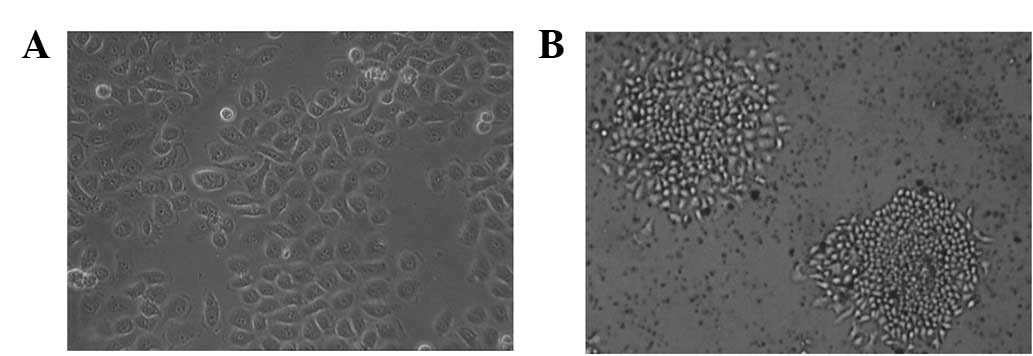
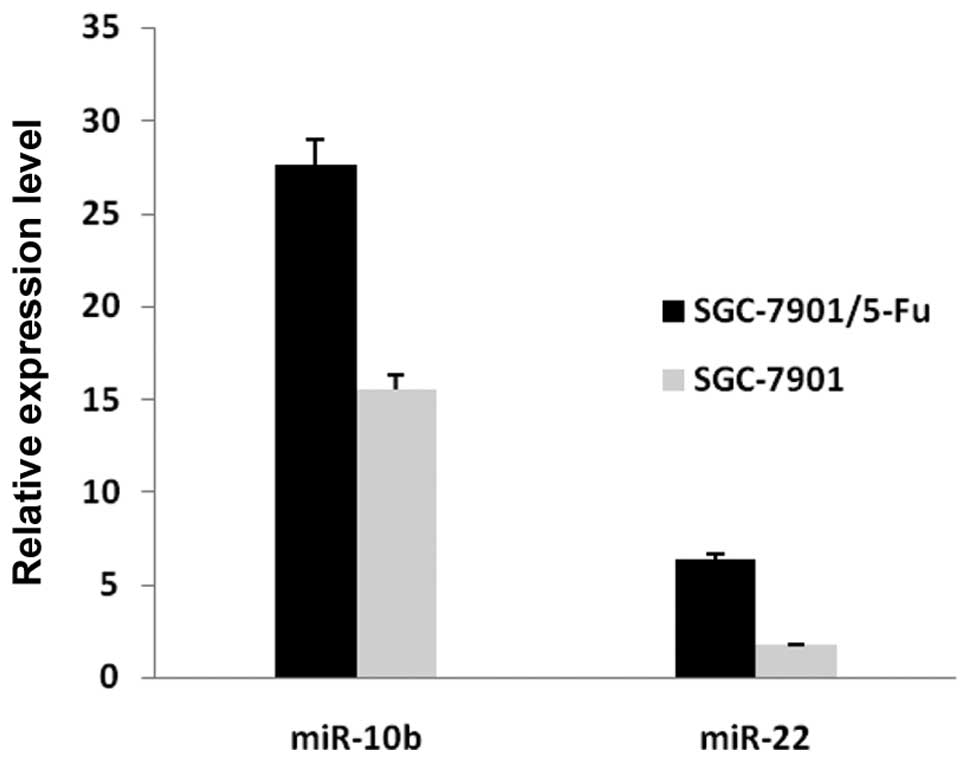
|
1
|
Zhao P, Dai M, Chen W and Li N: Cancer
trends in China. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 40:281–285. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
de Bree E, Charalampakis V, Melissas J and
Tsiftsis DD: The extent of lymph node dissection for gastric
cancer: a critical appraisal. J Surg Oncol. 102:552–562. 2010.
|
|
4
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J and Ford LP:
Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an
involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 33:1290–1297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Blower PE, Chung JH, Verducci JS, et al:
MicroRNAs modulate the chemosensitivity of tumor cells. Mol Cancer
Ther. 7:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zheng T, Wang J, Chen X and Liu L: Role of
microRNA in anticancer drug resistance. Int J Cancer. 126:2–10.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z, Kong D and Ali S:
Implication of microRNAs in drug resistance for designing novel
cancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat. 13:57–66. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rossi L, Bonmassar E and Faraoni I:
Modification of miR gene expression pattern in human colon cancer
cells following exposure to 5-fluorouracil in vitro. Pharmacol Res.
56:248–253. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nakajima G, Hayashi K, Xi Y, et al:
Non-coding microRNAs hsa-let-7g and hsa-miR-181b are associated
with chemoresponse to S-1 in colon cancer. Cancer Genomics
Proteomics. 3:317–324. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rosenfeld N, Aharonov R, Meiri E, et al:
MicroRNAs accurately identify cancer tissue origin. Nat Biotechnol.
26:462–469. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schmittgen TD, Lee EJ, Jiang J, et al:
Real-time PCR quantification of precursor and mature microRNA.
Methods. 44:31–38. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Luqmani YA: Mechanisms of drug resistance
in cancer chemotherapy. Med Princ Pract. 14(Suppl 1): 35–48. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ganguly A, Banerjee K, Chakraborty P, et
al: Overcoming multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer in vitro and in
vivo by a quinoline derivative. Biomed Pharmacother. 65:387–394.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gottesman MM and Pastan I: The multidrug
transporter, a double-edged sword. J Biol Chem. 263:1263–1266.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moscow JA and Cowan KH: Multidrug
resistance. J Natl Cancer Inst. 80:14–20. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Watson MB, Lind MJ and Cawkwell L:
Establishment of in-vitro models of chemotherapy resistance.
Anticancer Drugs. 18:749–754. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Singh R and Lillard JW Jr:
Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery. Exp Mol Pathol.
86:215–223. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hammond SM, Bernstein E, Beach D and
Hannon GJ: An RNA-directed nuclease mediates post-transcriptional
gene silencing in Drosophila cells. Nature. 404:293–296.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fujita Y, Kojima K, Hamada N, et al:
Effects of miR-34a on cell growth and chemoresistance in prostate
cancer PC3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 377:114–119. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Northcott PA, Fernandez-L A, Hagan JP, et
al: The miR-17/92 polycistron is up-regulated in sonic
hedgehog-driven medulloblastomas and induced by N-myc in sonic
hedgehog-treated cerebellar neural precursors. Cancer Res.
69:3249–3255. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li Y, Li W, Yang Y, et al: MicroRNA-21
targets LRRFIP1 and contributes to VM-26 resistance in glioblastoma
multiforme. Brain Res. 1286:13–18. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xia L, Zhang D, Du R, et al: miR-15b and
miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human
gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 123:372–379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J and Weinberg RA:
Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast
cancer. Nature. 449:682–688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gee HE, Camps C, Buffa FM, et al:
MicroRNA-10b and breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 455:E8–E9. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li G, Wu Z, Peng Y, et al: MicroRNA-10b
induced by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein-1
promotes the metastasis of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.
Cancer Lett. 299:29–36. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kakarala M, Brenner DE, Korkaya H, et al:
Targeting breast stem cells with the cancer preventive compounds
curcumin and piperine. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 122:777–785. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|