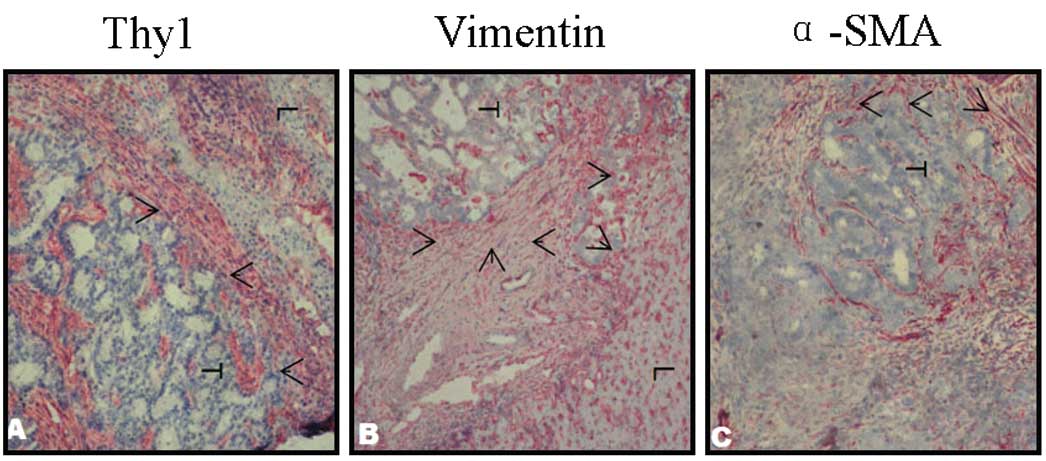
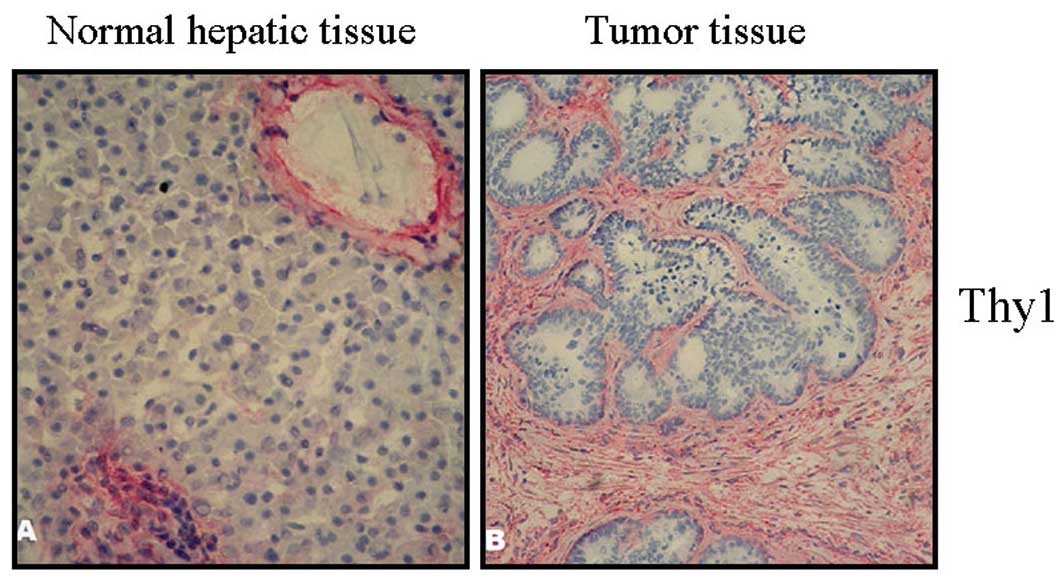
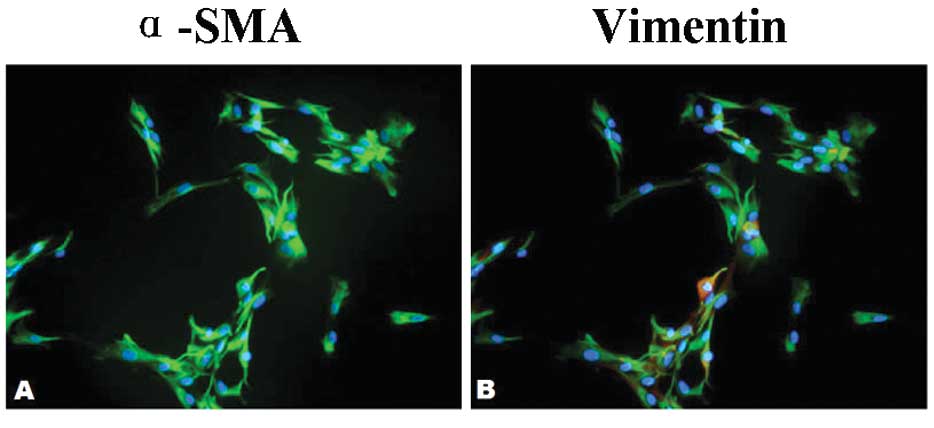
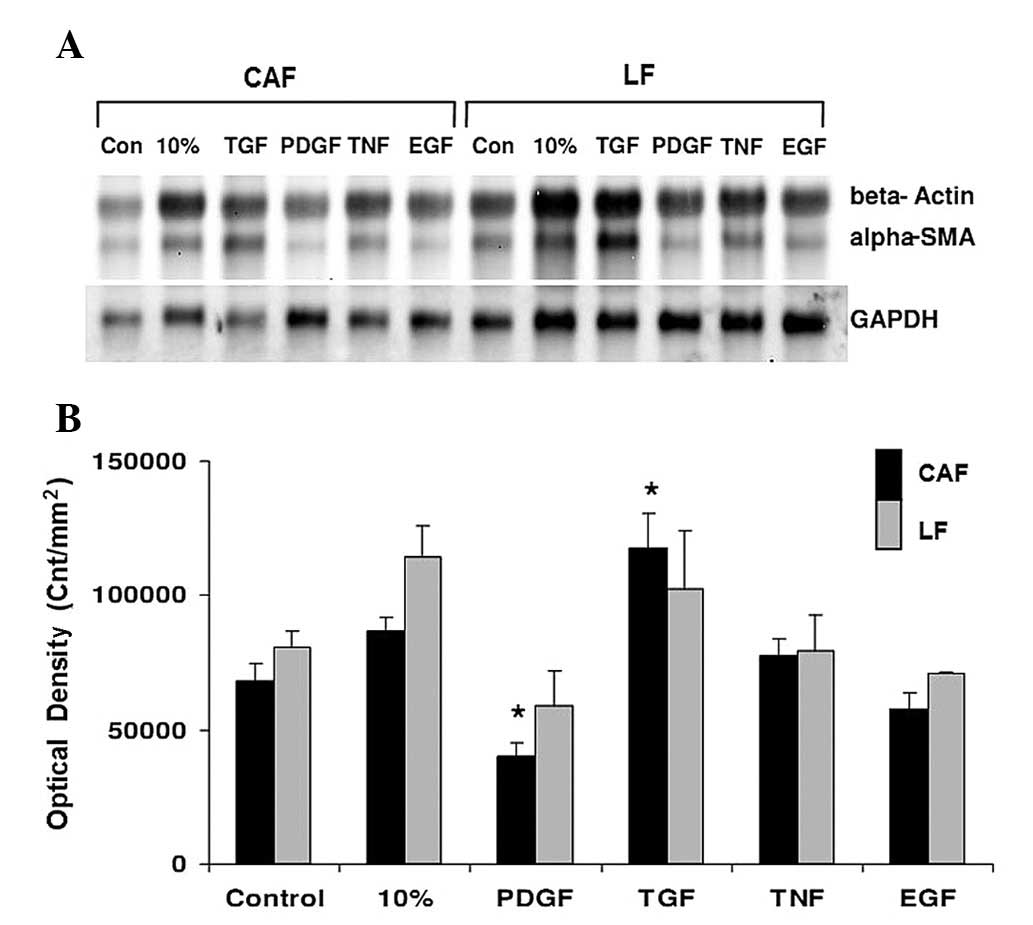
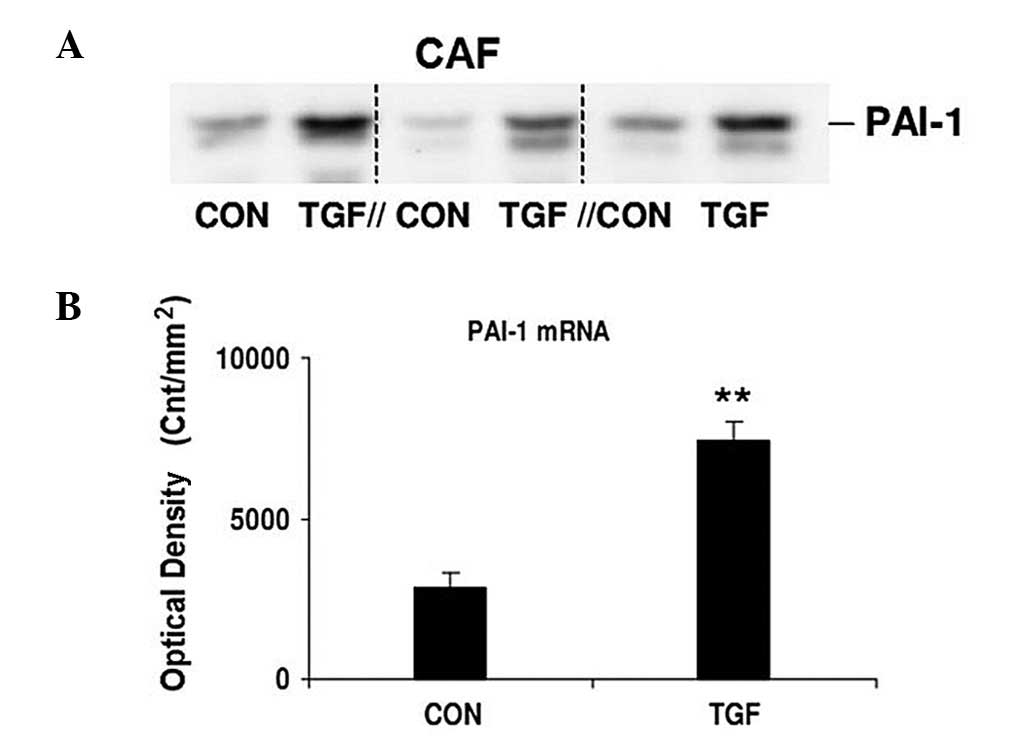
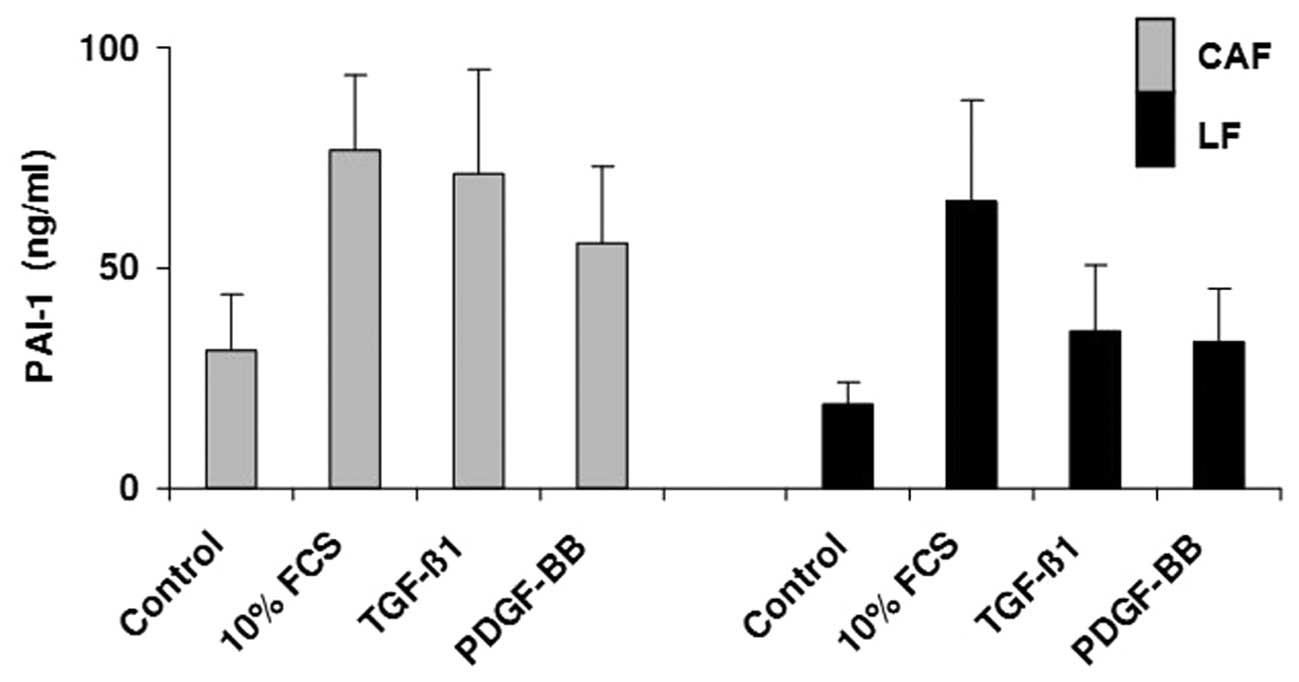
|
1
|
Welch DR, Steeg PS and Rinker-Schaefer CW:
Molecular biology of breast cancer metastasis. Genetic regulation
of human breast carcinoma metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2:408–416.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Duda DG, Duyverman AM, Kohno M, et al:
Malignant cells facilitate lung metastasis by bringing their own
soil. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:21677–21682. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bhowmick NA, Neilson EG and Moses HL:
