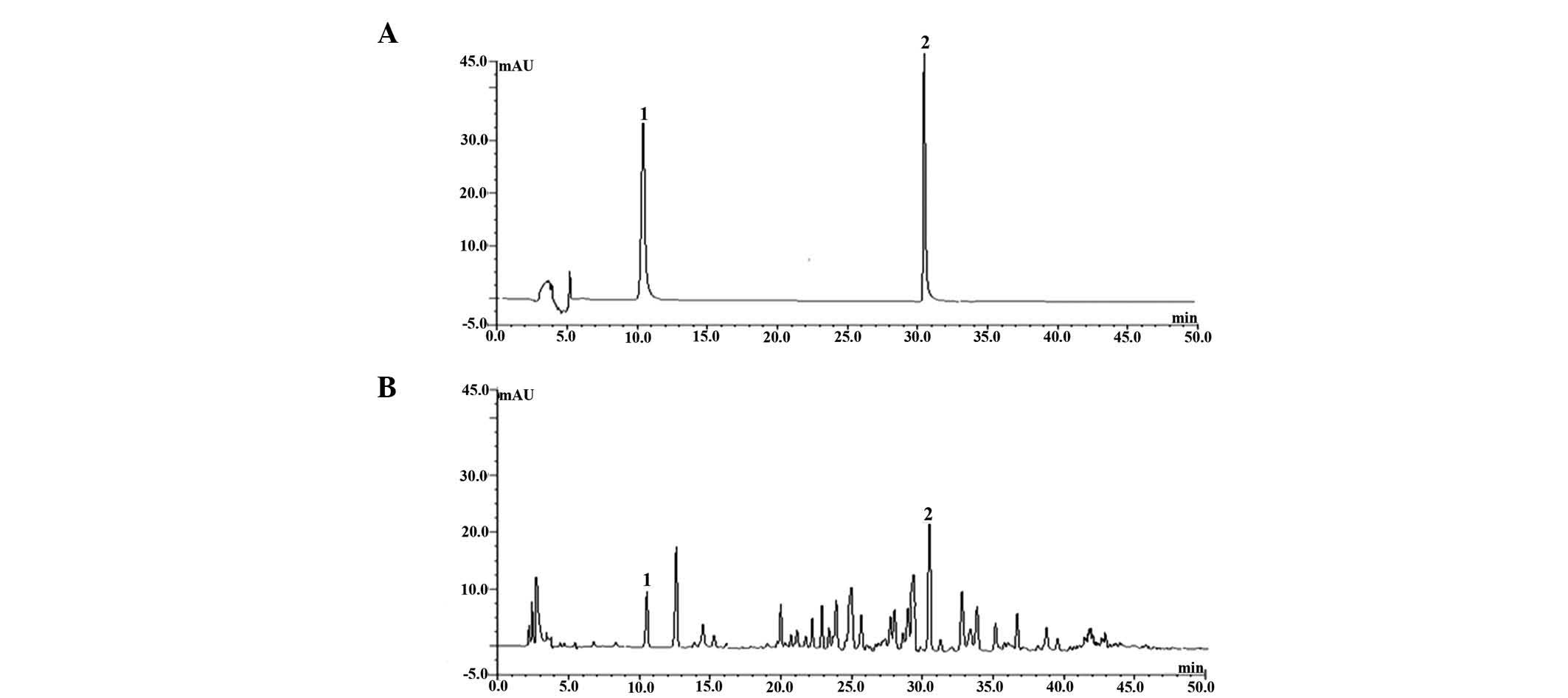
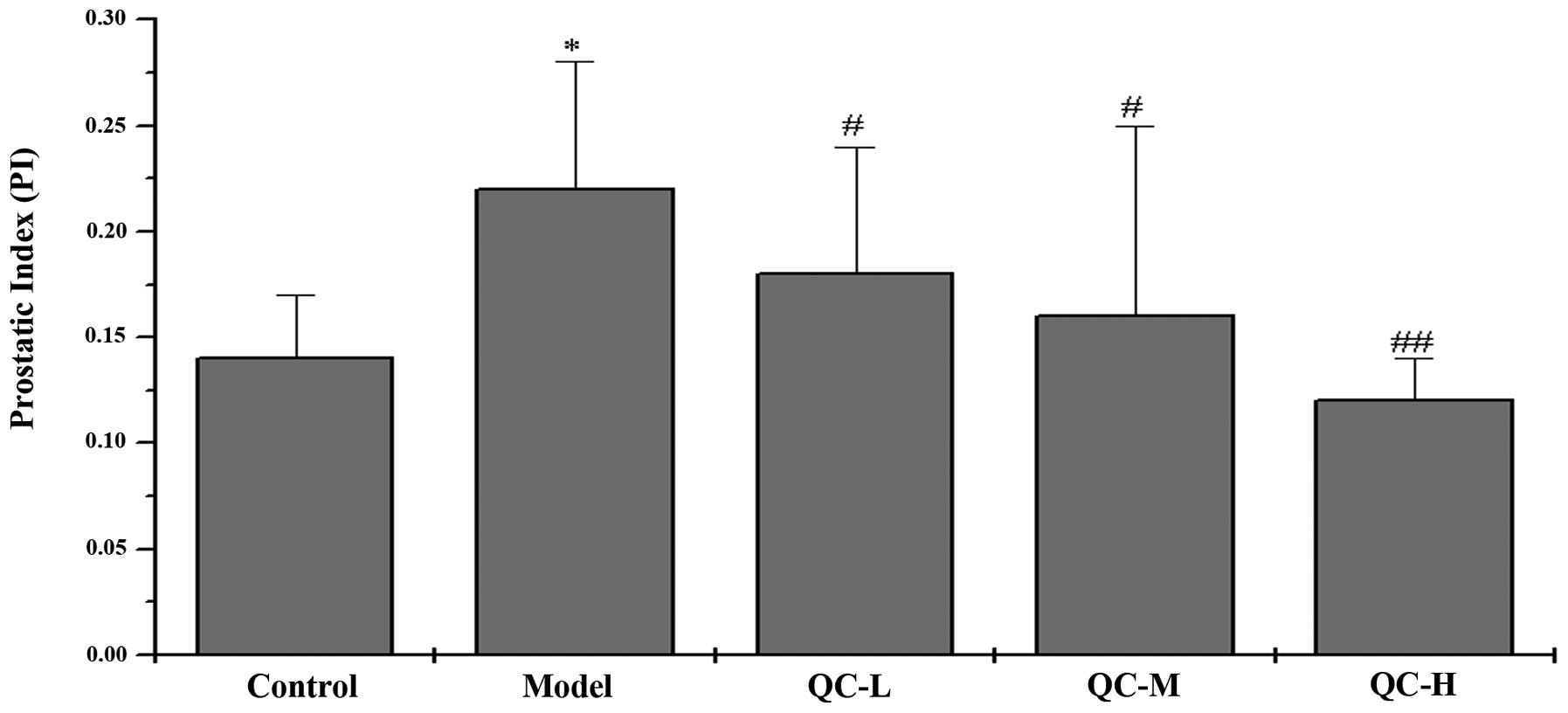
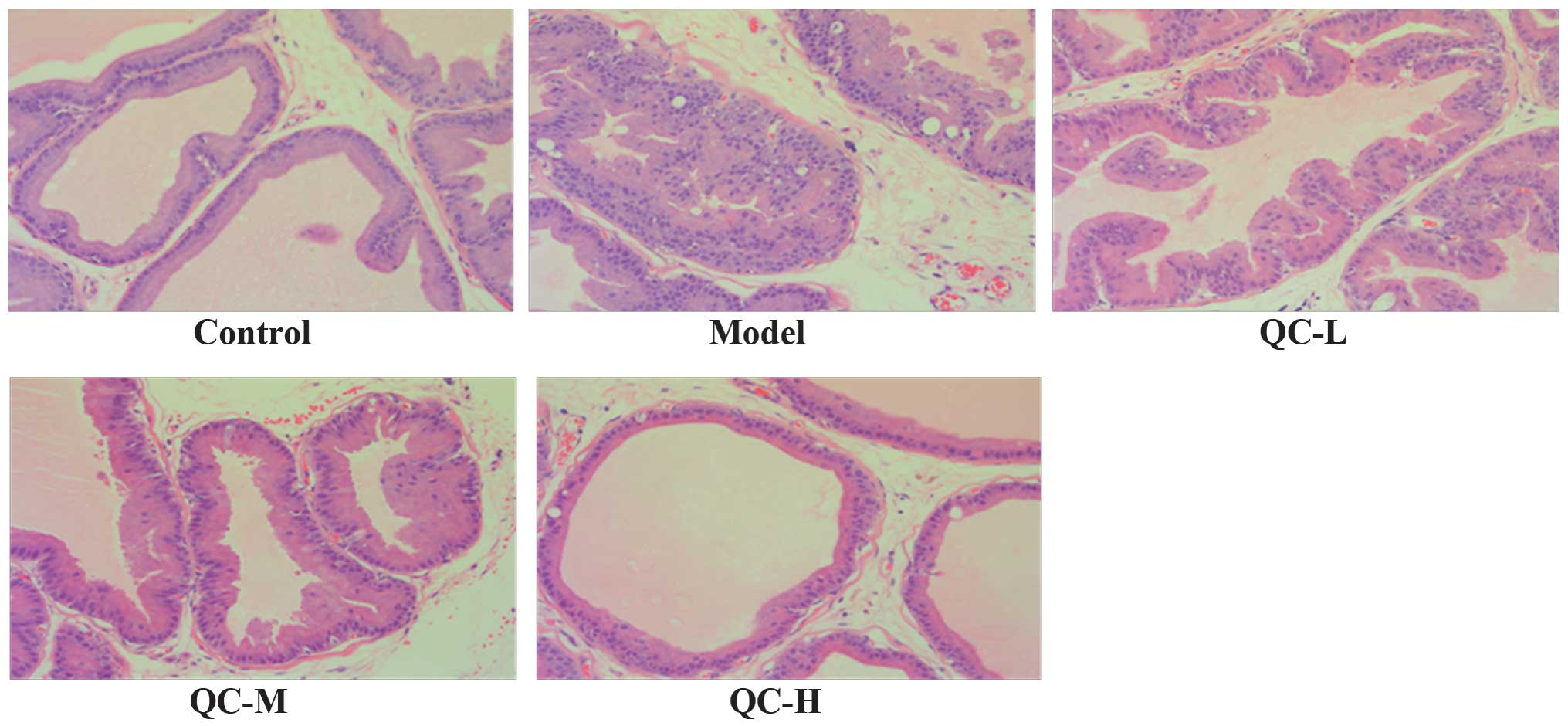
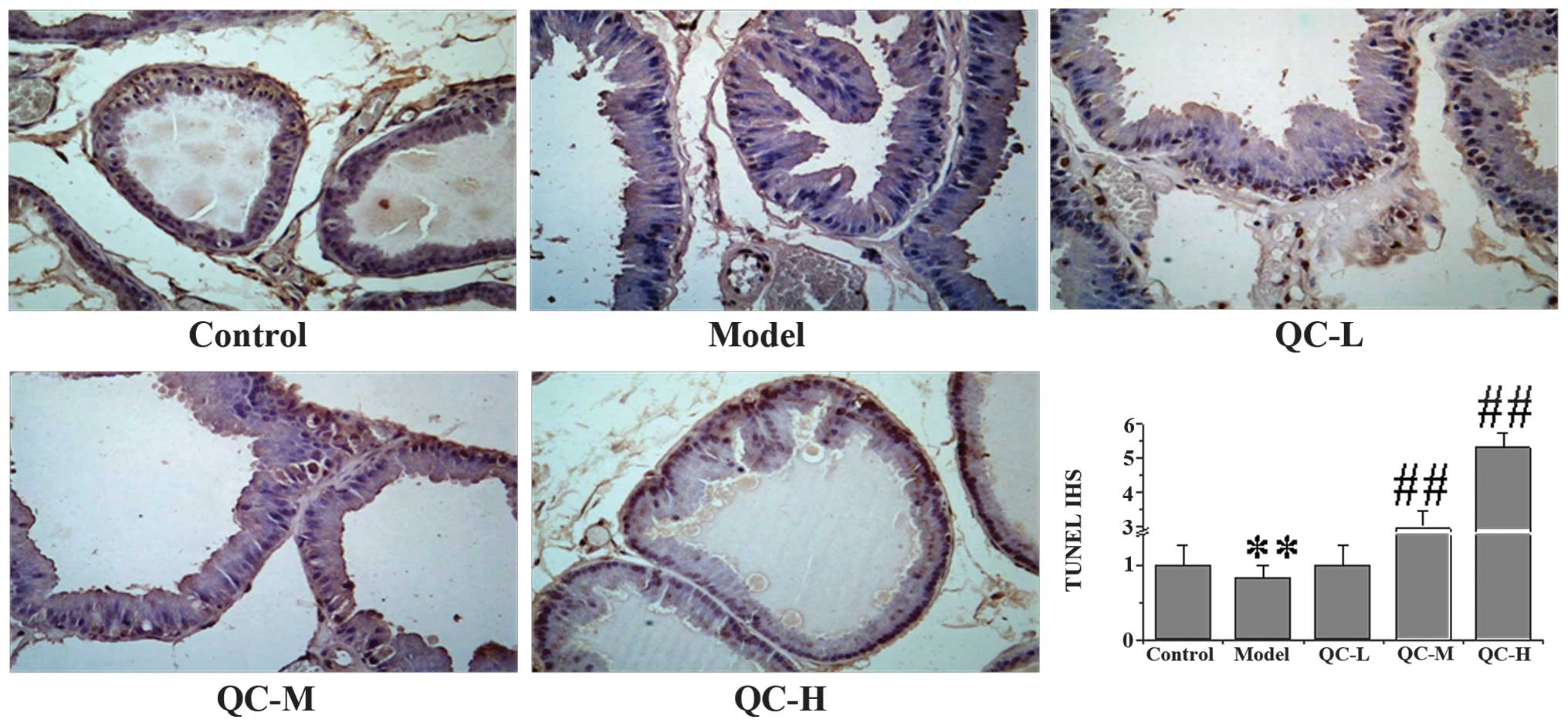
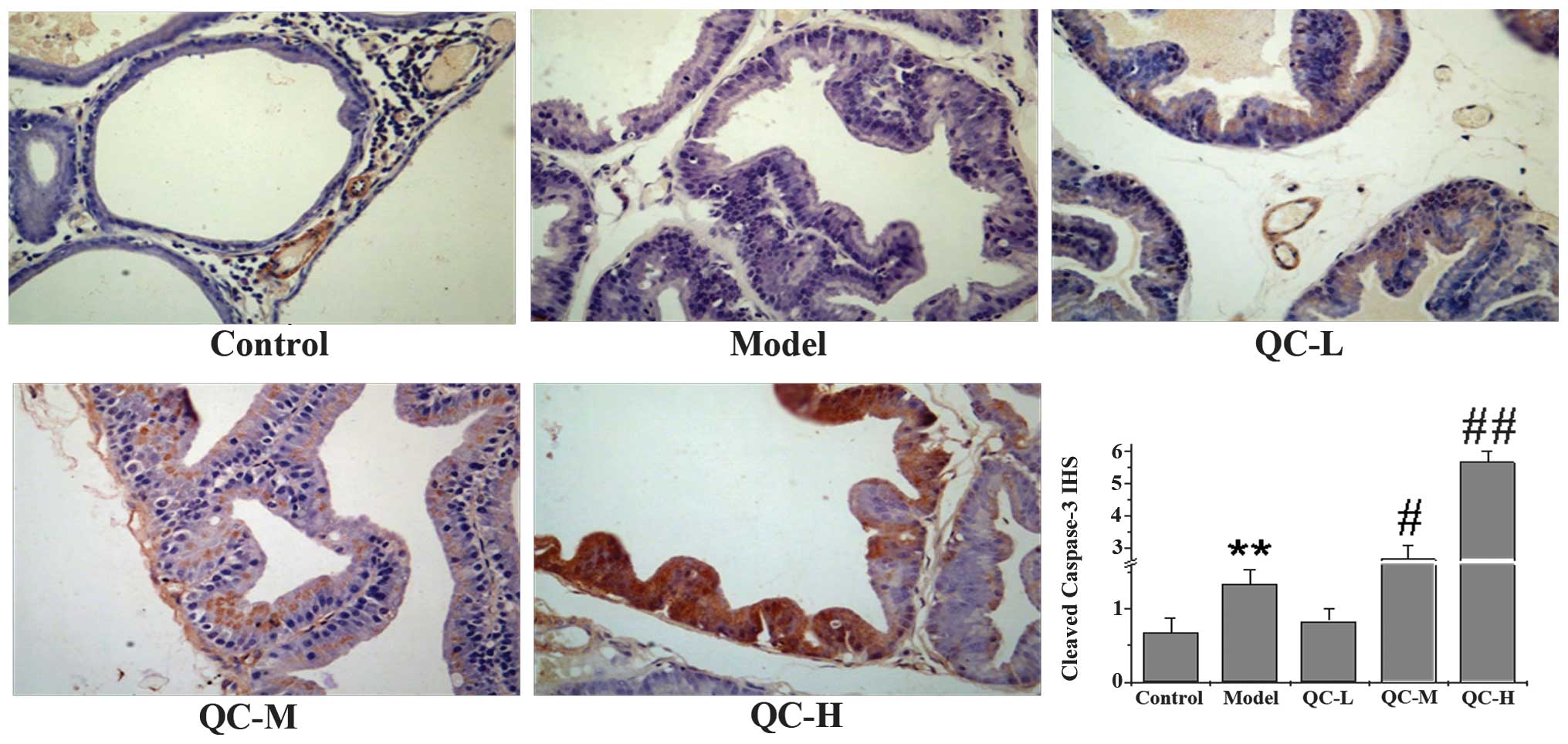
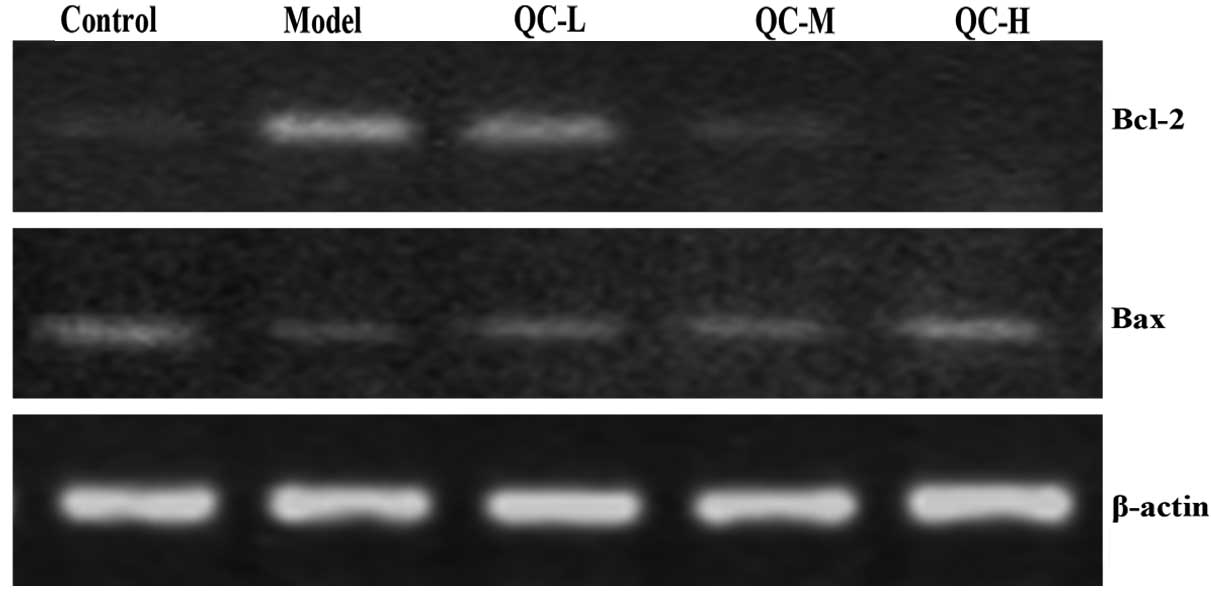
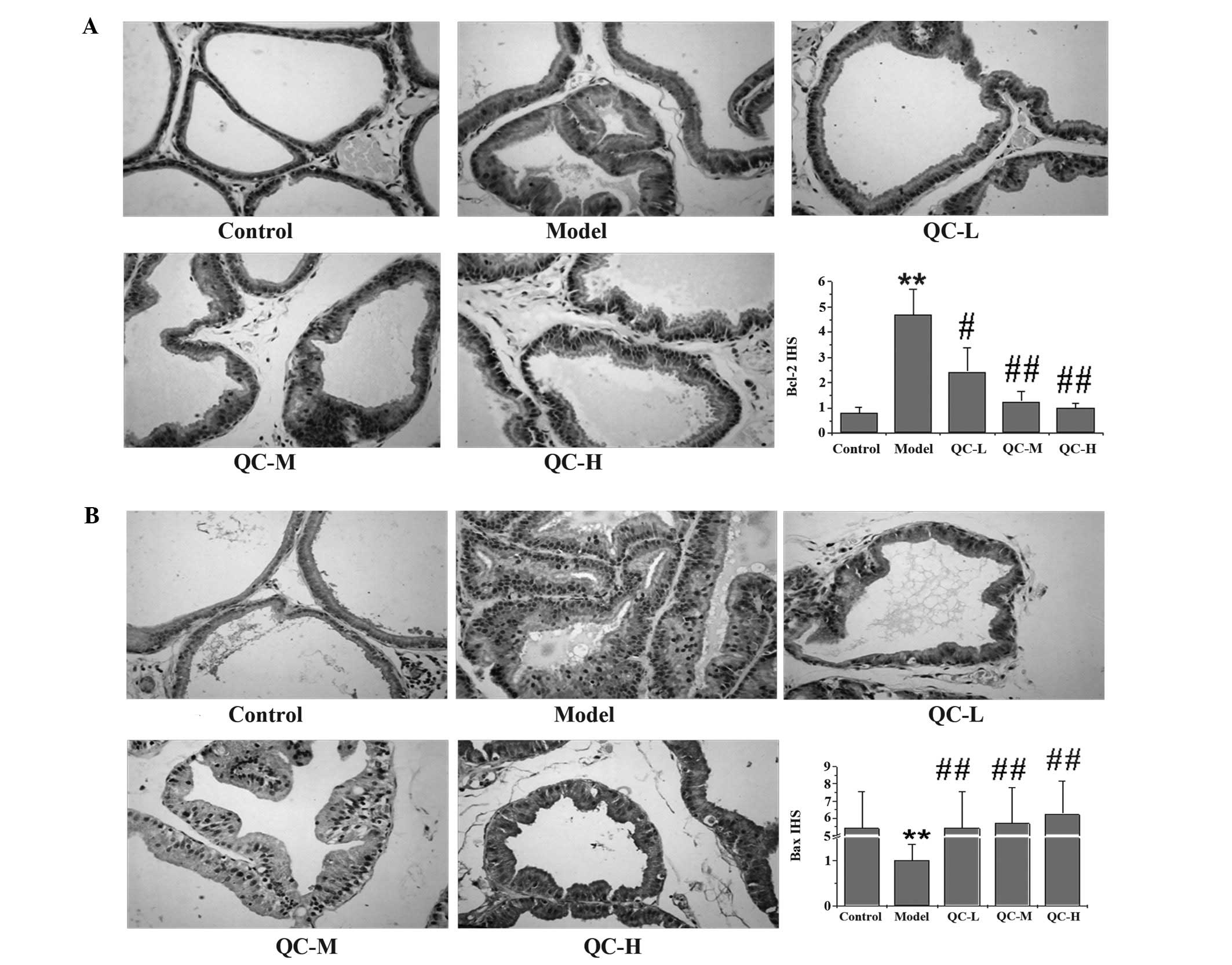
|
1
|
Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC and Ewing
LL: The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age.
