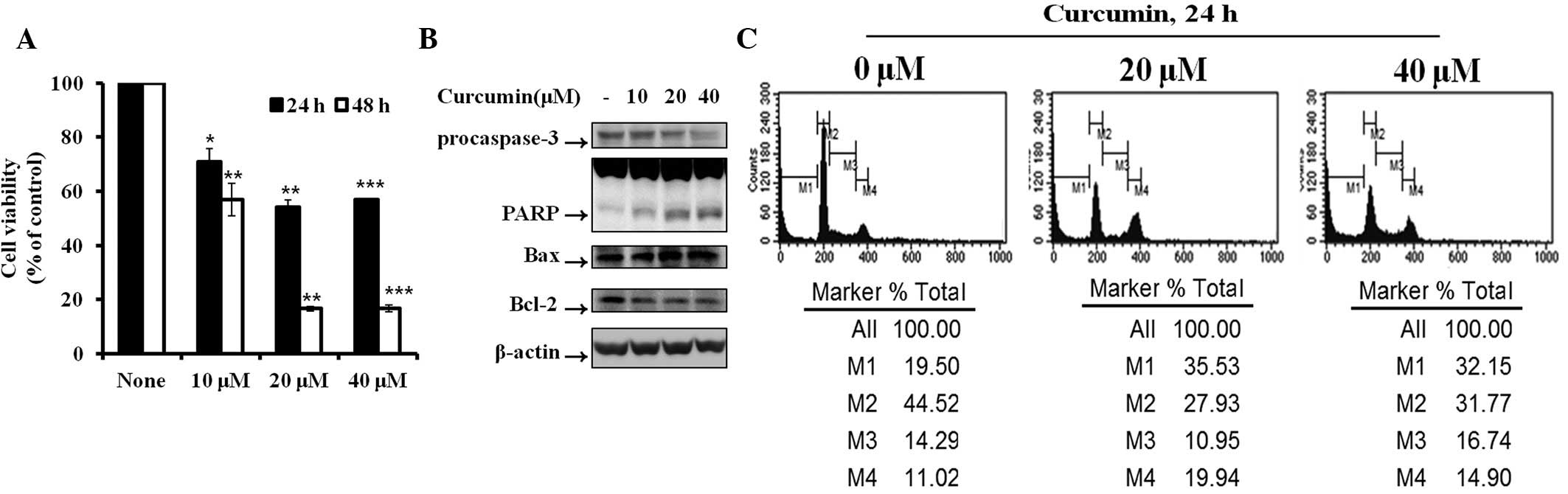
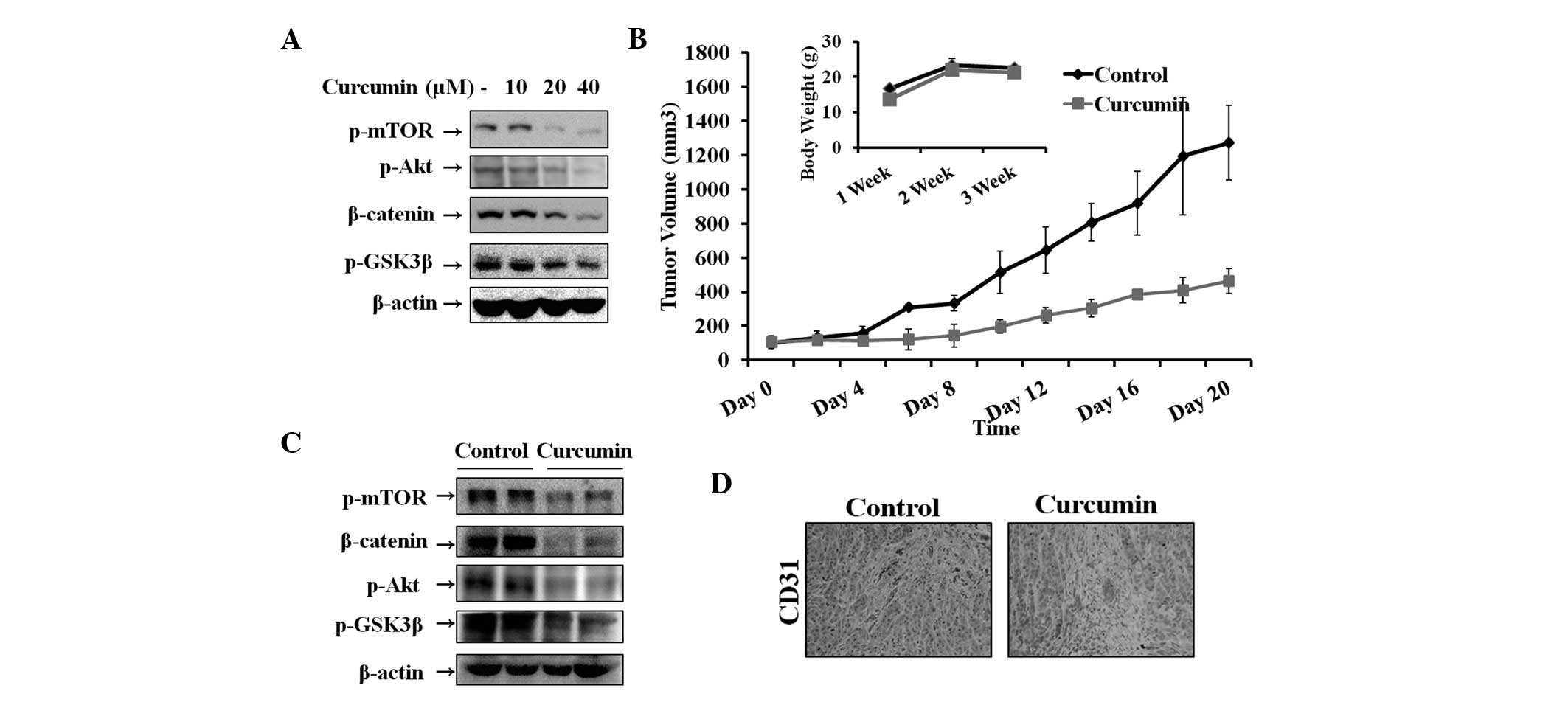
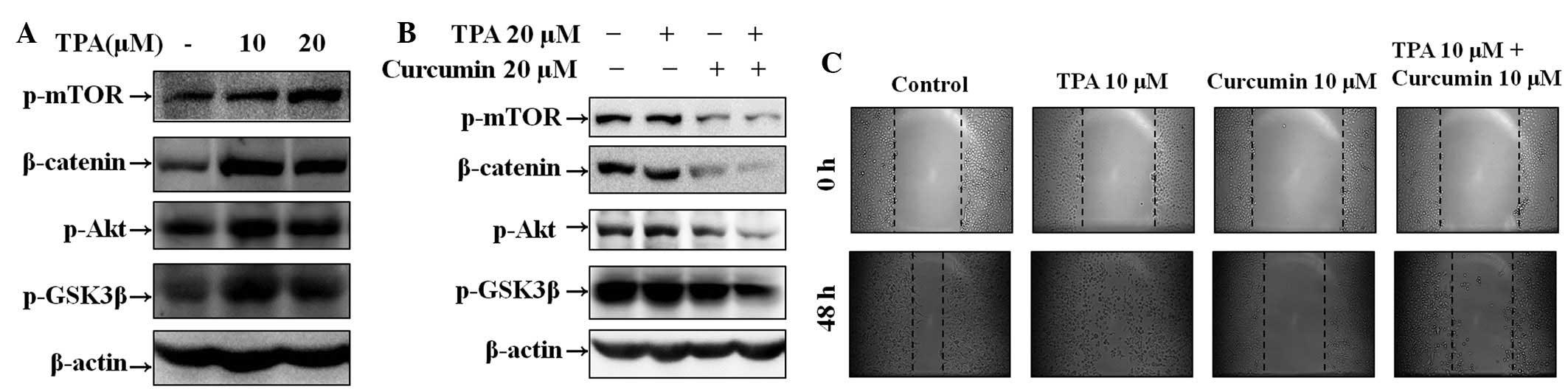
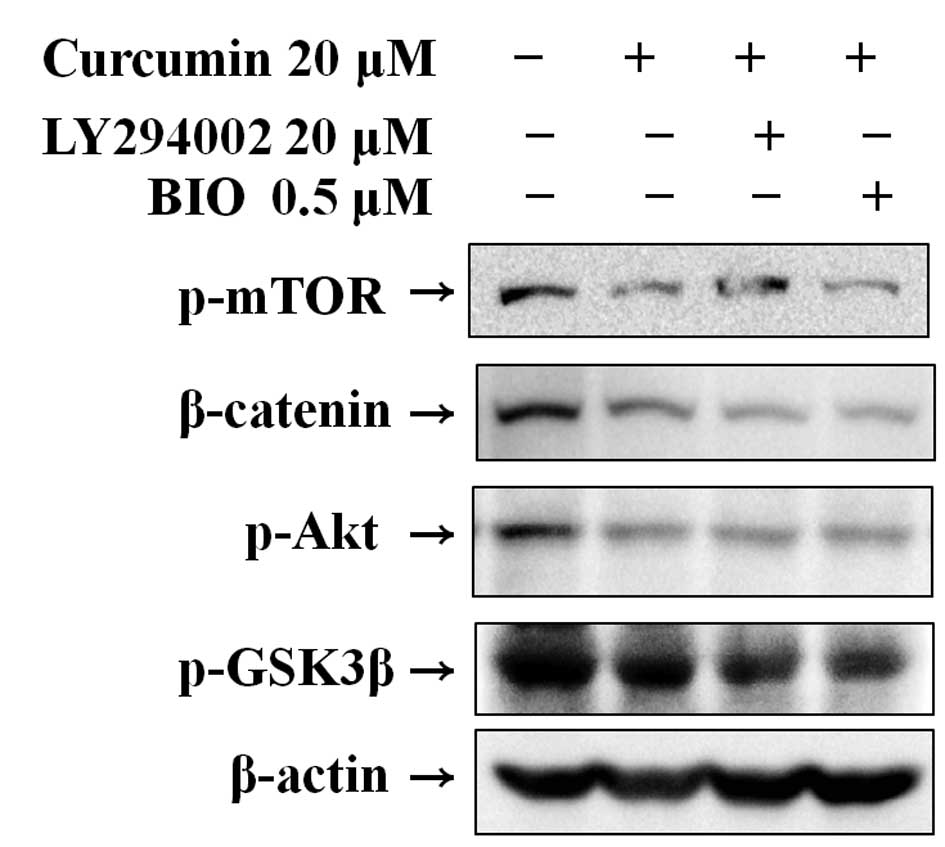
|
1
|
Surh YJ: Cancer chemoprevention with
dietary phytochemicals. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:768–780. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thangapazham RL, Sharma A and Maheshwari
RK: Multiple molecular targets in cancer chemoprevention by
curcumin. AAPS J. 8:443–449. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Johnson JJ and Mukhtar H: Curcumin for
chemoprevention of colon cancer. Cancer Lett. 255:170–181. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Radhakrishna Pillai G, Srivastava AS,
Hassanein TI, Chauhan DP and Carrier E: Induction of apoptosis in
human lung cancer cells by curcumin. Cancer Lett. 208:163–170.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shi M, Cai Q, Yao L, Mao Y, Ming Y and
Ouyang G: Antiproliferation and apoptosis induced by curcumin in
human ovarian cancer cells. Cell Biol Int. 30:221–226. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mehta K, Pantazis P, McQueen T and
Aggarwal BB: Antiproliferative effect of curcumin
(diferuloylmethane) against human breast tumor cell lines.
