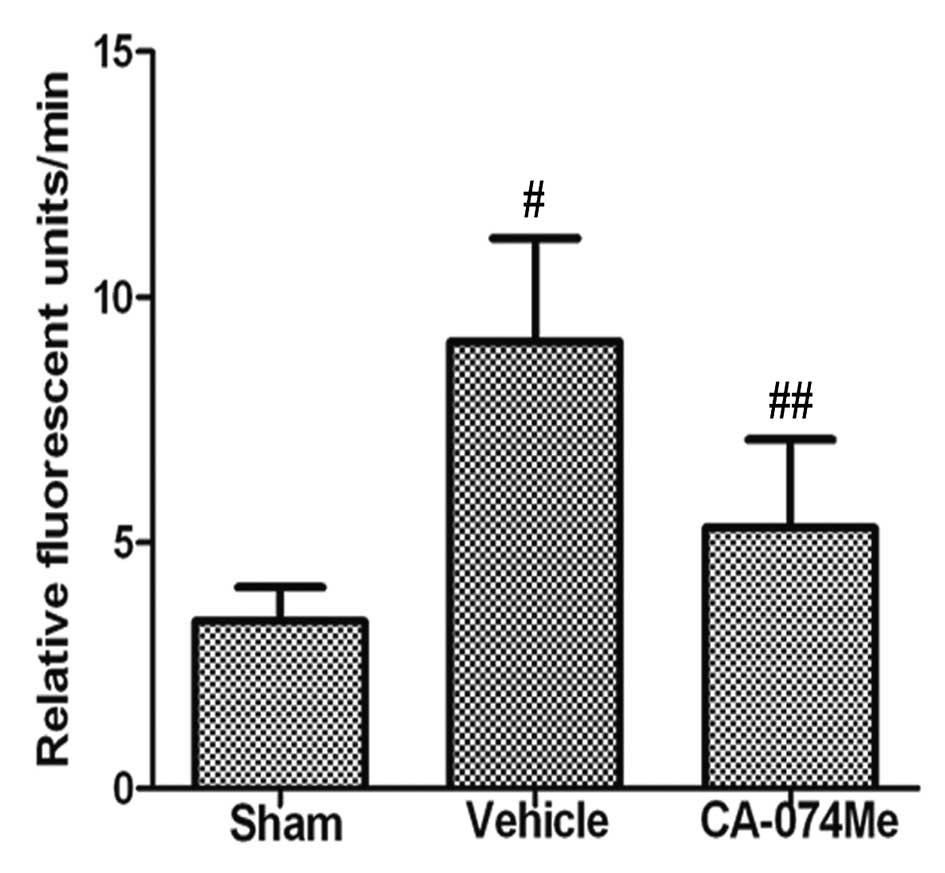
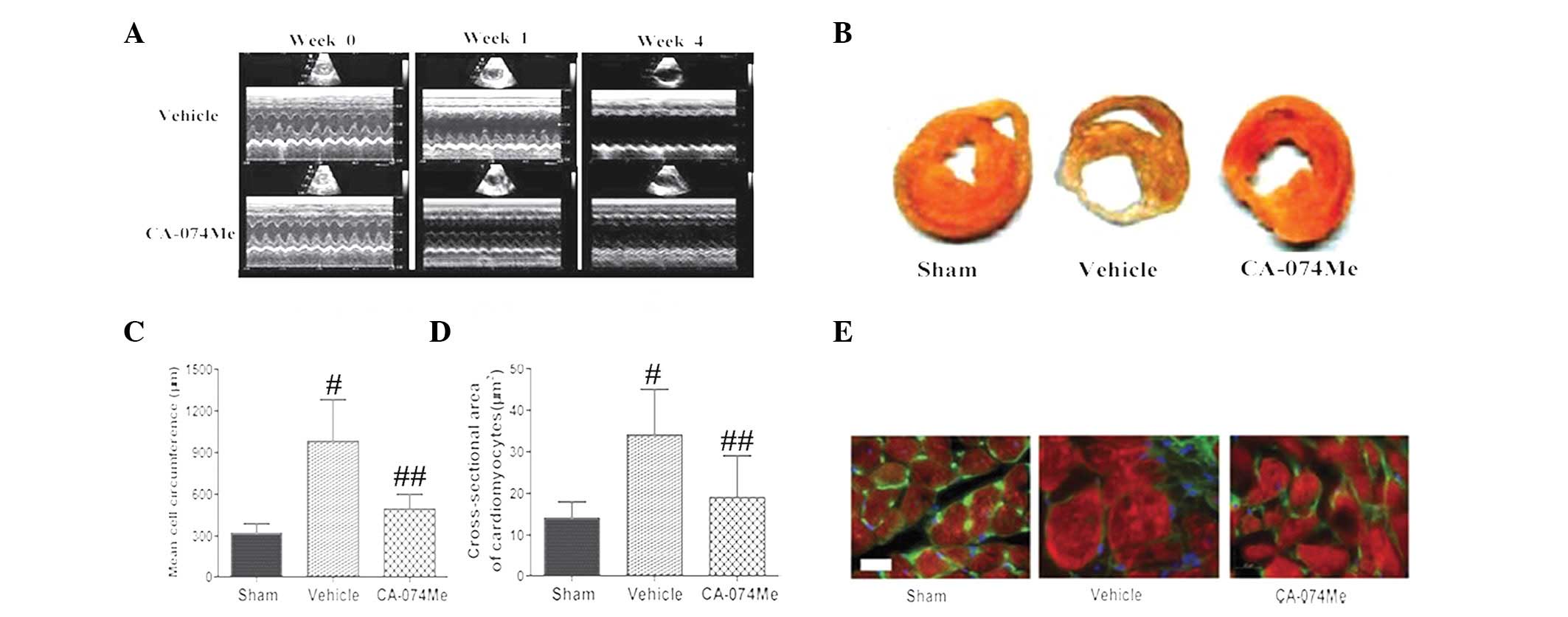
