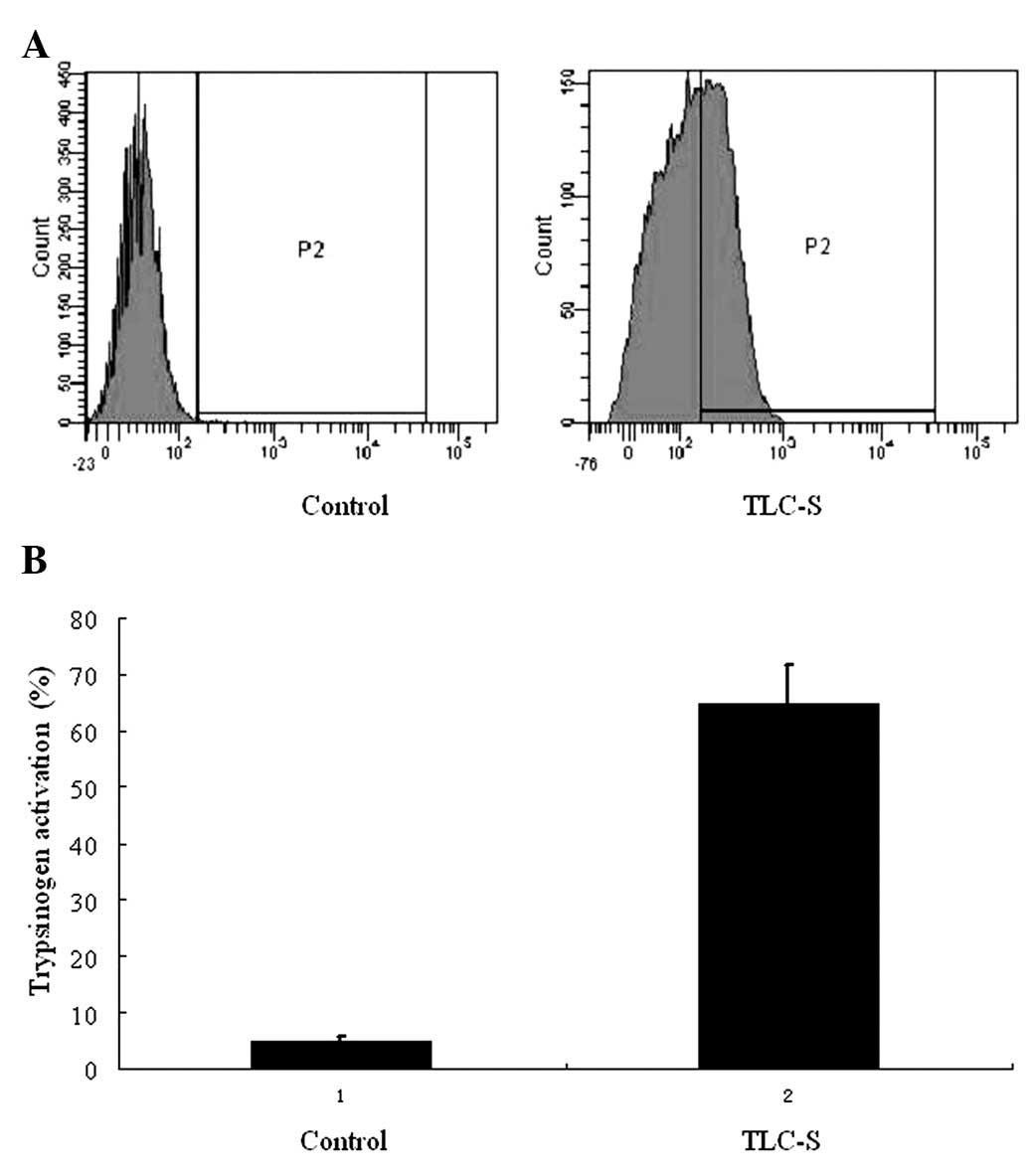
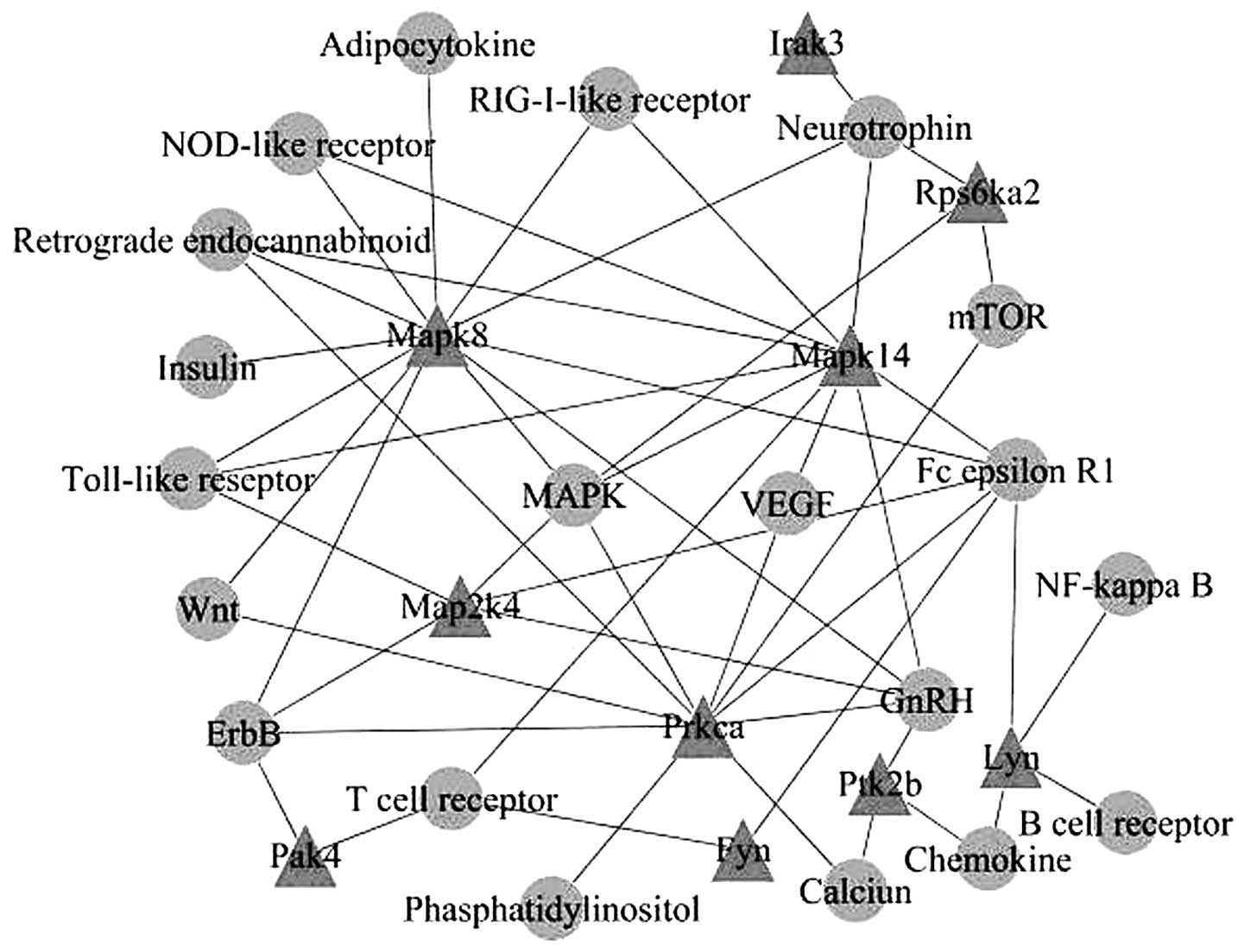
|
1
|
Voronina S, Longbottom R, Sutton R,
Petersen OH and Tepikin A: Bile acids induce calcium signals in
mose pancreatic acinar cells: implications for bile-induced
pancreatic pathology. J Physiol. 540:49–55. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gerasimenko JV, Flowerdew SE, Voronina SG,
et al: Bile acids induce Ca2+ release from both the
endoplasmic reticulum and acidic intracellular calcium stores
through activation of inositol trisphosphate receptors and
ryanodine receptors. J Biol Chem. 281:40154–40163. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Perides G, Laukkarinen JM, Vassileva G and
Steer ML: Biliary acute pancreatitis in mice is mediated by the
G-protein-coupled cell surface bile acid receptor Gpbar1.