J Urol. 132:474–479. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Djavan B: Lower urinary tract
symptoms/benign prostatic hyperplasia: fast control of the
patient's quality of life. Urology. 62:6–14. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang MD, Zhao YN and An LW: B-cell
lymphoma/leukemia-2 and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Zhonghua Nan
Ke Xue. 15:452–454. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
4
|
Kyprianou N, Tu H and Jacobs SC: Apoptotic
versus proliferative activities in human benign prostatic
hyperplasia. Hum Pathol. 27:668–675. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Claus S, Berges R, Senge T and Schulze H:
Cell kinetic in epithelium and stroma of benign prostatic
hyperplasia. J Urol. 158:217–221. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Roehrborn CG: Pathology of benign
prostatic hyperplasia. Int J Impot Res. 20:S11–S18. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev.
13:1899–1911. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Reed JC: Mechanisms of apoptosis. Am J
Pathol. 157:1415–1430. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 apoptotic
switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene. 26:1324–1337.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mäntymaa P, Siitonen T, Guttorm T, Säily
M, Kinnula V, Savolainen ER and Koistinen P: Induction of
mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase confers resistance to
apoptosis in acute myeloblastic leukaemia cells exposed to
etoposide. Br J Haematol. 108:574–581. 2000.
|
|
11
|
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, et al: Prevention
of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria
blocked. Science. 275:1129–1132. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR and
Newmeyer DD: The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a
primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science.
