|
1
|
Hu L, Xiao Y, Xiong Z, Zhao F, Yin C,
Zhang Y, Su P, Li D, Chen Z, Ma X, et al: MACF1, versatility in
tissue-specific function and in human disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
69:3–8. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
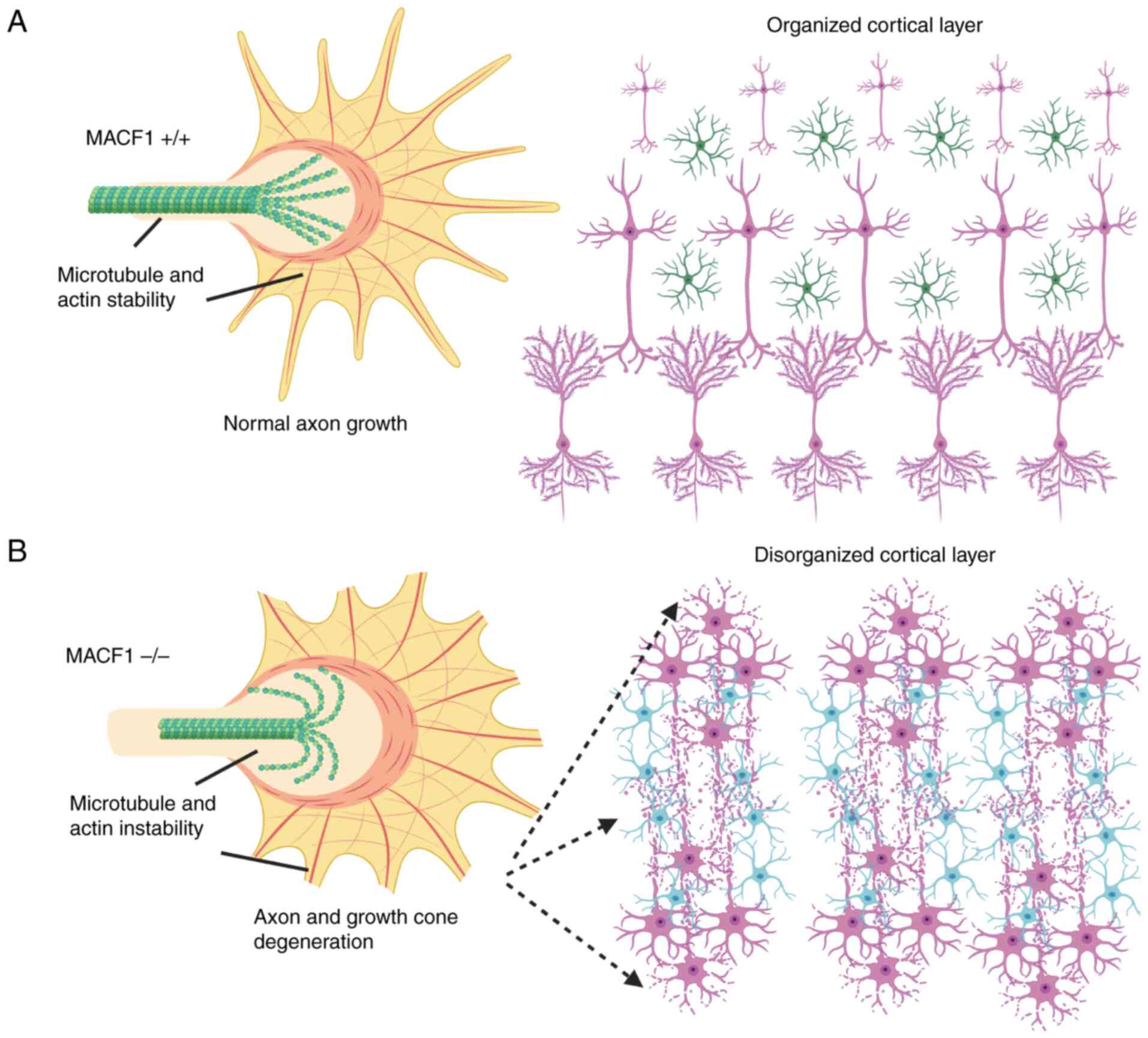
2
|
Applewhite DA, Grode KD, Duncan MC and
Rogers SL: The actin-microtubule cross-linking activity of
Drosophila Short stop is regulated by intramolecular inhibition.
