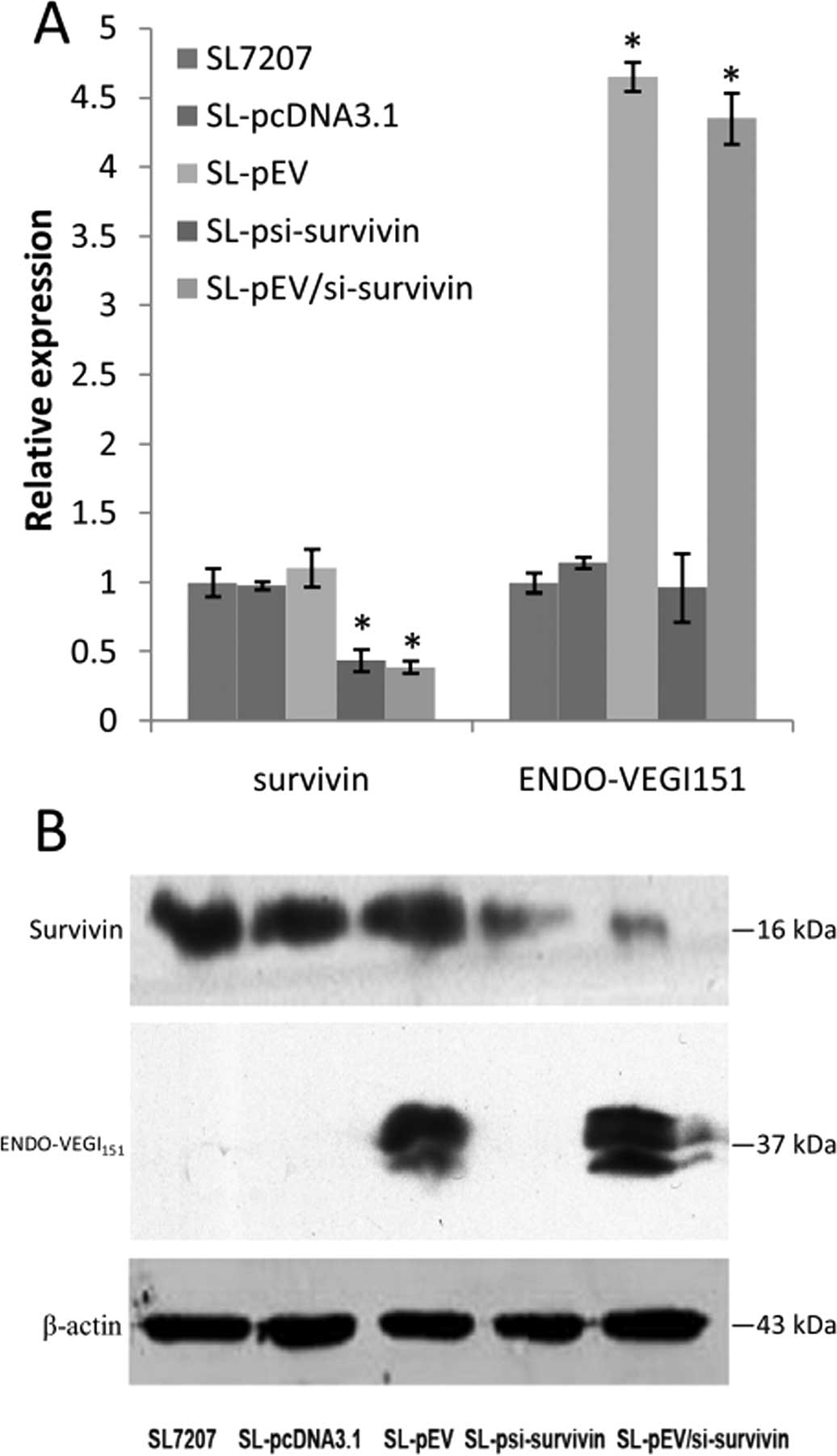
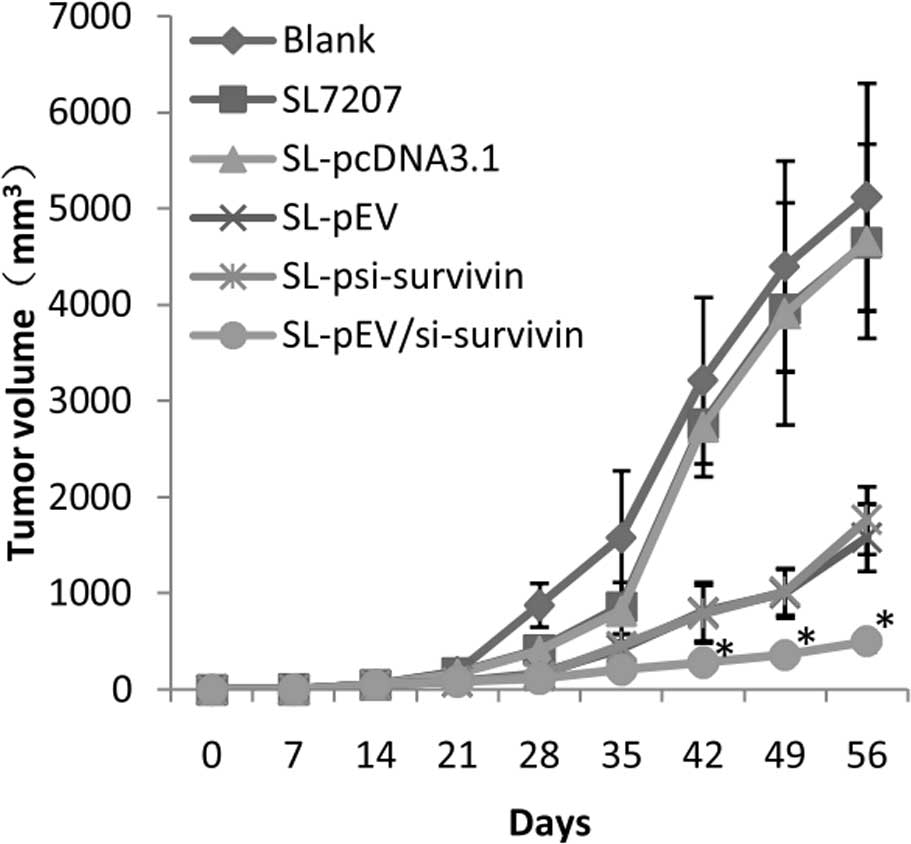
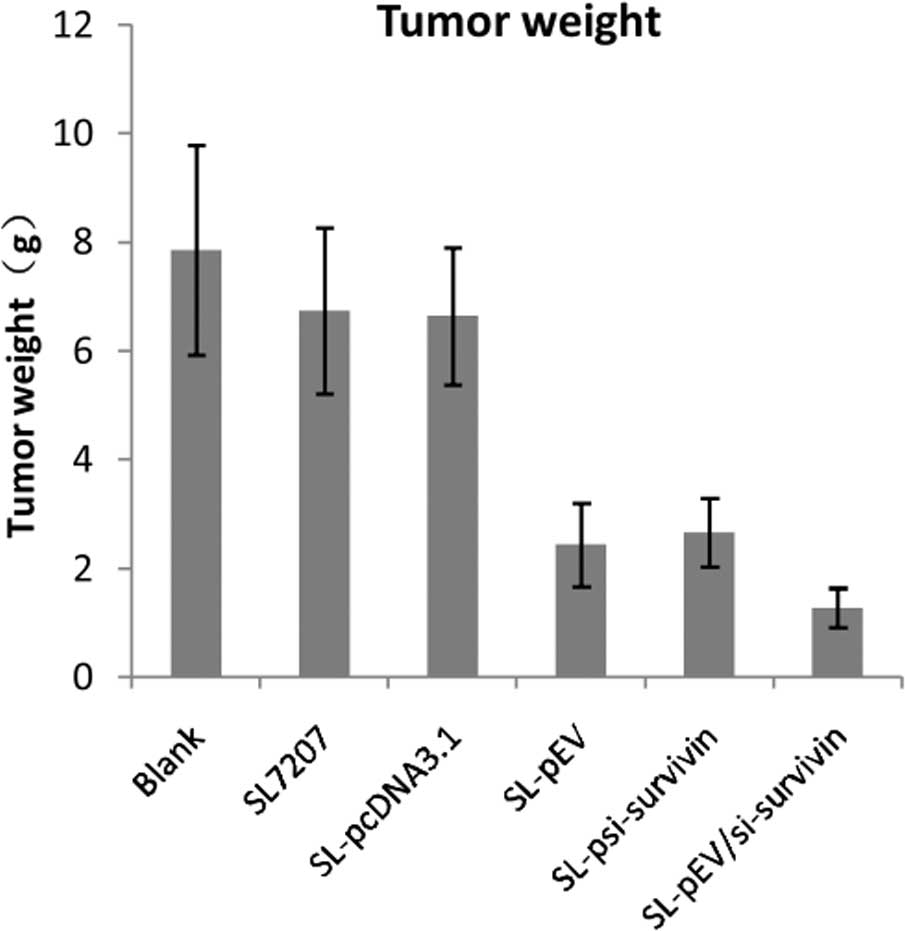
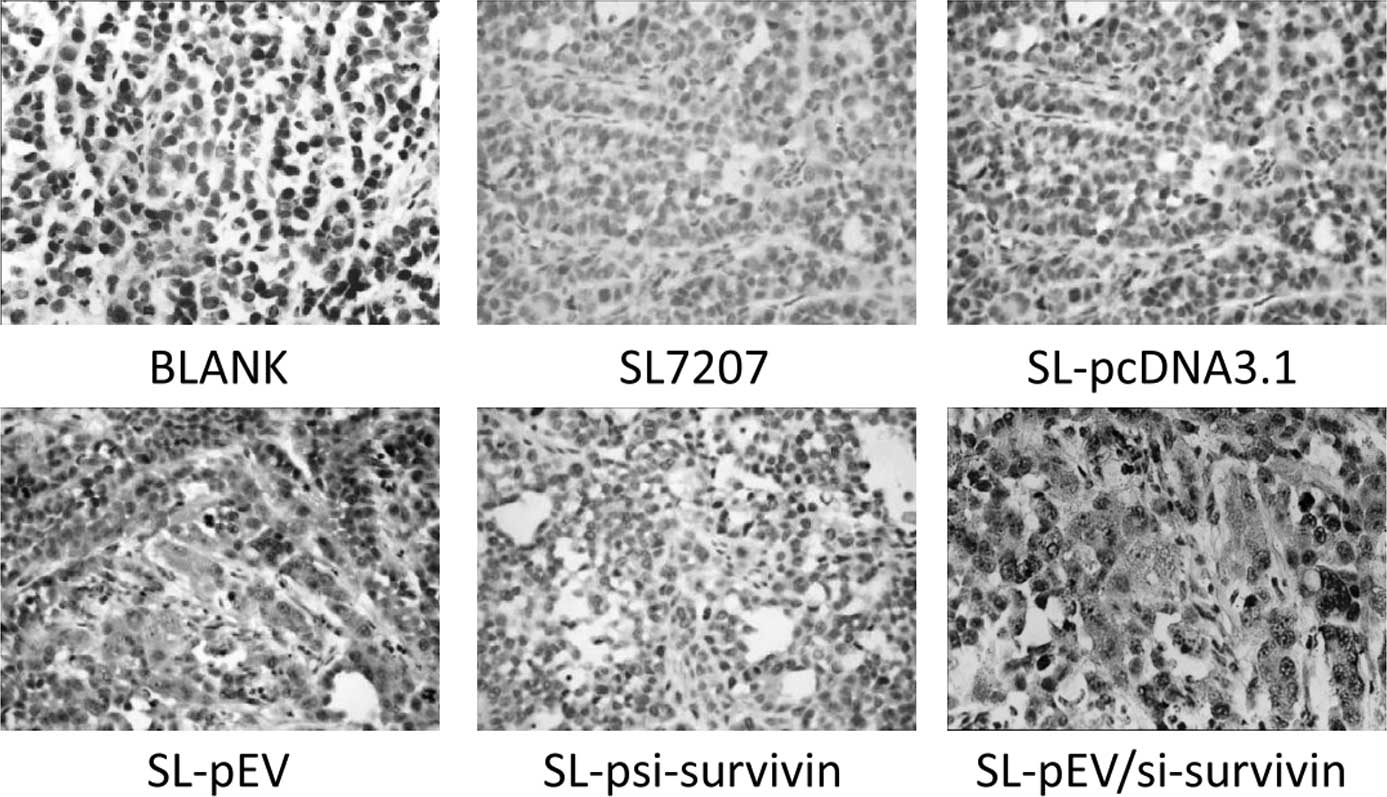
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Grammatikakis I, Zervoudis S and Kassanos
D: Synopsis of new antiangiogenetic factors, mutation compensation
agents, and monoclonal antibodies in target therapies of breast
cancer. J BUON. 15:639–646. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stoff-Khalili MA, Dall P and Curiel DT:
Gene therapy for carcinoma of the breast. Cancer Gene Ther.