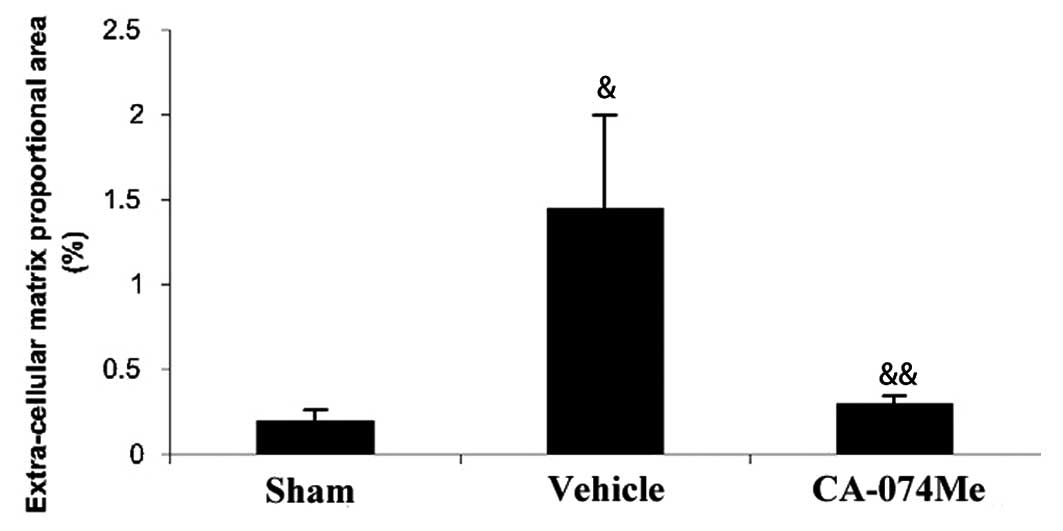
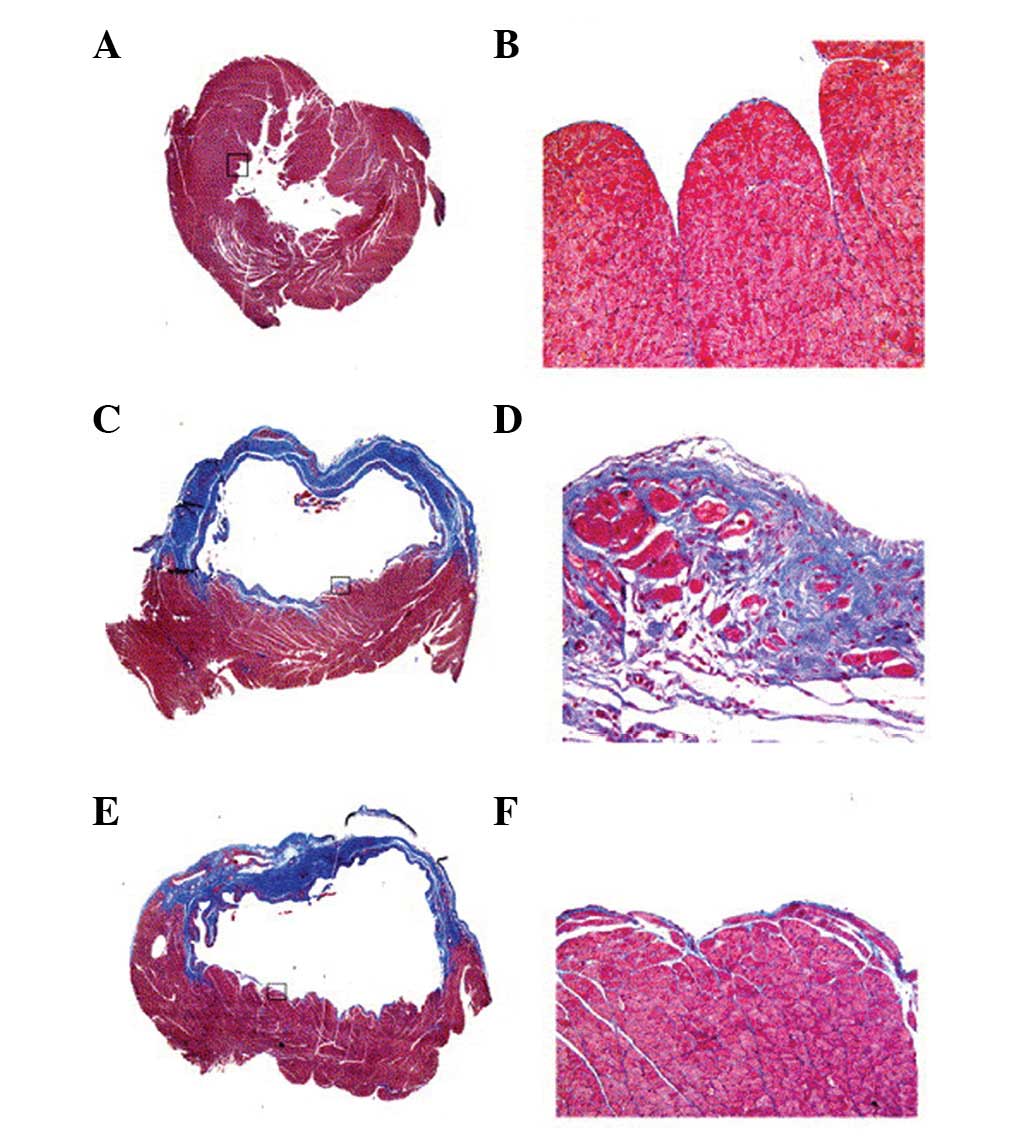
|
1
|
Weber C and Noels H: Atherosclerosis:
current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat Med.
