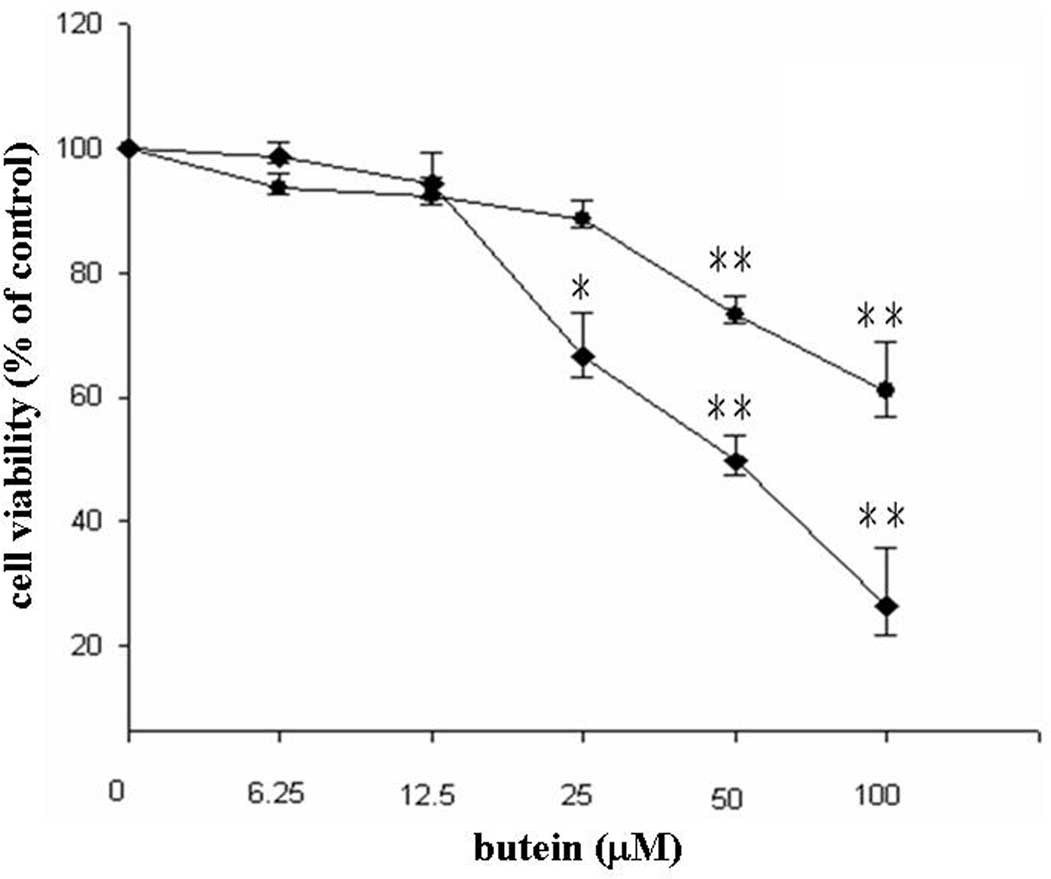
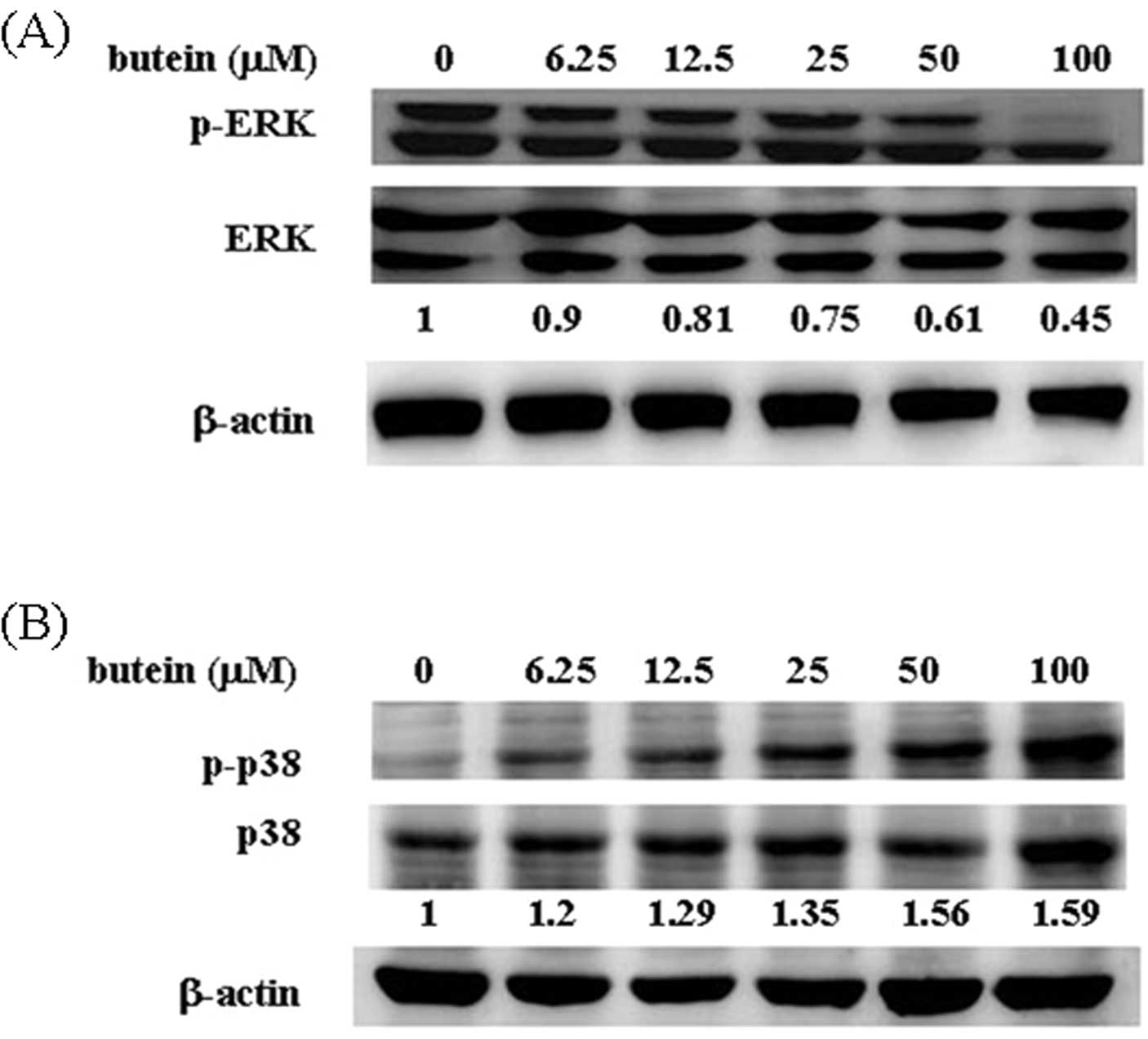
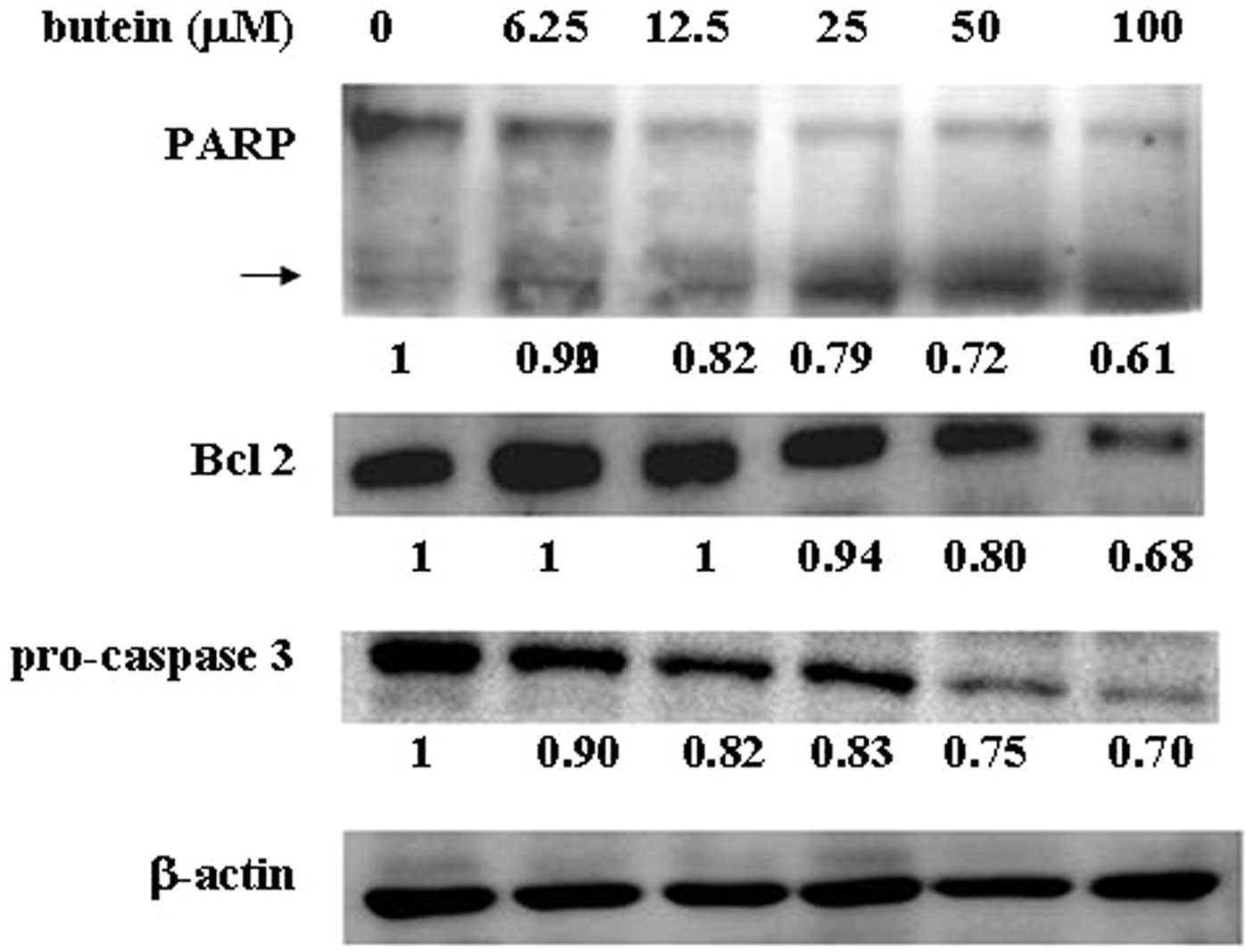
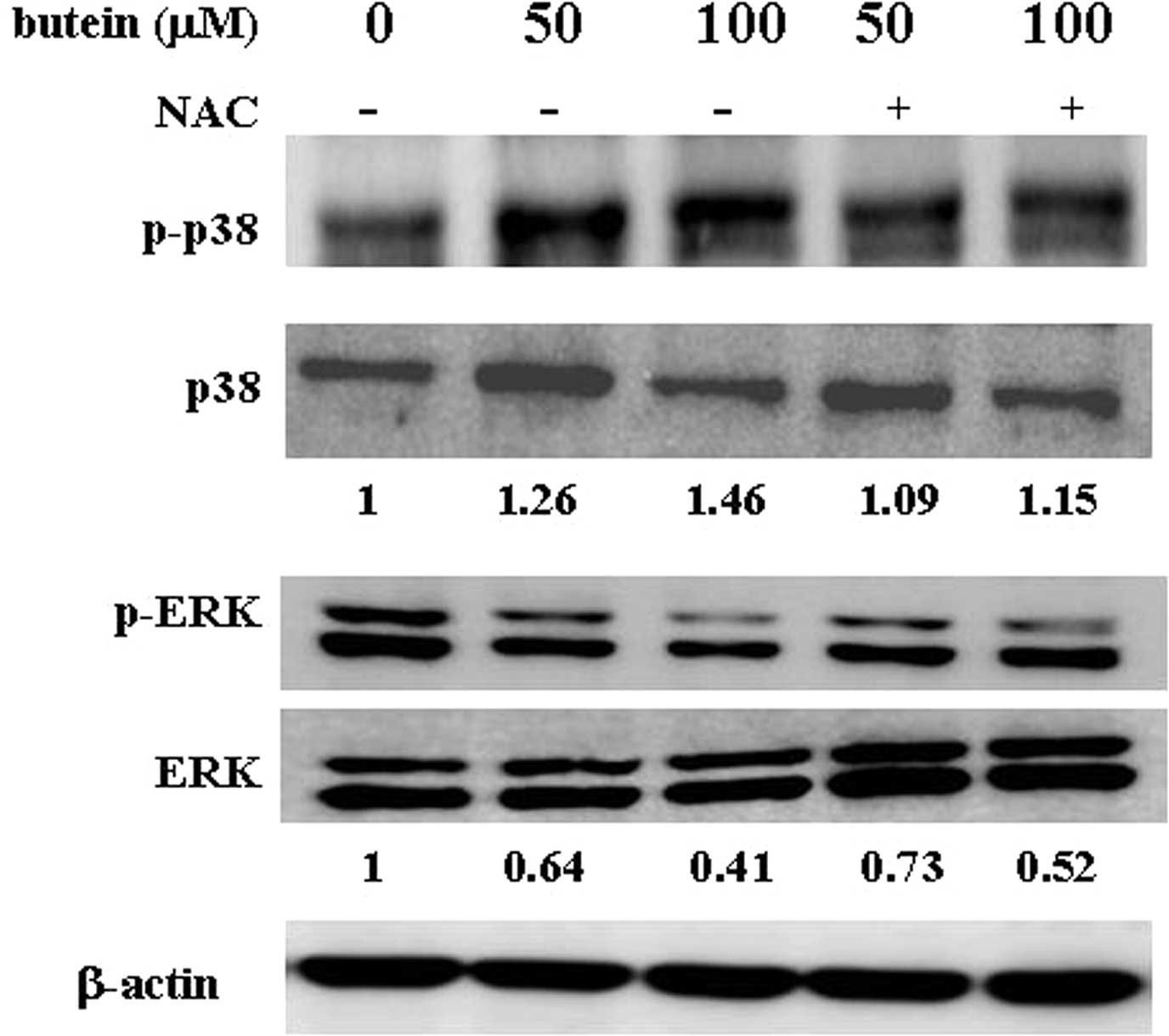
|
1
|
Kelloff GJ, Boone CW, Crowell JA, Steele
VE, Lubet R and Sigman CC: Chemopreventive drug development:
perspectives and progress. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
3:85–98. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khan N, Afaq F and Mukhtar H: Cancer
chemoprevention through dietary antioxidants: progress and promise.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 10:475–510. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee JC, Lee KY, Kim J, Na CS, et al:
Extract from Rhus verniciflua Stokes is capable of
inhibiting the growth of human lymphoma cells. Food Chem Toxicol.
42:1383–1388. 2004.
|
|
4
|
Jung CH, Jun CY, Lee S, Park CH, Cho K and
Ko SG: Rhus verniciflua stokes extract: radical scavenging
activities and protective effects on
H2O2-induced cytotoxicity in macrophage RAW
264.7 cell lines. Biol Pharm Bull. 29:1603–1607. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jung CH, Kim JH, Hong MH, et al:
