be adjusted according to the risk
factors of the patient. No consensus on what surveillance tests
should be carried out. In the high-risk groups, physical and
gynecological examinations are recommended every 3 months for the
first 3 years, and then every 6 months until 5 years. Imaging
should be guided by patient symptoms, risk assessment and clinical
concern for recurrent disease. As CT scans detect only 15% of
recurrences, routine use is not advocated. Nevertheless, it could
be considered in the high-risk group (for example, every 6 months
the first 3 years and then on an individual basis) (28).
Obesity is associated with low quality of life and
physical function. In terms of long-term management, lifestyle
interventions may improve fatigue, physical functioning and result
in weight loss and psycho-educational program could improve mood
disorders and sexuality complaints. Long-term management requires
careful attention to metabolic variables, including weight control.
Regular exercise, healthy diet and weight management should be
promoted with all EC survivors (28).
In summary, the patient was in the high-risk group
for EC. She had several risk factors for EC, such as obesity, high
blood pressure and PCOS, indicating that these risk factors caused
EC. However, she had never visited a gynecological clinic prior to
the diagnosis of EC. She was relatively young, therefore, she did
not consider this possibility. This case highlights the importance
of assessing gynecological conditions through a detailed review of
the patient's gynecological history, with caution when an obese
female patient presents with AUB, even during a non-gynecologic
assessment.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: The present study was supported by the Pusan National
University Hospital in 2024.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
HJY, YJS, DSS and KHK made substantial contributions
to the conception and design of the study, acquisition of data, and
analysis and interpretation of data. TSG and KBK contributed to
data interpretation and confirm the authenticity of all the raw
data. HJY, YJS, DSS and KHK contributed to data acquisition,
conception, and reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors
read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was reviewed and approved by the
Institutional Review Board of Pusan National University Hospital
(approval no. 2404-017-138; Busan, Korea).
Patient consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the
patient for publication of data of her medical case and all
associated images.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Gallup DG and Stock RJ: Adenocarcinoma of
the endometrium in women 40 years of age or younger. Obstet
Gynecol. 64:417–420. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Park EH, Jung KW, Park NJ, Kang MJ, Yun
EH, Kim HJ, Kim JE, Kong HJ, Im JS and Seo HG: Community of
Population-Based Regional Cancer Registries. Cancer statistics in
Korea: Incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2021.
Cancer Res Treat. 56:357–371. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jeong SM, Jung JH, Yang YS, Kim W, Cho IY,
Lee YB, Park KY, Nam GE and Han K: Taskforce Team of the Obesity
Fact Sheet of the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. 2023
obesity fact sheet: Prevalence of obesity and abdominal obesity in
adults, adolescents, and children in Korea from 2012 to 2021. J
Obes Metab Syndr. 33:27–35. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Liu L, Habeshian TS, Zhang J, Peeri NC, Du
M, De Vivo I and Setiawan VW: Differential trends in rising
endometrial cancer incidence by age, race, and ethnicity. JNCI
Cancer Spectr. 7(pkad001)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jo H, Kim SI, Wang W, Seol A, Han Y, Kim
J, Park IS, Lee J, Yoo J, Han KD and Song YS: Metabolic syndrome as
a risk factor of endometrial cancer: A nationwide population-based
cohort study of 2.8 million women in South Korea. Front Oncol.
12(872995)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Crawford G, Bahabri A and P'ng S: An
atypical presentation of endometrial cancer as angina secondary to
critically low hemoglobin and iron deficiency associated
pancytopenia: A case report. Case Rep Womens Health.
38(e00509)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jordan RW, Chapman AW, Buchanan D and
Makrides P: The role of intramedullary fixation in ankle
fractures-A systematic review. Foot Ankle Surg. 24:1–10.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Valle RF and Baggish MS: Endometrial
carcinoma after endometrial ablation: High-risk factors predicting
its occurrence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 179:569–572. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Aune D, Sen A and Vatten LH: Hypertension
and the risk of endometrial cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of case-control and cohort studies. Sci Rep.
7(44808)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wild CP, Weiderpass E and Stewart BW
(eds): World cancer report. Cancer research for cancer prevention.