13:633–647. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Butler JM, Kobayashi H and Rafii S:
Instructive role of the vascular niche in promoting tumour growth
and tissue repair by angiocrine factors. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:138–146. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Weigand M, Hantel P, Kreienberg R and
Waltenberger J: Autocrine vascular endothelial growth factor
signalling in breast cancer. Evidence from cell lines and primary
breast cancer cultures in vitro. Angiogenesis. 8:197–204. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li Z, Yang S, Chang T, Cao X, Shi L and
Fang G: Anti-angiogenesis and anticancer effects of a plasmid
expressing both ENDO-VEGI151 and small interfering RNA against
survivin. Int J Mol Med. 29:485–490. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cao S, Cripps A and Wei MQ: New strategies
for cancer gene therapy: progress and opportunities. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 37:108–114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jimeno A and Hidalgo M: Multitargeted
therapy: can promiscuity be praised in an era of political
correctness? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 59:150–158. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Qu ZH, Cui M, Guo C, Zhang XM, Ma
CH and Sun WS: Combined endostatin and TRAIL gene transfer
suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma growth and angiogenesis
in nude mice. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:466–473. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu B, Zhang Y, Zhan Y, Zha X, Wu Y, Zhang
X, Dong Q, Kong W and Yu X: Co-expression of herpes simplex virus
thymidine kinase and Escherichia coli nitroreductase by an
hTERT-driven adenovirus vector in breast cancer cells results in
additive anti-tumor effects. Oncol Rep. 26:255–264. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abdollahi A and Folkman J: Evading tumor
evasion: current concepts and perspectives of anti-angiogenic
cancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat. 13:16–28. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Miles DW, Chan A, Dirix LY, et al: Phase
III study of bevacizumab plus docetaxel compared with placebo plus
docetaxel for the first-line treatment of human epidermal growth
factor receptor 2-negative metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:3239–3247. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Robert NJ, Diéras V, Glaspy J, et al:
RIBBON-1: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III
trial of chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for first-line
treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative,
locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
29:1252–1260. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kerbel RS: Issues regarding improving the
impact of antiangiogenic drugs for the treatment of breast cancer.
Breast. 18(Suppl 3): S41–S47. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Leite de Oliveira R, Hamm A and Mazzone M:
Growing tumor vessels: more than one way to skin a cat
-implications for angiogenesis targeted cancer therapies. Mol
Aspects Med. 32:71–87. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pang RW and Poon RT: Clinical implications
of angiogenesis in cancers. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2:97–108. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Eichhorn ME, Kleespies A, Angele MK, Jauch
KW and Bruns CJ: Angiogenesis in cancer: molecular mechanisms,
clinical impact. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 392:371–379. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Carrasco RA, Stamm NB, Marcusson E,
Sandusky G, Iversen P and Patel BK: Antisense inhibition of
survivin expression as a cancer therapeutic. Mol Cancer Ther.
10:221–232. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rice C and Huang LE: From antiangiogenesis
to hypoxia: current research and future directions. Cancer Manag
Res. 3:9–16. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peng XH, Karna P, Cao Z, Jiang BH, Zhou M
and Yang L: Cross-talk between epidermal growth factor receptor and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha signal pathways increases
resistance to apoptosis by up-regulating survivin gene expression.
J Biol Chem. 281:25903–25914. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu C, Liang B, Wang Q, Wu J and Zou MH:
Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha1 alleviates
endothelial cell apoptosis by increasing the expression of
anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and survivin. J Biol Chem.
285:15346–15355. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gardlik R and Fruehauf JH: Bacterial
vectors and delivery systems in cancer therapy. IDrugs. 13:701–706.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gardlik R, Behuliak M, Palffy R, Celec P
and Li CJ: Gene therapy for cancer: bacteria-mediated
anti-angiogenesis therapy. Gene Ther. 18:425–431. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ji K, Wang B, Shao YT, et al: Synergistic
suppression of prostatic cancer cells by coexpression of both
murine double minute 2 small interfering RNA and wild-type p53 gene
in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 338:173–183. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu X, Zhou P, Cai J, Yang G, Liang S and
Ren D: Tumor antigen delivered by Salmonella III secretion protein
fused with heat shock protein 70 induces protection and eradication
against murine melanoma. Cancer Sci. 101:2621–2628. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu XL, Jiang XB, Liu RE and Zhang SM: The
enhanced anti-angiogenic and antitumor effects of combining
flk1-based DNA vaccine and IP-10. Vaccine. 26:5352–5357. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|