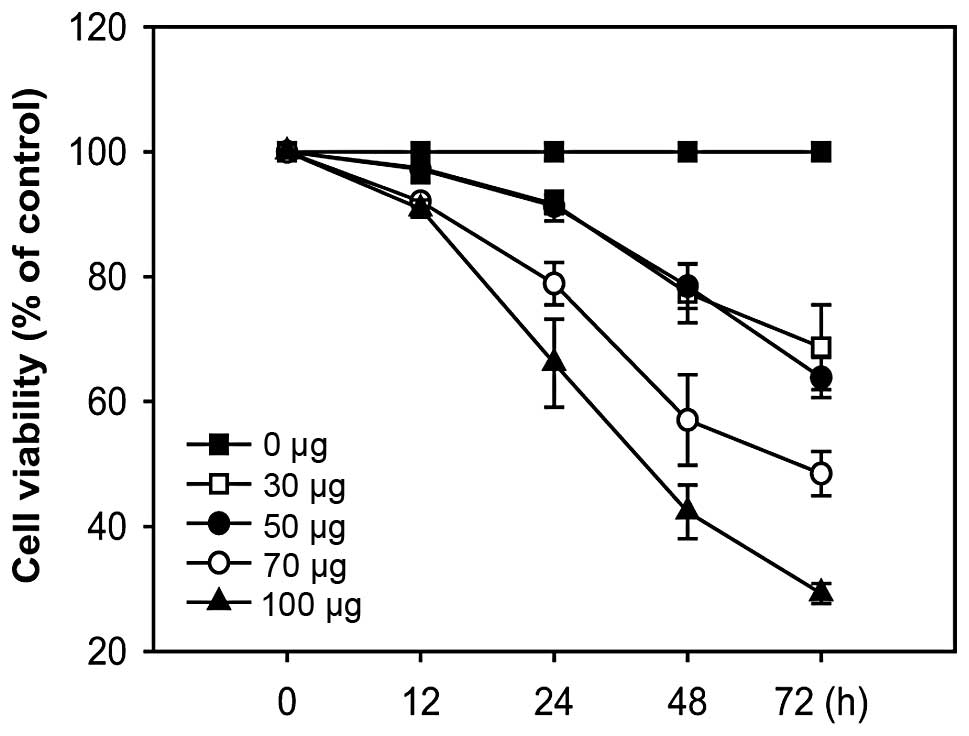
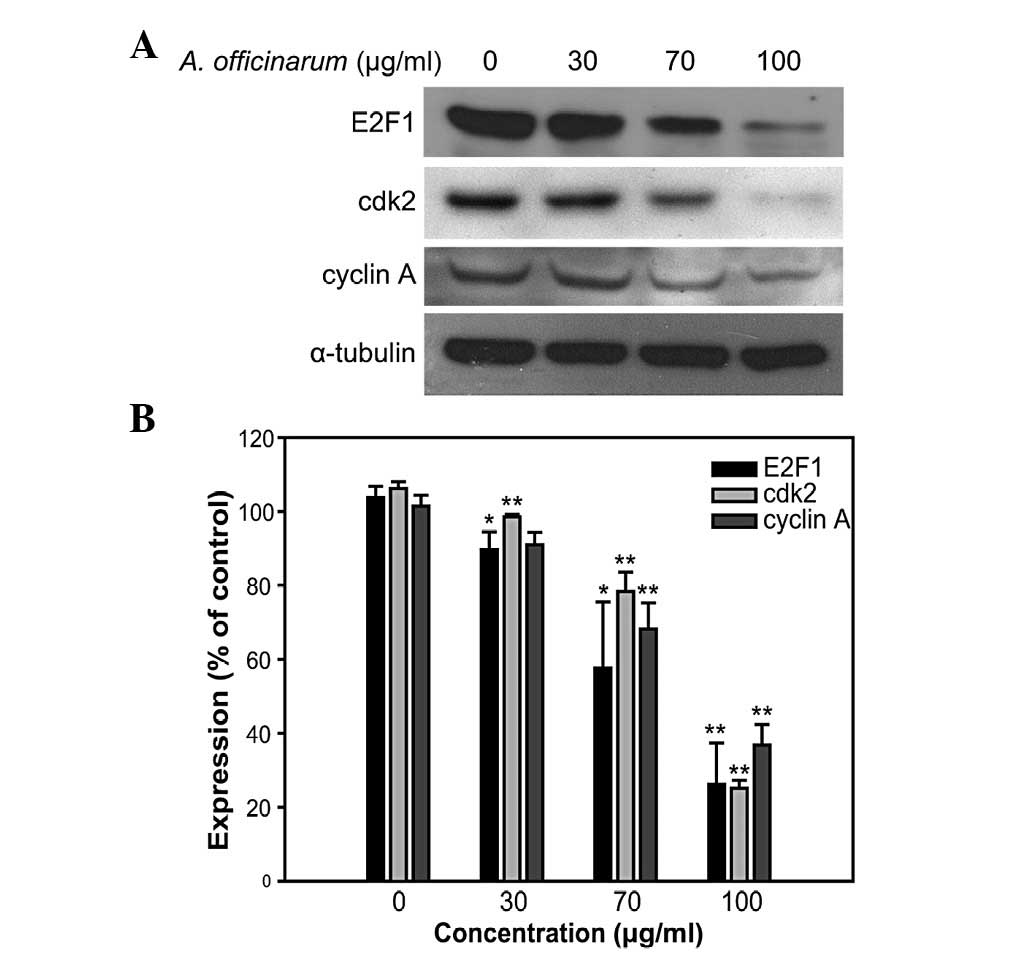
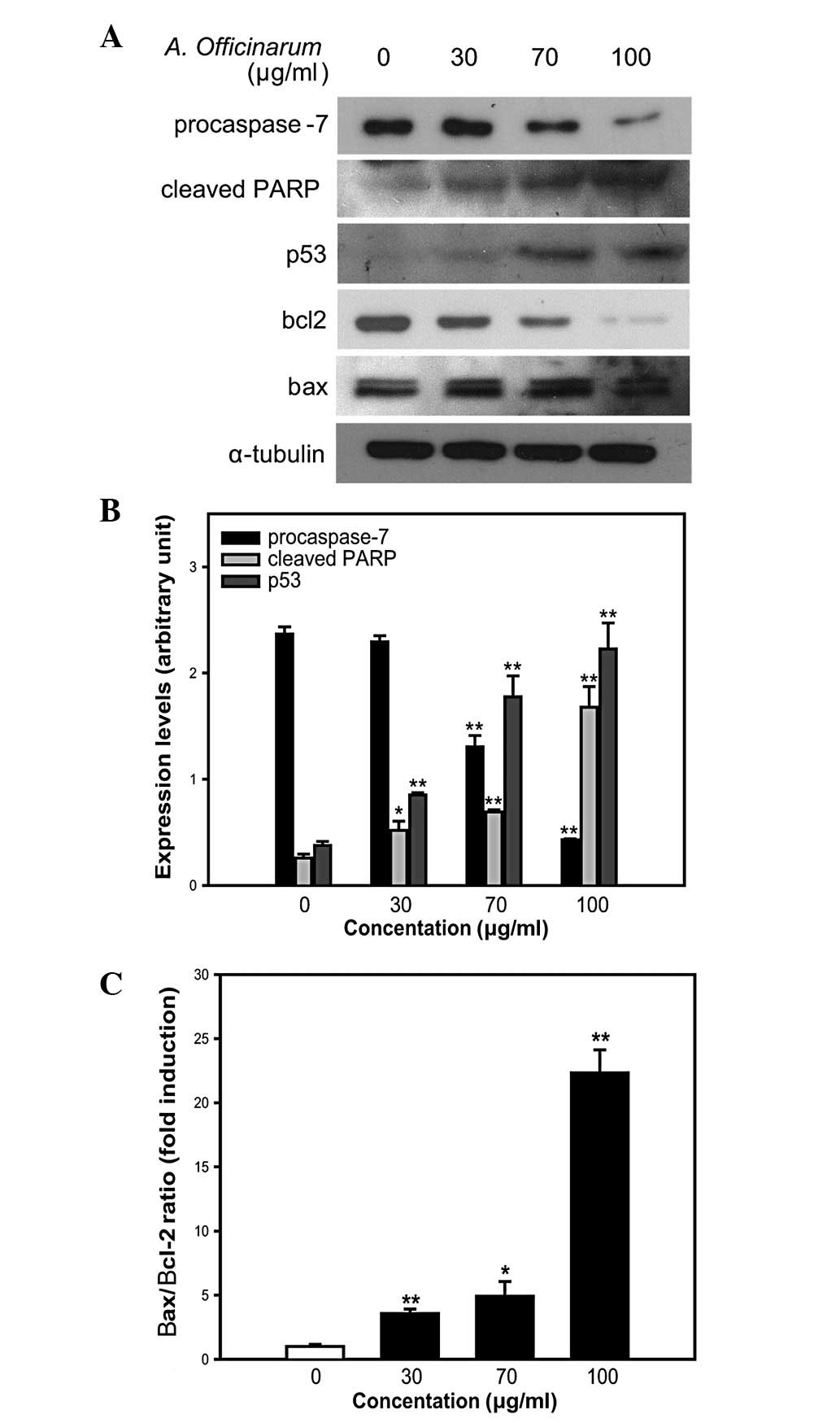
|
1
|
DeSantis C, Siegel R, Bandi P and Jemal A:
Breast cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:409–418. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tsavaris N, Kosmas C, Vadiaka M,
Kanelopoulos P and Boulamatsis D: Immune changes in patients with
advanced breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy with taxanes. Br J
Cancer. 87:21–27. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jordan MA, Horwitz SB, Lobert S and
Correia JJ: Exploring the mechanisms of action of the novel
microtubule inhibitor vinflunine. Semin Oncol. 35:S6–S12. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Baldwin EL and Osheroff N: Etoposide,
topoisomerase II and cancer. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents.
