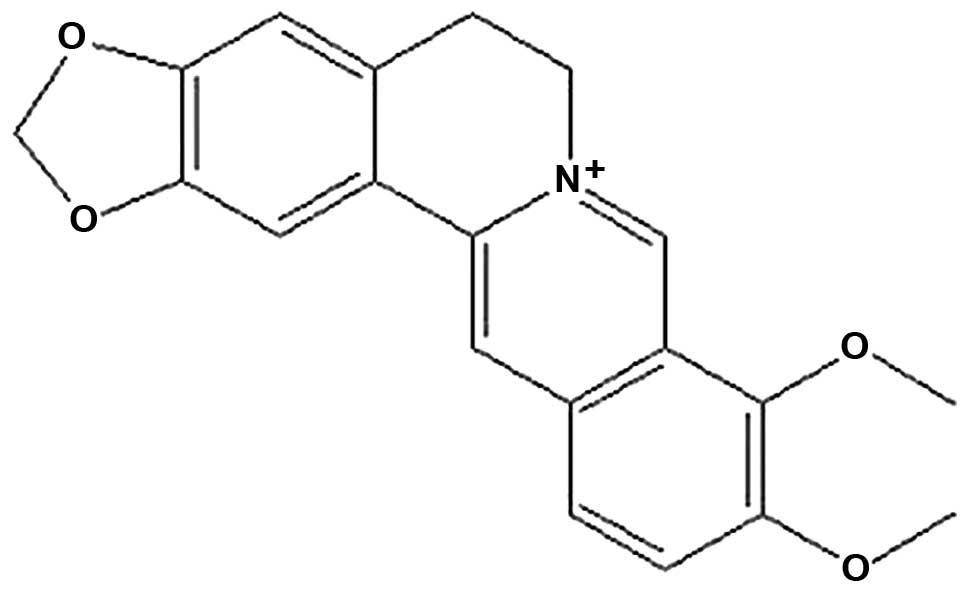
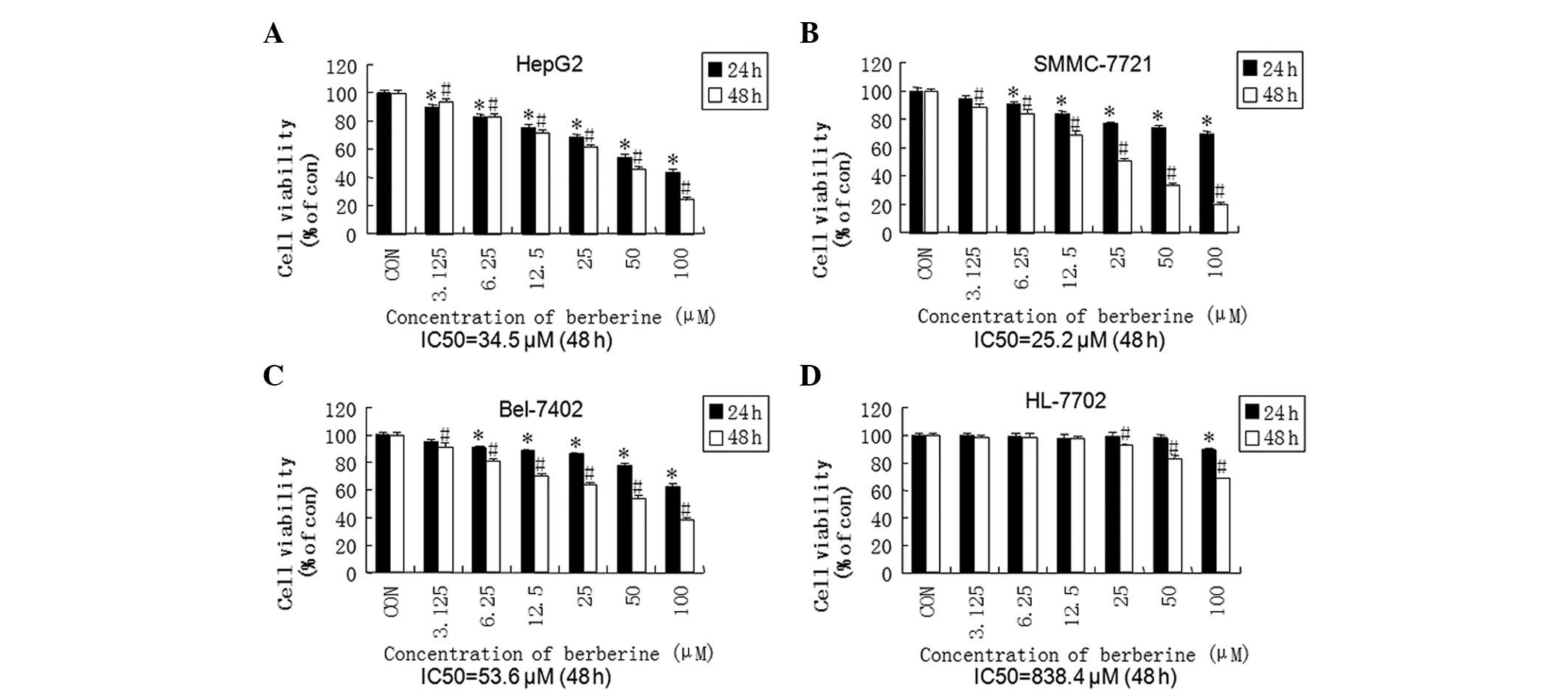
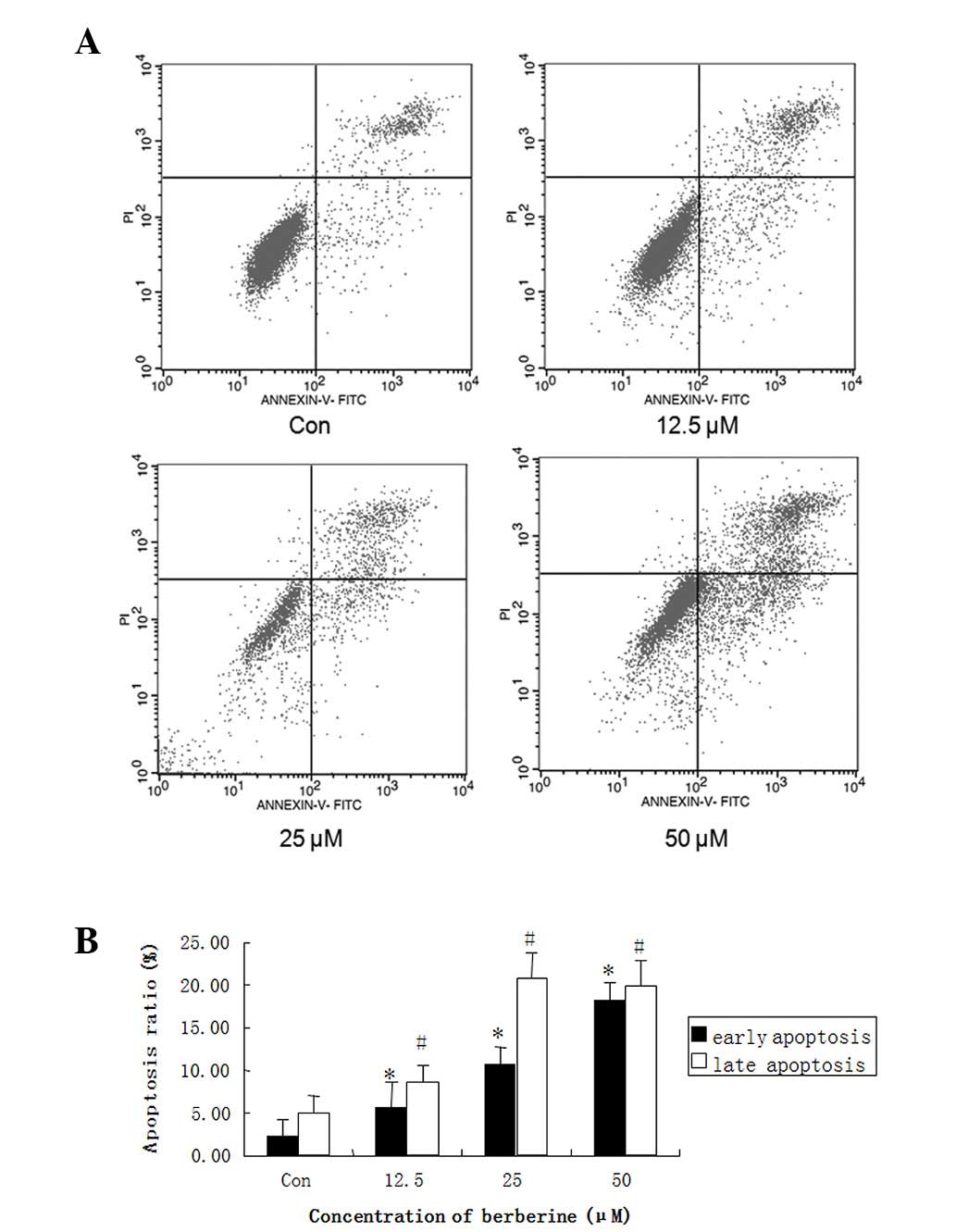
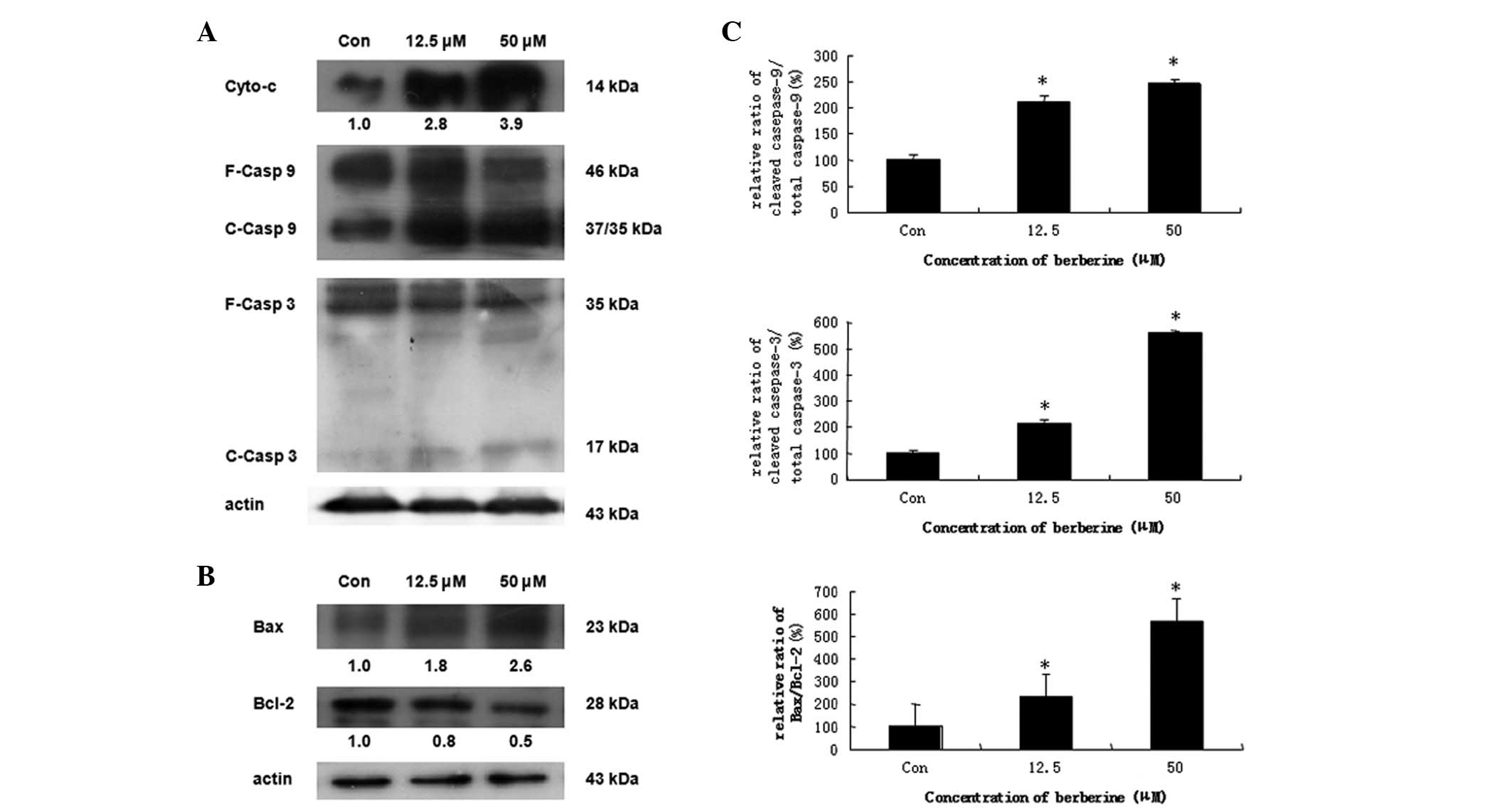
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu YK, et al: A decade’s
studies on metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 130:187–196. 2004.
|
|
3
|
Ming L, Thorgeirsson SS, Gail MH, et al:
Dominant role of hepatitis B virus and cofactor role of aflatoxin
in hepatocarcinogenesis in Qidong, China. Hepatology. 36:1214–1220.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
El-Serag HB: Epidemiology of
hepatocellular carcinoma in USA. Hepatol Res. 37(Suppl 2): S88–S94.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Parkin DM: The global health burden of
infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int J Cancer.