Stromal fibroblasts in cancer initiation and progression. Nature.
43:332–337. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Polanska UM, Acar A and Orimo A:
Experimental generation of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts (CAFs)
from human mammary fibroblasts. J Vis Exp. 56:e32012011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mazzocca A, Dituri F, Lupo L, et al:
Tumor-secreted lysophostatidic acid accelerates hepatocellular
carcinoma progression by promoting differentiation of peritumoral
fibroblasts in myofibroblasts. Hepatology. 54:920–930. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Fujiita M, Hayashi I, Yamashina S, et al:
Angiotensin type 1a receptor signaling-dependent induction of
vascular endothelial growth factor in stroma is relevant to
tumor-associated angiogenesis and tumor growth. Carcinogenesis.
26:271–219. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fabris VT, Sahores A, Vanzulli SI, et al:
Inoculated mammary carcinoma-associated fibroblasts: contribution
to hormone independent tumor growth. BMC Cancer. 10:2932010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ishikawa S, Takenaka K, Yanagihara K, et
al: Matrix metalloproteinase-2 status in stromal fibroblasts, not
in tumor cells, is a significant prognostic factor in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:6579–6585. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC, et al:
Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human breast carcinomas
promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through elevated SDF-1/CXCL12
secretion. Cell. 121:335–348. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Orimo A and Weinberg RA: Stromal
fibroblasts in cancer: a novel tumor-promoting cell type. Cell
Cycle. 5:1597–1601. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rosenthal E, McCrory A, Talbert M, et al:
Elevated expression of TGF-beta1 in head and neck cancer-associated
fibroblasts. Mol Carcinog. 40:116–121. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
LaRue A, Masuya M and Ebihara Y:
Hematopoietic origins of fibroblasts: I. in vivo studies of
fibroblasts associated with solid tumors. Exp Hematol. 34:208–218.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu C, Chen Z, Chen Z, et al: Multiple
tumor types may originate from bone marrow-derived cells.
