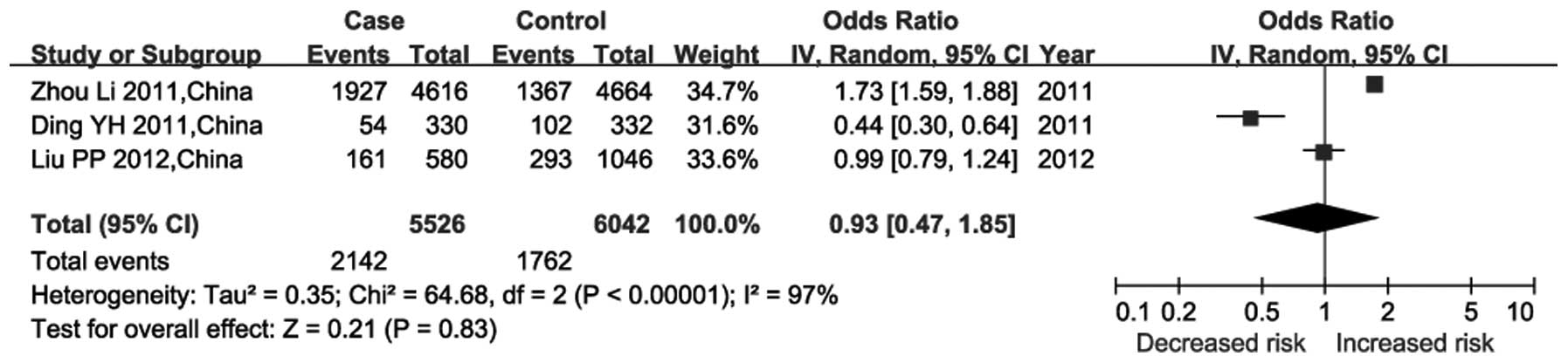
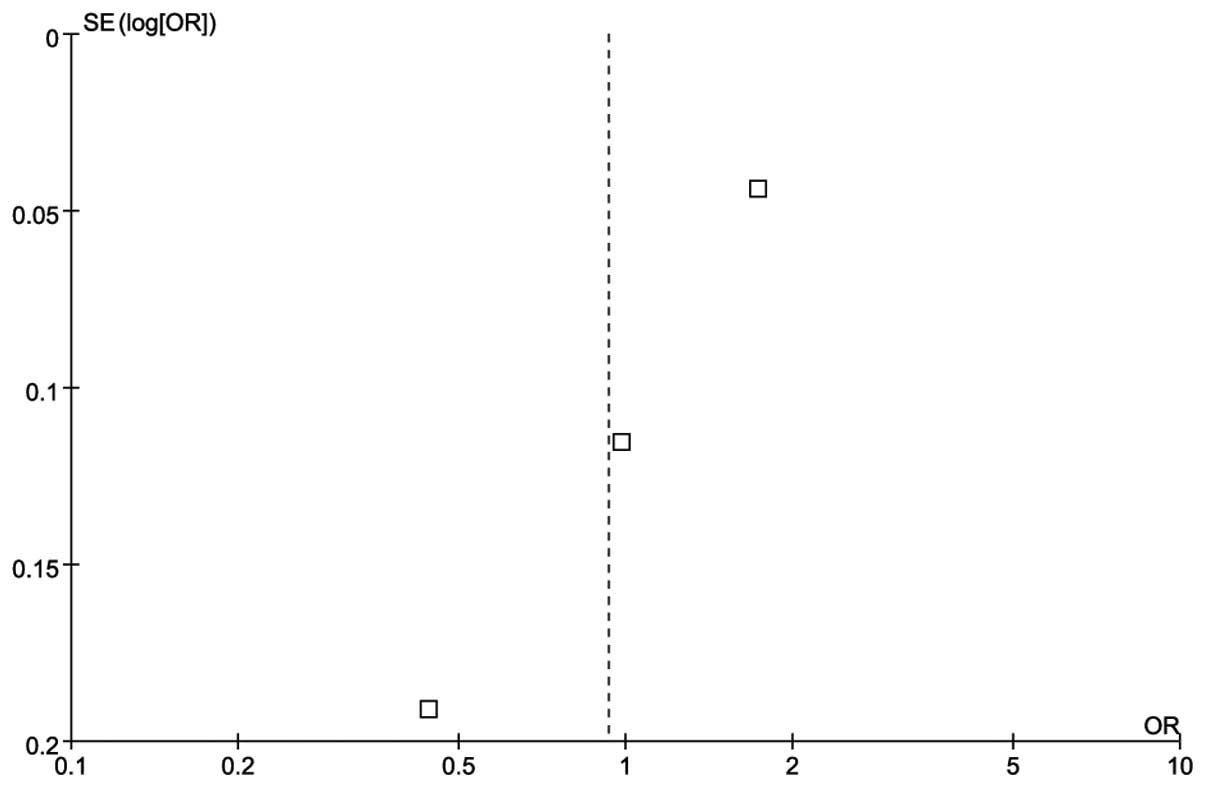
|
1
|
Yu J, Huang J, Liang Y, et al: Lack of
association between apolipoprotein C3 gene polymorphisms and risk
of coronary heart disease in a Han population in East China. Lipids
Health Dis. 10:2002011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sandhu MS, Waterworth DM, Debenham SL, et
al: LDL-cholesterol concentrations: a genome-wide association
study. Lancet. 371:483–491. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baigent C, Keech A, Kearney PM, et al:
Efficacy and safety of cholesterol-lowering treatment: prospective
meta-analysis of data from 90,056 participants in 14 randomised
trials of statins. Lancet. 366:1267–1278. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Willer CJ, Sanna S, Jackson AU, et al:
Newly identified loci that influence lipid concentrations and risk
of coronary artery disease. Nat Genet. 40:161–169. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lettre G, Palmer CD, Young T, et al:
Genome-wide association study of coronary heart disease and its
risk factors in 8,090 African Americans: the NHLBI CARe Project.
PLoS Genet. 7:e10013002011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
St-Pierre AC, Cantin B, Dagenais GR, et
al: Apolipoprotein-B, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and the
long-term risk of coronary heart disease in men. Am J Cardiol.
97:997–1001. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moss AJ, Goldstein RE, Marder VJ, et al:
Thrombogenic factors and recurrent coronary events. Circulation.
99:2517–2522. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Talmud PJ, Hawe E, Miller GJ and Humphries
SE: Nonfasting apolipoprotein B and triglyceride levels as a useful
predictor of coronary heart disease risk in middle-aged UK men.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 22:1918–1923. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Walldius G and Jungner I: The apoB/apoA-I
