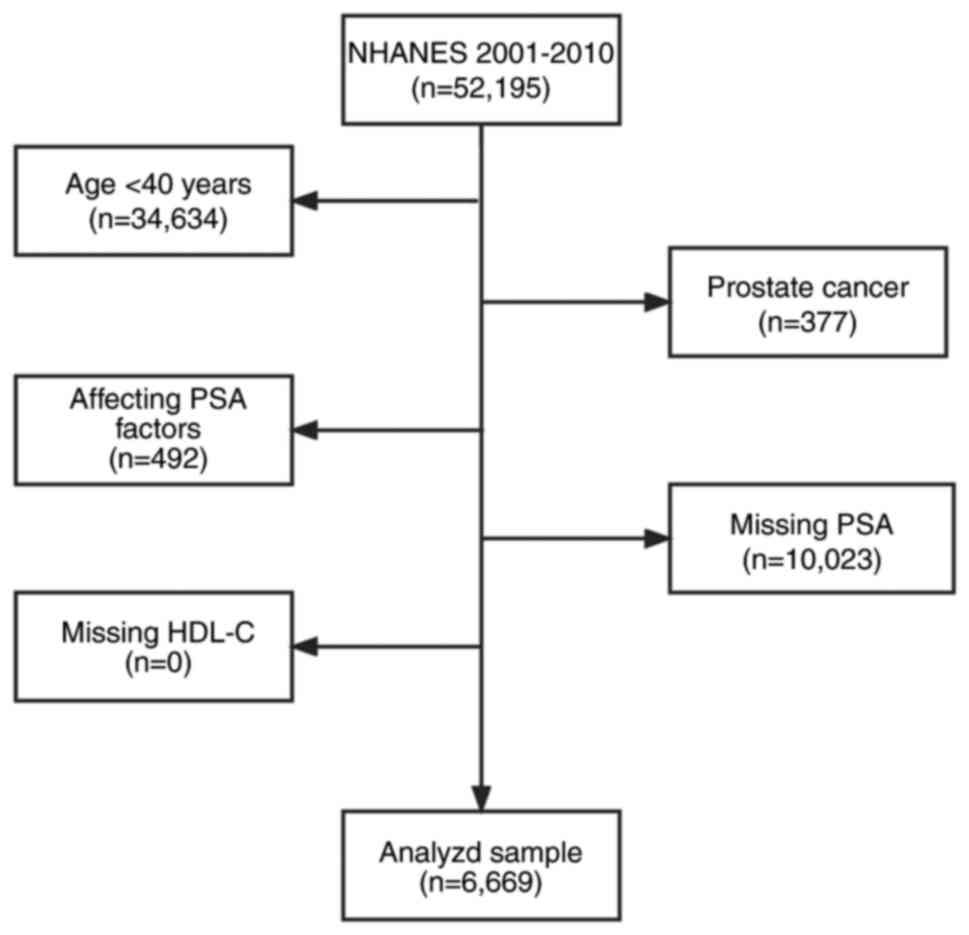
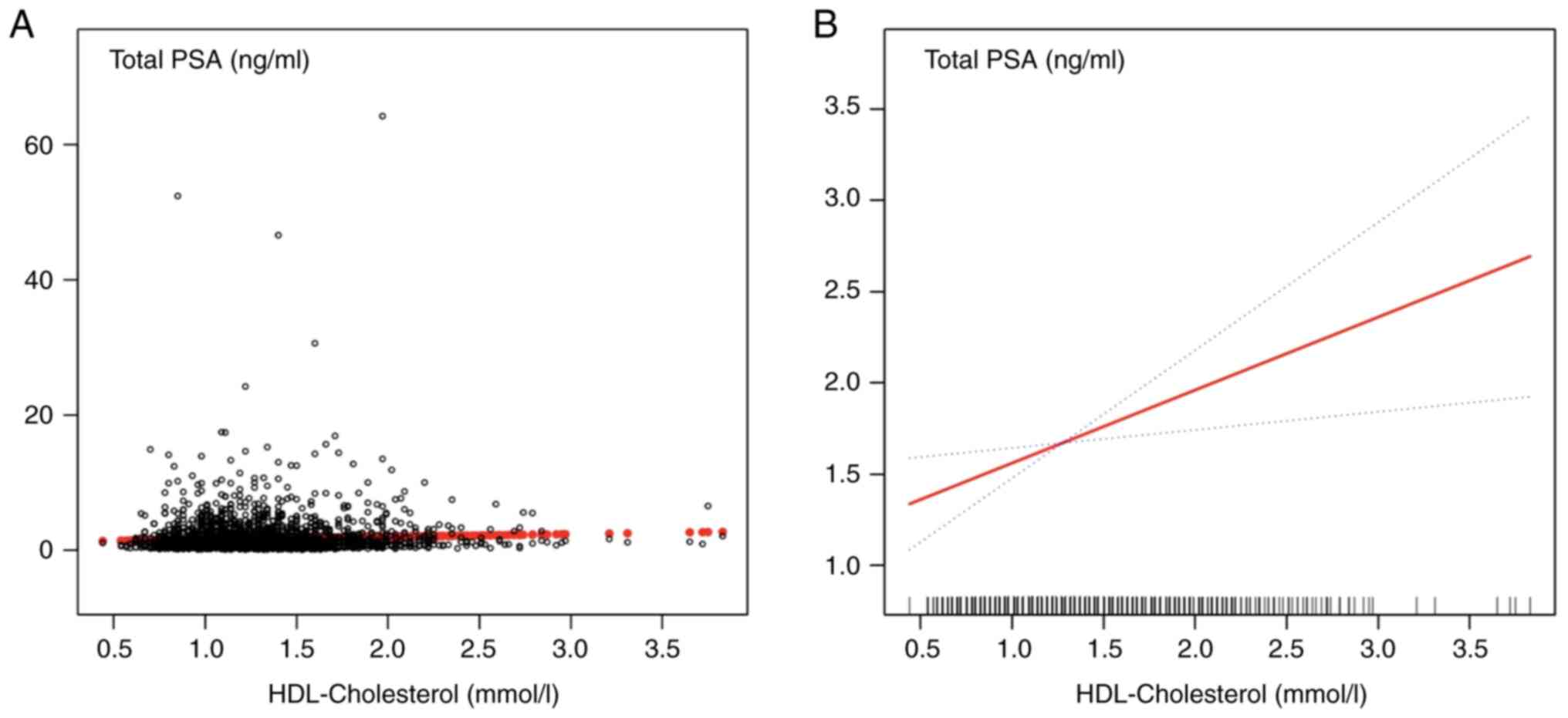
|
1
|
Wang L, Lu B, He M, Wang Y, Wang Z and Du
L: Prostate cancer incidence and mortality: Global status and
temporal trends in 89 countries from 2000 to 2019. Front Public
Health. 10(811044)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 72:7–33.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Grubb RL III: Prostate cancer: Update on
early detection and new biomarkers. Mo Med. 115:132–134.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Narain TA and Sooriakumaran P: Beyond
prostate specific antigen: New prostate cancer screening options.
World J Mens Health. 40:66–73. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Schröder FH, Hugosson J, Roobol MJ,
Tammela TL, Zappa M, Nelen V, Kwiatkowski M, Lujan M, Määttänen L,
Lilja H, et al: Screening and prostate cancer mortality: Results of
the European Randomised Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer
(ERSPC) at 13 years of follow-up. Lancet. 384:2027–2035.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Carlsson SV and Vickers AJ: Screening for
prostate cancer. Med Clin North Am. 104:1051–1062. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Parekh DJ, Punnen S, Sjoberg DD, Asroff
SW, Bailen JL, Cochran JS, Concepcion R, David RD, Deck KB,
Dumbadze I, et al: A multi-institutional prospective trial in the
USA Confirms that the 4Kscore accurately identifies men with
high-grade prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 68:464–470. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Buddingh KT, Maatje MGF, Putter H, Kropman
RF and Pelger RCM: Do antibiotics decrease prostate-specific
antigen levels and reduce the need for prostate biopsy in type IV
prostatitis? A systematic literature review. Can Urol Assoc J.