Anticancer Drugs. 8:470–481. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Perry MC, Demeule M, Régina A, Moumdjian R
and Béliveau R: Curcumin inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis in
glioblastoma xenografts. Mol Nutr Food Res. 54:1192–1201.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dujic J, Kippenberger S, Ramirez-Bosca A,
Diaz-Alperi J, Bereiter-Hahn J, Kaufmann R, Bernd A and Hofmann M:
Curcumin in combination with visible light inhibits tumor growth in
a xenograft tumor model. Int J Cancer. 124:1422–1428. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stagos D, Amoutzias GD, Matakos A, Spyrou
A, Tsatsakis AM and Kouretas D: Chemoprevention of liver cancer by
plant polyphenols. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:2155–2170. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Polakis P: Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes
Dev. 14:1837–1851. 2000.
|
|
11
|
Fatima S, Lee NP and Luk JM: Dickkopfs and
Wnt/β-catenin signalling in liver cancer. World J Clin Oncol.
2:311–325. 2011.
|
|
12
|
Esufali S and Bapat B: Cross-talk between
Rac1 GTPase and dysregulated Wnt signaling pathway leads to
cellular redistribution of beta-catenin and TCF/LEF-mediated
transcriptional activation. Oncogene. 23:8260–8271. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Whittaker S, Marais R and Zhu AX: The role
of signaling pathways in the development and treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 29:4989–5005. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cadigan KM and Nusse R: Wnt signaling: a
common theme in animal development. Genes Dev. 11:3286–3305. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim D and Chung J: Akt: versatile mediator
of cell survival and beyond. J Biochem Mol Biol. 35:106–115. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nojima H, Tokunaga C, Eguchi S, Oshiro N,
Hidayat S, Yoshino K, Hara K, Tanaka N, Avruch J and Yonezawa K:
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) partner, raptor, binds the
mTOR substrates p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1 through their TOR
signaling (TOS) motif. J Biol Chem. 278:15461–15464. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jung EM, Lim JH, Lee TJ, Park JW, Choi KS
and Kwon TK: Curcumin sensitizes tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis through
reactive oxygen species-mediated upregulation of death receptor 5
(DR5). Carcinogenesis. 26:1905–1913. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yu S, Shen G, Khor TO, Kim JH and Kong AN:
Curcumin inhibits Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling
through protein phosphatase-dependent mechanism. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:2609–2620. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chiu TL and Su CC: Curcumin inhibits
proliferation and migration by increasing the Bax to Bcl-2 ratio
and decrasing NF-Bp65 expression in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells.
Int J Mol Med. 23:468–475. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shankar S and Srivastava RK: Involvement
of Bcl-2 family members, phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/AKT and
mitochondrial p53 in curcumin (diferulolylmethane)-induced
apoptosis in prostate cancer. Int J Oncol. 30:905–918. 2007.
|
|
22
|
Murayama K, Kimura T, Tarutani M, Tomooka
M, Hayashi R, Okabe M, Nishida K, Itami S, Katayama I and Nakano T:
Akt activation induces epidermal hyperplasia and proliferation of
epidermal progenitors. Oncogene. 26:4882–4888. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Inoki K, Ouyang H, Zhu T, Lindvall C, Wang
Y, Zhang X, Yang Q, Bennett C, Harada Y, Stankunas K, Wang CY, He
X, MacDougald OA, You M, Williams BO and Guan KL: TSC2 integrates
Wnt and energy signals via a coordinated phosphorylation by AMPK
and GSK3 to regulate cell growth. Cell. 126:955–968. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen RH, Ding WV and McCormick F: Wnt
signaling to beta-catenin involves two interactive components.
Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibition and activation of protein
kinase C. J Biol Chem. 275:17894–17899. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dal Col J and Dolcetti R: GSK-3beta
inhibition: at the crossroad between Akt and mTOR constitutive
activation to enhance cyclin D1 protein stability in mantle cell
lymphoma. Cell Cycle. 7:2813–2816. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|