ratio: a strong, new risk factor for cardiovascular disease and a
target for lipid-lowering therapy - a review of the evidence. J
Intern Med. 259:493–519. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kamstrup PR, Tybjærg-Hansen A and
Nordestgaard BG: Genetic evidence that lipoprotein(a) associates
with atherosclerotic stenosis rather than venous thrombosis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:1732–1741. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Szilágyi S, Péter A, Magyar MT, et al:
Recurrent arterial thrombosis associated with the antithrombin
basel variant and elevated lipoprotein(a) plasma level in an
adolescent patient. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 34:276–279.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Terres W, Tatsis E, Pfalzer B, et al:
Rapid angiographic progression of coronary artery disease in
patients with elevated lipoprotein(a). Circulation. 91:948–950.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Deshmukh HA, Colhoun HM, Johnson T, et al:
Genome-wide association study of genetic determinants of LDL-c
response to atorvastatin therapy: importance of Lp(a). J Lipid Res.
53:1000–1011. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Teslovich TM, Musunuru K, Smith AV, et al:
Biological, clinical and population relevance of 95 loci for blood
lipids. Nature. 466:707–713. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Trégouët DA, König IR, Erdmann J, et al:
Genome-wide haplotype association study identifies the
SLC22A3-LPAL2-LPA gene cluster as a risk locus for coronary artery
disease. Nat Genet. 41:283–285. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Qi L, Ma J, Qi Q, et al: Genetic risk
score and risk of myocardial infarction in Hispanics. Circulation.
123:374–380. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Butterworth AS, Braund PS, Farrall M, et
al; IBC 50K CAD Consortium. Large-scale gene-centric analysis
identifies novel variants for coronary artery disease. PLoS Genet.