118:3030–3044. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Petraccia L, Onori P, Sferra R, et al: MDR
(multidrug resistance) in hepatocarcinoma clinical-therapeutic
implications. Clin Ter. 154:325–335. 2003.(In Italian).
|
|
7
|
Zhang C, Liu L, Yu Y, Chen B, Tang C and
Li X: Antitumor effects of ginsenoside Rg3 on human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 5:1295–1298. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hardie DG, Carling D and Carlson M: The
AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinase subfamily: metabolic sensors of
the eukaryotic cell. Annu Rev Biochem. 67:821–855. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hardie DG: Minireview: the AMP-activated
protein kinase cascade: the key sensor of cellular energy status.
Endocrinology. 144:5179–5183. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hardie DG and Sakamoto K: AMPK: a key
sensor of fuel and energy status in skeletal muscle. Physiology.
21:48–60. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Garcia-Gil M, Pesi R, Perna S, et al:
5′-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside induces apoptosis in human
neuroblastoma cells. Neuroscience. 117:811–820. 2003.
|
|
12
|
Akhter MH, Sabir M and Bhide NK:
Anti-inflammatory effect of berberine in rats injected locally with
cholera toxin. Indian J Med Res. 65:133–141. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hwang JM, Wang CJ, Chou FP, Tseng TH,
Hsieh YS, Lin WL and Chu CY: Inhibitory effect of berberine on
tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative damage in rat liver.
Arch Toxicol. 76:664–670. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tsai CS and Ochillo RF: Pharmacological
effects of berberine on the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig
isolated ileum. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 310:116–131.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang GY, Lv QH, Dong Q, Xu RZ and Dong QH:
Berbamine induces Fas-mediated apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma HepG2 cells and inhibits its tumor growth in nude mice. J
Asian Nat Prod Res. 11:219–228. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang N, Feng Y, Zhu M, et al: Berberine
induces autophagic cell death and mitochondrial apoptosis in liver
cancer cells: the cellular mechanism. J Cell Biochem.
111:1426–1436. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Patil JB, Kim J and Jayaprakasha GK:
Berberine induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells (MCF-7) through
mitochondrial-dependent pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 645:70–78. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ho YT, Lu CC, Yang JS, et al: Berberine
induced apoptosis via promoting the expression of caspase-8, -9 and
-3, apoptosis-inducing factor and endonuclease G in SCC-4 human
tongue squamous carcinoma cancer cells. Anticancer Res.
29:4063–4070. 2009.
|
|
19
|
Vichai V and Kirtikara K: Sulforhodamine B
colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat Protoc.
1:1112–1116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim YM, Hwang JT, Kwak DW, et al:
Involvement of AMPK signaling cascade in capsaicin-induced
apoptosis of HT-29 colon cancer cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1095:496–503. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ji CB, Yang B, Yang YL, et al: Exogenous
cell-permeable C6 ceramide sensitizes multiple cancer cell lines to
Doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by promoting AMPK activation and
mTORC1 inhibition. Oncogene. 29:6557–6568. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dorai T and Aggarwal BB: Role of
chemopreventive agents in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 5:129–140.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hwang JM, Kuo HC, Tseng TH, Liu JY and Chu
CY: Berberine induces apoptosis through a mitochondria/caspases
pathway in human hepatoma cells. Arch Toxicol. 80:62–73. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hur JM, Hyun MS, Lim SY, Lee WY and Kim D:
The combination of berberine and irradiation enhances anti-cancer
effects via activation of p38 MAPK pathway and ROS generation in
human hepatoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 107:955–964. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu B, Wang G, Yang J, Pan X, Yang Z and
Zang L: Berberine inhibits human hepatoma cell invasion without
cytotoxicity in healthy hepatocytes. PLoS One. 6:e214162011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chao DC, Lin LJ, Kao ST, et al: Inhibitory
effects of Zuo-Jin-Wan and its alkaloidal ingredients on activator
protein 1, nuclear factor-κB, and cellular transformation in HepG2
cells. Fitoterapia. 82:696–703. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Motoshima H, Goldstein BJ, Igata M and
Araki E: AMPK and cell proliferation - AMPK as a therapeutic target
for atherosclerosis and cancer. J Physiol. 574:63–71. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Luo Z, Saha AK, Xiang X and Ruderman NB:
AMPK, the metabolic syndrome and cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
26:69–76. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|