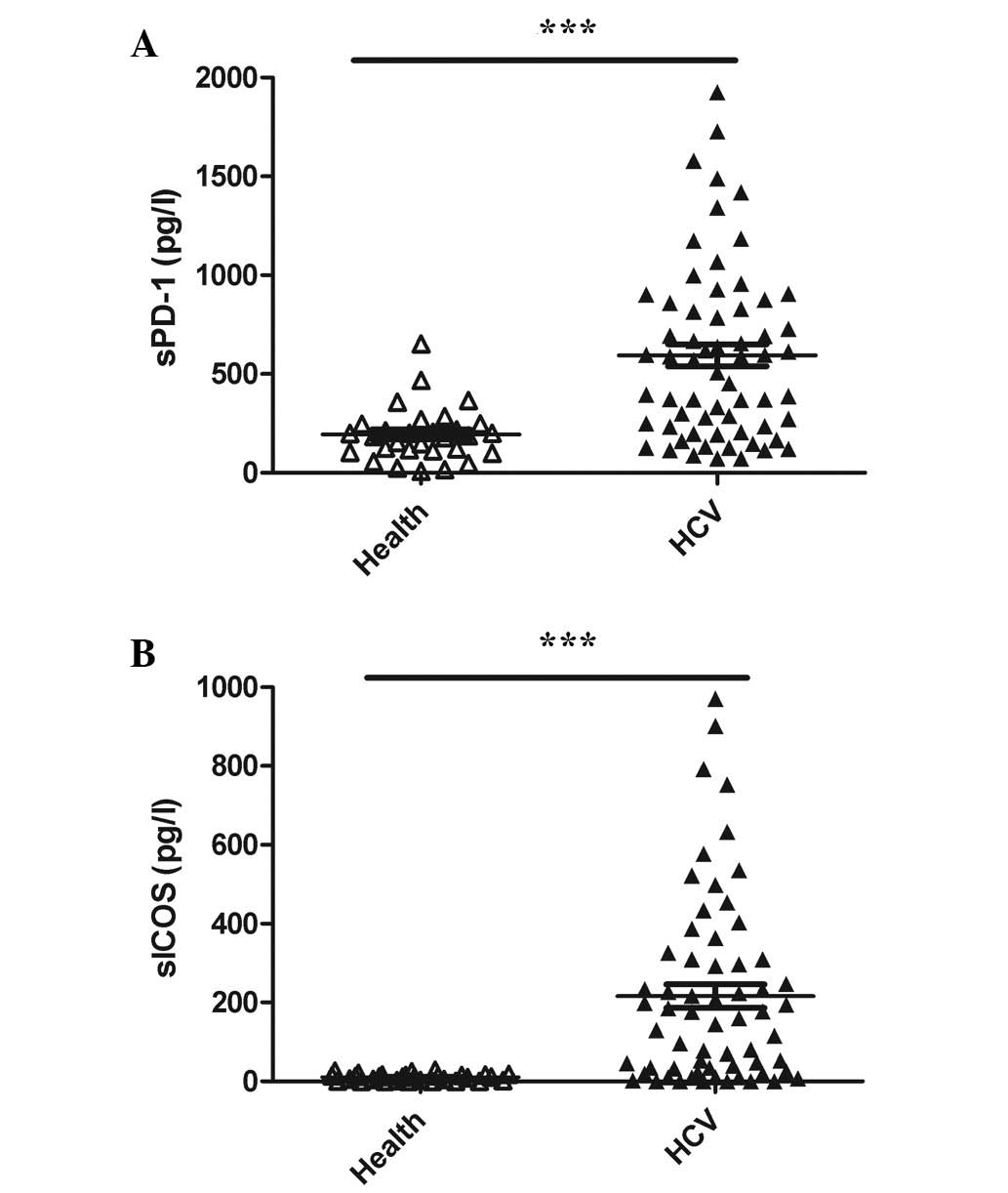
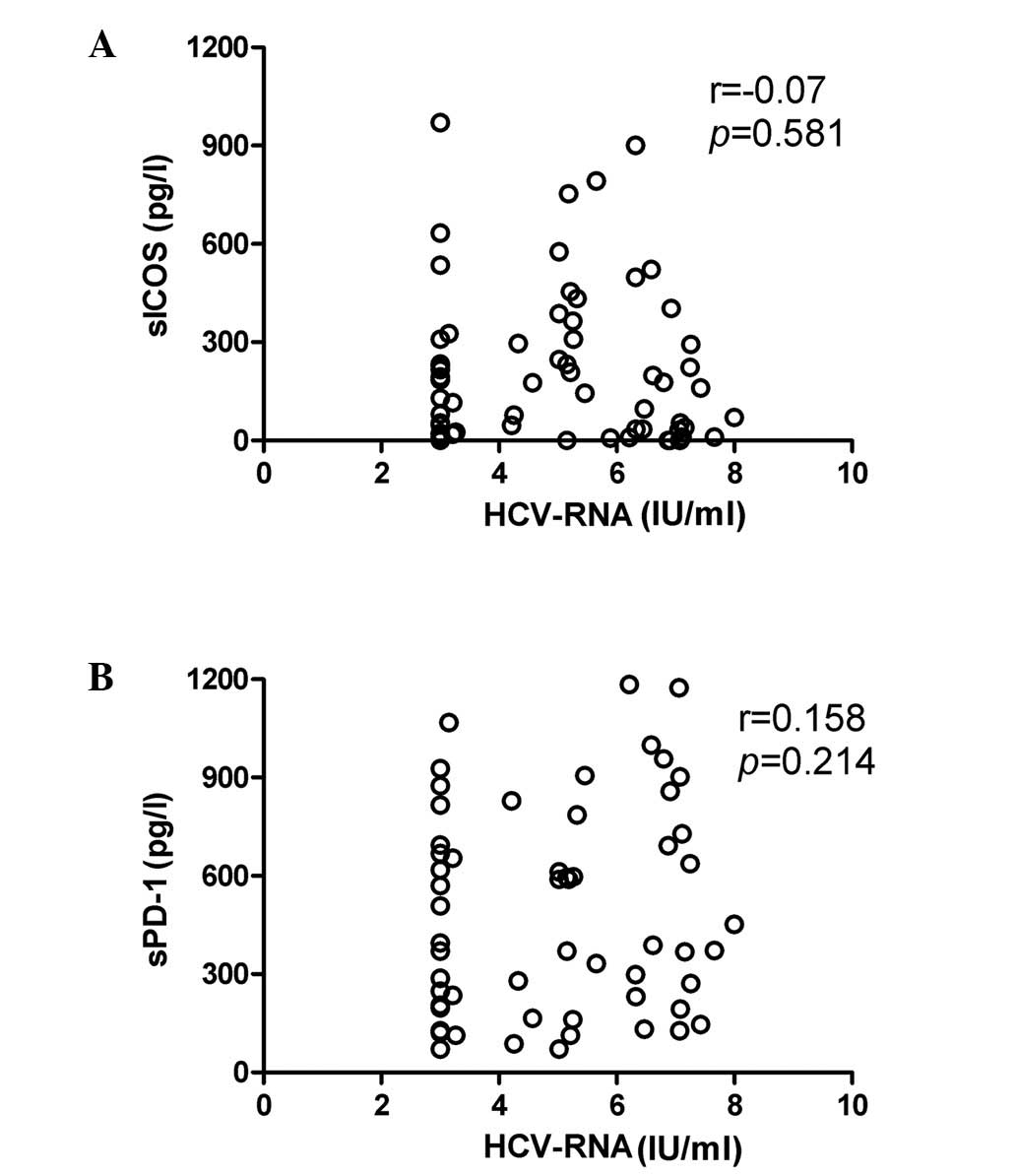
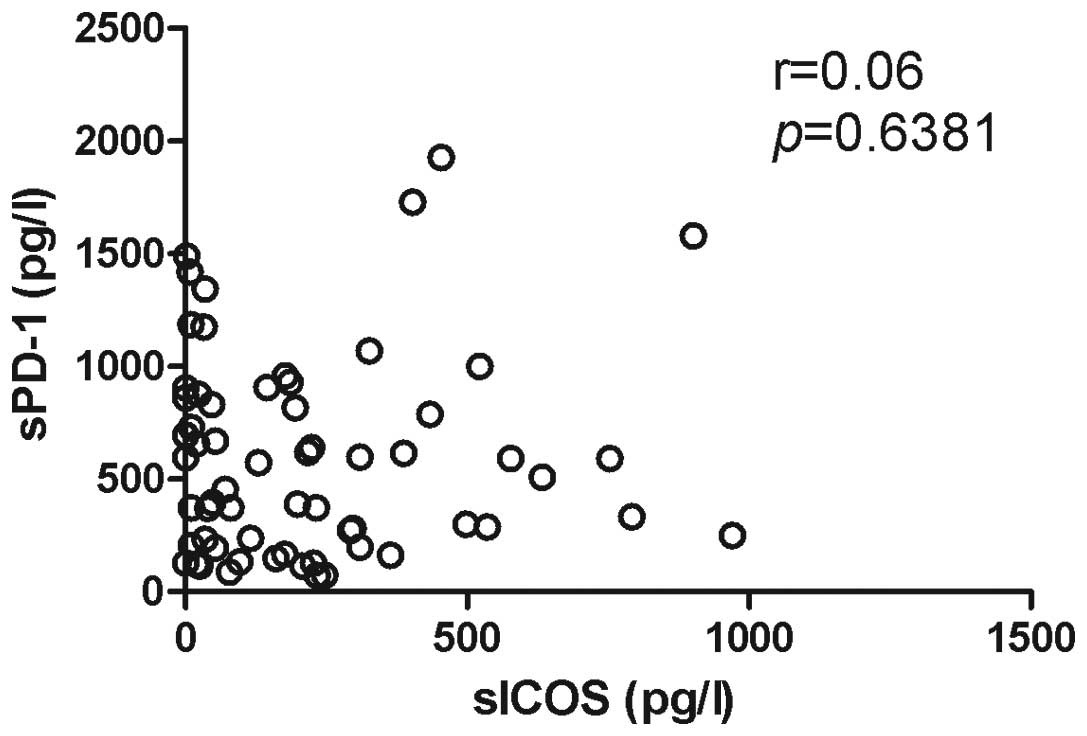
|
1
|
Sorrell MF, Belongia EA, Costa J, Gareen
IF, Grem JL, Inadomi JM, Kern ER, McHugh JA, Petersen GM, Rein MF,
et al: National Institutes of Health consensus development
conference statement: management of hepatitis B. Hepatology.
49:S4–S12. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rodriguez-Luna H and Vargas HE: Management
of hepatitis C virus infection in the setting of liver
transplantation. Liver Transpl. 11:479–489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mengshol JA, Golden-Mason L and Rosen HR:
Mechanisms of Disease: HCV-induced liver injury. Nat Clin Pract
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 4:622–634. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sharpe AH and Freeman GJ: The B7-CD28
