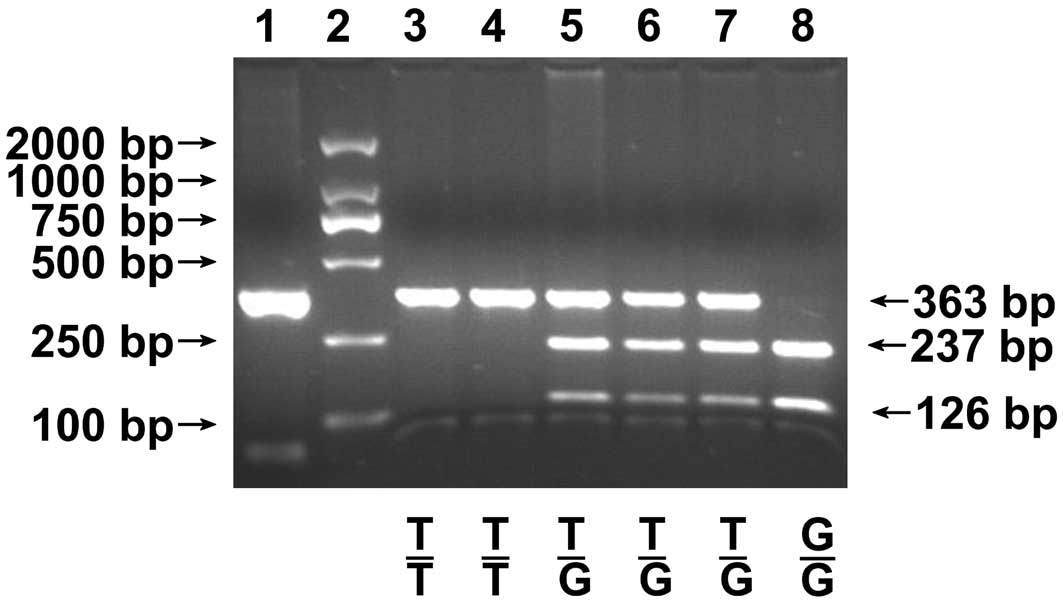
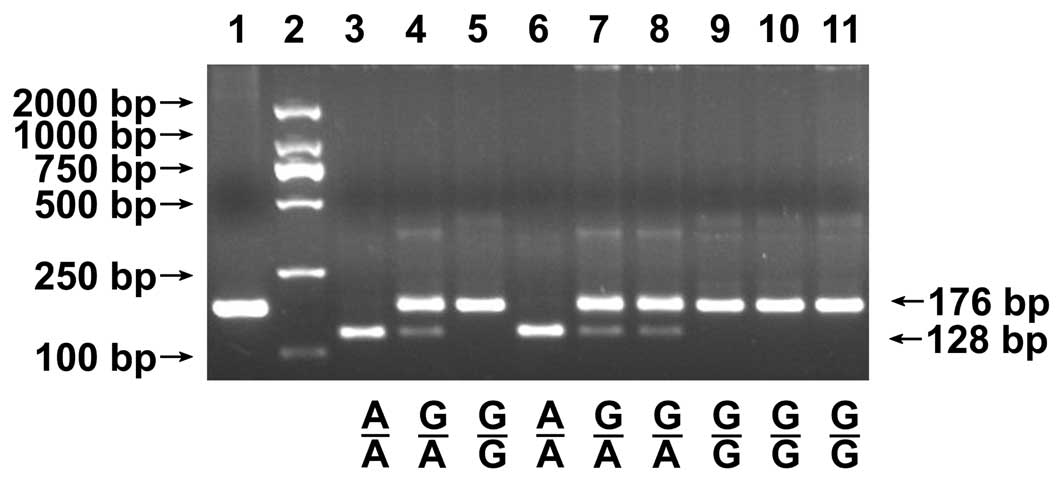
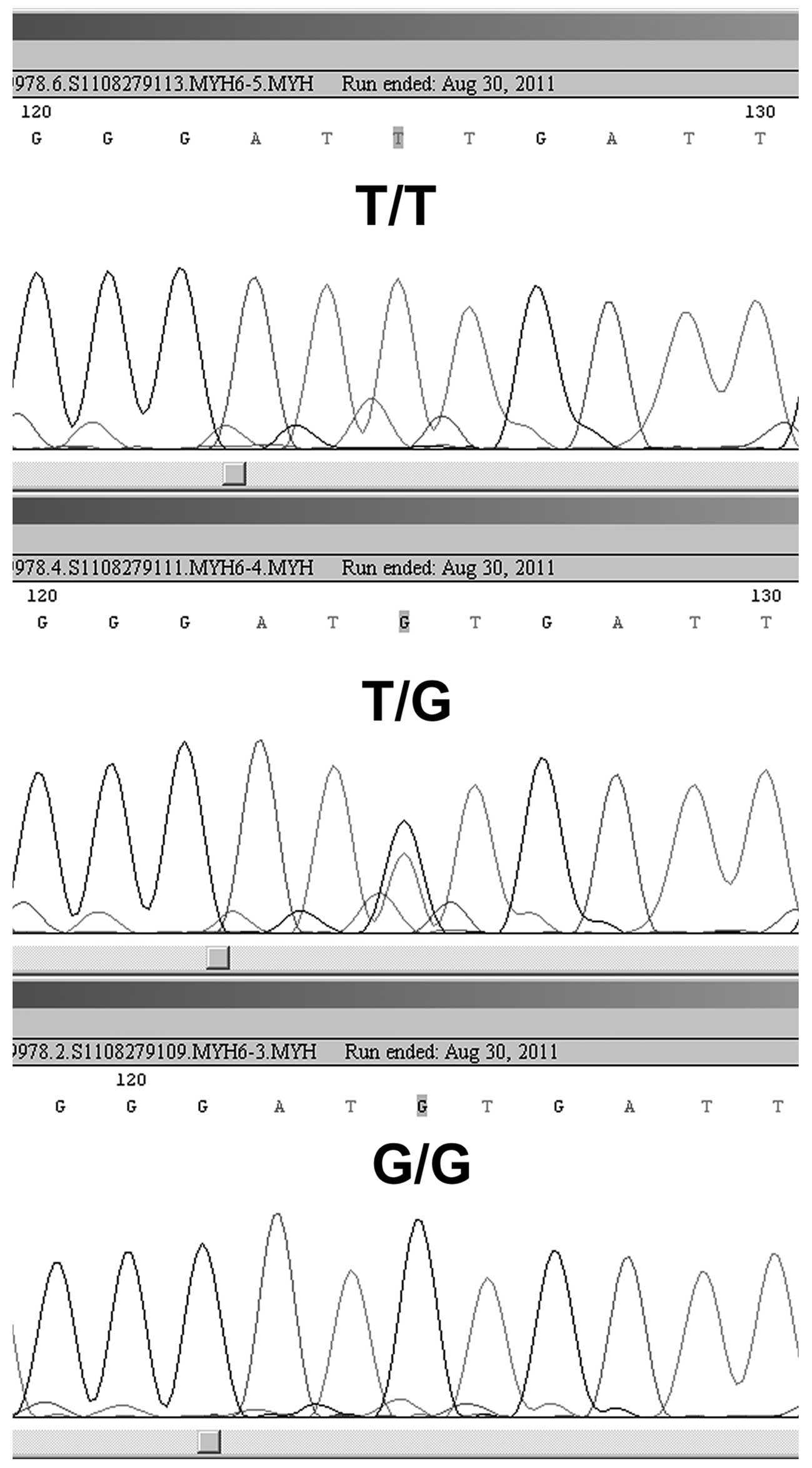
|
1
|
Isomoto H: Epigenetic alterations
associated with cholangiocarcinoma (Review). Oncol Rep. 22:227–232.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Petrowsky H and Hong JC: Current surgical
management of hilar and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: the role
of resection and orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplant Proc.
