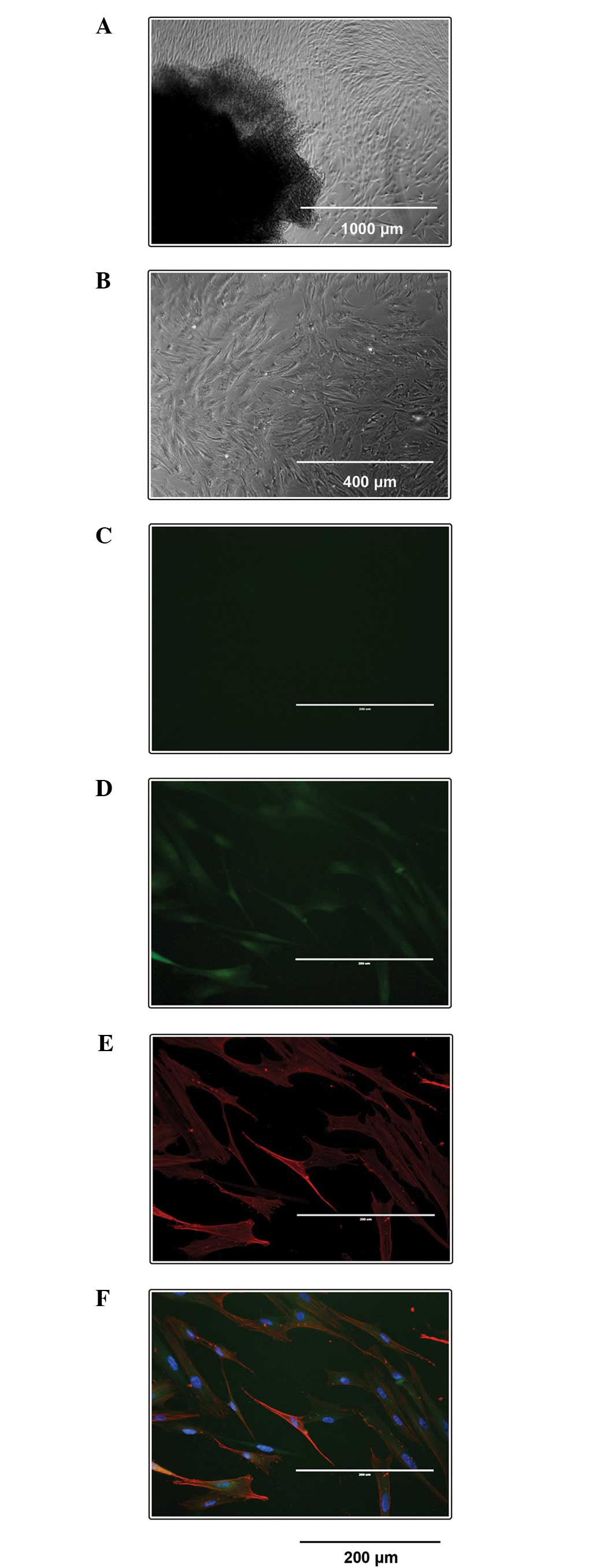
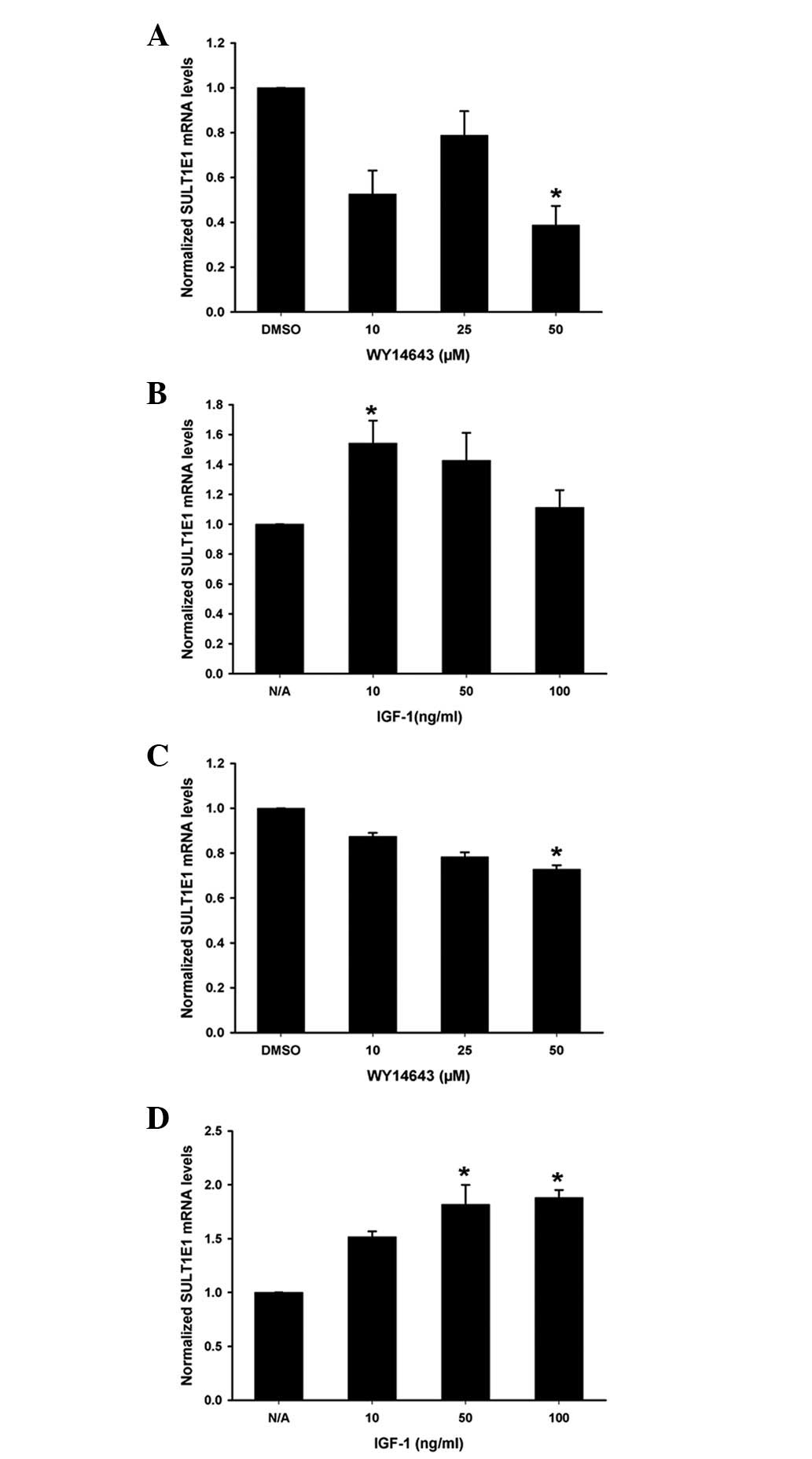
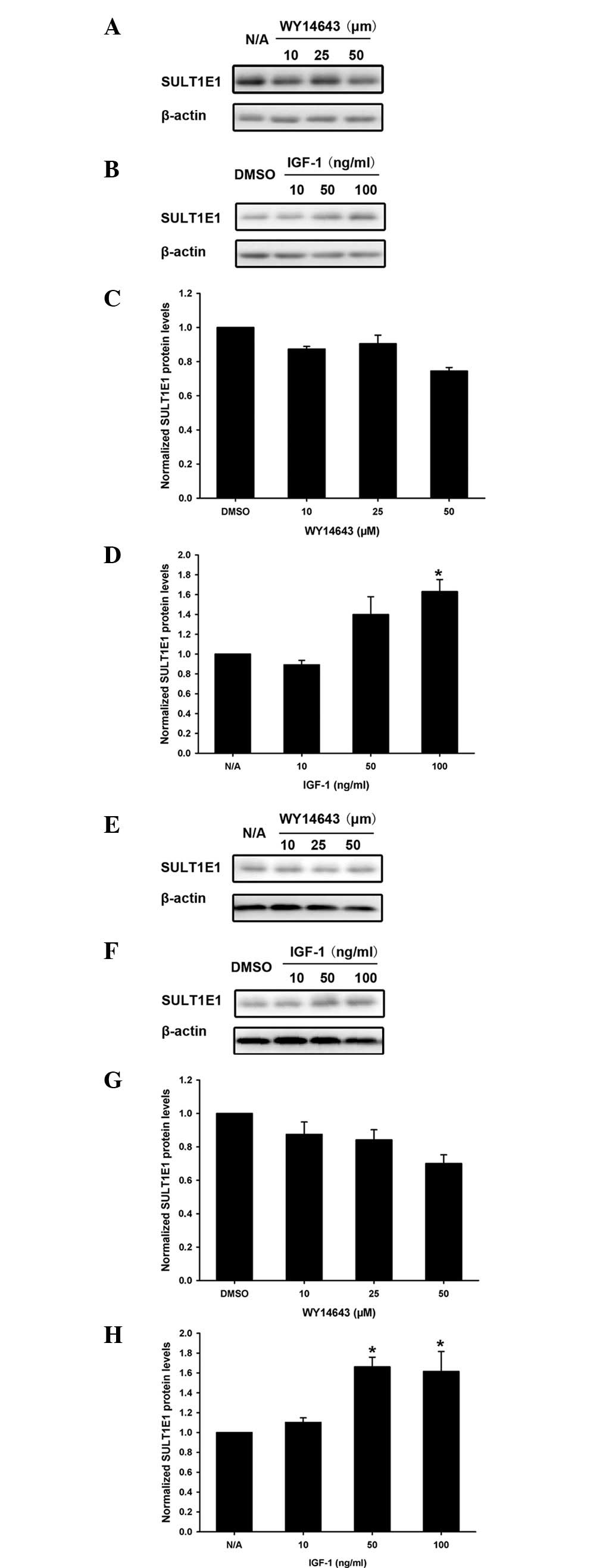
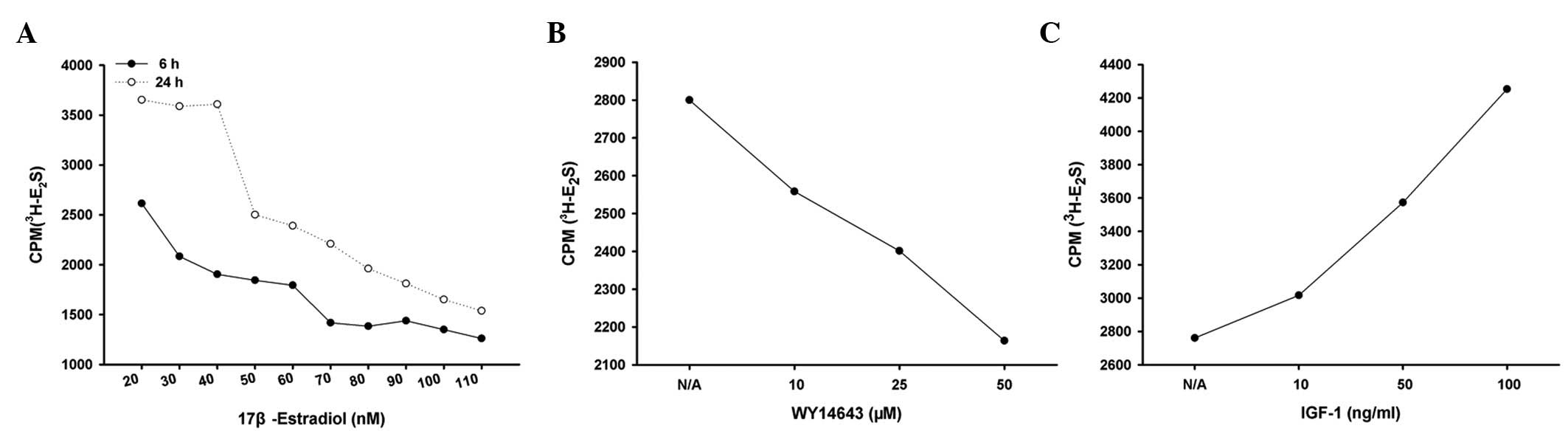
|
1
|
Nofer JR: Estrogens and atherosclerosis:
insights from animal models and cell systems. J Mol Endocrinol.
48:R13–R29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ishibashi H, Suzuki T, Suzuki S, et al:
Estrogen inhibits cell proliferation through in situ production in
human thymoma. Clin Cancer Res. 11:6495–6504. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu Y, Liu X, Guo F, et al: Effect of
estrogen sulfation by SULT1E1 and PAPSS on the development of
estrogen-dependent cancers. Cancer Sci. 103:1000–1009. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tong MH, Jiang H, Liu P, Lawson JA, Brass
LF and Song WC: Spontaneous fetal loss caused by placental
thrombosis in estrogen sulfotransferase-deficient mice. Nat Med.
