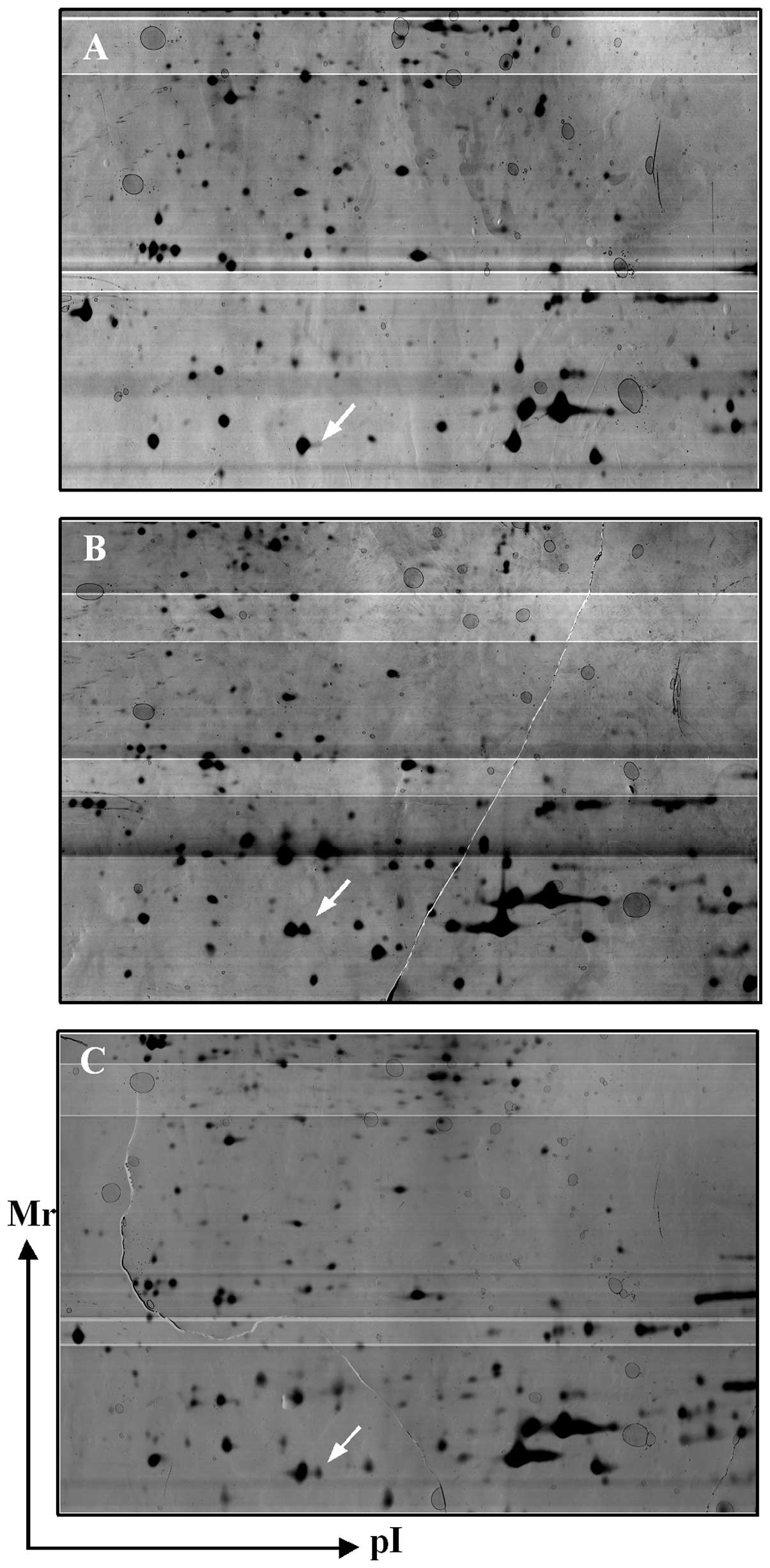
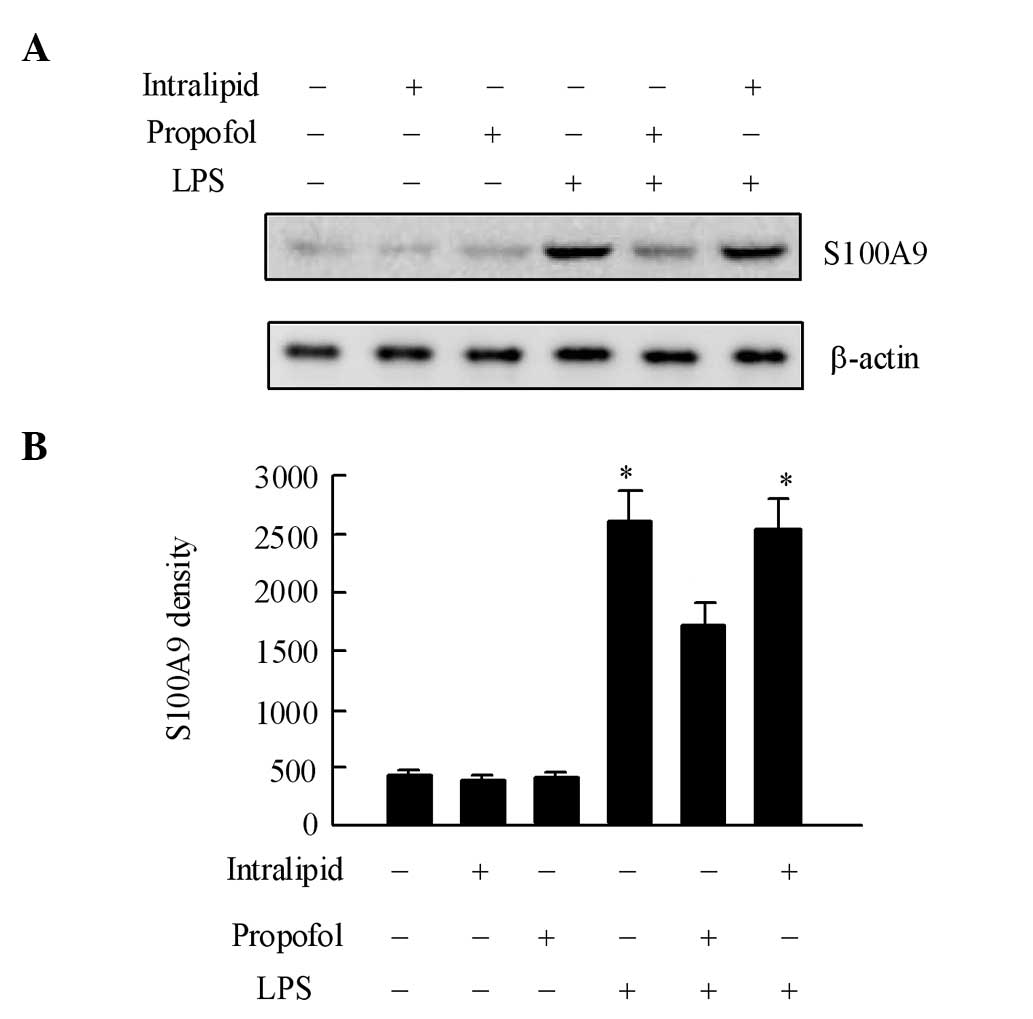
|
1
|
Brunkhorst FM and Reinhart K: Diagnosis
and causal treatment of sepsis. Internist (Berl). 50:810–816. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sharma S and Kumar A: Septic shock,
multiple organ failure, and acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Curr Opin Pulm Med. 9:199–209. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schneider J and Muleta M: Septic shock.
Ethiop Med J. 41:89–104. 2003.
|
|
4
|
Tabbutt S: Heart failure in pediatric
septic shock: utilizing inotropic support. Crit Care Med. 29(Suppl
10): S231–S236. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Heine H, Rietschel ET and Ulmer AJ: The
biology of endotoxin. Mol Biotechnol. 19:279–296. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Leslie DB, Vietzen PS, Lazaron V, et al:
Comparison of endotoxin antagonism of linear and cyclized peptides
derived from limulus anti-lipopolysaccharide factor. Surg Infect
(Larchmt). 7:45–52. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu JF, Ma J, Chen J, et al: Changes of
monocyte human leukocyte antigen-DR expression as a reliable
predictor of mortality in severe sepsis. Crit Care. 15:R2202011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Monneret G, Lepape A, Voirin N, et al:
Persisting low monocyte human leukocyte antigen-DR expression
predicts mortality in septic shock. Intensive Care Med.
