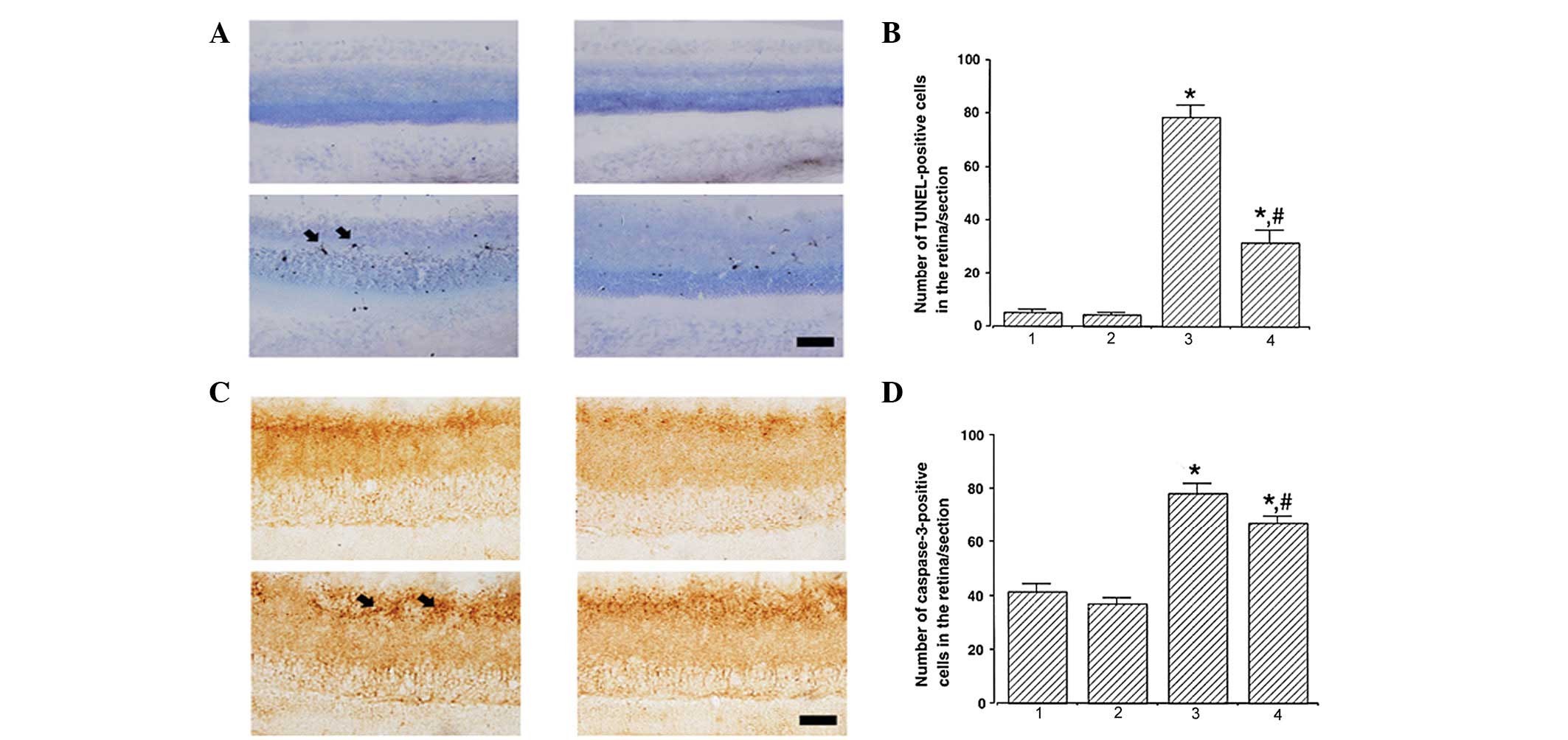
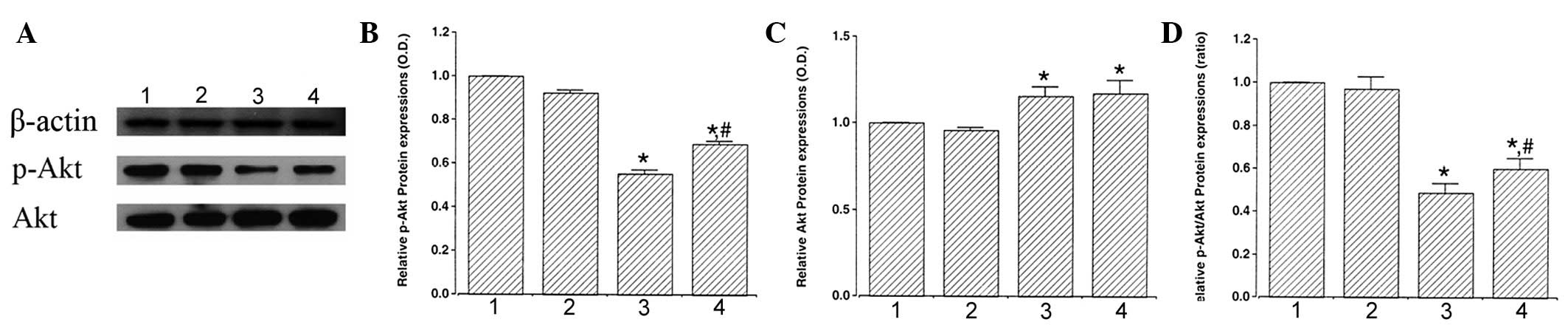
|
1
|
Tang J, Mohr S, Du YD and Kern TS:
Non-uniform distribution of lesions and biochemical abnormalities
within the retina of diabetic humans. Curr Eye Res. 27:7–13. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim DH, Ko IG, Kim BK, Kim TW, Kim SE,
Shin MS, Kim CJ, Kim H, Kim KM and Baek SS: Treadmill exercise
inhibits traumatic brain injury-induced hippocampal apoptosis.
