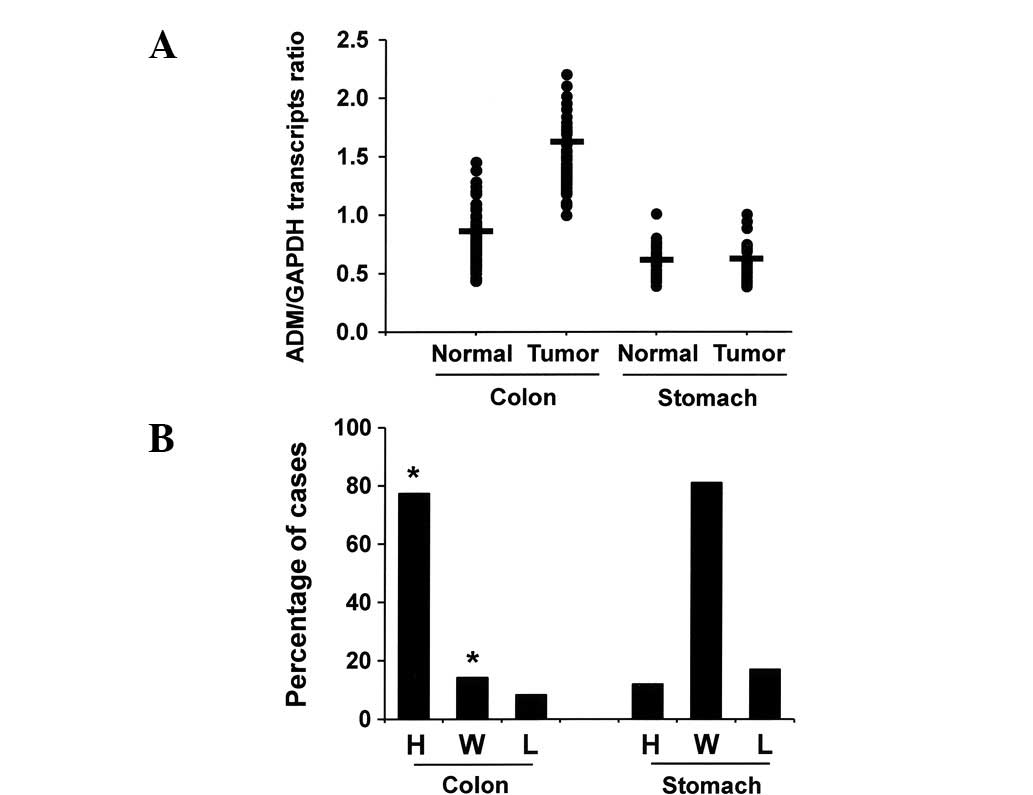
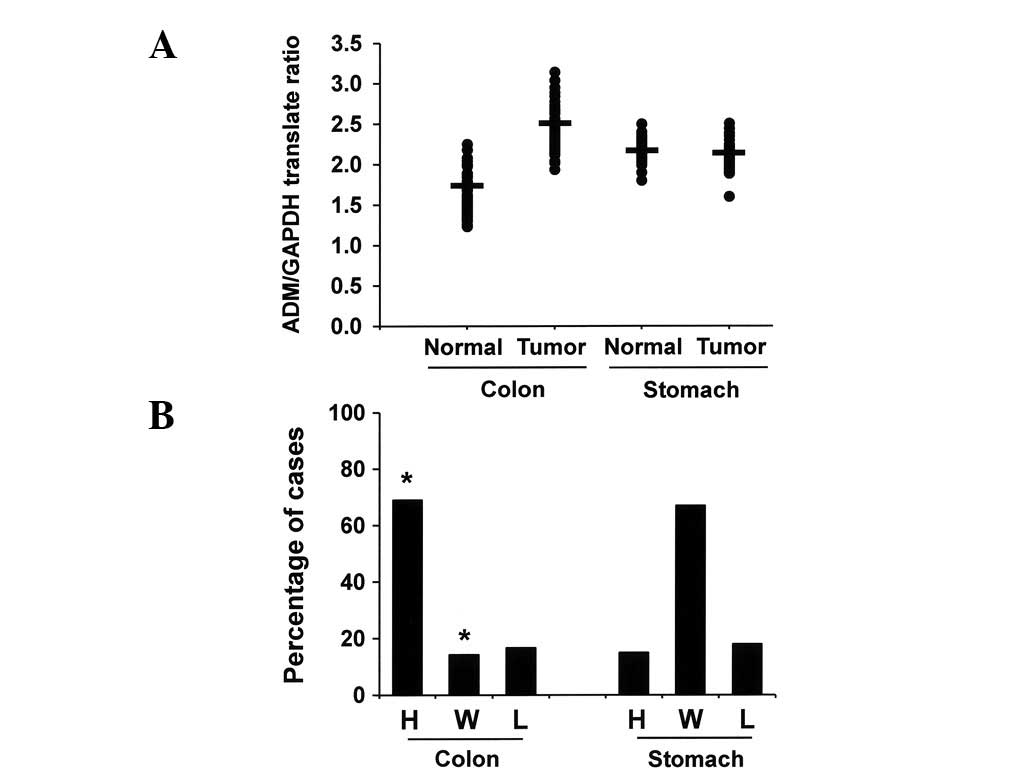
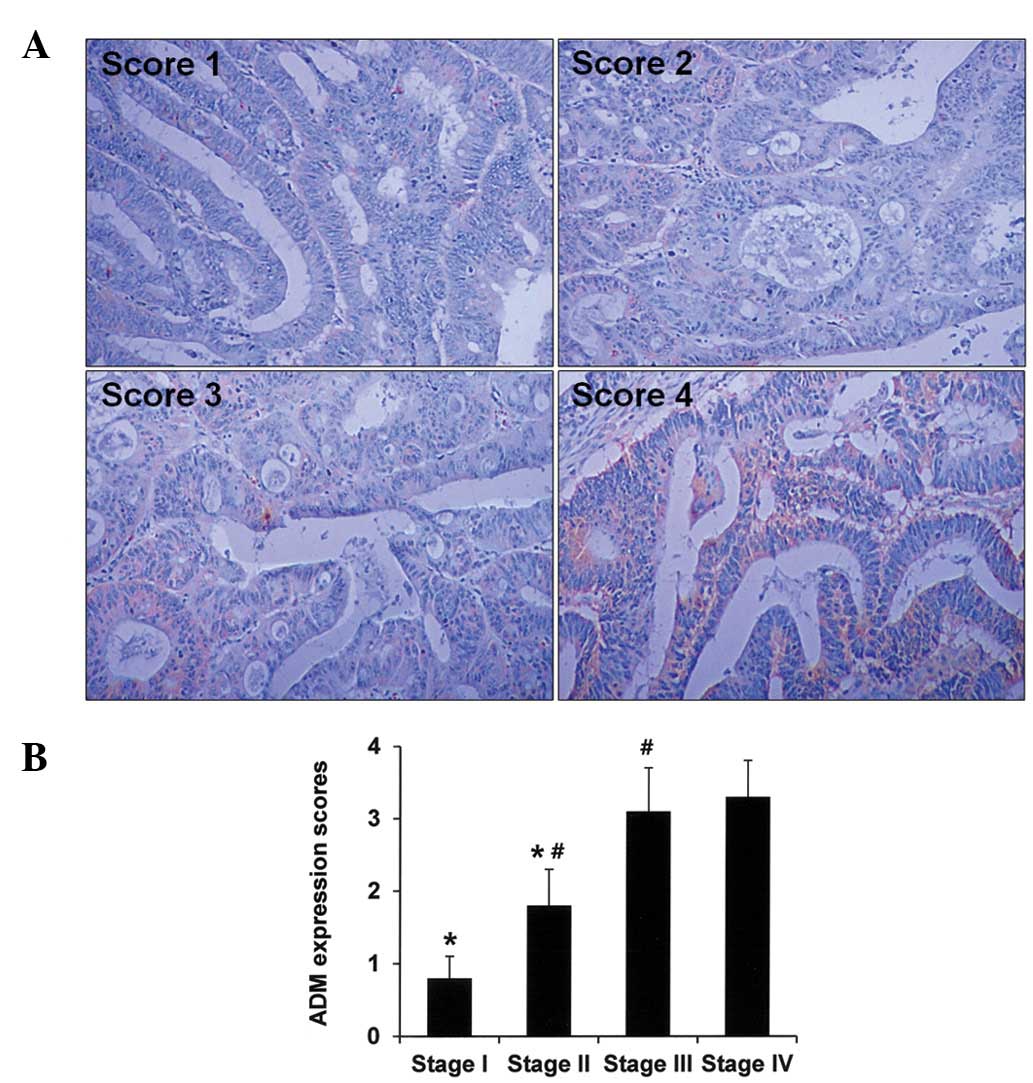
|
1
|
Kitamura K, Kangawa K, Kawamoto M, Ichiki
Y, Nakamura S, Matsuo H and Eto T: Adrenomedullin: a novel
hypotensive peptide isolated from human pheochromocytoma. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 192:553–560. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Eipper BA, Stoffers DA and Mains RE: The
biosynthesis of neuropeptides: peptide α-amidation (Review). Annu
Rev Neurosci. 15:57–85. 1992.
|
|
3
|
Kamitani S, Asakawa M, Shimekake Y,
Kuwasako K, Nakahara K and Sakata T: The RAMP2/CRLR complex is a
functional adrenomedullin receptor in human endothelial and
vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 448:111–114. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hinson JP, Kapas S and Smith DM:
Adrenomedullin, a multifunctional regulatory peptide (Review).
