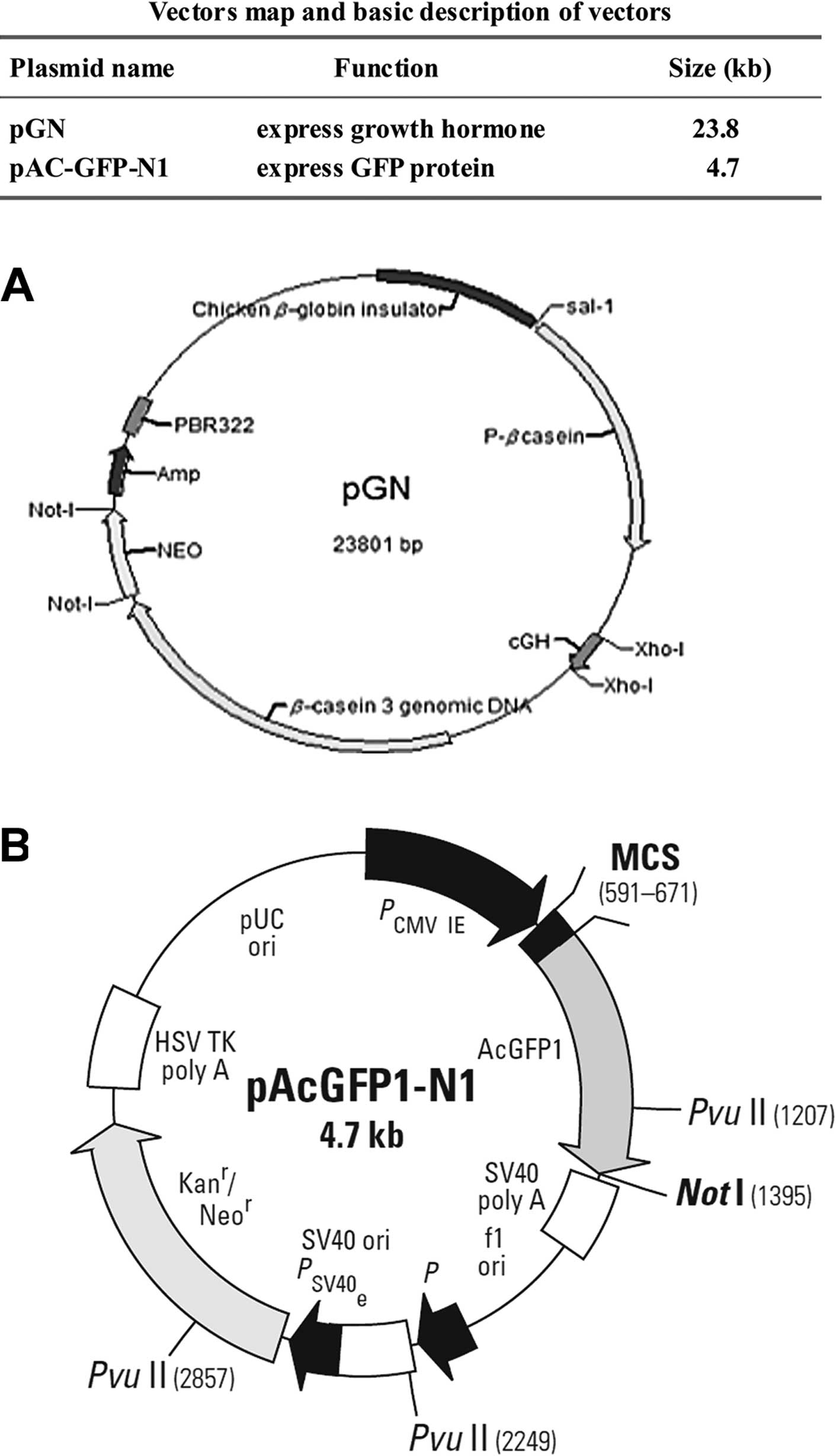
|
1
|
Lechardeur D and Lukacs GL: Intracellular
barriers to non-viral gene transfer. Curr Gene Ther. 2:183–194.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Leong KW, Mao HQ, Truong-Le VL, Roy K,
Walsh SM and August JT: DNA-polycation nanospheres as non-viral
gene delivery vehicles. J Control Release. 53:183–193. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kamiya H, Tsuchiya H, Yamazaki J and
Harashima H: Intracellular trafficking and transgene expression of
viral and non-viral gene vectors. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 52:153–164.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou M, Liu H, Xu X, et al: Identification
of nuclear localization signal that governs nuclear import of BRD7
and its essential roles in inhibiting cell cycle progression. J
Cell Biochem. 98:920–930. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Man N, Yu L, Zheng F, Li Y and Wen LP:
Efficient gene transfer to rat fetal osteoblastic cells by
synthetic peptide vector system. Protein Pept Lett. 16:368–372.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Notman R, den Otter WK, Noro MG, Briels WJ
and Anwar J: The permeability enhancing mechanism of DMSO in
ceramide bilayers simulated by molecular dynamics. Biophys J.
