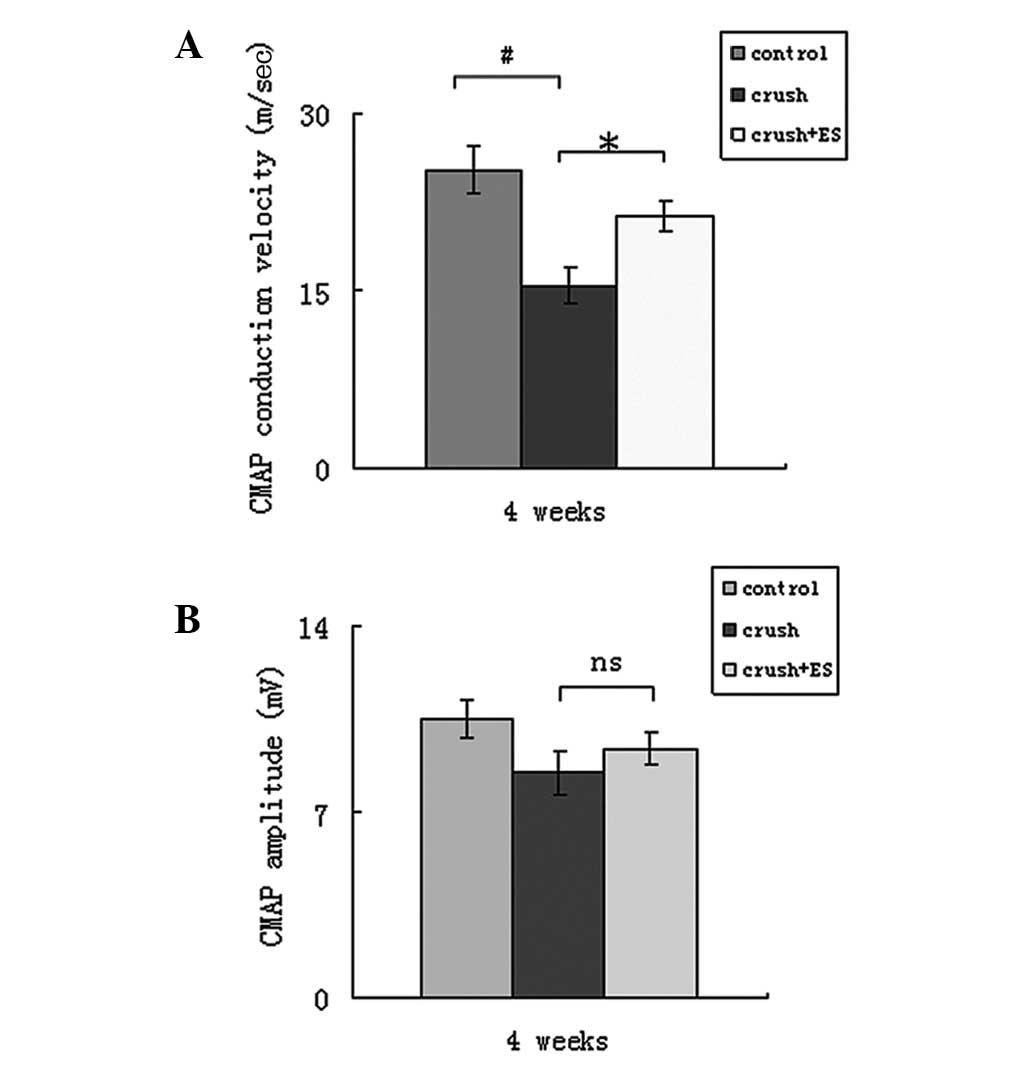
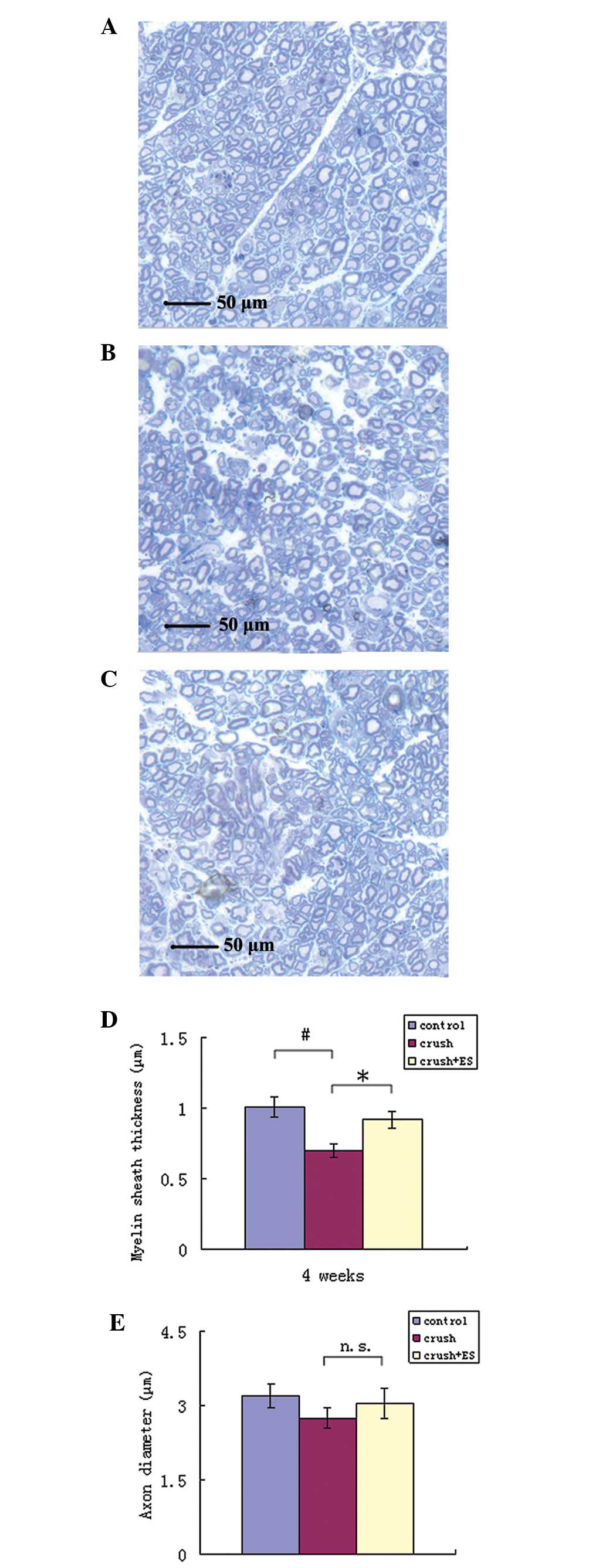
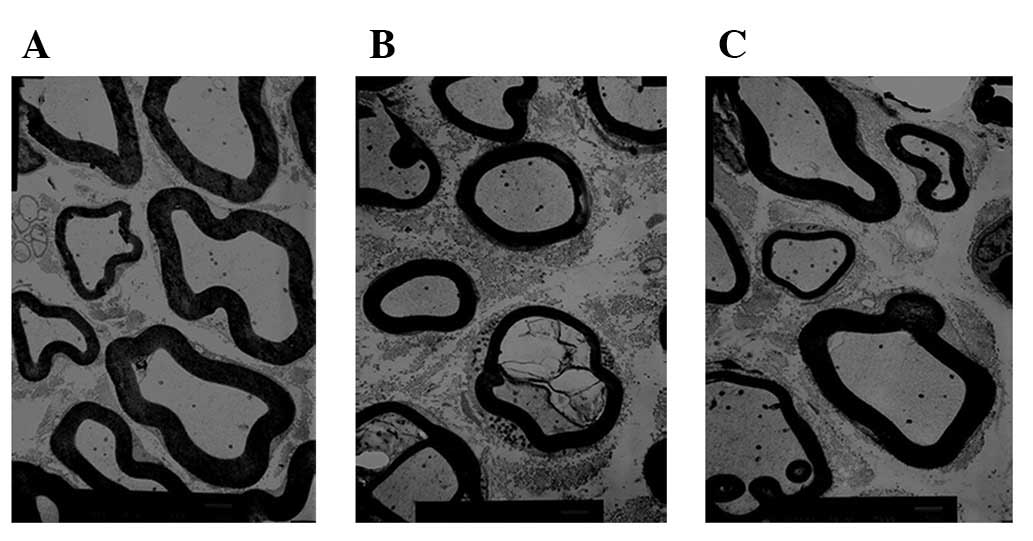
|
1
|
Al-Majed AA, Brushart TM and Gordon T:
Electrical stimulation accelerates and increases expression of BDNF
and trkB mRNA in regenerating rat femoral motoneurons. Eur J
Neurosci. 12:4381–4390. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gordon T, Brushart TM and Chan KM:
Augmenting nerve regeneration with electrical stimulation. Neurol
Res. 30:1012–1022. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lal D, Hetzler LT, Sharma N, Wurster RD,
Marzo SJ, Jones KJ and Foecking EM: Electrical stimulation
facilitates rat facial nerve recovery from a crush injury.
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 139:68–73. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim J, Han SJ, Shin DH, Lee WS and Choi
JY: Subthreshold continuous electrical stimulation facilitates
functional recovery of facial nerve after crush injury in rabbit.
Muscle Nerve. 43:251–258. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Al-Majed AA, Neumann CM, Brushart TM and
Gordon T: Brief electrical stimulation promotes the speed and
accuracy of motor axonal regeneration. J Neurosci. 20:2602–2608.
