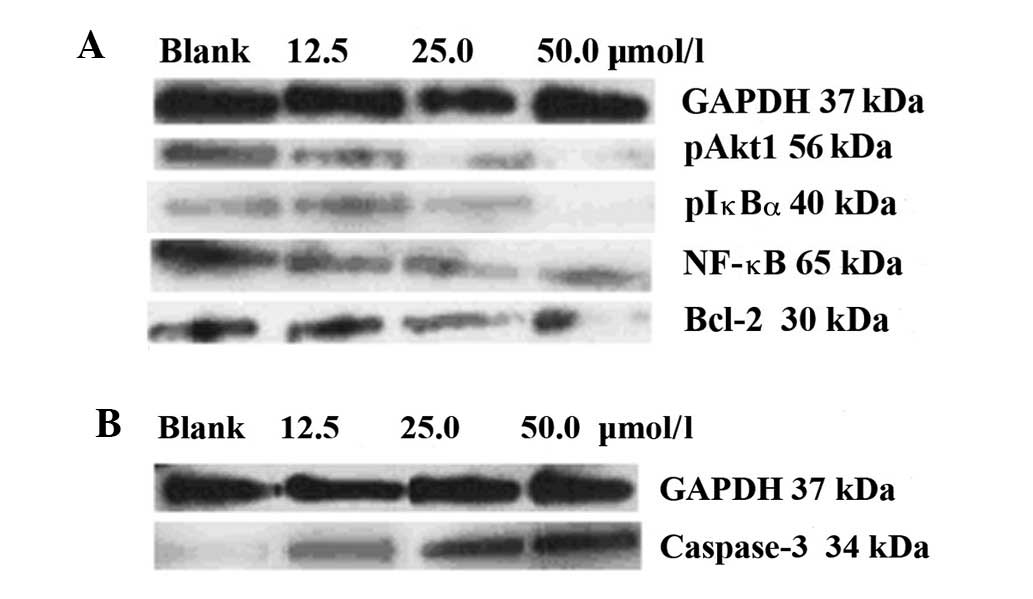
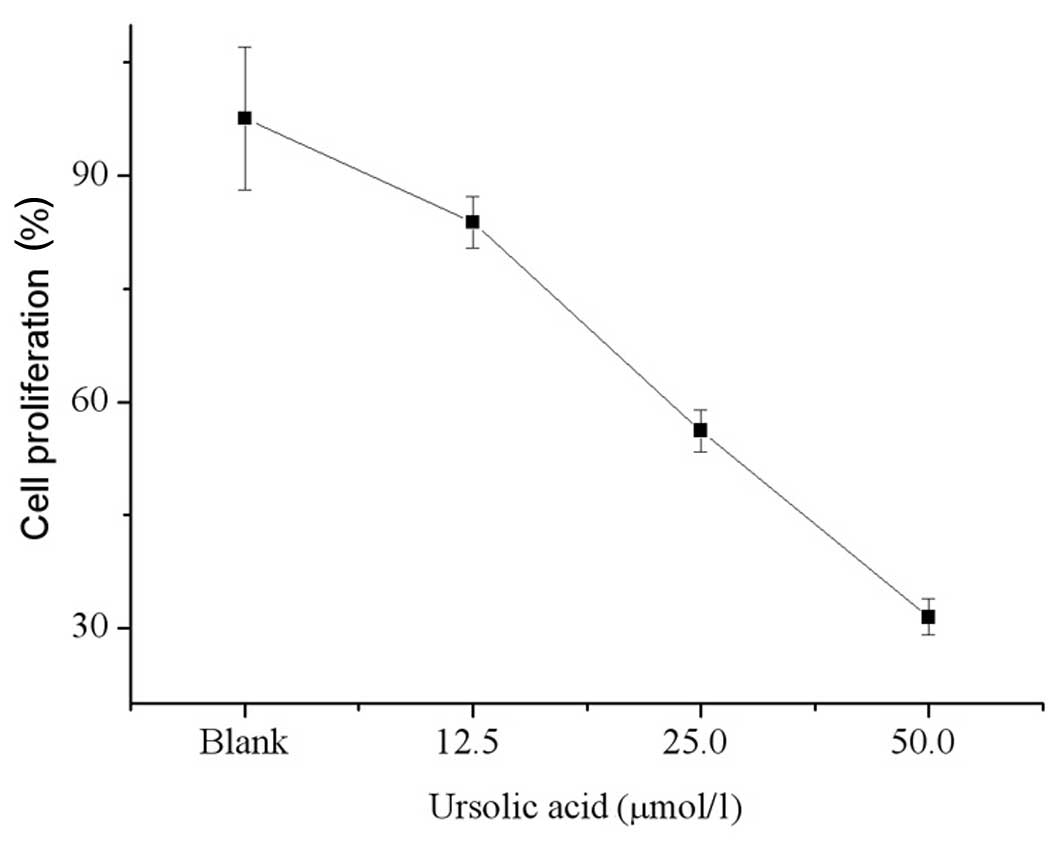
|
1
|
Achiwa Y, Hasegawa K, Komiya T and Udagawa
Y: Ursolic acid induces Bax-dependent apoptosis through the
caspase-3 pathway in endometrial cancer SNG-II cells. Oncol Rep.