Lyon (FR): International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2020.
Available online: https://www.iarc.who.int/cards_page/world-cancer-report.
|
|
11
|
Pati S, Irfan W, Jameel A, Ahmed S, Ahmed
S and Shahid RK: Obesity and cancer: A current overview of
epidemiology, pathogenesis, outcomes, and management. Cancers
(Basel). 15(485)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Marin AG, Filipescu A and Petca A: The
role of obesity in the etiology and carcinogenesis of endometrial
cancer. Cureus. 16(e59219)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Donnez J, Carmona F, Maitrot-Mantelet L,
Dolmans MM and Chapron C: Uterine disorders and iron deficiency
anemia. Fertil Steril. 118:615–624. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Soliman PT, Oh JC, Schmeler KM, Sun CC,
Slomovitz BM, Gershenson DM, Burke TW and Lu KH: Risk factors for
young premenopausal women with endometrial cancer. Obstet Gynecol.
105:575–580. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC).
Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and
obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416
population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children,
adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 390:2627–2642. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Khalenko VV, Guiglia RA and Alioto M: Are
women with PCOS more at risk for endometrial cancer? What approach
for such patients? Acta Biomed. 94(e2023081)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Reeves GK, Pirie K, Beral V, Green J,
Spencer E and Bull D: Million Women Study Collaboration. Cancer
incidence and mortality in relation to body mass index in the
Million Women Study: Cohort study. BMJ. 335(1134)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Connaughton M and Dabagh M: Association of
hypertension and organ-specific cancer: A meta-analysis. Healthcare
(Basel). 10(1074)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Habeshian TS, Peeri NC, De Vivo I,
Schouten LJ, Shu XO, Cote ML, Bertrand KA, Chen Y, Clarke MA,
Clendenen TV, et al: Hypertension and risk of endometrial cancer: A
pooled analysis in the epidemiology of endometrial cancer
consortium (E2C2). Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 33:788–795.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Rodriguez VE, Tanjasiri SP, Ro A, Hoyt MA,
Bristow RE and LeBrón AMW: Trends in endometrial cancer incidence
in the United States by race/ethnicity and age of onset from 2000
to 2019. Am J Epidemiol: kwae178, 2024 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
21
|
Sung H, Siegel RL, Rosenberg PS and Jemal
A: Emerging cancer trends among young adults in the USA: Analysis
of a population-based cancer registry. Lancet Public Health.
4:e137–e147. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Huang BZ, Liu L and Zhang J: USC Pancreas
Research Team. Pandol SJ, Grossman SR and Setiawan VW: Rising
incidence and racial disparities of early-onset pancreatic cancer
in the United States, 1995-2018. Gastroenterology. 163:310–312.e1.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yu M, Wang Y, Yuan Z, Zong X, Huo X, Cao
DY, Yang JX and Shen K: Fertility-sparing treatment in young
patients with grade 2 presumed stage IA endometrioid endometrial
adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 10(1437)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Artioli G, Cassaro M, Pedrini L, Borgato
L, Corti L, Cappetta A, Lombardi G and Nicoletto MO: Rare
presentation of endometrial carcinoma with singular bone
metastasis. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 19:694–698. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ryan M, Laios A, Pathak D, Weston M and
Hutson R: An unusual presentation of endometrial cancer with
bilateral adrenal metastases at the time of presentation and an
updated descriptive literature review. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol.
2019(3515869)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jones ER, O'Flynn H, Njoku K and Crosbie
EJ: Detecting endometrial cancer. Obstet Gynaecol. 23:103–112.
2021.
|
|
27
|
Cabrera S, de la Calle I, Baulies S,
Gil-Moreno A and Colas E: Screening strategies to improve early
diagnosis in endometrial cancer. J Clin Med.
13(5445)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Oaknin A, Bosse TJ, Creutzberg CL,
Giornelli G, Harter P, Joly F, Lorusso D, Marth C, Makker V, Mirza
MR, et al: Endometrial cancer: ESMO clinical practice guideline for
diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 33:860–877.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|