Phenolic-rich fraction from Rhus verniciflua Stokes (RVS)
suppress inflammatory response via NF-kappaB and JNK pathway in
lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol.
110:490–497. 2007.
|
|
6
|
Aizu E, Nakadate T, Yamamoto S and Kato R:
Inhibition of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-mediated
epidermal ornithine decarboxylase induction and skin tumor
promotion by new lipoxygenase inhibitors lacking protein kinase C
inhibitory effects. Carcinogenesis. 7:1809–1812. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kang DG, Lee AS, Mun YJ, et al: Butein
ameliorates renal concentrating ability in cisplatin-induced acute
renal failure in rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 27:366–370. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lim SS, Jung SH, Ji J, Shin KH and Keum
SR: Synthesis of flavonoids and their effects on aldose reductase
and sorbitol accumulation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat
tissues. J Pharm Pharmacol. 53:653–668. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee SH, Nan JX, Zhao YZ, et al: The
chalcone butein from Rhus verniciflua shows antifibrogenic
activity. Planta Med. 69:990–994. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jang HS, Kook SH, Son YO, et al:
Flavonoids purified from Rhus verniciflua Stokes actively
inhibit cell growth and induce apoptosis in human osteosarcoma
cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1726:309–316. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kook SH, Son YO, Chung SW, et al:
Caspase-independent death of human osteosarcoma cells by flavonoids
is driven by p53-mediated mitochondrial stress and nuclear
translocation of AIF and endonuclease G. Apoptosis. 12:1289–1298.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ramanathan R, Tan CH and Das NP: Cytotoxic
effect of plant polyphenols and fat-soluble vitamins on malignant
human cultured cells. Cancer Lett. 62:217–224. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yit CC and Das NP: Cytotoxic effect of
butein on human colon adenocarcinoma cell proliferation. Cancer
Lett. 82:65–72. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Iwashita K, Kobori M, Yamaki K and
Tsushida T: Flavonoids inhibit cell growth and induce apoptosis in
B16 melanoma 4A5 cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 64:1813–1820.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pandey MK, Sung B, Ahn KS and Aggarwal BB:
Butein suppresses constitutive and inducible signal transducer and
activator of transcription (STAT) 3 activation and STAT3-regulated
gene products through the induction of a protein tyrosine
phosphatase SHP-1. Mol Pharmacol. 75:525–533. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rajendran P, Ong TH, Chen L, et al:
Suppression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
activation by butein inhibits growth of human hepatocellular
carcinoma in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1425–1439. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moon DO, Choi YH, Moon SK, Kim WJ and Kim
GY: Butein suppresses the expression of nuclear factor-kappa
B-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 and vascular endothelial
growth factor in prostate cancer cells. Toxicol In Vitro.