superfamily. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:116–126. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cooper S, Erickson AL, Adams EJ, Kansopon
J, Weiner AJ, Chien DY, Houghton M, Parham P and Walker CM:
Analysis of a successful immune response against hepatitis C virus.
Immunity. 10:439–449. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thimme R, Oldach D, Chang KM, Steiger C,
Ray SC and Chisari FV: Determinants of viral clearance and
persistence during acute hepatitis C virus infection. J Exp Med.
194:1395–1406. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Puig M, Mihalik K, Tilton JC, Williams O,
Merchlinsky M, Connors M, Feinstone SM and Major ME:
CD4+ immune escape and subsequent T-cell failure
following chimpanzee immunization against hepatitis C virus.
Hepatology. 44:736–745. 2006.
|
|
8
|
Rehermann B, Chang KM, McHutchinson J,
Kokka R, Houghton M, Rice CM and Chisari FV: Differential cytotoxic
T-lymphocyte responsiveness to the hepatitis B and C viruses in
chronically infected patients. J Virol. 70:7092–7102.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nelson DR, Marousis CG, Davis GL, Rice CM,
Wong J, Houghton M and Lau JY: The role of hepatitis C
virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in chronic hepatitis C. J
Immunol. 158:1473–1481. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cabrera R, Tu Z, Xu Y, Firpi RJ, Rosen HR,
Liu C and Nelson DR: An immunomodulatory role for CD4(+)CD25(+)
regulatory T lymphocytes in hepatitis C virus infection.