17:1410–1422. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yousef Z, Redwood S and Marber M:
Postinfarction left ventricular remodelling: where are the theories
and trials leading us? Heart. 83:76–80. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bujak M, Dobaczewski M, Chatila K, Mendoza
LH, Li N, Reddy A and Frangogiannis NG: Interleukin-1 receptor type
I signaling critically regulates infarct healing and cardiac
remodeling. Am J Pathol. 173:57–67. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bracey NA, Beck PL, Muruve DA, Hirota SA,
Guo J, Jabagi H, Wright JR Jr, Macdonald JA, Lees-Miller JP, Roach
D, et al: The Nlrp3 inflammasome promotes myocardial dysfunction in
structural cardiomyopathy through IL-1β. Exp Physiol. 98:462–472.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mezzaroma E, Toldo S, Farkas D, Seropian
IM, Van Tassell BW, Salloum FN, Kannan HR, Menna AC, Voelkel NF and
Abbate A: The inflammasome promotes adverse cardiac remodeling
following acute myocardial infarction in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 108:19725–19730. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Niemi K, Teirilä L, Lappalainen J,
Rajamäki K, Baumann MH, Öörni K, Wolff H, Kovanen PT, Matikainen S
and Eklund KK: Serum amyloid A activates the NLRP3 inflammasome via
P2X7 receptor and a cathepsin B-sensitive pathway. J Immunol.
186:6119–6128. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boyle AJ, Kelly DJ, Zhang Y, Cox AJ, Gow
RM, Way K, Itescu S, Krum H and Gilbert RE: Inhibition of protein
kinase C reduces left ventricular fibrosis and dysfunction
following myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 39:213–221.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Van Acker GJ, Saluja AK, Bhagat L, Singh
VP, Song AM and Steer ML: Cathepsin B inhibition prevents
trypsinogen activation and reduces pancreatitis severity. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 283:G794–G800. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Matarrese P, Ascione B, Ciarlo L, Vona R,
Leonetti C, Scarsella M, Mileo AM, Catricalà C, Paggi MG and
Malorni W: Cathepsin B inhibition interferes with metastatic
potential of human melanoma: an in vitro and in vivo study. Mol
Cancer. 9:2072010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cavallo-Medved D, Dosescu J, Linebaugh BE,
Sameni M, Rudy D and Sloane BF: Mutant K-ras regulates cathepsin B
localization on the surface of human colorectal carcinoma cells.
Neoplasia. 5:507–519. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takaya T, Wada H, Morimoto T, Sunagawa Y,
Kawamura T, Takanabe-Mori R, Shimatsu A, Fujita Y, Sato Y, Fujita
M, et al: Left ventricular expression of lectin-like oxidized
low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 in failing rat hearts. Circ J.
74:723–729. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Saito T, Rodger IW, Hu F, Robinson R,
Huynh T and Giaid A: Some histological methods: Inhibition of COX
pathway in experimental myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
37:71–77. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Masson P: Trichrome stainings and their
preliminary technique. J Tech Methods. 2:75–90. 1929.