24:1927–1934. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang CS, Yang GY, Landau JM, Kim S and
Liao J: Tea and tea polyphenols inhibit cell hyperproliferation,
lung tumorigenesis, and tumor progression. Exp Lung Res.
24:629–639. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim JH, Jung CH, Jang BH, et al: Selective
cytotoxic effects on human cancer cell lines of phenolic-rich
ethyl-acetate fraction from Rhus verniciflua Stokes. Am J
Chin Med. 37:609–620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chua AW, Hay HS, Rajendran P, et al:
Butein downregulates chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression and
function through suppression of NF-kappaB activation in breast and
pancreatic tumor cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:1553–1562. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lau GT, Huang H, Lin SM and Leung LK:
Butein downregulates phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-induced COX-2
transcriptional activity in cancerous and non-cancerous breast
cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 648:24–30. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang W and Liu HT: MAPK signal pathways
in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Res. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shankar S, Ganapathy S and Srivastava RK:
Green tea polyphenols: biology and therapeutic implications in
cancer. Front Biosci. 12:4881–4899. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stoner GD and Mukhtar H: Polyphenols as
cancer chemopreventive agents. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 22:169–180.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Raman M, Chen W and Cobb MH: Differential
regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene. 26:3100–3112. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cross TG, Scheel-Toellner D, Henriquez NV,
Deacon E, Salmon M and Lord JM: Serine/threonine protein kinases
and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 256:34–41. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chang IC, Huang YJ, Chiang TI, Yeh CW and
Hsu LS: Shikonin induces apoptosis through reactive oxygen
species/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in
osteosarcoma cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 33:816–824. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Fresco P, Borges F, Diniz C and Marques
MP: New insights on the anticancer properties of dietary
polyphenols. Med Res Rev. 26:747–766. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z and Kong D:
Cellular signaling perturbation by natural products. Cell Signal.
21:1541–1547. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shankar S, Suthakar G and Srivastava RK:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits cell cycle and induces
apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. Front Biosci. 12:5039–5051. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Granado-Serrano AB, Martin MA, Bravo L,
Goya L and Ramos S: Quercetin induces apoptosis via caspase
activation, regulation of Bcl-2, and inhibition of PI-3-kinase/Akt
and ERK pathways in a human hepatoma cell line (HepG2). J Nutr.
136:2715–2721. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim EJ, Choi CH, Park JY, Kang SK and Kim
YK: Underlying mechanism of quercetin-induced cell death in human
glioma cells. Neurochem Res. 33:971–979. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang L, Chen W and Li X: A novel
anticancer effect of butein: inhibition of invasion through the
ERK1/2 and NF-kappa B signaling pathways in bladder cancer cells.
FEBS Lett. 582:1821–1828. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee SH, Seo GS, Jin XY, Ko G and Sohn DH:
Butein blocks tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced interleukin 8 and
matrix metalloproteinase 7 production by inhibiting p38 kinase and
osteopontin mediated signaling events in HT-29 cells. Life Sci.
81:1535–1543. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cory S and Adams JM: The Bcl2 family:
regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:647–656. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim NY, Pae HO, Oh GS, et al: Butein, a
plant polyphenol, induces apoptosis concomitant with increased
caspase-3 activity, decreased Bcl-2 expression and increased Bax
expression in HL-60 cells. Pharmacol Toxicol. 88:261–266. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bechtel W and Bauer G: Modulation of
intercellular ROS signaling of human tumor cells. Anticancer Res.
29:4559–4570. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Victor VM, Rocha M, Sola E, Banuls C,
Garcia-Malpartida K and Hernandez-Mijares A: Oxidative stress,
endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Curr Pharm Des.
15:2988–3002. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shukla S and Gupta S: Apigenin-induced
prostate cancer cell death is initiated by reactive oxygen species
and p53 activation. Free Radic Biol Med. 44:1833–1845. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nakazato T, Ito K, Ikeda Y and Kizaki M:
Green tea component, catechin, induces apoptosis of human malignant
B cells via production of reactive oxygen species. Clin Cancer Res.
11:6040–6049. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sharma V, Joseph C, Ghosh S, Agarwal A,
Mishra MK and Sen E: Kaempferol induces apoptosis in glioblastoma
cells through oxidative stress. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:2544–2553. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Moon DO, Kim MO, Choi YH, Hyun JW, Chang
WY and Kim GY: Butein induces G(2)/M phase arrest and apoptosis in
human hepatoma cancer cells through ROS generation. Cancer Lett.
288:204–213. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen YH, Yeh CW, Lo HC, Su SL, Hseu YC and
Hsu LS: Generation of reactive oxygen species mediates
butein-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Oncol Rep.
27:1233–1237. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|