Hepatology. 40:1062–1071. 2004.
|
|
11
|
Yao ZQ, King E, Prayther D, Yin D and
Moorman J: T cell dysfunction by hepatitis C virus core protein
involves PD-1/PDL-1 signaling. Viral Immunol. 20:276–287. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li S, Roberts S, Plebanski M, Gouillou M,
Spelman T, Latour P, Jackson D, Brown L, Sparrow RL, Prince HM, et
al: Induction of multi-functional T cells in a phase I clinical
trial of dendritic cell immunotherapy in hepatitis C virus infected
individuals. PLoS One. 7:e393682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kasprowicz V, Schulze Zur Wiesch J,
Kuntzen T, Nolan BE, Longworth S, Berical A, Blum J, McMahon C,
Reyor LL, Elias N, et al: High level of PD-1 expression on
hepatitis C virus (HCV)-specific CD8+ and
CD4+ T cells during acute HCV infection, irrespective of
clinical outcome. J Virol. 82:3154–3160. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rutebemberwa A, Ray SC, Astemborski J,
Levine J, Liu L, Dowd KA, Clute S, Wang C, Korman A, Sette A, et
al: High-programmed death-1 levels on hepatitis C virus-specific T
cells during acute infection are associated with viral persistence
and require preservation of cognate antigen during chronic
infection. J Immunol. 181:8215–8225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Atsukawa M, Nakatsuka K, Kobayashi T,
Shimizu M, Tamura H, Harimoto H, Takahashi H and Sakamoto C:
Ribavirin downmodulates inducible costimulator on CD4+ T
cells and their interleukin-10 secretion to assist in hepatitis C
virus clearance. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27:823–831.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nielsen C, Ohm-Laursen L, Barington T,
Husby S and Lillevang ST: Alternative splice variants of the human
PD-1 gene. Cell Immunol. 235:109–116. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Meng Q, Yang P, Li B, Zhou H, Huang X, Zhu
L, Ren Y and Kijlstra A: CD4+PD-1+ T cells
acting as regulatory cells during the induction of anterior
chamber-associated immune deviation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
47:4444–4452. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Klenerman P and Semmo N: Cellular immune
responses against persistent hepatitis C virus: gone but not
forgotten. Gut. 55:914–916. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koziel MJ: Cellular immune responses
against hepatitis C virus. Clin Infect Dis. 41(Suppl 1): S25–S31.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Magistrelli G, Jeannin P, Elson G, Gauchat
JF, Nguyen TN, Bonnefoy JY and Delneste Y: Identification of three
alternatively spliced variants of human CD28 mRNA. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 259:34–37. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nishimura H, Nose M, Hiai H, Minato N and
Honjo T: Development of lupus-like autoimmune diseases by
disruption of the PD-1 gene encoding an ITIM motif-carrying
immunoreceptor. Immunity. 11:141–151. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Greenwald RJ, Freeman GJ and Sharpe AH:
The B7 family revisited. Annu Rev Immunol. 23:515–548. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Witsch EJ, Peiser M, Hutloff A, Buchner K,
Dorner BG, Jonuleit H, Mages HW and Kroczek RA: ICOS and CD28
reversely regulate IL-10 on re-activation of human effector T cells
with mature dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 32:2680–2686. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Warnatz K, Bossaller L, Salzer U,
Skrabl-Baumgartner A, Schwinger W, van der Burg M, van Dongen JJ,
Orlowska-Volk M, Knoth R, Durandy A, et al: Human ICOS deficiency
abrogates the germinal center reaction and provides a monogenic
model for common variable immunodeficiency. Blood. 107:3045–3052.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakamoto N, Cho H, Shaked A, Olthoff K,
Valiga ME, Kaminski M, Gostick E, Price DA, Freeman GJ, Wherry EJ
and Chang KM: Synergistic reversal of intrahepatic HCV-specific CD8
T cell exhaustion by combined PD-1/CTLA-4 blockade. PLoS Pathog.
5:e10003132009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|