Mol Biol Cell. 24:2885–2893. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Goryunov D and Liem RK: Microtubule-Actin
cross-linking factor 1: Domains, interaction partners, and
tissue-specific functions. Methods Enzymol. 569:331–353.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cusseddu R, Robert A and Côté JF: Strength
through unity: The power of the mega-scaffold MACF1. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 9(641727)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yin C, Zhang Y, Hu L, Tian Y, Chen Z, Li
D, Zhao F, Su P, Ma X, Zhang G, et al: Mechanical unloading reduces
microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1 expression to inhibit
β-catenin signaling and osteoblast proliferation. J Cell Physiol.
233:5405–5419. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
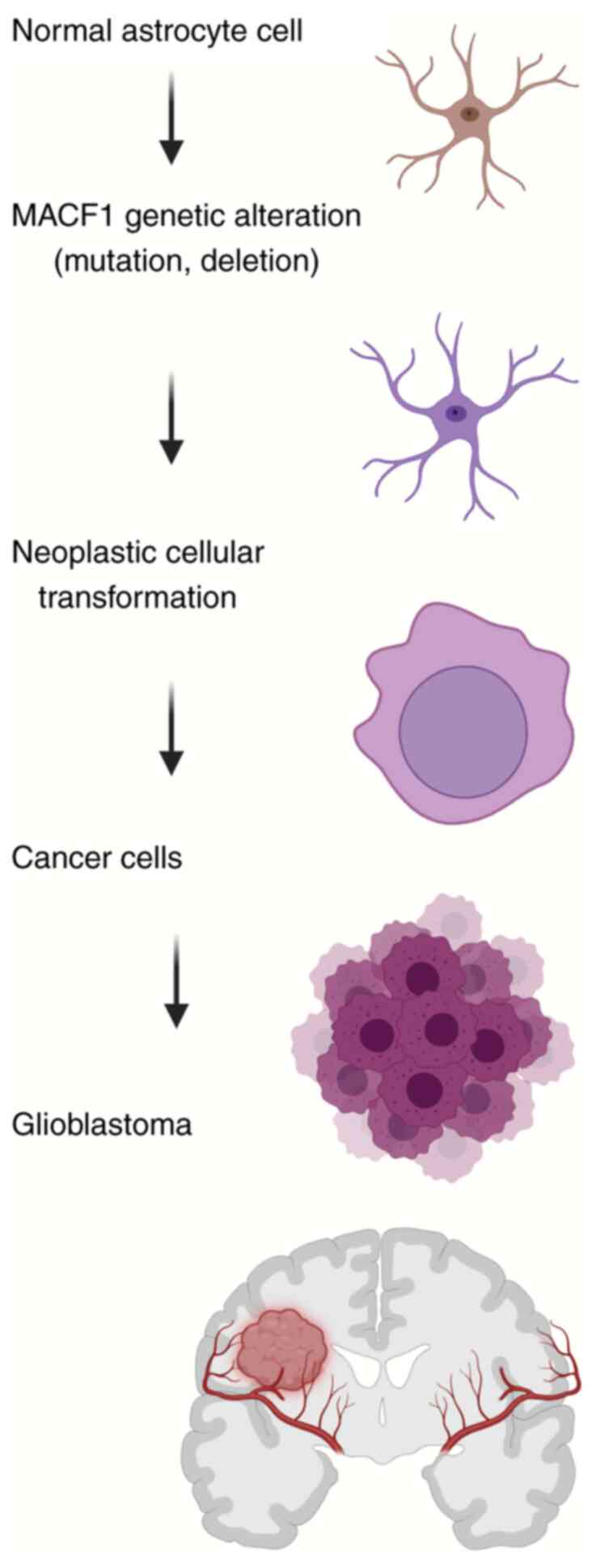
6
|
Bouameur JE, Favre B and Borradori L:
Plakins, a versatile family of cytolinkers: Roles in skin integrity
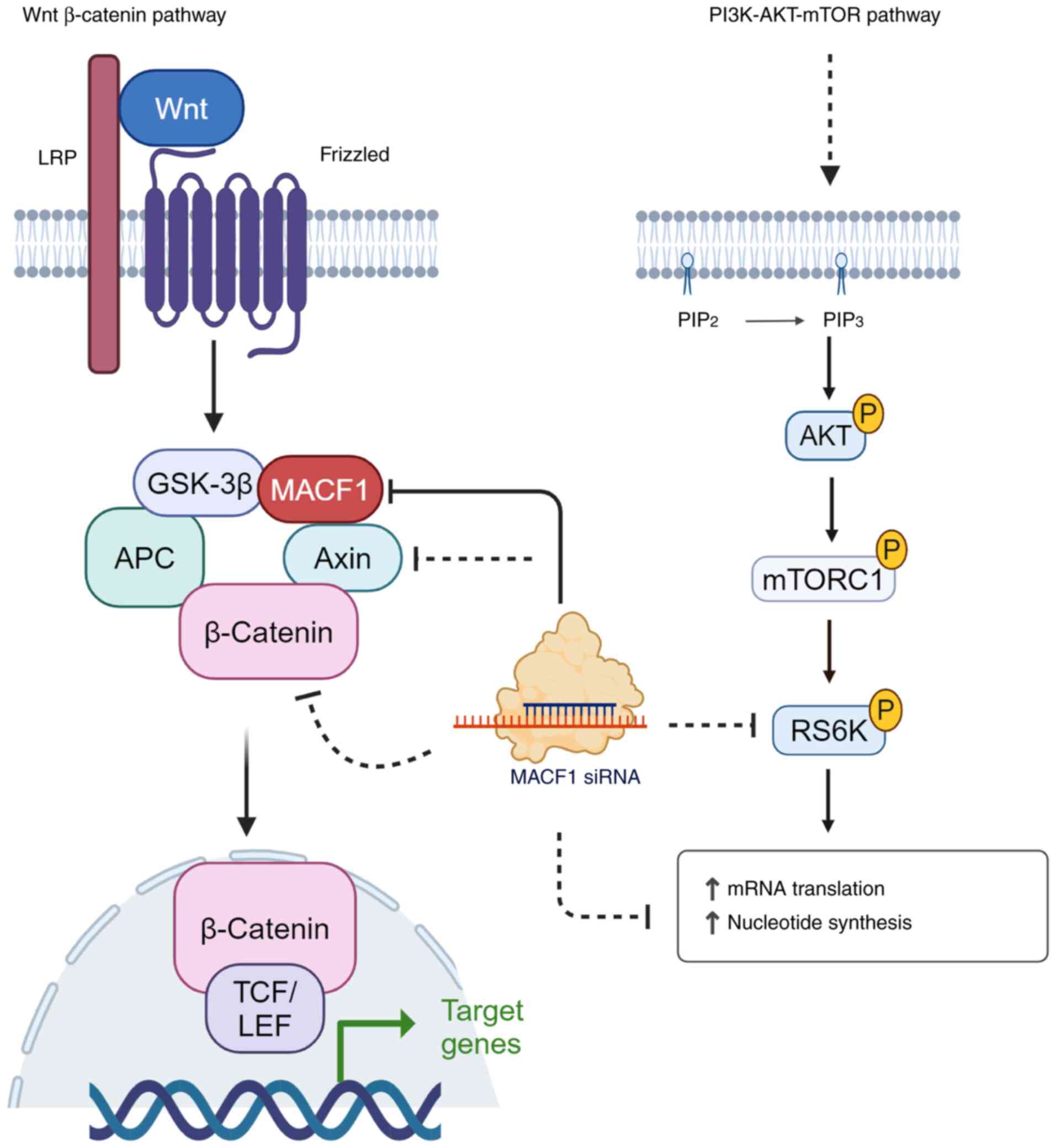
and in human diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 134:885–894.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hu L, Su P, Li R, Yin C, Zhang Y, Shang P,
Yang T and Qian A: Isoforms, structures, and functions of versatile
spectraplakin MACF1. BMB Rep. 49:37–44. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Quick QA: Microtubule-Actin crosslinking
factor 1 and plakins as therapeutic drug targets. Int J Mol Sci.