Neoplasia. 8:716–724. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Direkze N, Hodivala-Dilke K, Jeffery R, et
al: Bone marrow contribution to tumor-associated myofibroblasts and
fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 64:8492–8495. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al: Global
cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rougier P and Mitry E: Epidemiology,
treatment and chemoprevention in colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol.
14:ii3–5. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tajima Y, Ishibashi K, Ishiguro T, et al:
Analysis of hepatic lymph node metastasis in liver metastases from
colorectal cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 38:2228–2231. 2011.(In
Japanese).
|
|
18
|
Olaso E, Salado C, Egilegor E, et al:
Proangiogenic role of tumor-activated hepatic stellate cells in
experimental melanoma metastasis. Hepatology. 37:674–685. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Claffey KP, Abrams K, Shih SC, et al:
Fibroblasts growth factor 2 activation of stromal cell vascular
endothelial growth factor expression and angiogenesis. Lab Invest.
81:61–75. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee HO, Mullins SR, Franco-Barraza J, et
al: FAP-overexpressing fibroblasts produce an extracellular matrix
that enhances invasive velocity and directionality of pancreatic
cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 11:2452011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gulubova MV: Ito cell morphology,
alpha-smooth muscle actin and collagen type IV expression in the
liver of patients with gastric and colorectal tumors. Histochem J.
32:151–164. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Koumas L, Smith TJ, Feldon S, et al: Thy-1
expression in human fibroblast subsets defines myofibroblastic or
lipofibroblastic phenotypes. Am J Pathol. 163:1291–1300. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Barker TH, Grenett HE, MacEwen MW, et al:
Thy-1 regulates fibroblast focal adhesions, cytoskeletal
organization and migration through modulation of p190 RhoGAP and
Rho GTPase activity. Exp Cell Res. 295:4884–4896. 2004.
|
|
24
|
Wakahara K, Kobayashi H, Yagyu T, et al:
Transforming growth factor-beta1- dependent activation of Smad2/3
and up-regulation of PAI-1 expression is negatively regulated by
Src in SKOV-3 human ovarian cancer cells. J Cell Biochem.
93:437–453. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hirashima Y, Kobayashi H, Suzuki M, et al:
Transforming growth factor-beta1 produced by ovarian cancer cell
line HRA stimulates attachement and invasion through an
up-regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 in human
peritoneal mesothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 278:26793–26802. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Halamkova J, Kiss I, Pavlovsky Z, et al:
Clinical significance of the plasminogen activator system in
relation to grade of tumor and treatment response in colorectal
carcinoma patients. Neoplasma. 58:377–385. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zubac DP, Wentzel-Larsen T, Seidal T, et
al: Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) and its impact on angiogenesis,
progression and patient survival after radical nephrectomy. BMC
Urol. 10:202010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Grebenchtchikov N, Maguire TM, Riisbro R,
et al: Measurement of plasminogen activator system components in
plasma and tumor tissue extracts obtained from patients with breast
cancer: an EORTC Receptor and Biomarker Group. Oncol Rep.
14:235–239. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nishioka N, Matsuoka T, Yashiro M, et al:
Linoleic acid enhances angiogenesis through suppression of
angiostatin induced by plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. Br J
Cancer. 105:1750–1758. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Romer MU, Due AK, Larsen JK, et al:
Indication of a role of plasminogen activator inhibitor type I in
protecting murine fibrosarcoma cells against apoptosis. Thromb
haemost. 94:859–866. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|