13:51–57. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim KH, Seo HS, Choi HS, Choi I, Shin YC
and Ko SG: Induction of apoptotic cell death by ursolic acid
through mitochondrial death pathway and extrinsic death receptor
pathway in MDA-MB-231 cells. Arch Pharm Res. 34:1363–1372. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Manu KA and Kuttan G: Ursolic acid induces
apoptosis by activating p53 and caspase-3 gene expressions and
suppressing NF-kappaB mediated activation of bcl-2 in B16F-10
melanoma cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 8:974–981. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu JJ, Liu WD, Yang HZ, Zhang Y, Fang ZG,
Liu PQ, Lin DJ, Xiao RZ, Hu Y, Wang CZ, Li XD, He Y and Huang RW:
Inactivation of PI3k/Akt signaling pathway and activation of
caspase-3 are involved in tanshinone I-induced apoptosis in myeloid
leukemia cells in vitro. Ann Hematol. 89:1089–1097. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li J, Liang X and Yang X: Ursolic acid
inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in gemcitabine-resistant
human pancreatic cancer via the JNK and PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathways.
Oncol Rep. 28:501–510. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shishodia S, Majumdar S, Banerjee S and
Aggarwal BB: Ursolic acid inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB activation
induced by carcinogenic agents through suppression of IkappaBalpha
kinase and p65 phosphorylation: correlation with down-regulation of
cyclooxygenase 2, matrix metalloproteinase 9, and cyclin D1. Cancer
Res. 63:4375–4383. 2003.
|
|
7
|
Tang C, Lu YH, Xie JH, Wang F, Zou JN,
Yang JS, Xing YY and Xi T: Downregulation of survivin and
activation of caspase-3 through the PI3K/Akt pathway in ursolic
acid-induced HepG2 cell apoptosis. Anticancer Drugs. 20:249–258.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu B, Wang X, Chi ZF, Hu R, Zhang R, Yang
W and Liu ZG: Ursolic acid-induced apoptosis in K562 cells
involving upregulation of PTEN gene expression and inactivation of
the PI3K/Akt pathway. Arch Pharm Res. 35:543–548. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang J, Li Y, Wang X and Jiang C: Ursolic
acid inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human
glioblastoma cell lines U251 by suppressing TGF-β1/miR-21/PDCD4
pathway. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 111:106–112. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang JS, Ren TN and Xi T: Ursolic acid
induces apoptosis by suppressing the expression of FoxM1 in MCF-7
human breast cancer cells. Med Oncol. 29:10–15. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kassi E, Papoutsi Z, Pratsinis H,
Aligiannis N, Manoussakis M and Moutsatsou P: Ursolic acid, a
naturally occurring triterpenoid, demonstrates anticancer activity
on human prostate cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
133:493–500. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y, Kong C, Zeng Y, Wang L, Li Z,
Wang H, Xu C and Sun Y: Ursolic acid induces PC-3 cell apoptosis
via activation of JNK and inhibition of Akt pathways in vitro. Mol
Carcinog. 49:374–385. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shanmugam MK, Rajendran P, Li F, Nema T,
Vali S, Abbasi T, Kapoor S, Sharma A, Kumar AP, Ho PC, Hui KM and
Sethi G: Ursolic acid inhibits multiple cell survival pathways
leading to suppression of growth of prostate cancer xenograft in
nude mice. J Mol Med (Berl). 89:713–727. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Limami Y, Pinon A, Leger DY, Pinault E,
Delage C, Beneytout JL, Simon A and Liagre B: The
P2Y2/Src/p38/COX-2 pathway is involved in the resistance to ursolic
acid-induced apoptosis in colorectal and prostate cancer cells.
