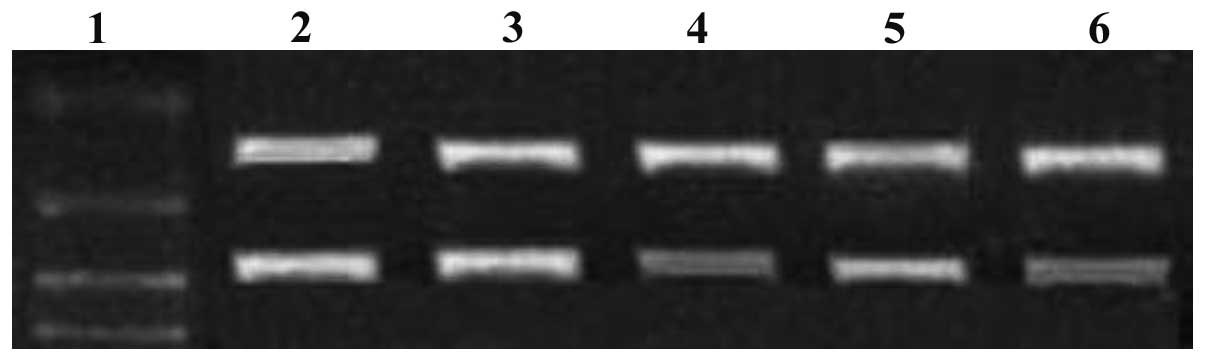
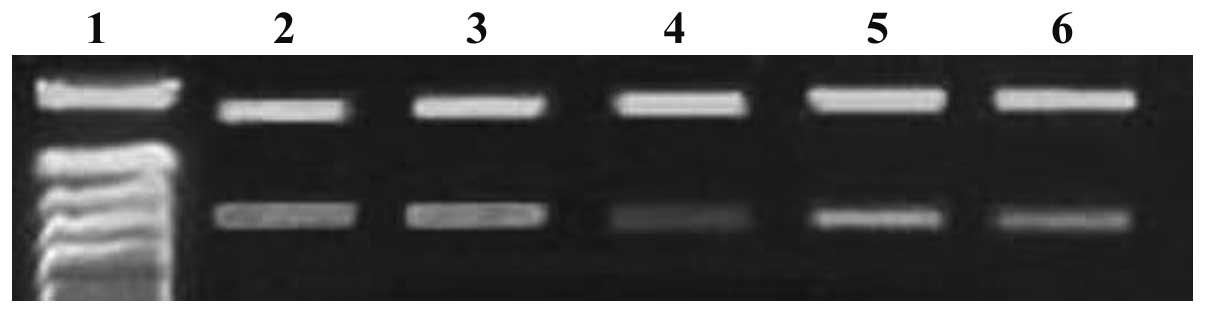
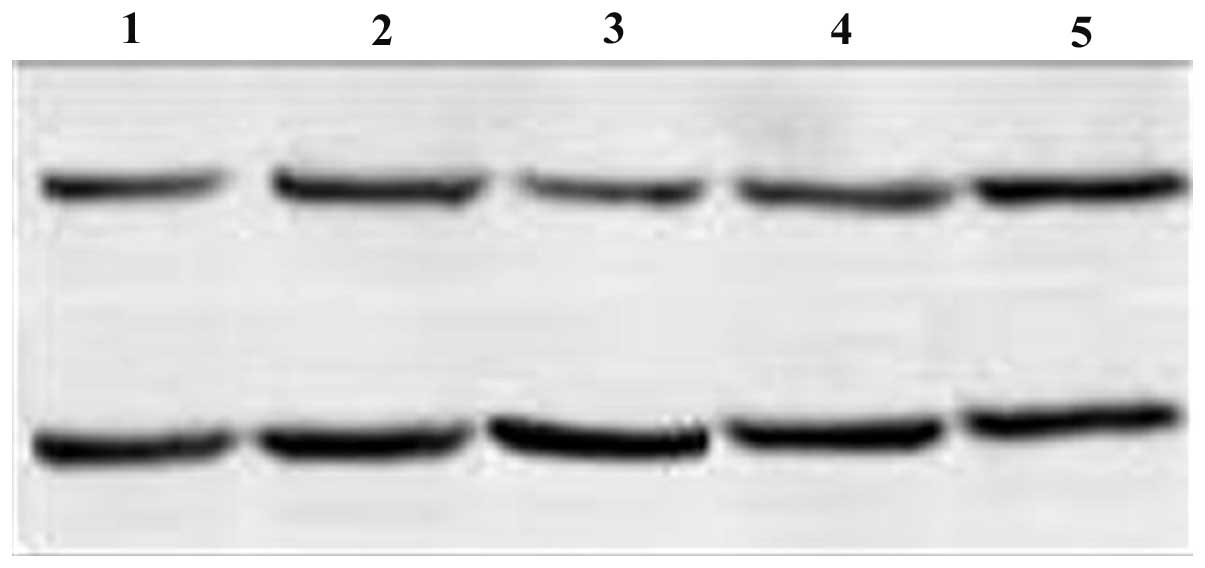
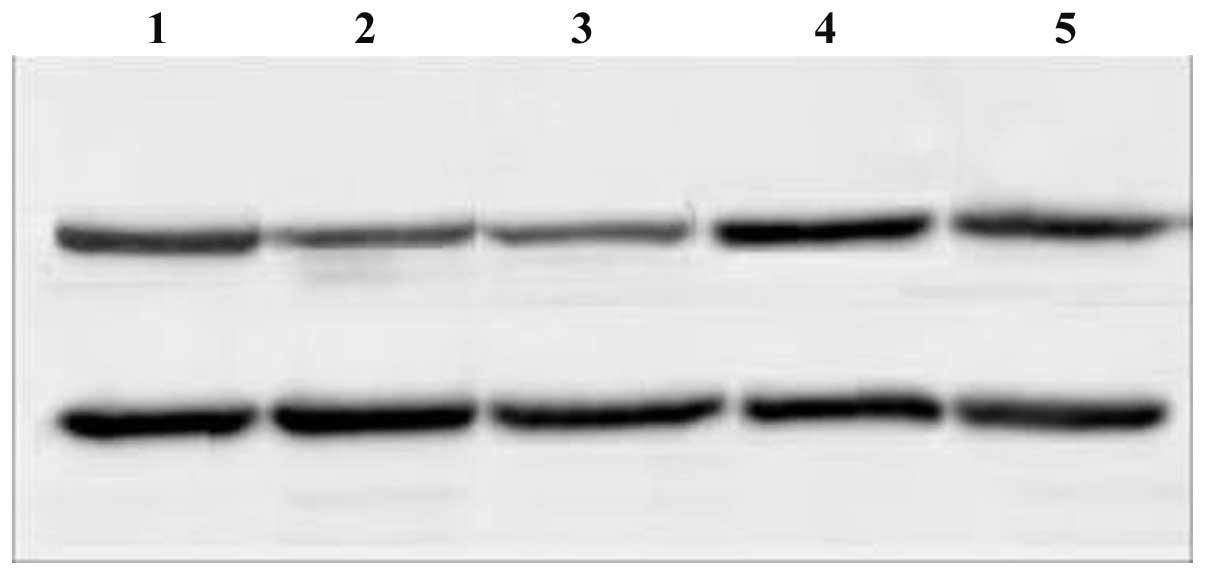
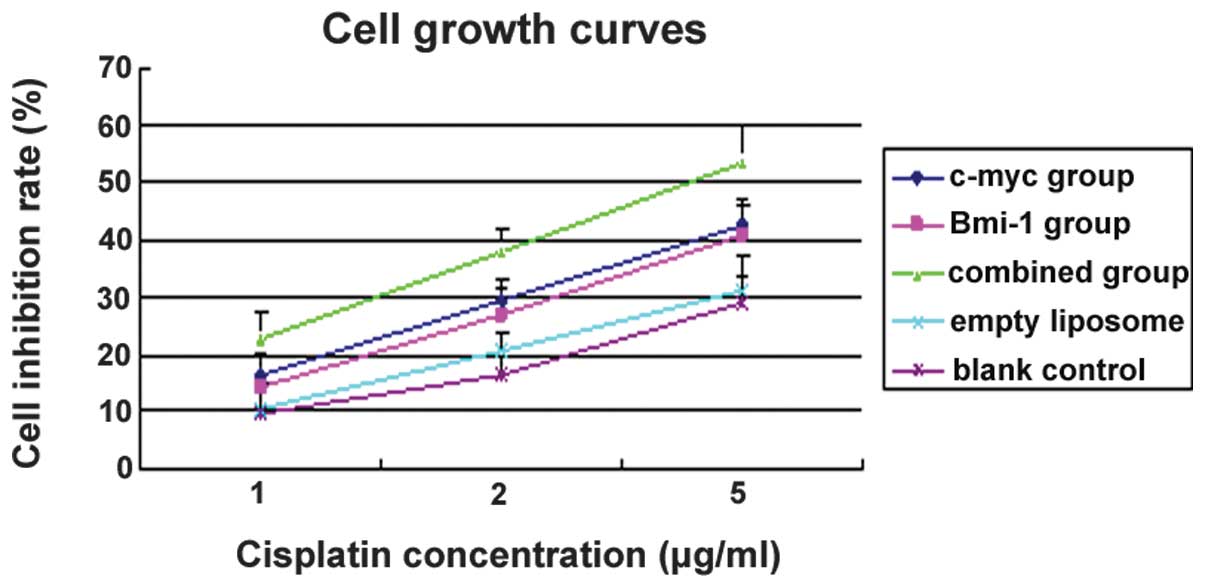
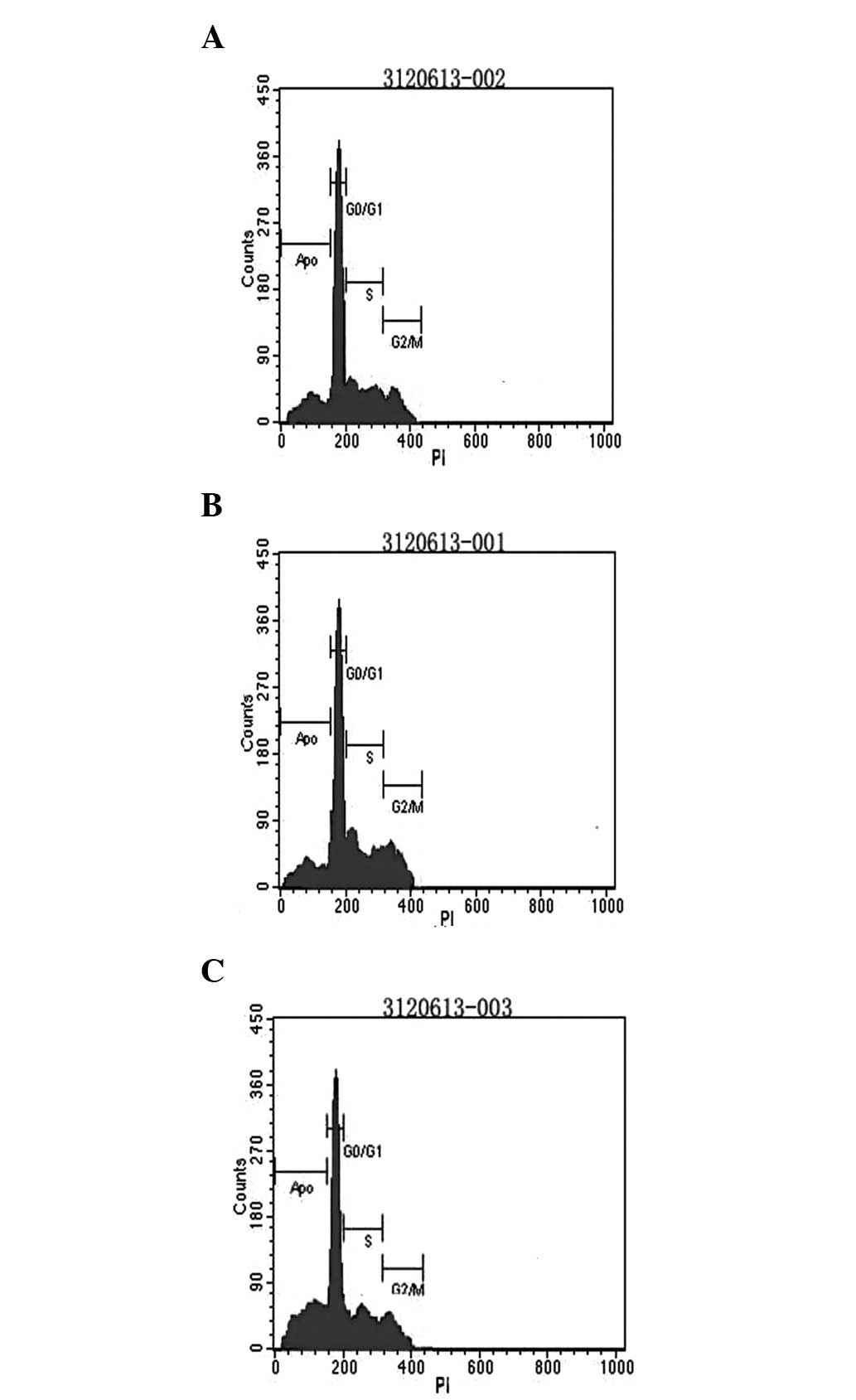
|
1
|
Poletajew S, Fus L and Wasiutyński A:
Current concepts on pathogenesis and biology of metastatic
osteosarcoma tumors. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 13:537–545. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bernthal NM, Federman N, Eilber FR, Nelson
SD, Eckardt JJ, Eilber FC and Tap WD: Long-term results (>25
years) of a randomized, prospective clinical trial evaluating
chemotherapy in patients with high-grade, operable osteosarcoma.
