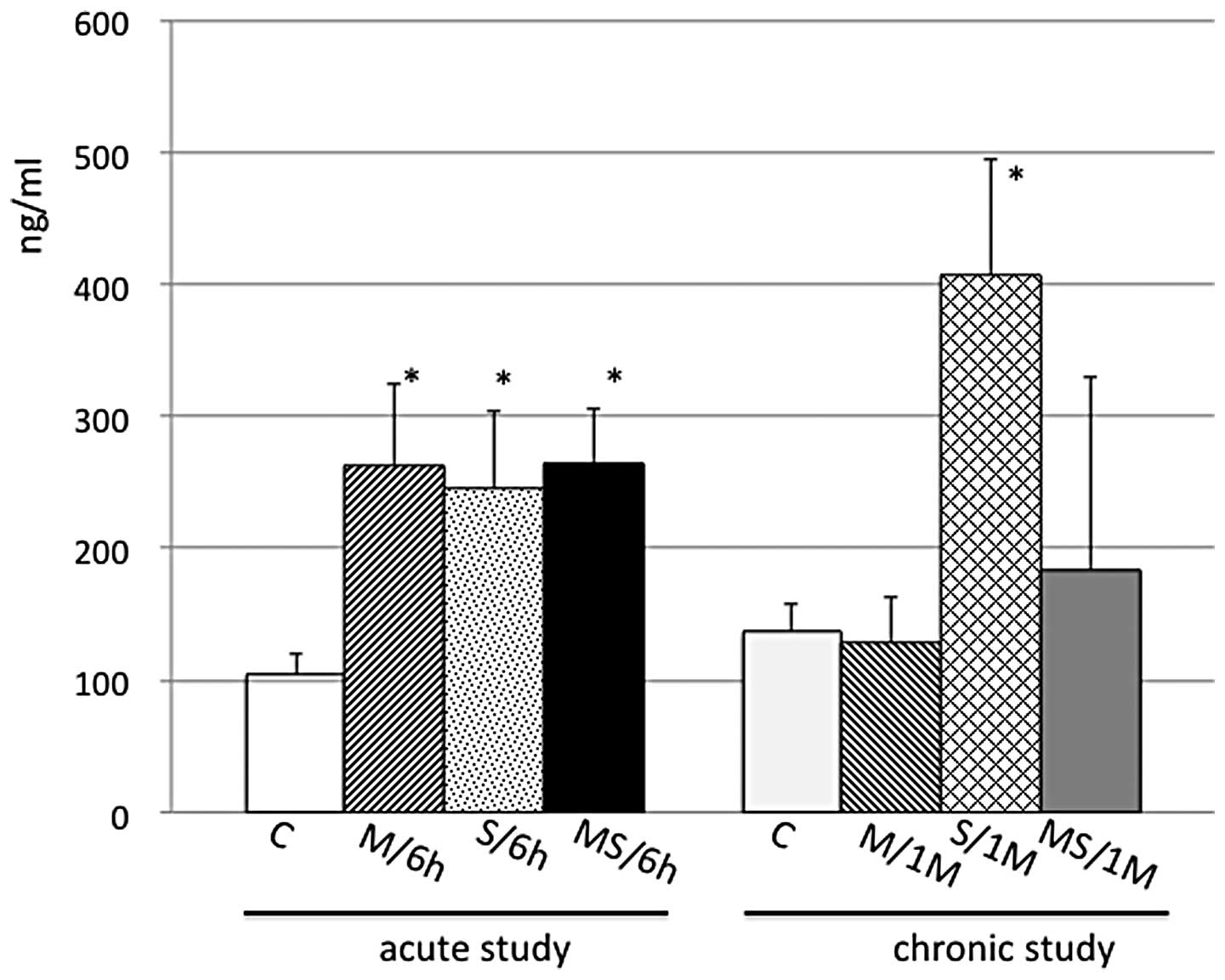
|
1
|
Brecht ML, von Mayrhauser C and Anglin MD:
Predictors of relapse after treatment for methamphetamine use. J
Psychoactive Drugs. 32:211–220. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Comer SD, Hart CL, Ward AS, Haney M,
Foltin RW and Fischman MW: Effects of repeated oral methamphetamine
administration in humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 155:397–404.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wada K: The history and current state of
drug abuse in Japan. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1216:62–72. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Saito T, Takeichi S, Nakajima Y, Yukawa N
and Osawa M: Fatal methamphetamine poisoning in police custody. J
Clin Forensic Med. 3:183–185. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Inoue H, Ikeda N, Kudo K, Ishida T, Terada
M and Matoba R: Methamphetamine-related sudden death with a
concentration which was of a ‘toxic level’. Leg Med (Tokyo).