11:153–159. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wada T, Ihunnah CA, Gao J, et al: Estrogen
sulfotransferase inhibits adipocyte differentiation. Mol
Endocrinol. 25:1612–1623. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gong H, Jarzynka MJ, Cole TJ, et al:
Glucocorticoids antagonize estrogens by glucocorticoid
receptor-mediated activation of estrogen sulfotransferase. Cancer
Res. 68:7386–7393. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kodama S, Hosseinpour F, Goldstein JA and
Negishi M: Liganded pregnane X receptor represses the human
sulfotransferase SULT1E1 promoter through disrupting its chromatin
structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:8392–8403. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fruchart JC: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPARalpha): at the
crossroads of obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Atherosclerosis. 205:1–8. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hennuyer N, Tailleux A, Torpier G, et al:
PPARalpha, but not PPARgamma, activators decrease macrophage-laden
atherosclerotic lesions in a nondiabetic mouse model of mixed
dyslipidemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:1897–1902. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Srivastava RA: Evaluation of
anti-atherosclerotic activities of PPAR-alpha, PPAR-gamma, and LXR
agonists in hyperlipidemic atherosclerosis-susceptible F(1)B
hamsters. Atherosclerosis. 214:86–93. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zahradka P, Yurkova N, Litchie B, Moon MC,
Del Rizzo DF and Taylor CG: Activation of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors alpha and gamma1 inhibits human
smooth muscle cell proliferation. Mol Cell Biochem. 246:105–110.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hamblin M, Chang L, Fan Y, Zhang J and
Chen YE: PPARs and the cardiovascular system. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 11:1415–1452. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Fang HL, Strom SC, Cai H, Falany CN,
Kocarek TA and Runge-Morris M: Regulation of human hepatic
hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase gene expression by the peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor alpha transcription factor. Mol
Pharmacol. 67:1257–1267. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Higashi Y, Sukhanov S, Anwar A, Shai SY
and Delafontaine P: IGF-1, oxidative stress and atheroprotection.
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 21:245–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Higashi Y, Sukhanov S, Anwar A, Shai SY
and Delafontaine P: Aging, atherosclerosis, and IGF-1. J Gerontol A
Biol Sci Med Sci. 67:626–639. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han Y, Qi Y, Kang J, Li N, Tian X and Yan
C: Nerve growth factor promotes formation of lumen-like structures
in vitro through inducing apoptosis in human umbilical vein
endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 366:685–691. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vadiveloo PK, Filonzi EL, Stanton HR and
Hamilton JA: G1 phase arrest of human smooth muscle cells by
heparin, IL-4 and cAMP is linked to repression of cyclin D1 and
cdk2. Atherosclerosis. 133:61–69. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yeong P, Ning Y, Xu Y, Li X and Yin L:
Tryptase promotes human monocyte-derived macrophage foam cell
formation by suppressing LXRalpha activation. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1801:567–576. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang X, Spandidos A, Wang H and Seed B:
PrimerBank: a PCR primer database for quantitative gene expression
analysis, 2012 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:D1144–D1149. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kushida A, Hattori K, Yamaguchi N,
Kobayashi T, Date A and Tamura H: Sulfation of estradiol in human
epidermal keratinocyte. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:1147–1151. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu Y, Yang X, Wang Z, et al: Estrogen
sulfotransferase (SULT1E1) regulates inflammatory response and
lipid metabolism of human endothelial cells via PPARgamma. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 369:140–149. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lalloyer F, Wouters K, Baron M, et al:
Peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptor-alpha gene level
differently affects lipid metabolism and inflammation in
apolipoprotein E2 knock-in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
31:1573–1579. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chinetti G, Lestavel S, Bocher V, et al:
PPAR-alpha and PPAR-gamma activators induce cholesterol removal
from human macrophage foam cells through stimulation of the ABCA1
pathway. Nat Med. 7:53–58. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gizard F, Nomiyama T, Zhao Y, et al: The
PPARalpha/p16INK4a pathway inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation by repressing cell cycle-dependent telomerase
activation. Circ Res. 103:1155–1163. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Plutzky J: The PPAR-RXR transcriptional
complex in the vasculature: energy in the balance. Circ Res.
108:1002–1016. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zoete V, Grosdidier A and Michielin O:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor structures: ligand
specificity, molecular switch and interactions with regulators.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1771:915–925. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sukhanov S, Higashi Y, Shai SY, et al:
Differential requirement for nitric oxide in IGF-1-induced
anti-apoptotic, anti-oxidant and anti-atherosclerotic effects. FEBS
Lett. 585:3065–3072. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang J, Razuvaev A, Folkersen L, et al:
The expression of IGFs and IGF binding proteins in human carotid
atherosclerosis, and the possible role of IGF binding protein-1 in
the regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation.
Atherosclerosis. 220:102–109. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Delafontaine P, Song YH and Li Y:
Expression, regulation, and function of IGF-1, IGF-1R, and IGF-1
binding proteins in blood vessels. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
24:435–444. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|