Cancer. 118:5888–5893. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Broadhead ML, Clark JC, Myers DE, Dass CR
and Choong PF: The molecular pathogenesis of osteosarcoma: a
review. Sarcoma. 2011:9592482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dang CV: MYC on the path to cancer. Cell.
149:22–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hattinger CM, Stoico G, Michelacci F,
Pasello M, Scionti I, Remondini D, Castellani GC, Fanelli M,
Scotlandi K, Picci P and Serra M: Mechanisms of gene amplification
and evidence of coamplification in drug-resistant human
osteosarcoma cell lines. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 48:289–309.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Godlewski J, Nowicki MO, Bronisz A,
Williams S, Otsuki A, Nuovo G, Raychaudhury A, Newton HB, Chiocca
EA and Lawler S: Targeting of the Bmi-1 oncogene/stem cell renewal
factor by microRNA-128 inhibits glioma proliferation and
self-renewal. Cancer Res. 68:9125–9130. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jagani Z, Wiederschain D, Loo A, He D,
Mosher R, Fordjour P, Monahan J, Morrissey M, Yao YM, Lengauer C,
Warmuth M, Sellers WR and Dorsch M: The Polycomb group protein
Bmi-1 is essential for the growth of multiple myeloma cells. Cancer
Res. 70:5528–5538. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Douglas D, Hsu JH, Hung L, Cooper A,
Abdueva D, van Doorninck J, Peng G, Shimada H, Triche TJ and Lawlor
ER: BMI-1 promotes ewing sarcoma tumorigenicity independent of
CDKN2A repression. Cancer Res. 68:6507–6515. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Savage KJ, Johnson NA, Ben-Neriah S,
Connors JM, Sehn LH, Farinha P, Horsman DE and Gascoyne RD: MYC
gene rearrangements are associated with a poor prognosis in diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP chemotherapy.
Blood. 114:3533–3537. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qin L, Zhang X, Zhang L, Feng Y, Weng GX,
Li MZ, Kong QL, Qian CN, Zeng YX, Zeng MS, Liao DF and Song LB:
Downregulation of BMI-1 enhances 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
371:531–535. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Scionti I, Michelacci F, Pasello M,
Hattinger CM, Alberghini M, Manara MC, Bacci G, Ferrari S,
Scotlandi K, Picci P and Serra M: Clinical impact of the
methotrexate resistance-associated genes C-MYC and dihydrofolate
reductase (DHFR) in high-grade osteosarcoma. Ann Oncol.
19:1500–1508. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wu Z, Min L, Chen D, Hao D, Duan Y, Qiu G
and Wang Y: Overexpression of BMI-1 promotes cell growth and
resistance to cisplatin treatment in osteosarcoma. PLoS One.
6:e146482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xie XK, Yang DS, Ye ZM and Tao HM:
Enhancement effect of adenovirus mediated antisense C-myc and
caffeine on the cytotoxicity of cisplatin in osteosarcoma cell
lines. Chemotherapy. 55:433–440. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lonning PE: Molecular basis for therapy
resistance. Mol Oncol. 4:284–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li YT, Chua MJ, Kunnath AP and Chowdhury
EH: Reversing multidrug resistance in breast cancer cells by
silencing ABC transporter genes with nanoparticle-facilitated
delivery of target siRNAs. Int J Nanomedicine. 7:2473–2481.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guney I, Wu S and Sedivy JM: Reduced c-Myc
signaling triggers telomere- independent senescence by regulating
Bmi-1 and p16INK4a. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:3645–3650. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qin L, Zhang X, Zhang L, Feng Y, Weng GX,
Li MZ, Kong QL, Qian CN, Zeng YX, Zeng MS, Liao DF and Song LB:
Downregulation of BMI-1 enhances 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
371:531–535. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guney I and Sedivy JM: Cellular
senescence, epigenetic switches and c-Myc. Cell Cycle. 5:2319–2323.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lüscher B and Vervoorts J: Regulation of
gene transcription by the oncoprotein MYC. Gene. 494:145–160.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jain M, Arvanitis C, Chu K, Dewey W,
Leonhardt E, Trinh M, Sundberg CD, Bishop JM and Felsher DW:
Sustained loss of a neoplastic phenotype by brief inactivation of
MYC. Science. 297:102–104. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu YL, Jiang SX, Yang YM, Xu H, Liu JL
and Wang XS: USP22 acts as an oncogene by the activation of
BMI-1-mediated INK4a/ARF pathway and Akt pathway. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 62:229–235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Datta S, Hoenerhoff MJ, Bommi P, Sainger
R, Guo WJ, Dimri M, Band H, Band V, Green JE and Dimri GP: Bmi-1
cooperates with H-Ras to transform human mammary epithelial cells
via dysregulation of multiple growth-regulatory pathways. Cancer
Res. 67:10286–10295. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|