19(368)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Goryunov D, He CZ, Lin CS, Leung CL and
Liem RK: Nervous-tissue-specific elimination of microtubule-actin
crosslinking factor 1a results in multiple developmental defects in
the mouse brain. Mol Cell Neurosci. 44:1–14. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ka M, Moffat JJ and Kim WY: MACF1 controls
migration and positioning of cortical GABAergic interneurons in
mice. Cereb Cortex. 27:5525–5538. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Qu Y, Alves-Silva J, Gupta K, Hahn I,
Parkin J, Sánchez-Soriano N and Prokop A: Re-evaluating the
actin-dependence of spectraplakin functions during axon growth and
maintenance. Dev Neurobiol. 82:288–307. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Alves-Silva J, Sánchez-Soriano N, Beaven
R, Klein M, Parkin J, Millard TH, Bellen HJ, Venken KJ, Ballestrem
C, Kammerer RA and Prokop A: Spectraplakins promote
microtubule-mediated axonal growth by functioning as structural
microtubule-associated proteins and EB1-dependent +TIPs (tip
interacting proteins). J Neurosci. 32:9143–9158. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ka M and Kim WY: Microtubule-Actin
crosslinking factor 1 is required for dendritic arborization and
axon outgrowth in the developing brain. Mol Neurobiol.
53:6018–6032. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ka M, Jung EM, Mueller U and Kim WY: MACF1
regulates the migration of pyramidal neurons via microtubule
dynamics and GSK-3 signaling. Dev Biol. 395:4–18. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Moffat JJ, Ka M, Jung EM, Smith AL and Kim
WY: The role of MACF1 in nervous system development and
maintenance. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 69:9–17. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dobyns WB, Aldinger KA, Ishak GE, Mirzaa
GM, Timms AE, Grout ME, Dremmen MHG, Schot R, Vandervore L, van
Slegtenhorst MA, et al: MACF1 mutations encoding highly conserved
zinc-binding residues of the GAR domain cause defects in neuronal
migration and axon guidance. Am J Hum Genet. 103:1009–1021.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Misquitta-Ali CM, Cheng E, O'Hanlon D, Liu
N, McGlade CJ, Tsao MS and Blencowe BJ: Global profiling and
molecular characterization of alternative splicing events
misregulated in lung cancer. Mol Cell Biol. 31:138–150.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Arai E, Sakamoto H, Ichikawa H, Totsuka H,
Chiku S, Gotoh M, Mori T, Nakatani T, Ohnami S, Nakagawa T, et al:
Multilayer-omics analysis of renal cell carcinoma, including the
whole exome, methylome and transcriptome. Int J Cancer.
135:1330–1342. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chang YS, Huang HD, Yeh KT and Chang JG:
Identification of novel mutations in endometrial cancer patients by
whole-exome sequencing. Int J Oncol. 50:1778–1784. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tian Y, Zhu K, Li Y, Ren Z and Wang J:
MACF1 mutations predict poor prognosis: A novel potential
therapeutic target for breast cancer. Am J Transl Res.
14:7670–7688. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 6(pl1)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
de Bruijn I, Kundra R, Mastrogiacomo B,
Tran TN, Sikina L, Mazor T, Li X, Ochoa A, Zhao G, Lai B, et al:
Analysis and visualization of longitudinal genomic and clinical
data from the AACR project GENIE biopharma collaborative in
cBioPortal. Cancer Res. 83:3861–3867. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang P, Zhang J, Zhang H and Zhang F: The
role of MACF1 on acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation is
involved in Runx2-targeted PI3K/Akt signaling. Mol Cell Biochem.