|
|
14
|
Lal A, Veinot JP and Leenen FH: Critical
role of CNS effects of aldosterone in cardiac remodeling
post-myocardial infarction in rats. Cardiovasc Res. 64:437–447.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lehr HA, Mankoff DA, Corwin D, Santeusanio
G and Gown AM: Application of photoshop-based image analysis to
quantification of hormone receptor expression in breast cancer. J
Histochem Cytochem. 45:1559–1565. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lehr HA, Van der Loos CM, Teeling P and
Gown AM: Complete chromogen separation and analysis in double
immunohistochemical stains using Photoshop-based image analysis. J
Histochem Cytochem. 47:119–126. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Duncan DJ, Yang Z, Hopkins PM, Steele DS
and Harrison SM: TNF-alpha and IL-1beta increase Ca2+
leak from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and susceptibility to
arrhythmia in rat ventricular myocytes. Cell Calcium. 47:378–386.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bujak M and Frangogiannis NG: The role of
IL-1 in the pathogenesis of heart disease. Arch Immunol Ther Exp
(Warsz). 57:165–176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abbate A, Salloum FN, Vecile E, Das A,
Hoke NN, Straino S, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Houser JE, Qureshi IZ, Ownby
ED, et al: Anakinra, a recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor
antagonist, inhibits apoptosis in experimental acute myocardial
infarction. Circulation. 117:2670–2683. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Van Tassell BW, Arena RA, Toldo S,
Mezzaroma E, Azam T, Seropian IM, Shah K, Canada J, Voelkel NF,
Dinarello CA and Abbate A: Enhanced interleukin-1 activity
contributes to exercise intolerance in patients with systolic heart
failure. PLoS One. 7:e334382012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Abbate A, Kontos MC, Grizzard JD,
Biondi-Zoccai GG, Van Tassell BW, Robati R, Roach LM, Arena RA,
Roberts CS, Varma A, et al: Interleukin-1 blockade with anakinra to
prevent adverse cardiac remodeling after acute myocardial
infarction [Virginia Commonwealth University Anakinra Remodeling
Trial (VCU-ART) Pilot study]. Am J Cardiol. 105:1371–1377.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hoegen T, Tremel N, Klein M, Angele B,
Wagner H, Kirschning C, Pfister HW, Fontana A, Hammerschmidt S and
Koedel U: The NLRP3 inflammasome contributes to brain injury in
pneumococcal meningitis and is activated through ATP-dependent
lysosomal cathepsin B release. J Immunol. 187:5440–5451. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hirota SA, Ng J, Lueng A, Khajah M, Parhar
K, Li Y, Lam V, Potentier MS, Ng K, Bawa M, et al: NLRP3
inflammasome plays a key role in the regulation of intestinal
homeostasis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 17:1359–1372. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
McDonald B, Pittman K, Menezes GB, Hirota
SA, Slaba I, Waterhouse CC, Beck PL, Muruve DA and Kubes P:
Intravascular danger signals guide neutrophils to sites of sterile
inflammation. Science. 330:362–366. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cheng XW, Obata K, Kuzuya M, Izawa H,
Nakamura K, Asai E, Nagasaka T, Saka M, Kimata T, Noda A, et al:
Elastolytic cathepsin induction/activation system exists in
myocardium and is upregulated in hypertensive heart failure.
Hypertension. 48:979–987. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ge J, Zhao G, Chen R, Li S, Wang S, Zhang
X, Zhuang Y, Du J, Yu X, Li G and Yang Y: Enhanced myocardial
cathepsin B expression in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur
J Heart Fail. 8:284–289. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kumaran KS and Prince PS: Preventive
effect of caffeic acid on lysosomal dysfunction in
isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarcted rats. J Biochem Mol
Toxicol. 24:115–122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jugdutt BI: Ventricular remodeling after
infarction and the extracellular collagen matrix: when is enough
enough? Circulation. 108:1395–1403. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Borg TK, Ranson WF, Moslehy FA and
Caulfield JB: Structural basis of ventricular stiffness. Lab
Invest. 44:49–54. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Strain JE, Grose RM, Factor SM and Fisher
JD: Results of endomyocardial biopsy in patients with spontaneous
ventricular tachycardia but without apparent structural heart
disease. Circulation. 68:1171–1181. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Artlett CM: The role of the NLRP3
inflammasome in fibrosis. Open Rheumatol J. 6:80–86. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu JF, Washko GR, Nakahira K, Hatabu H,
Patel AS, Fernandez IE, Nishino M, Okajima Y, Yamashiro T, Ross C,
et al: Statins and pulmonary fibrosis: the potential role of NLRP3
inflammasome activation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 185:547–556.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Watanabe A, Sohail MA, Gomes DA, Hashmi A,
Nagata J, Sutterwala FS, Mahmood S, Jhandier MN, Shi Y, Flavell RA
and Mehal WZ: Inflammasome-mediated regulation of hepatic stellate
cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 296:G1248–G1257.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|