41:4023–4035. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Valle J, Wasan H, Palmer DH, et al:
Cisplatin plus gemcitabine versus gemcitabine for biliary tract
cancer. N Engl J Med. 362:1273–1281. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gatto M, Bragazzi MC, Semeraro R, et al:
Cholangiocarcinoma: update and future perspectives. Dig Liver Dis.
42:253–260. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shen FZ, Zhang BY, Feng YJ, et al: Current
research in perineural invasion of cholangiocarcinoma. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 29:242010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meza-Junco J, Montano-Loza AJ, Ma M, Wong
W, Sawyer MB and Bain VG: Cholangiocarcinoma: has there been any
progress? Can J Gastroenterol. 24:52–57. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ustundag Y and Bayraktar Y:
Cholangiocarcinoma: a compact review of the literature. World J
Gastroenterol. 14:6458–6466. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shields PG and Harris CC: Cancer risk and
low-penetrance susceptibility genes in gene-environment
interactions. J Clin Oncol. 18:2309–2315. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Galvan A, Ioannidis JP and Dragani TA:
Beyond genome-wide association studies: genetic heterogeneity and
individual predisposition to cancer. Trends Genet. 26:132–141.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Martin SA, Hewish M, Lord CJ and Ashworth
A: Genomic instability and the selection of treatments for cancer.
J Pathol. 220:281–289. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jiang J, Zhang X, Yang H and Wang W:
Polymorphisms of DNA repair genes: ADPRT, XRCC1, and XPD and cancer
risk in genetic epidemiology. Methods Mol Biol. 471:305–333. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
David SS, O’Shea VL and Kundu S:
Base-excision repair of oxidative DNA damage. Nature. 447:941–950.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kasahara M, Osawa K, Yoshida K, et al:
Association of MUTYH Gln324His and APEX1 Asp148Glu with colorectal
cancer and smoking in a Japanese population. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
27:492008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Baudhuin LM, Roberts LR, Enders FT, et al:
MYH Y165C and G382D mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma and
cholangiocarcinoma patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 132:159–162.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang X, You SH, He W, et al: hOGG1
Ser326Cys polymorphisms and genetic susceptibility of
cholangiocarcinomas. Journal of Medical Postgraduates.
23:1156–1159. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
You SH, Wang X, Huang S, Gao Y, Xia JR and
Fan ZN: XRCC1 polymorphisms and genetic susceptibility of
cholangiocarcinomas. Chinese Journal of Clinical Research.
23:1068–1072. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Tsukino H, Hanaoka T, Otani T, et al:
hOGG1 Ser326Cys polymorphism, interaction with environmental
exposures, and gastric cancer risk in Japanese populations. Cancer
Sci. 95:977–983. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jones S, Emmerson P, Maynard J, et al:
Biallelic germline mutations in MYH predispose to multiple
colorectal adenoma and somatic G:C->T:A mutations. Hum Mol
Genet. 11:2961–2967. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thyagarajan B, Lindgren B, Basu S, et al:
Association between genetic variants in the base excision repair
pathway and outcomes after hematopoietic cell transplantations.
Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 16:1084–1089. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Van Beers BE: Diagnosis of
cholangiocarcinoma. HPB (Oxford). 10:87–93. 2008.
|
|
21
|
Sieber OM, Lipton L, Crabtree M, et al:
Multiple colorectal adenomas, classic adenomatous polyposis, and
germ-line mutations in MYH. N Engl J Med. 348:791–799. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Forsbring M, Vik ES, Dalhus B, et al:
Catalytically impaired hMYH and NEIL1 mutant proteins identified in
patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis and
cholangiocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 30:1147–1154. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang L, Zhou M, Zhu M, et al: Variation
analysis of the MYH gene associated with sporadic colorectal
cancer. Carcinogenesis, Teratogenesis and Mutagenesis. 21:435–438.
2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Yang L, Zhu M, Chen SQ, et al: Research on
MUTYH gene polymorphism associated with colorectal cancer. Shandong
Medical Journal. 49:3–5. 2009.(In Chinese).
|