478:433–441. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu L, Hu K, Zeng Z, Xu C, Lv J, Lin Z and
Wen B: Expression and clinical significance of microtubule-actin
cross-linking factor 1 in serous ovarian cancer. Recent Pat
Anticancer Drug Discov. 16:66–72. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fan D, Yang Y and Zhang W: A novel
circ_MACF1/miR-942-5p/TGFBR2 axis regulates the functional
behaviors and drug sensitivity in gefitinib-resistant non-small
cell lung cancer cells. BMC Pulm Med. 22(27)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Žugec M, Furlani B, Castañon MJ, Rituper
B, Fischer I, Broggi G, Caltabiano R, Barbagallo GMV, Di Rosa M,
Tibullo D, et al: Plectin plays a role in the migration and volume
regulation of astrocytes: A potential biomarker of glioblastoma. J
Biomed Sci. 31(14)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kubelt C, Hattermann K, Sebens S, Mehdorn
HM and Held-Feindt J: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
paired human primary and recurrent glioblastomas. Int J Oncol.
46:2515–2525. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Žugec M, Furlani B, Castañon MJ, Rituper
B, Fischer I, Broggi G, Caltabiano R, Barbagallo GMV, Di Rosa M,
Tibullo D, et al: Plectin plays a role in the migration and volume
regulation of astrocytes: A potential biomarker of glioblastoma. J
Biomed Sci. 31(14)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ostrom QT, Cioffi G, Gittleman H, Patil N,
Waite K, Kruchko C and Barnholtz-Sloan JS: CBTRUS statistical
report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors
diagnosed in the United States in 2012-2016. Neuro Oncol. 21 (Suppl
5):v1–v100. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ostrom QT, Price M, Neff C, Cioffi G,
Waite KA, Kruchko C and Barnholtz-Sloan JS: CBTRUS statistical
report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors
diagnosed in the United States in 2016-2020. Neuro Oncol. 25 (12
Suppl 2):iv1–iv99. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang P, Xia Q, Liu L, Li S and Dong L:
Current opinion on molecular characterization for GBM
classification in guiding clinical diagnosis, prognosis, and
therapy. Front Mol Biosci. 7(562798)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Georgescu MM: Translation into clinical
practice of the G1-g7 molecular subgroup classification of
glioblastoma: Comprehensive demographic and molecular pathway
profiling. Cancers (Basel). 16(361)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lazzarini E, Silvestris DA, Benvenuto G,
Osti D, Fattore L, Paterra R, Finocchiaro G, Malatesta P, Daga A,
Gallotti AL, et al: Genome-wide profiling of patient-derived
glioblastoma stem-like cells reveals recurrent genetic and
transcriptomic signatures associated with brain tumors. J
Neurooncol. 163:47–59. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ludwig K and Kornblum HI: Molecular
markers in glioma. J Neurooncol. 134:505–512. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Robertson FL, Marqués-Torrejón MA,
Morrison GM and Pollard SM: Experimental models and tools to tackle
glioblastoma. Dis Model Mech. 12(dmm040386)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Miyai M, Tomita H, Soeda A, Yano H, Iwama
T and Hara A: Current trends in mouse models of glioblastoma. J
Neurooncol. 135:423–432. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ciechomska IA, Wojnicki K, Wojtas B,
Szadkowska P, Poleszak K, Kaza B, Jaskula K, Dawidczyk W, Czepko R,
Banach M, et al: Exploring novel therapeutic opportunities for
glioblastoma using patient-derived cell cultures. Cancers (Basel).
15(1562)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chen Z, Herting CJ, Ross JL, Gabanic B,
Vallcorba MP, Szulzewsky F, Wojciechowicz ML, Cimino PJ,
Ezhilarasan R, Sulman EP, et al: Genetic driver mutations
introduced in identical cell-of-origin in murine glioblastoma
reveal distinct immune landscapes but similar response to
checkpoint blockade. Glia. 68:2148–2166. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Quick Q and Skalli O: Alpha-actinin 1 and
alpha-actinin 4: Contrasting roles in the survival, motility, and
RhoA signaling of astrocytoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 316:1137–1147.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Afghani N, Mehta T, Wang J, Tang N, Skalli
O and Quick QA: Microtubule actin cross-linking factor 1, a novel
target in glioblastoma. Int J Oncol. 50:310–316. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Quick Q and Bonner K: Immunoblot, cell
viability, and transformation bar graphs. 2023 https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.24391903
(unpublished data).
|
|
43
|
Quick Q and Bonner K: Cell motility bar
graph and images. 2023 https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.24392593
(unpublished data).