Gastroenterology. 138:715–725. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thrower EC, Gorelick FS and Husain SZ:
Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pancreatic injury. Curr Opin
Gastroenterol. 26:484–489. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Halangk W and Lerch MM: Early events in
acute pancreatitis. Clin Lab Med. 25:1–15. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Reiser J, Adair B and Reinheckel T:
Specialized roles for cysteine cathepsins in health and disease. J
Clin Invest. 120:3421–3431. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lindkvist B, Fajardo I, Pejler G and
Borgström A: Cathepsin B activates human trypsinogen 1 but not
proelastase 2 or procarboxypeptidase B. Pancreatology. 6:224–231.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wartmann T, Mayerle J, Kähne T, et al:
Cathepsin L inactivates human trypsinogen, whereas cathepsin
L-deletion reduces the severity of pancreatitis in mice.
Gastroenterology. 138:726–737. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shah AU, Sarwar A, Orabi AI, et al:
Protease activation during in vivo pancreatitis is dependent on
calcineurin activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
297:G967–G973. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gerasimenko JV, Lur G, Sherwood MW, et al:
Pancreatic protease activation by alcohol metabolite depends on
Ca2+ release via acid store IP3 receptors. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:10758–10763. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Weber H, Hühns S, Lüthen F and Jonas L:
Calpain-mediated breakdown of cytoskeletal proteins contributes to
cholecystokinin-induced damage of rat pancreatic acini. Int J Exp
Pathol. 90:387–399. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Husain SZ, Prasad P, Grant WM, Kolodecik
TR, Nathanson MH and Gorelick FS: The ryanodine receptor mediates
early zymogen activation in pancreatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:14386–14391. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thrower EC, Yuan J, Usmani A, et al: A
novel protein kinase D inhibitor attenuates early events of
experimental pancreatitis in isolated rat acini. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 300:G120–G129. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Awla D, Hartman H, Abdulla A, et al:
Rho-kinase signalling regulates trypsinogen activation and tissue
damage in severe acute pancreatitis. Br J Pharmacol. 162:648–658.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Namkung W, Yoon JS, Kim KH and Lee MG:
PAR2 exerts local protection against acute pancreatitis via
modulation of MAP kinase and MAP kinase phosphatase signaling. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 295:G886–G894. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gorelick F, Pandol S and Thrower E:
Protein kinase C in the pancreatic acinar cell. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 23:S37–S41. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Z, Lu M, Chu J, Qiao X, Meng X, Sun B,
Zhang W and Xue D: Early proteome analysis of rat pancreatic acinar
AR42J cells treated with taurolithocholic acid 3-sulfate.
