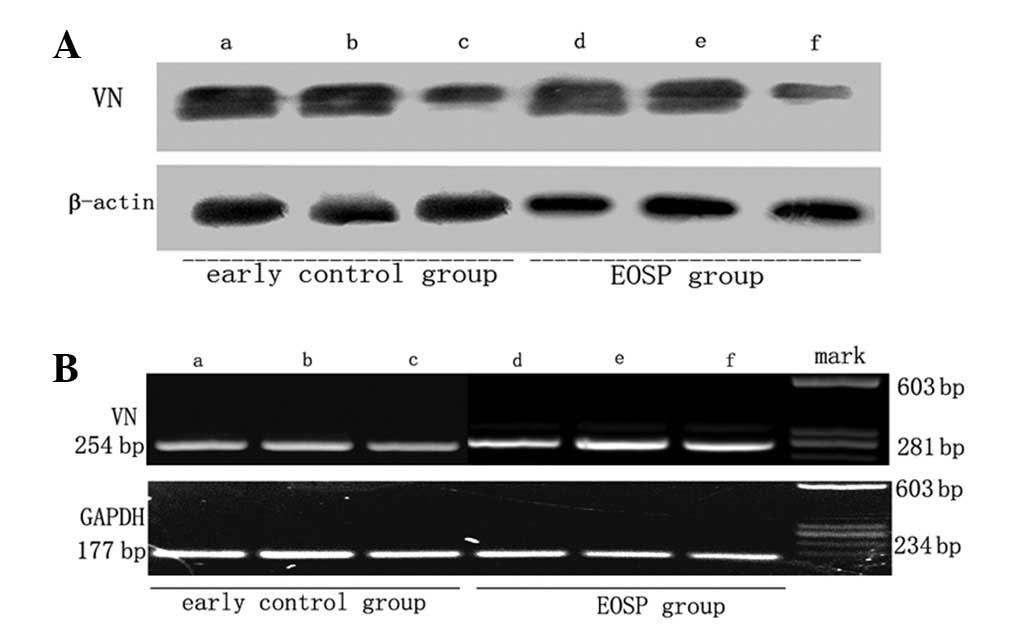
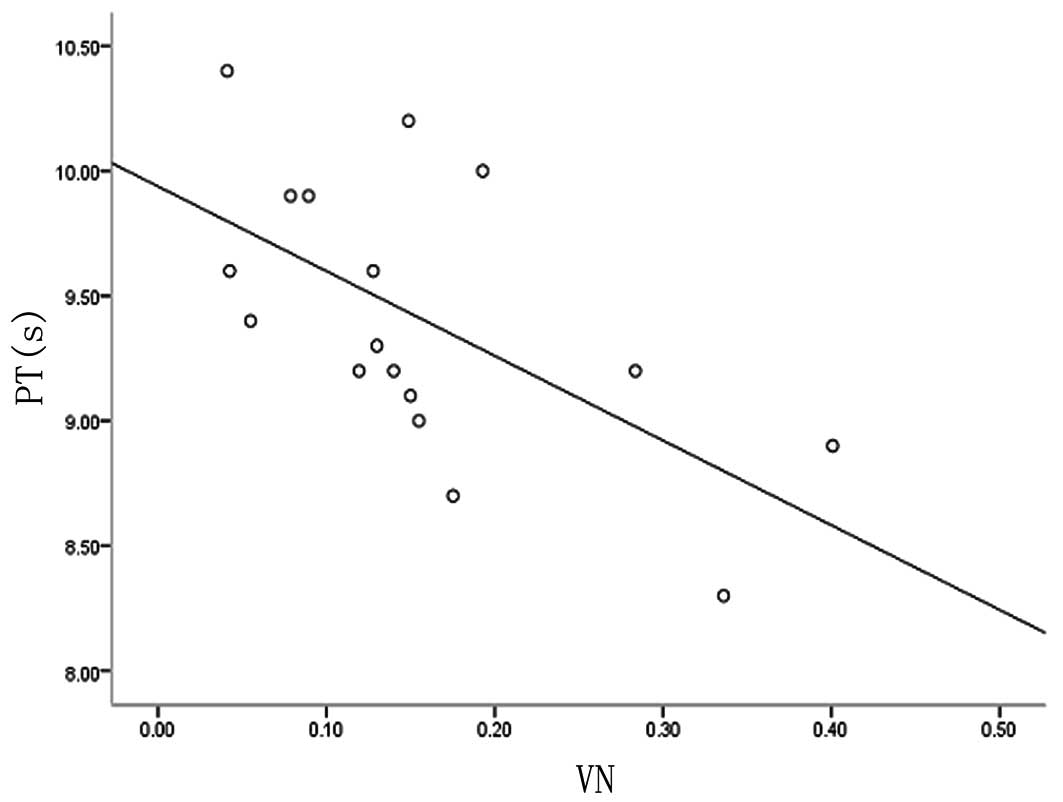
|
1
|
Marzioni D, Todros T, Cardaropoli S, et
al: Activating protein-1 family of transcription factors in the
human placenta complicated by preeclampsia with and without fetal
growth restriction. Placenta. 31:919–927. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lindheimer MD, Taler SJ and Cunningham FG:
Hypertension in pregnancy. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2:484–494. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
World Health Organization (WHO). Attending
to 136 million births, every year. The World Health Report 2005:
Make Every Mother and Child Count. 1st edition. WHO Press; Geneva,
Switzerland: pp. 642005
|
|
4
|
Blumenstein M, Prakash R, Cooper GJ and
North RA: Aberrant processing of plasma vitronectin and
high-molecular-weight kininogen precedes the onset of preeclampsia.