Biochimie. 94:1754–1763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tu HY, Huang AM, Wei BL, Gan KH, Hour TC,
Yang SC, Pu YS and Lin CN: Ursolic acid derivatives induce cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis in NTUB1 cells associated with reactive
oxygen species. Bioorg Med Chem. 17:7265–7274. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zheng QY, Jin FS, Yao C, Zhang T, Zhang GH
and Ai X: Ursolic acid-induced AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)
activation contributes to growth inhibition and apoptosis in human
bladder cancer T24 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 419:741–747.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun CH, Chang YH and Pan CC: Activation of
the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway correlates with tumour progression and
reduced survival in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the
urinary bladder. Histopathology. 58:1054–1063. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Plissonnier ML, Fauconnet S, Bittard H and
Lascombe I: The antidiabetic drug ciglitazone induces high grade
bladder cancer cells apoptosis through the up-regulation of TRAIL.
PLoS One. 6:e283542011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jayasooriya RG, Choi YH, Moon SK, Kim WJ
and Kim GY: Methanol extract of Hydroclathrus clathratus
suppresses matrix metalloproteinase-9 in T24 bladder carcinoma
cells by suppressing the NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Oncol Rep.
27:541–546. 2012.
|
|
20
|
Kunze D, Kraemer K, Erdmann K, Froehner M,
Wirth MP and Fuessel S: Simultaneous siRNA-mediated knockdown of
antiapoptotic BCL2, Bcl-xL, XIAP and survivin in bladder cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. Jul 6–2012.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen CC, Cheng YY, Chen SC, Tuan YF, Chen
YJ, Chen CY and Chen LC: Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is
up-regulated by 2-aminobiphenyl in a ROS and MAPK-dependent
signaling pathway in a bladder cancer cell line. Chem Res Toxicol.
25:695–705. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu CC, Ko FY, Yu CS, Lin CC, Huang YP,
Yang JS, Lin JP and Chung JG: Norcantharidin triggers cell death
and DNA damage through S-phase arrest and ROS-modulated apoptotic
pathways in TSGH 8301 human urinary bladder carcinoma cells. Int J
Oncol. 41:1050–1060. 2012.
|
|
23
|
Lee SJ, Lim JH, Choi YH, Kim WJ and Moon
SK: Interleukin-28A triggers wound healing migration of bladder
cancer cells via NF-κB-mediated MMP-9 expression inducing the MAPK
pathway. Cell Signal. 24:1734–1742. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Takeuchi A, Eto M, Shiota M, Tatsugami K,
Yokomizo A, Kuroiwa K, Itsumi M and Naito S: Sunitinib enhances
antitumor effects against chemotherapy-resistant bladder cancer
through suppression of ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Int J Oncol.
40:1691–1696. 2012.
|
|
25
|
Huang WW, Yang JS, Pai SJ, Wu PP, Chang
SJ, Chueh FS, Fan MJ, Chiou SM, Kuo HM, Yeh CC, Chen PY, Tsuzuki M
and Chung JG: Bufalin induces G(0)/G(1) phase arrest through
inhibiting the levels of cyclin D, cyclin E, CDK2 and CDK4, and
triggers apoptosis via mitochondrial signaling pathway in T24 human
bladder cancer cells. Mutat Res. 732:26–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Weizhong Z, Shuohui G, Hanjiao Q, Yuhong
M, Xiaohua Y, Jian C and Lisen L: Inhibition of cytohesin-1 by
siRNA leads to reduced IGFR signaling in prostate cancer. Braz J
Med Biol Res. 44:642–646. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Barkett M and Gilmore TD: Control of
apoptosis by Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Oncogene.
18:6910–6924. 1999.
|
|
28
|
Tang G, Yang J, Minemoto Y and Lin A:
Blocking caspase-3-mediated proteolysis of IKKbeta suppresses
TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell. 8:1005–1016. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ravi R, Mookerjee B, van Hensbergen Y,
Bedi GC, Giordano A, El-Deiry WS, Fuchs EJ and Bedi A: p53-mediated
repression of nuclear factor-kappaB RelA via the transcriptional
integrator p300. Cancer Res. 58:4531–4536. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|