Physiol Behav. 101:660–665. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee HH, Shin MS, Kim YS, Yang HY, Chang
HK, Lee TH, Kim CJ, Cho S and Hong SP: Early treadmill exercise
decreases intrastriatal hemorrhage-induced neuronal cell death and
increases cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus of
streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemic rats. J Diabetes
Complications. 19:356–360. 2005.
|
|
4
|
Santiago AR, Cristóvão AJ, Santos PF,
Carvalho CM and Ambrósio AF: High glucose induces
caspase-independent cell death in retinal neural cells. Neurobiol
Dis. 25:464–472. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abu El-Asrar AM, Dralands L, Missotten L
and Geboes K: Expression of antiapoptotic and proapoptotic
molecules in diabetic retinas. Eye (Lond). 21:238–245.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Busik JV, Mohr S and Grant MB:
Hyperglycemia-induced reactive oxygen species toxicity to
endothelial cells is dependent on paracrine mediators. Diabetes.
57:1952–1965. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gao XY, Kuang HY, Zou W, Liu XM, Lin HB
and Yang Y: The timing of re-institution of good blood glucose
control affects apoptosis and expression of Bax and Bcl-2 in the
retina of diabetic rats. Mol Biol Rep. 36:1977–1982. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Barber AJ, Antonetti DA, Kern TS, Reiter
CE, Soans RS, Krady JK, Levison SW, Gardner TW and Bronson SK: The
Ins2Akita mouse as a model of early retinal complications in
diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 46:2210–2218. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Martin PM, Roon P, Van TK, Ganapathy V and
Smith SB: Death of retinal neurons in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 45:3330–3336. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Behl Y, Krothapalli P, Desta T, DiPiazza
A, Roy S and Graves DT: Diabetes enhanced tumor necrosis factor-α
production promotes apoptosis and the loss of retinal microvascular
cells in type 1 and type 2 models of diabetic retinopathy. Am J
Pathol. 172:1411–1418. 2008.
|
|
11
|
Abu El-Asrar AM, Dralands L, Missotten L,
Jadaan IA and Geboes K: Expression of apoptosis markers in the
retinas of human subjects with diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
45:2760–2766. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Antonsson B, Montessuit S, Sanchez B and
Martinou JC: Bax is present as a high molecular weight
oligomer/complex in the mitochondrial membrane of apoptotic cells.
J Biol Chem. 276:11615–11623. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dejean LM, Martinez-Caballero S, Guo L,
Hughes C, Teijido O, Ducret T, Ichas F, Korsmeyer SJ, Antonsson B,
Jonas EA and Kinnally KW: Oligomeric Bax is a component of the
putative cytochrome c release channel MAC, mitochondrial
apoptosis-induced channel. Mol Biol Cell. 16:2424–2432. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Podestà F, Romeo G, Liu WH, Krajewski S,
Reed JC, Gerhardinger C and Lorenzi M: Bax is increased in the
retina of diabetic subjects and is associated with pericyte
apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Am J Pathol.
156:1025–1032. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mikhailov V, Mikhailova M, Pulkrabek DJ,
Dong Z, Venkatachalam MA and Saikumar P: Bcl-2 prevents Bax
oligomerization in the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Biol Chem.
276:18361–18374. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen
GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S and Reed JC: Regulation of
cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science.
282:1318–1321. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H,
Gotoh Y and Greenberg ME: Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples
survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell.