Reprod Sci. 16:1144–1152. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chanprapaph P: Update in pre-eclampsia. J
Med Assoc Thai. 87(Suppl 3): S104–S112. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Alanis MC, Robinson CJ, Hulsey TC, Ebeling
M and Johnson DD: Early-onset severe preeclampsia: induction of
labor vs elective cesarean delivery and neonatal outcomes. Am J
Obstet Gynecol. 199:262.e1–262.e6. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aris A, Benali S, Ouellet A, Moutquin JM
and Leblanc S: Potential biomarkers of preeclampsia: inverse
correlation between hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide early in
maternal circulation and at term in placenta of women with
preeclampsia. Placenta. 30:342–347. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang AG, Yen MY, Hsu WM and Fann MJ:
Induction of vitronectin and integrin alphav in the retina after
optic nerve injury. Mol Vis. 12:76–84. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Singh B, Su YC and Riesbeck K: Vitronectin
in bacterial pathogenesis: a host protein used in complement escape
and cellular invasion. Mol Microbiol. 78:545–560. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lam C, Lim KH and Karumanchi SA:
Circulating angiogenic factors in the pathogenesis and prediction
of preeclampsia. Hypertension. 46:1077–1085. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Keeton M, Eguchi Y, Sawdey M, Ahn C and
Loskutoff DJ: Cellular localization of type 1 plasminogen activator
inhibitor messenger RNA and protein in murine renal tissue. Am J
Pathol. 142:59–70. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tedesco F, Radillo O, Candussi G, Nazzaro
A, Mollnes TE and Pecorari D: Immunohistochemical detection of
terminal complement complex and S protein in normal and
pre-eclamptic placentae. Clin Exp Immunol. 80:236–240. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rasul A, Yu B, Khan M, et al: Magnolol, a
natural compound, induces apoptosis of SGC-7901 human gastric
adenocarcinoma cells via the mitochondrial and PI3K/Akt signaling
pathways. Int J Oncol. 40:1153–1161. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rasul A, Yu B, Zhong L, Khan M, Yang H and
Ma T: Cytotoxic effect of evodiamine in SGC-7901 human gastric
adenocarcinoma cells via simultaneous induction of apoptosis and
autophagy. Oncol Rep. 27:1481–1487. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
James JL, Whitley GS and Cartwright JE:
Pre-eclampsia: fitting together the placental, immune and
cardiovascular pieces. J Pathol. 221:363–378. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Redman CW and Sargent IL: Latest advances
in understanding preeclampsia. Science. 308:1592–1594. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vedin JA, Wilhelmsson CE and Werkö L:
Comparative study of alprenolol and methyldopa in previously
untreated essential hypertension. Br Heart J. 35:1285–1292. 1973.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Egbor M, Ansari T, Morris N, Green CJ and
Sibbons PD: Morphometric placental villous and vascular
abnormalities in early- and late-onset pre-eclampsia with and
without fetal growth restriction. BJOG. 113:580–589. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meler E, Figueras F, Bennasar M, Gomez O,
Crispi F and Gratacos E: The prognostic role of uterine artery
Doppler investigation in patients with severe early-onset
preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 202:559.e1–559.e4.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ohkuchi A, Hirashima C, Matsubara S, et
al: Alterations in placental growth factor levels before and after
the onset of preeclampsia are more pronounced in women with early
onset severe preeclampsia. Hypertens Res. 30:151–159. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wikström AK, Nash P, Eriksson UJ and
Olovsson MH: Evidence of increased oxidative stress and a change in
the plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI)-1 to PAI-2 ratio in
early-onset but not late-onset preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
201:597.e1–597.e8. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kobayashi J, Yamada S and Kawasaki H:
Distribution of vitronectin in plasma and liver tissue:
relationship to chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 20:1412–1417.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aaboe M, Offersen BV, Christensen A and
Andreasen PA: Vitronectin in human breast carcinomas. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1638:72–82. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chauhan AK and Moore TL: Presence of
plasma complement regulatory proteins clusterin (Apo J) and
vitronectin (S40) on circulating immune complexes (CIC). Clin Exp
Immunol. 145:398–406. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li DQ, Lundberg F and Ljungh A: Binding of
vitronectin and clusterin by coagulase-negative staphylococci
interfering with complement function. J Mater Sci Mater Med.
12:979–982. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Preissner KT: Structure and biological
role of vitronectin. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 7:275–310. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|