32:1175–1183. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sztark F and Lagneau F: Agents for
sedation and analgesia in the intensive care unit. Ann Fr Anesth
Reanim. 27:560–566. 2008.(In French).
|
|
10
|
Lee CJ, Subeq YM, Lee RP, et al: Low-dose
propofol ameliorates haemorrhagic shock-induced organ damage in
conscious rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 35:766–774. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chu CH, David LD, Hsu YH, et al: Propofol
exerts protective effects on the acute lung injury induced by
endotoxin in rats. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 20:503–512. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tsao CM, Ho ST, Chen A, et al: Propofol
ameliorates liver dysfunction and inhibits aortic superoxide level
in conscious rats with endotoxic shock. Eur J Pharmacol.
477:183–193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang J, Sun Y, Wu WK, et al: Propofol
lowers serum PF4 level and partially corrects hypercoagulopathy in
endotoxemic rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1804:1895–1901. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zimmermann M: Ethical guidelines for
investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain.
16:109–110. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Simard JC, Girard D and Tessier PA:
Induction of neutrophil degranulation by S100A9 via a
MAPK-dependent mechanism. J Leukoc Biol. 87:905–914. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hessian PA, Edgeworth J and Hogg N: MRP-8
and MRP-14, two abundant Ca(2+)-binding proteins of neutrophils and
monocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 53:197–204. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chi ZL, Hayasaka Y, Zhang XY, et al:
S100A9-positive granulocytes and monocytes in
lipopolysaccharide-induced anterior ocular inflammation. Exp Eye
Res. 84:254–265. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shibata F, Miyama K, Shinoda F, et al:
Fibroblast growth-stimulating activity of S100A9 (MRP-14). Eur J
Biochem. 271:2137–2143. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gebhardt C, Nemeth J, Angel P, et al:
S100A8 and S100A9 in inflammation and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol.
72:1622–1631. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yin LM, Jiang GH, Wang Y, et al: Use of
serial analysis of gene expression to reveal the specific
regulation of gene expression profile in asthmatic rats treated by
acupuncture. J Biomed Sci. 16:462009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Manitz MP, Horst B, Seeliger S, et al:
Loss of S100A9 (MRP14) results in reduced interleukin-8-induced
CD11b surface expression, a polarized microfilament system, and
diminished responsiveness to chemoattractants in vitro. Mol Cell
Biol. 23:1034–1043. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schnekenburger J, Schick V, Kruger B, et
al: The calcium binding protein S100A9 is essential for pancreatic
leukocyte infiltration and induces disruption of cell-cell
contacts. J Cell Physiol. 216:558–567. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang YH, Toh ML, Clyne CD, et al: Annexin
1 negatively regulates IL-6 expression via effects on p38 MAPK and
MAPK phosphatase-1. J Immunol. 177:8148–8153. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kaminska B: MAPK signalling pathways as
molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy--from molecular
mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1754:253–262. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pouliot P, Plante I, Raquil MA, et al:
Myeloid-related proteins rapidly modulate macrophage nitric oxide
production during innate immune response. J Immunol. 181:3595–3601.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hiratsuka S, Watanabe A, Aburatani H, et
al: Tumour-mediated upregulation of chemoattractants and
recruitment of myeloid cells predetermines lung metastasis. Nat
Cell Biol. 8:1369–1375. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tang J, Chen X, Tu W, et al: Propofol
inhibits the activation of p38 through up-regulating the expression
of annexin A1 to exert its anti-inflammation effect. PLoS One.
6:e278902011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
El-Rifai W, Moskaluk CA, Abdrabbo MK, et
al: Gastric cancers overexpress S100A calcium-binding proteins.
Cancer Res. 62:6823–6826. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Stulik J, Osterreicher J, Koupilova K, et
al: The analysis of S100A9 and S100A8 expression in matched sets of
macroscopically normal colon mucosa and colorectal carcinoma: the
S100A9 and S100A8 positive cells underlie and invade tumor mass.
Electrophoresis. 20:1047–1054. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tsuchiya M, Asada A, Arita K, et al:
Induction and mechanism of apoptotic cell death by propofol in
HL-60 cells. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 46:1068–1074. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|