7:e10022602011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Peden JF, Hopewell JC, Saleheen D, et al:
Coronary Artery Disease (C4D) Genetics Consortium: A genome-wide
association study in Europeans and South Asians identifies five new
loci for coronary artery disease. Nat Genet. 43:339–344. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Higgs ZC, Macafee DA, Braithwaite BD and
Maxwell-Armstrong CA: The Seldinger technique: 50 years on. Lancet.
366:1407–1409. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Reilly MP, Li M, He J, et al:
Identification of ADAMTS7 as a novel locus for coronary
atherosclerosis and association of ABO with myocardial infarction
in the presence of coronary atherosclerosis: two genome-wide
association studies. Lancet. 377:383–392. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gabriel S, Ziaugra L and Tabbaa D: SNP
genotyping using the Sequenom MassARRAY iPLEX platform. Curr Protoc
Hum Genet. Chapter 2(Unit 2): 122009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Excoffier L and Lischer HE: Arlequin suite
ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics
analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Resour. 10:564–567.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dupont WD and Plummer WD Jr: Power and
sample size calculations. A review and computer program. Control
Clin Trials. 11:116–128. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Emslie C: Women, men and coronary heart
disease: a review of the qualitative literature. J Adv Nurs.
51:382–395. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Robinson JG, Wang S and Jacobson TA:
Meta-analysis of comparison of effectiveness of lowering
apolipoprotein B versus low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and
nonhigh-density lipoprotein cholesterol for cardiovascular risk
reduction in randomized trials. Am J Cardiol. 110:1468–1476. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li S, Lei ZW, Chen Z, et al: Relationship
between apolipoprotein E and apolipoprotein B polymorphisms in
youths with coronary heart disease. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za
Zhi. 20:241–243. 2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Huang G, Zhong H, Re HM, et al: Coalition
of DNA polymorphisms of ApoB and ApoAI genes is related with
coronary artery disease in Kazaks. J Geriatr Cardiol. 9:33–37.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Boffa MB, Marcovina SM and Koschinsky ML:
Lipoprotein(a) as a risk factor for atherosclerosis and thrombosis:
mechanistic insights from animal models. Clin Biochem. 37:333–343.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kamstrup PR: Lipoprotein(a) and ischemic
heart disease - a causal association? A review. Atherosclerosis.
211:15–23. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rath M, Niendorf A, Reblin T, et al:
Detection and quantification of lipoprotein(a) in the arterial wall
of 107 coronary bypass patients. Arteriosclerosis. 9:579–592.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kiechl S and Willeit J: The mysteries of
lipoprotein(a) and cardiovascular disease revisited. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 55:2168–2170. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Clarke R, Peden JF, Hopewell JC, et al;
PROCARDIS Consortium. Genetic variants associated with Lp(a)
lipoprotein level and coronary disease. N Engl J Med.
361:2518–2528. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chasman DI, Shiffman D, Zee RY, et al:
Polymorphism in the apolipoprotein(a) gene, plasma lipoprotein(a),
cardiovascular disease, and low-dose aspirin therapy.
Atherosclerosis. 203:371–376. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Luke MM, Kane JP, Liu DM, et al: A
polymorphism in the protease-like domain of apolipoprotein(a) is
associated with severe coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 27:2030–2036. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schunkert H, König IR, Kathiresan S, et
al: Large-scale association analysis identifies 13 new
susceptibility loci for coronary artery disease. Nat Genet.
43:333–338. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Anderson RA and Sando GN: Cloning and
expression of cDNA encoding human lysosomal acid lipase/cholesteryl
ester hydrolase. Similarities to gastric and lingual lipases. J
Biol Chem. 266:22479–22484. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Anderson RA, Rao N, Byrum RS, et al: In
situ localization of the genetic locus encoding the lysosomal acid
lipase/cholesteryl esterase (LIPA) deficient in Wolman disease to
chromosome 10q23.2-q23.3. Genomics. 15:245–247. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zschenker O, Illies T and Ameis D:
Overexpression of lysosomal acid lipase and other proteins in
atherosclerosis. J Biochem. 140:23–38. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Klima H, Ullrich K, Aslanidis C, et al: A
splice junction mutation causes deletion of a 72-base exon from the
mRNA for lysosomal acid lipase in a patient with cholesteryl ester
storage disease. J Clin Invest. 92:2713–2718. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|