12:E25–E30. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Stattin P, Carlsson S, Holmstrom B,
Vickers A, Hugosson J, Lilja H and Jonsson H: Prostate cancer
mortality in areas with high and low prostate cancer incidence. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 106(dju007)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tall AR: Cholesterol efflux pathways and
other potential mechanisms involved in the athero-protective effect
of high density lipoproteins. J Intern Med. 263:256–273.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Murtola TJ, Syvälä H, Pennanen P, Bläuer
M, Solakivi T, Ylikomi T and Tammela TL: The importance of LDL and
Cholesterol metabolism for prostate epithelial cell growth. PLoS
One. 7(e39445)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Platz EA, Clinton SK and Giovannucci E:
Association between plasma cholesterol and prostate cancer in the
PSA era. Int J Cancer. 123:1693–1698. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mondul AM, Clipp SL, Helzlsouer KJ and
Platz EA: Association between plasma total cholesterol
concentration and incident prostate cancer in the CLUE II cohort.
Cancer Causes Control. 21:61–68. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm.
|
|
16
|
Mondul AM, Weinstein SJ, Virtamo J and
Albanes D: Serum total and HDL cholesterol and risk of prostate
cancer. Cancer Causes Control. 22:1545–1552. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhao R, Cheng G, Wang B, Qin C, Liu Y, Pan
Y, Wang J, Hua L, Zhu W and Wang Z: BMI and serum lipid parameters
predict increasing risk and aggressive prostate cancer in Chinese
people. Oncotarget. 8:66051–66060. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Platz EA, Leitzmann MF, Visvanathan K,
Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC and Giovannucci E: Statin drugs
and risk of advanced prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
98:1819–1825. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mørland JG, Magnus P, Vollset SE, Leon DA,
Selmer R and Tverdal A: Associations between serum high-density
lipoprotein cholesterol levels and cause-specific mortality in a
general population of 345 000 men and women aged 20-79 years. Int J
Epidemiol. 52:1257–1267. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ioannidou A, Watts EL, Perez-Cornago A,
Platz EA, Mills IG, Key TJ and Travis RC: PRACTICAL consortium,
CRUK BPC3, et al. The relationship between lipoprotein A and
other lipids with prostate cancer risk: A multivariable Mendelian
randomisation study. PLoS Med. 19(e1003859)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Senapati D, Sharma V, Rath SK, Rai U and
Panigrahi N: Functional implications and therapeutic targeting of
androgen response elements in prostate cancer. Biochimie. 214(Pt
B):188–198. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Baio R, Napodano G, Caruana C, Molisso G,
Di Mauro U, Intilla O, Pane U, D'Angelo C, Francavilla AB,
Guarnaccia C, et al: Association between obesity and frequency of
high-grade prostate cancer on biopsy in men: A single-center
retrospective study. Mol Clin Oncol. 17(127)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jamnagerwalla J, Howard LE, Allott EH,
Vidal AC, Moreira DM, Castro-Santamaria R, Andriole GL, Freeman MR
and Freedland SJ: Serum cholesterol and risk of high-grade prostate
cancer: Results from the REDUCE study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic
Dis. 21:252–259. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Van Hemelrijck M, Garmo H, Holmberg L,
Walldius G, Jungner I, Hammar N and Lambe M: Prostate cancer risk
in the Swedish AMORIS study The interplay among triglycerides,
total cholesterol, and glucose. Cancer. 117:2086–2095.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kotani K, Sekine Y, Ishikawa S, Ikpot IZ,
Suzuki K and Remaley AT: High-density lipoprotein and prostate
cancer: An overview. J Epidemiol. 23:313–319. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Van Hemelrijck M, Walldius G, Jungner I,
Hammar N, Garmo H, Binda E, Hayday A, Lambe M and Holmberg L: Low
levels of apolipoprotein A-I and HDL are associated with risk of
prostate cancer in the Swedish AMORIS study. Cancer Causes Control.
22:1011–1019. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Albertsen PC: Prostate cancer screening
and treatment: Where have we come from and where are we going? BJU
Int. 126:218–224. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|