8:150–155. 2006.
|
|
6
|
Wijetunga M, Seto T, Lindsay J and Schatz
I: Crystal methamphetamine-associated cardiomyopathy: tip of the
iceberg? J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 41:981–986. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tsigos C and Chrousos GP:
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, neuroendocrine factors and
stress. J Psychosom Res. 53:865–871. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miller GE, Chen E and Zhou ES: If it goes
up, must it come down? Chronic stress and the
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis in humans. Psychol Bull.
133:25–45. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kishi T: Heart failure as an autonomic
nervous system dysfunction. J Cardiology. 59:117–122. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pickering TG: Does psychological stress
contribute to the development of hypertension and coronary heart
disease? Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 39(Suppl 1): S1–S7. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tidey JW and Miczek KA: Acquisition of
cocaine self-administration after social stress: role of accumbens
dopamine. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 130:203–212. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Piazza PV and Le Moal M: The role of
stress in drug self-administration. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 19:67–74.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Perkins KA and Grobe JE: Increased desire
to smoke during acute stress. Br J Addict. 87:1037–1040. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sinha R: How does stress increase risk of
drug abuse and relapse? Psychopharmacology (Berl). 158:343–359.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sinha R, Catapano D and O’Malley S:
Stress-induced craving and stress response in cocaine dependent
individuals. Psycho- pharmacology (Berl). 142:343–351. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao LY, Shi J, Zhang XL and Lu L:
Psychosocial stress enhances non-drug-related positive memory
retrieval in male abstinent heroin addicts. Neurosci Lett.
485:16–20. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Söderpalm AH, Nikolayev L and de Wit H:
Effects of stress on responses to methamphetamine in humans.
Psychopharmacology (Berl). 170:188–199. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stratton SJ, Rogers C, Brickett K and
Gruzinski G: Factors associated with sudden death of individuals
requiring restraint for excited delirium. Am J Emerg Med.
19:187–191. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Uemura K, Ueyama T, Shintani-Ishida K,
Unuma K and Yoshida K: An autopsy report on four sudden cardiac
death cases by immobilization. Int Med J. 15:301–305. 2008.
|
|
20
|
Tomita M, Katsuyama H, Watanabe Y, et al:
Water-restraint stress enhances methamphetamine-induced
cardiotoxicity. Chem Biol Interact. 190:54–61. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ikeda U, Ohkawa F, Seino Y, et al: Serum
interleukin 6 levels become elevated in acute myocardial
infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 24:579–84. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jirik FR, Podor TJ, Hirano T, et al:
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide and inflammatory mediators augment
IL-6 secretion by human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 142:144–147.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yamauchi-Takihara K, Ihara Y, Ogata A,
Yoshizaki K, Azuma J and Kishimoto T: Hypoxic stress induces
cardiac myocyte-derived interleukin-6. Circulation. 91:1520–1524.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kang YJ: The antioxidant function of
metallothionein in the heart. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 222:263–273.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nath R, Kumar D, Li T and Singal PK:
Metallothioneins, oxidative stress and the cardiovascular system.
Toxicology. 155:17–26. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Canton M, Menazza S, Sheeran FL, Polverino
de Laureto P, Di Lisa F and Pepe SP: Oxidation of myofibrillar
proteins in human heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 57:300–309.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jung F, Palmer LA, Zhou N and Johns RA:
Hypoxic regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase via hypoxia
inducible factor-1 in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res. 86:319–325. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rus A, del Moral ML, Molina F and Peinado
MA: Does inducible NOS have a protective role against
hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in rat heart ? Cardiovasc Pathol.
20:e17–e25. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miguel-Carrasco JL, Zambrano S, Blanca AJ,
et al: Captopril reduces cardiac inflammatory markers in
spontaneously hypertensive rats by inactivation of NF-kB. J Inflamm
(Lond). 7:212010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Katragadda S and Arora RR: Role of
angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in vascular modulation:
beyond the hypertensive effects. Am J Ther. 17:e11–e23. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chan EC, Dusting GJ, Guo N, et al:
Prostacyclin receptor suppresses cardiac fibrosis: role of CREB
phosphorylation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 49:176–185. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maulik N, Engelman RM, Rousou JA, Flack JE
III, Deaton D and Das DK: Ischemic preconditioning reduces
apoptosis by upregulating anti-death gene Bcl-2. Circulation.
100(19 Suppl): II369–II375. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu S, Storey JM and Storey KB:
Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 expression responds to freezing, anoxia,
and dehydration stresses in the freeze tolerant wood frog, Rana
sylvatica. J Exp Zool A Ecol Genet Physiol. 311:57–67. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang XC, Tall AR, Qin S, et al:
Phospholipid transfer protein deficiency protects circulating
lipoproteins from oxidation due to the enhanced accumulation of
vitamin E. J Biol Chem. 277:31850–31856. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cavusoglu E, Marmur JD, Chhabraa S,
Choprab V, Eng C and Jiangc XC: Relation of baseline plasma
phospholipid transfer protein (PLTP) activity to left ventricular
systolic dysfunction in patients referred for coronary angiography.
Atherosclerosis. 207:261–265. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|