|
|
44
|
Quick Q and Bonner K: Methods. 2023
https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.24393145
(unpublished data).
|
|
45
|
Li GF, Cheng YY, Li BJ, Zhang C, Zhang XX,
Su J, Wang C, Chang L, Zhang DZ, Tan CL and Wang N: miR-375
inhibits the proliferation and invasion of glioblastoma by
regulating Wnt5a. Neoplasma. 66:350–356. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Precilla DS, Kuduvalli SS, Purushothaman
M, Marimuthu P, Muralidharan AR and Anitha TS: Wnt/β-catenin
antagonists: Exploring new avenues to trigger old drugs in
alleviating glioblastoma multiforme. Curr Mol Pharmacol.
15:338–360. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
De Robertis A, Valensin S, Rossi M, Tunici
P, Verani M, De Rosa A, Giordano C, Varrone M, Nencini A, Pratelli
C, et al: Identification and characterization of a small-molecule
inhibitor of Wnt signaling in glioblastoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
12:1180–1189. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Kaur N, Chettiar S, Rathod S, Rath P,
Muzumdar D, Shaikh ML and Shiras A: Wnt3a mediated activation of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes tumor progression in glioblastoma.
Mol Cell Neurosci. 54:44–57. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Bonner K, Borlay D, Kutten O and Quick QA:
Inhibition of the spectraplakin protein microtubule actin
crosslinking factor 1 sensitizes glioblastomas to radiation. Brain
Tumor Res Treat. 8:43–52. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Langhans J, Schneele L, Trenkler N, von
Bandemer H, Nonnenmacher L, Karpel-Massler G, Siegelin MD, Zhou S,
Halatsch ME, Debatin KM and Westhoff MA: The effects of
PI3K-mediated signaling on glioblastoma cell behaviour.
Oncogenesis. 6(398)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Li X, Wu C, Chen N, Gu H, Yen A, Cao L,
Wang E and Wang L: PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and targeted
therapy for glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 7:33440–33450.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Suwala AK, Koch K, Rios DH, Aretz P,
Uhlmann C, Ogorek I, Felsberg J, Reifenberger G, Köhrer K, Deenen
R, et al: Inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling downregulates
expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase isoform 3A1 (ALDH3A1) to
reduce resistance against temozolomide in glioblastoma in vitro.
Oncotarget. 9:22703–22716. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Von Achenbach C, Weller M, Kaulich K,
Gramatzki D, Zacher A, Fabbro D, Reifenberger G and Szabó E:
Synergistic growth inhibition mediated by dual PI3K/mTOR pathway
targeting and genetic or direct pharmacological AKT inhibition in
human glioblastoma models. J Neurochem. 153:510–524.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Salphati L, Alicke B, Heffron TP,
Shahidi-Latham S, Nishimura M, Cao T, Carano RA, Cheong J, Greve J,
Koeppen H, et al: Brain distribution and efficacy of the brain
penetrant PI3K inhibitor GDC-0084 in orthotopic mouse models of
human glioblastoma. Drug Metab Dispos. 44:1881–1889.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Guo T, Wu C, Zhang J, Yu J, Li G, Jiang H,
Zhang X, Yu R and Liu X: Dual blockade of EGFR and PI3K signaling
pathways offers a therapeutic strategy for glioblastoma. Cell
Commun Signal. 21(363)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wang Y, Tong H, Wang J, Hu L and Huang Z:
LRRC1 knockdown downregulates MACF1 to inhibit the malignant
progression of acute myeloid leukemia by inactivating
β-catenin/c-Myc signaling. J Mol Histol. 55:37–50. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Zhang K, Qiu W, Li H, Li J, Wang P, Chen
Z, Lin X and Qian A: MACF1 overexpression in BMSCs alleviates
senile osteoporosis in mice through TCF4/miR-335-5p signaling
pathway. J Orthop Translat. 39:177–190. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Wang X, Jian X, Dou J, Wei Z and Zhao F:
Decreasing microtubule actin cross-linking factor 1 inhibits
melanoma metastasis by decreasing epithelial to mesenchymal
transition. Cancer Manag Res. 12:663–673. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|