93:2056–2068. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ribbeck K and Gorlich D: The permeability
barrier of nuclear pore complexes appears to operate via
hydrophobic exclusion. Embo J. 21:2664–2671. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brunner S, Sauer T, Carotta S, Cotten M,
Saltik M and Wagner E: Cell cycle dependence of gene transfer by
lipoplex, polyplex and recombinant adenovirus. Gene Ther.
7:401–407. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guillard EC, Laugel C and Baillet-Guffroy
A: Molecular interactions of penetration enhancers within ceramides
organization: a FTIR approach. Eur J Pharm Sci. 36:192–199. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hewitt PG, Poblete N, Wester RC, Maibach
HI and Shainhouse JZ: In vitro cutaneous disposition of a topical
diclofenac lotion in human skin: effect of a multi-dose regimen.
Pharm Res. 15:988–992. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mittal A, Sara UV, Ali A and Aqil M: The
effect of penetration enhancers on permeation kinetics of
nitrendipine in two different skin models. Biol Pharm Bull.
31:1766–1772. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li L, Shen W, Min L, Dong H, Sun Y and Pan
Q: Human lactoferrin transgenic rabbits produced efficiently using
dimethylsulfoxide-sperm-mediated gene transfer. Reprod Fertil Dev.
18:689–695. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Brain KR, Green DM, Dykes PJ, Marks R and
Bola TS: The role of menthol in skin penetration from topical
formulations of ibuprofen 5% in vivo. Skin Pharmacol Physiol.
19:17–21. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ho HO, Chen LC, Lin HM and Sheu MT:
Penetration enhancement by menthol combined with a solubilization
effect in a mixed solvent system. J Control Release. 51:301–311.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bremner KH, Seymour LW, Logan A and Read
ML: Factors influencing the ability of nuclear localization
sequence peptides to enhance nonviral gene delivery. Bioconjug
Chem. 15:152–161. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jain PT and Gewirtz DA: Enhancement of
liposomal gene delivery in human breast cancer cells by dimethyl
sulfoxide. Int J Mol Med. 1:609–611. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fiore M, Zanier R and Degrassi F:
Reversible G(1) arrest by dimethyl sulfoxide as a new method to
synchronize Chinese hamster cells. Mutagenesis. 17:419–424. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Escriou V, Carriere M, Bussone F, Wils P
and Scherman D: Critical assessment of the nuclear import of
plasmid during cationic lipid-mediated gene transfer. J Gene Med.
3:179–187. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mir LM: Nucleic acids
electrotransfer-based gene therapy (electrogenetherapy): past,
current, and future. Mol Biotechnol. 43:167–176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ramezani A and Hawley RG: Strategies to
insulate lentiviral vector-expressed transgenes. Methods Mol Biol.
614:77–100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Heckert RA, Elankumaran S, Oshop GL and
Vakharia VN: A novel transcutaneous plasmid-dimethylsulfoxide
delivery technique for avian nucleic acid immunization. Vet Immunol
Immunopathol. 89:67–81. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sultana Y, Jain R, Aqil M and Ali A:
Review of ocular drug delivery. Curr Drug Deliv. 3:207–217. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang H, Zhong CY, Wu JF, Huang YB and Liu
CB: Enhancement of TAT cell membrane penetration efficiency by
dimethyl sulphoxide. J Control Release. 143:64–70. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Campeau P, Chapdelaine P, Seigneurin-Venin
S, Massie B and Tremblay JP: Transfection of large plasmids in
primary human myoblasts. Gene Ther. 8:1387–1394. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Migita S, Hanagata N, Tsuya D, Yamazaki T,
Sugimoto Y and Ikoma T: Transfection efficiency for size-separated
cells synchronized in cell cycle by microfluidic device. Biomed
Microdevices. 13:725–729. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Srinivas S, Sironmani TA and Shanmugam G:
Dimethyl sulfoxide inhibits the expression of early growth-response
genes and arrests fibroblasts at quiescence. Exp Cell Res.
196:279–286. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Collas P and Alestrom P: Rapid targeting
of plasmid DNA to zebrafish embryo nuclei by the nuclear
localization signal of SV40 T antigen. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol.
6:48–58. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Arenal A, Pimentel R, Garcia C, Pimentel E
and Alestrom P: The SV40 T antigen nuclear localization sequence
enhances nuclear import of vector DNA in embryos of a crustacean
(Litopenaeus schmitti). Gene. 337:71–77. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Medina-Kauwe LK, Xie J and Hamm-Alvarez S:
Intracellular trafficking of nonviral vectors. Gene Ther.
12:1734–1751. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xavier J, Singh S, Dean DA, Rao NM and
Gopal V: Designed multi-domain protein as a carrier of nucleic
acids into cells. J Control Release. 133:154–160. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dean DA, Strong DD and Zimmer WE: Nuclear
entry of nonviral vectors. Gene Ther. 12:881–890. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|