91:231–241. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brazil DP and Hemmings BA: Ten years of
protein kinase B signalling: a hard Akt to follow. Trends Biochem
Sci. 26:657–664. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakazawa T, Shimura M, Tomita H, Akiyama
H, Yoshioka Y, Kudou H and Tamai M: Intrinsic activation of
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and its neuroprotective effect against
retinal injury. Curr Eye Res. 26:55–63. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Weishaupt JH, Rodhe G, Pölking E, Siren
AL, Ehrenreich H and Bähr M: Effect of erythropoietin
axotomy-induced apoptosis in rat retinal ganglion cells. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 45:1514–1522. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Asa C, Maria S, Katharina SS and Bert A:
Aquatic exercise is effective in improving exercise performance in
patients with heart failure and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:3492092012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kadoglou NP, Vrabas IS, Kapelouzou A,
Lampropoulos S, Sailer N, Kostakis A, Liapis CD and Angelopoulou N:
The impact of aerobic exercise training on novel adipokines, apelin
and ghrelin, in patients with type 2 diabetes. Med Sci Monit.
18:CR290–CR295. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Selaqzi H, Buyukakilli B, Cimen B, Yilmaz
N and Erdogan S: Protective and therapeutic effects of swimming
exercise training on diabetic peripheral neuropathy of
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Endocrinol Invest.
31:971–978. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Derouich M and Boutayeb A: The effect of
physical exercise on the dynamics of glucose and insulin. J
Biomech. 35:911–917. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu G, Keeler BE, Zhukareva V and Houlé
JD: Cycling exercise affects the expression of apoptosis-associated
microRNAs after spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol.
226:200–206. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen J, Miao Y, Wang XH and Wang Z:
Elevation of p-NR2AS1232 by Cdk5/p35 contributes to retinal
ganglion cell apoptosis in a rat experimental glaucoma model.
Neurobiol Dis. 43:455–464. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kielczewski JL, Hu P, Shaw LC, Li Calzi S,
Mames RN, Gardiner TA, McFarland E, Chan-Ling T and Grant MB: Novel
protective properties of IGFBP-3 result in enhanced pericyte
ensheathment, reduced microglial activation, increased microglial
apoptosis and neuronal protection after ischemic retinal injury. Am
J Pathol. 178:1517–1528. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mohr S, Xi X, Tang J and Kern TS: Caspase
activation in retinas of diabetic and galactosemic mice and
diabetic patients. Diabetes. 51:1172–1179. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang KR, Liu HT, Zhang HF, Zhang QJ, Li
QX, Yu QJ, Guo WY, Wang HC and Gao F: Long-term aerobic exercise
protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury via PI3
kinase-dependent and Akt-mediated mechanism. Apoptosis.
12:1579–1588. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oshitari T and Roy S: Diabetes: a
potential enhancer of retinal injury in rat retinas. Neurosci Lett.
390:25–30. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ:
BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev.
13:1899–1911. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nuñez G and del Peso L: Linking
extracellular survival signals and the apoptotic machinery. Curr
Opin Neurobiol. 8:613–618. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J,
Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C and González-Barón M: PI3K/Akt signalling
pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:193–204. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fujita S, Rasmussen BB, Cadenas JG,
Drummond MJ, Glynn EL, Sattler FR and Volpi E: Aerobic exercise
overcomes the age-related insulin resistance of muscle protein
metabolism by improving endothelial function and Akt/mammalian
target of rapamycin signaling. Diabetes. 56:1615–1622. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Aguiar AS Jr, Castro AA, Moreira EL,
Glaser V, Santos AR, Tasca CI, Latini A and Prediger RD: Short
bouts of mild-intensity physical exercise improve spatial learning
and memory in aging rats: involvement of hippocampal plasticity via
AKT, CREB and BDNF signaling. Mech Ageing Dev. 132:560–567. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Um HS, Kang EB, Koo JH, Kim HT, Jin-Lee,
Kim EJ, Yang CH, An GY, Cho IH and Cho JY: Treadmill exercise
represses neuronal cell death in an aged transgenic mouse model of
Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Res. 69:161–173. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Q, Pfister F, Dorn-Beineke A, vom
Hagen F, Lin J, Feng Y and Hammes HP: Low-dose erythropoietin
inhibits oxidative stress and early vascular changes in the
experimental diabetic retina. Diabetologia. 53:1227–1238. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim H, Heo HI, Kim DH, Ko IG, Lee SS, Kim
SE, Kim BK, Kim TW, Ji ES, Kim JD, Shin MS, Choi YW and Kim CJ:
Treadmill exercise and methylphenidate ameliorate symptoms of
attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder through enhancing dopamine
synthesis and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in
spontaneous hypertensive rats. Neurosci Lett. 504:35–39. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sung YH, Kim SC, Hong HP, Park CY, Shin
MS, Kim CJ, Seo JH, Kim DY, Kim DJ and Cho HJ: Treadmill exercise
ameliorates dopaminergic neuronal loss through suppressing
microglial activation in Parkinson’s disease mice. Life Sci.
91:1309–1316. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Seo JH, Kim TW, Kim CJ, Sung YH and Lee
SJ: Treadmill exercise during pregnancy ameliorates post-traumatic
stress disorder-induced anxiety-like responses in maternal rats.
Mol Med Rep. 7:389–395. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|