Pancreatology. 12:248–256. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Andrzejewska A and Dlugosz JW:
Differential effects of endothelins on histological and
ultrastructural changes and trypsinogen activation in the
secretagogue-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. Exp Toxicol
Pathol. 63:371–378. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Andrzejewska A, Dlugosz JW and
Augustynowicz A: Effect of endothelin-1 receptor antagonists on
histological and ultrastructural changes in the pancreas and
trypsinogen activation in the early course of caerulein-induced
acute pancreatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 11:1115–1121.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zheng XL, Kitamoto Y and Sadler JE:
Enteropeptidase, a type II transmembrane serine protease. Front
Biosci (Elite Ed). 1:242–249. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hartwig W, Kolvenbach M, Hackert T,
Fortunato F, Schneider L, Büchler MW and Werner J: Enterokinase
induces severe necrosis and rapid mortality in cerulein
pancreatitis: characterization of a novel noninvasive rat model of
necro-hemorrhagic pancreatitis. Surgery. 142:327–336. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Morel M, Couturier J, Lafay-Chebassier C,
Paccalin M and Page G: PKR, the double stranded RNA-dependent
protein kinase as a critical target in Alzheimer’s disease. J Cell
Mol Med. 13:1476–1488. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kanda S, Miyata Y, Kanetake H and
Smithgall TE: Non-receptor protein-tyrosine kinases as molecular
targets for antiangiogenic therapy. Int J Mol Med. 20:113–121.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Katoh Y and Katoh M: FGFR2-related
pathogenesis and FGFR2-targeted therapeutics (Review). Int J Mol
Med. 23:307–311. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ward JB, Petersen OH, Jenkins SA and
Sutton R: Is an elevated concentration of acinar cytosolic free
ionized calcium the trigger for acute pancreatitis? Lancet.
346:1016–1019. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mooren FCh, Hlouschek V, Finkes T, et al:
Early changes in pancreatic acinar cell calcium signaling after
pancreatic duct obstruction. J Biol Chem. 278:9361–9369. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Frick TW: The role of calcium in acute
pancreatitis. Surgery. 152:S157–S163. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim JY, Kim KH, Lee JA, et al:
Transporter-mediated bile acid uptake causes
Ca2+-dependent cell death in rat pancreatic acinar
cells. Gastroenterology. 122:1941–1953. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Raraty M, Ward J, Erdemil G, Vaillant C,
Neoptolemos JP, Sutton R and Petersen OH: Calcium-dependent enzyme
activation and vacuole formation in the apical granular region of
pancreatic acinar cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:13126–13131.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ozawa T: FK506 induces biphasic
Ca2+ release from microsomal vesicles of rat pancreatic
acinar cells. Int J Mol Med. 18:187–191. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kessen U, Schaloske R, Aichem A and Mutzel
R: Ca(2+)/calmodulin-independent activation of calcineurin from
Dictyostelium by unsaturated long chain fatty acids. J Biol
Chem. 274:37821–37826. 1999.
|
|
32
|
Conze D, Krahl T, Kennedy N, et al: c-Jun
NH(2)-terminal kinase(JNK)1 and JNK2 have distinct roles in CD8(+)
T cell activation. J Exp Med. 195:811–823. 2002.
|
|
33
|
Yang J, Murphy C, Denham W, Botchkina G,
Tracey KJ and Norman J: Evidence of a central role for p38 map
kinase induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha in
pancreatitis-associated pulmonary injury. Surgery. 126:216–222.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pereda J, Sabater L, Cassinello N, et al:
Effect of simultaneous inhibition of TNF-alpha production and
xanthine oxidase in experimental acute pancreatitis: the role of
mitogen activated protein kinases. Ann Surg. 240:108–116. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Araki Y, Andoh A, Yokono T, et al: The
free radical scavenger edaravone suppresses experimental closed
duodenal loop-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. Int J Mol Med.
12:121–124. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Williard DE, Twait E, Yuan Z, Carter AB
and Samuel I: Nuclear factor kappa B-dependent gene transcription
in cholecystokinin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha-stimulated
isolated acinar cells is regulated by p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase. Am J Surg. 200:283–290. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Samuel I, Zaheer S, Fisher RA and Zaheer
A: Cholinergic receptor induction and JNK activation in acute
pancreatitis. Am J Surg. 186:569–574. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu HS, Pan CE, Liu QG, Yang W and Liu XM:
Effect of NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK in activated monocytes/macrophages
on pro-inflammatory cytokines of rats with acute pancreatitis.
World J Gastroenterol. 9:2513–2518. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|