5:363–372. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
An N, Zou ZM, Tian Z, Luo XZ, Yang SL and
Xu LZ: Diarylheptanoids from the rhizomes of Alpinia
officinarum and their anticancer activity. Fitoterapia.
79:27–31. 2008.
|
|
6
|
Lee CC and Houghton P: Cytotoxicity of
plants from Malaysia and Thailand used traditionally to treat
cancer. J Ethnopharmacol. 100:237–243. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tabata K, Yamazaki Y, Okada M, Fukumura K,
Shimada A, Sun Y, Yasukawa K and Suzuki T: Diarylheptanoids derived
from Alpinia officinarum induce apoptosis, S-phase arrest
and differentiation in human neuroblastoma cells. Anticancer Res.
29:4981–4988. 2009.
|
|
8
|
Zhang HT, Wu J, Wen M, Su LJ and Luo H:
Galangin induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
through the caspase 8/t-Bid mitochondrial pathway. J Asian Nat Prod
Res. 14:626–633. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim DY, Kang SH and Ghil SH: Cirsium
japonicum extract induces apoptosis and anti-proliferation in
the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Mol Med Rep. 3:427–432.
2010.
|
|
10
|
Jung HW and Ghil SH: A Torilis
japonica extract exerts anti-proliferative activities on the
U87MG human glioblastoma cell line. Mol Med Rep. 3:1041–1045.
2010.
|
|
11
|
Boatright KM and Salvesen GS: Mechanisms
of caspase activation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 15:725–731. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Das A, Tang KS, Gopalakrishnan S, Waring
MJ and Tomasz M: Reactivity of guanine at m5CpG steps in DNA:
evidence for electronic effects transmitted through the base pairs.
Chem Biol. 6:461–471. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X
and Wang X: Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during
apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 15:269–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang HL, Chen CS, Chang WH, Lu FJ, Lai YC,
Chen CC, Hseu TH, Kuo CT and Hseu YC: Growth inhibition and
induction of apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by Antrodia
camphorata. Cancer Lett. 231:215–227. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shim HY, Park JH, Paik HD, Nah SY, Kim DS
and Han YS: Acacetin-induced apoptosis of human breast cancer MCF-7
cells involves caspase cascade, mitochondria-mediated death
signaling and SAPK/JNK1/2-c-Jun activation. Mol Cells. 24:95–104.
2007.
|
|
16
|
Chibazakura T, McGrew SG, Cooper JA,
Yoshikawa H and Roberts JM: Regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase
activity during mitotic exit and maintenance of genome stability by
p21, p27, and p107. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:4465–4470. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen T and Wong YS: Selenocystine induces
S-phase arrest and apoptosis in human breast adenocarcinoma MCF-7
cells by modulating ERK and Akt phosphorylation. J Agric Food Chem.
56:10574–10581. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu M, Sheppard KA, Peng CY, Yee AS and
Piwnica-Worms H: Cyclin A/CDK2 binds directly to E2F-1 and inhibits
the DNA-binding activity of E2F-1/DP-1 by phosphorylation. Mol Cell
Biol. 14:8420–8431. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koopman G, Reutelingsperger CP, Kuijten
GA, Keehnen RM, Pals ST and van Oers MH: Annexin V for flow
cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on B cells
undergoing apoptosis. Blood. 84:1415–1420. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Martin SJ, Reutelingsperger CP, McGahon
AJ, Rader JA, van Schie RC, LaFace DM and Green DR: Early
redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general
feature of apoptosis regardless of the initiating stimulus:
inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl. J Exp Med.
182:1545–1556. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang XP, Liu F and Wang W: Two-phase
dynamics of p53 in the DNA damage response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:8990–8995. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Basu A and Haldar S: The relationship
between BcI2, Bax and p53: consequences for cell cycle progression
and cell death. Mol Hum Reprod. 4:1099–1109. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim R, Emi M and Tanabe K:
Caspase-dependent and -independent cell death pathways after DNA
damage. Oncol Rep. 14:595–599. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|