2000.
|
|
6
|
Alrashdan MS, Park JC, Sung MA, et al:
Thirty minutes of low intensity electrical stimulation promotes
nerve regeneration after sciatic nerve crush injury in a rat model.
Acta Neurol Belg. 110:168–179. 2010.
|
|
7
|
Wan L, Xia R and Ding W: Short-term
low-frequency electrical stimulation enhanced remyelination of
injured peripheral nerves by inducing the promyelination effect of
brain-derived neurotrophic factor on Schwann cell polarization. J
Neurosci Res. 88:2578–2587. 2010.
|
|
8
|
Al-Majed AA, Tam SL and Gordon T:
Electrical stimulation accelerates and enhances expression of
regeneration-associated genes in regenerating rat femoral
motoneurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 24:397–402. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Geremia NM, Gordon T, Brushart TM,
Al-Majed AA and Verge VM: Electrical stimulation promotes sensory
neuron regeneration and growth-associated gene expression. Exp
Neurol. 205:347–359. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
English AW, Schwartz G, Meador W, Sabatier
MJ and Mulligan A: Electrical stimulation promotes peripheral axon
regeneration by enhanced neuronal neurotrophin signaling. Dev
Neurobiol. 67:158–172. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Alrashdan MS, Sung MA, Kwon YK, Chung HJ,
Kim SJ and Lee JH: Effects of combining electrical stimulation with
BDNF gene transfer on the regeneration of crushed rat sciatic
nerve. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 153:2021–2029. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yeh CC, Lin YC, Tsai FJ, Huang CY, Yao CH
and Chen YS: Timing of applying electrical stimulation is an
important factor deciding the success rate and maturity of
regenerating rat sciatic nerves. Neurorehabil Neural Repair.
24:730–735. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ahlborn P, Schachner M and Irintchev A:
One hour electrical stimulation accelerates functional recovery
after femoral nerve repair. Exp Neurol. 208:137–144. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Asensio-Pinilla E, Udina E, Jaramillo J
and Navarro X: Electrical stimulation combined with exercise
increase axonal regeneration after peripheral nerve injury. Exp
Neurol. 219:258–265. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vivó M, Puigdemasa A, Casals L, Asensio E,
Udina E and Navarro X: Immediate electrical stimulation enhances
regeneration and reinnervation and modulates spinal plastic changes
after sciatic nerve injury and repair. Exp Neurol. 211:180–193.
2008.
|
|
16
|
Huang J, Lu L, Hu X, et al: Electrical
stimulation accelerates motor functional recovery in the rat model
of 15-mm sciatic nerve gap bridged by scaffolds with longitudinally
oriented microchannels. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 24:736–745.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yao CH, Chang RL, Chang SL, Tsai CC, Tsai
FJ and Chen YS: Electrical stimulation improves peripheral nerve
regeneration in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Trauma
Acute Care Surg. 72:199–205. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Baptista AF, Gomes JR, Oliveira JT, Santos
SM, Vannier-Santos MA and Martinez AM: High- and low-frequency
transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation delay sciatic nerve
regeneration after crush lesion in the mouse. J Peripher Nerv Syst.
13:71–80. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gigo-Benato D, Russo TL, Geuna S,
Domingues NR, Salvini TF and Parizotto NA: Electrical stimulation
impairs early functional recovery and accentuates skeletal muscle
atrophy after sciatic nerve crush injury in rats. Muscle Nerve.
41:685–693. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hamilton SK, Hinkle ML, Nicolini J, et al:
Misdirection of regenerating axons and functional recovery
following sciatic nerve injury in rats. J Comp Neurol. 519:21–33.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu MC, Ho CY, Hsu SF, Lee HC, Lin JH, Yao
CH and Chen YS: Effects of electrical stimulation at different
frequencies on regeneration of transected peripheral nerve.
Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 22:367–373. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li FQ, Fowler KA, Neil JE, Colton CA and
Vitek MP: An apolipoprotein E-mimetic stimulates axonal
regeneration and remyelination after peripheral nerve injury. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 334:106–115. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Beer GM, Steurer J and Meyer VE:
Standardizing nerve crushes with a non-serrated clamp. J Reconstr
Microsurg. 17:531–534. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bain JR, Mackinnon SE and Hunter DA:
Functional evaluation of complete sciatic, peroneal, and posterior
tibial nerve lesions in the rat. Plast Reconstr Surg. 83:129–138.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao L and Zheng Y: Correlation and
toxicological significance between myelin protein zero and
peripheral nerve disease. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 39:635–638. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Shen D, Zhang Q, Gao X, Gu X and Ding F:
Age-related changes in myelin morphology, electrophysiological
property and myelin-associated protein expression of mouse sciatic
nerves. Neurosci Lett. 502:162–167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Mirsky R, Jessen KR, Brennan A, et al:
Schwann cells as regulators of nerve development. J Physiol Paris.
96:17–24. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|