275:1132–1136. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jürgensmeier JM, Xie Z, Deveraux Q,
Ellerby L, Bredesen D and Reed JC: Bax directly induces release of
cytochrome c from isolated mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:4997–5002. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Antonsson B, Montessuit S, Lauper S, Eskes
R and Martinou JC: Bax oligomerization is required for
channel-forming activity in liposomes and to trigger cytochrome c
release from mitochondria. Biochem J. 345:271–278. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hsu YT, Wolter K and Youle RJ:
Cytosol-to-membrane redistribution of Bax and Bcl-X(L) during
apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:3668–3672. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wolter KG, Hsu YT, Smith CL, Nechushtan A,
Xi XG and Youle RJ: Movement of Bax from the cytosol to
mitochondria during apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 139:1281–1292. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wei MC, Lindsten T, Mootha VK, et al:
tBid, a membrane-targeted death ligand, oligomerizes Bak to release
cytochrome c. Genes Dev. 14:2060–2071. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thomenius MJ, Wang NS, Reineks EZ, Wang Z
and Distelhorst CW: Bcl-2 on the endoplasmic reticulum regulates
Bax activity by binding to BH3-only proteins. J Biol Chem.
278:6243–6250. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Antonsson B, Conti F, Ciavatta A, et al:
Inhibition of Bax channel-forming activity by Bcl-2. Science.
277:370–372. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Roehrborn CG, Nuckolls JG, Wei JT and
Steers W: BPH Registry and Patient Survey Steering Committee. The
benign prostatic hyperplasia registry and patient survey: study
design, methods and patient baseline characteristics. BJU Int.
100:813–819. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Black L, Naslund MJ, Gilbert TD Jr, Davis
EA and Ollendorf DA: An examination of treatment patterns and costs
of care among patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Am J
Manag Care. 12:S99–S110. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
MacDonald R and Wilt TJ: Alfuzosin for
treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms compatible with benign
prostatic hyperplasia: A systematic review of efficacy and adverse
effects. Urology. 66:780–788. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Roehrborn CG: Efficacy and safety of
once-daily alfuzosin in the treatment of lower urinary tract
symptoms and clinical benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized,
placebo-controlled trial. Urology. 58:953–959. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Djavan B and Marberger M: A meta-analysis
on the efficacy and tolerability of alpha1-adrenoceptor antagonists
in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign
prostatic obstruction. Eur Urol. 36:1–13. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gormley GJ, Stoner E, Bruskewitz RC, et
al: The effect of finasteride in men with benign prostatic
hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 327:1185–1191. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Roehrborn CG, Boyle P, Nickel JC, et al:
Efficacy and safety of a dual inhibitor of 5-alpha-reductase types
1 and 2 (dutasteride) in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Urology. 60:434–441. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou JH, Lin JM, Xu W, Zhong XY, Xie JD
and Hong ZF: Effects of Qianliening capsule on the expression of
IL-10 and TNF-α in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Chin Archives Trad
Chin Med. 28:2657–2569. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou JH, Hong ZF, Lin JM, Zhao JY and Zhou
HT: Effect of Qianliening granule on experimental hyperplasia of
prostate. J Fujian Univ Trad Chin Med. 18:45–47. 2008.
|
|
30
|
Lin JM, Zhou JH, Zhong XY, et al: Effects
of Qianliening capsule on the expression of EGF and EGFR in BPH
Rats. Fujian J Trad Chin Med. 41:45–47. 2010.
|
|
31
|
Zhou HT, Lin JM, Zhao JY, Zhou JH and Hong
ZF: Inhibition effects of Qianliening granule on IL-1β and its mRNA
expression in model rats. J Fujian Univ Trad Chin Med. 20:21–24.
2010.
|
|
32
|
Huang W, Li M, Lin ZZ, Li ZM, Lai XP and
Su ZR: HPLC determination of emodin and oleanolic acid in
Yigankangfuling capsules. Chin J Pharm Anal. 28:1728–1731.
2008.
|
|
33
|
Soslow RA, Dannenberg AJ, Rush D, Woerner
BM, Khan KN, Masferrer J and Koki AT: Cox-2 is expressed in human
pulmonary, colonic, and mammary tumors. Cancer. 89:2637–2645. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|