Endocr Rev. 21:138–167. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li Z, Takeuchi S, Otani T and Maruo T:
Implications of adrenomedullin expression in the invasion of
squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Int J Clin Oncol.
6:263–270. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Martínez A, Vos M, Guédez L, Kaur G, Chen
Z, Garayoa M, Pío R, Moody T, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Kleinman HK and
Cuttitta F: The effects of adrenomedullin overexpression in breast
tumor cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 94:1226–1237. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zudaire E, Martínez A and Cuttitta F:
Adrenomedullin and cancer (Review). Regul Pept. 112:175–183. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer (Review). Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Möller P, Koretz K, Leithäuser F,
Brüderlein S, Henne C, Quentmeier A and Krammer PH: Expression of
APO-1 (CD95), a member of the NGF/TNF receptor superfamily, in
normal and neoplastic colon epithelium. Int J Cancer. 57:371–377.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rich JN, Borton AJ and Wang X:
Transforming growth factor-b signaling in cancer (Review). Microsc
Res Tech. 52:363–373. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Oehler MK, Norbury C, Hague S, Rees MC and
Bicknell R: Adrenomedullin inhibits hypoxic cell death by
upregulation of Bcl-2 in endometrial cancer cells: a possible
promotion mechanism for tumour growth. Oncogene. 20:2937–2945.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ryu BK, Lee MG, Chi SG, Kim YW and Park
JH: Increased expression of cFLIP(L) in colonic adenocarcinoma. J
Pathol. 194:15–19. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hinson JP, Thomson LM and Kapas S:
Adrenomedullin and CGRP receptors mediate different effects in the
rat adrenal cortex. Endocr Res. 24:725–728. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Satoh F, Takahashi K, Murakami O, Totsune
K, Sone M, Ohneda M, Abe K, Miura Y, Hayashi Y and Sasano H:
Adrenomedullin in human brain, adrenal glands and tumor tissues of
pheochromocytoma, ganglioneuroblastoma and neuroblastoma. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 80:1750–1752. 1995.
|
|
15
|
Martinez A, Miller MJ, Unsworth EJ,
Siegfried JM and Cuttitta F: Expression of adrenomedullin in normal
human lung and in pulmonary tumors. Endocrinology. 136:4099–4105.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ouafik L, Sauze S, Boudouresque F, Chinot
O, Delfino C, Fina F, Vuaroqueaux V, Dussert C, Palmari J, Dufour
H, et al: Neutralization of adrenomedullin inhibits the growth of
human glioblastoma cell lines in vitro and suppresses tumor
xenograft growth in vivo. Am J Pathol. 160:1279–1292. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miller MJ, Martínez A, Unsworth EJ, Thiele
CJ, Moody TW, Elsasser T and Cuttitta F: Adrenomedullin expression
in human tumor cell lines. Its potential role as an autocrine
growth factor. J Biol Chem. 271:23345–23351. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakayama M, Takahashi K, Murakami O,
Shirato K and Shibahara S: Induction of adrenomedullin by hypoxia
and cobalt chloride in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 243:514–517. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kitani M, Sakata J, Asada Y, Kitamura K
and Eto T: Distribution and expression of adrenomedullin in human
gastrointestinal tissue. Ann Clin Biochem. 35:643–648. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Marutsuka K, Nawa Y, Asada Y, Hara S,
Kitamura K, Eto T and Sumiyoshi A: Adrenomedullin and
proadrenomudullin N-terminal 20 peptide (PAMP) are present in human
colonic epithelia and exert an antimicrobial effect. Exp Physiol.
86:543–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Garayoa M, Martínez A, Lee S, Pio R, An
WG, Neckers L, Trepel J, Montuenga LM, Ryan H, Johnson R, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) up-regulates adrenomedullin
expression in human tumor cell lines during oxygen deprivation: a
possible promotion mechanism of carcinogenesis. Mol Endocrinol.
14:848–862. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhao Y, Hague S, Manek S, Zhang L,
Bicknell R and Rees MC: PCR display identifies tamoxifen induction
of the novel angiogenic factor adrenomedullin by an non estrogenic
mechanism in the human endometrium. Oncogene. 16:409–415. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim W, Moon SO, Sung MJ, Kim SH, Lee S,
Kim HJ, Koh GY and Park SK: Protective effect of adrenomedullin in
mannitol-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis. 7:527–536. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kamoi H, Kanazawa H, Hirata K, Kurihara N,
Yano Y and Otani S: Adrenomedullin inhibits the secretion of
cytokine-induced neurtophil chemoattractant, a member of the
interleukin-8 family, from rat alveolar macrophages. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 211:1031–1035. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|