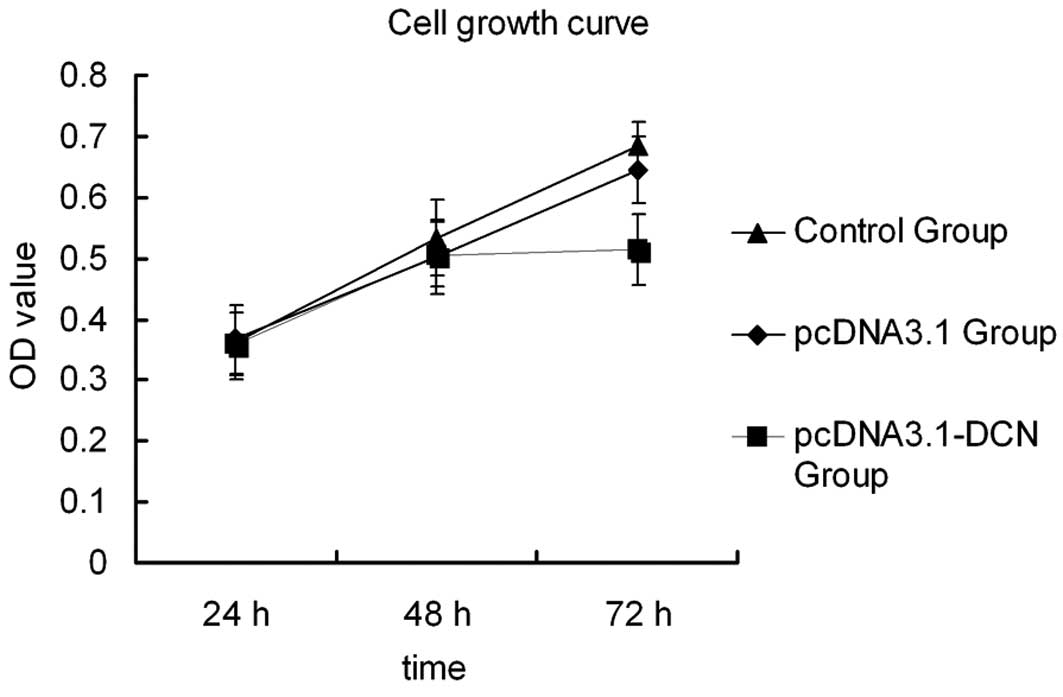
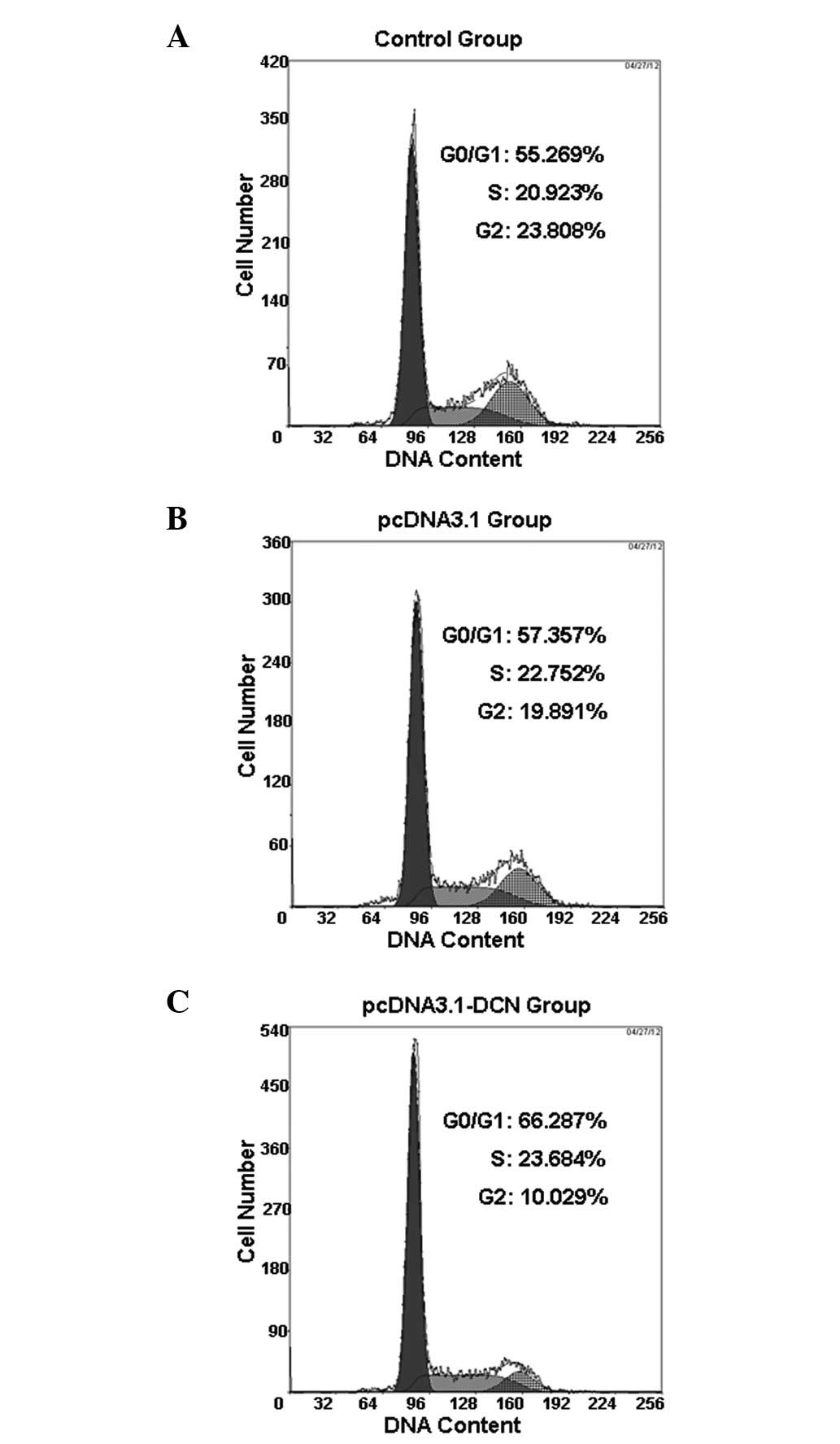
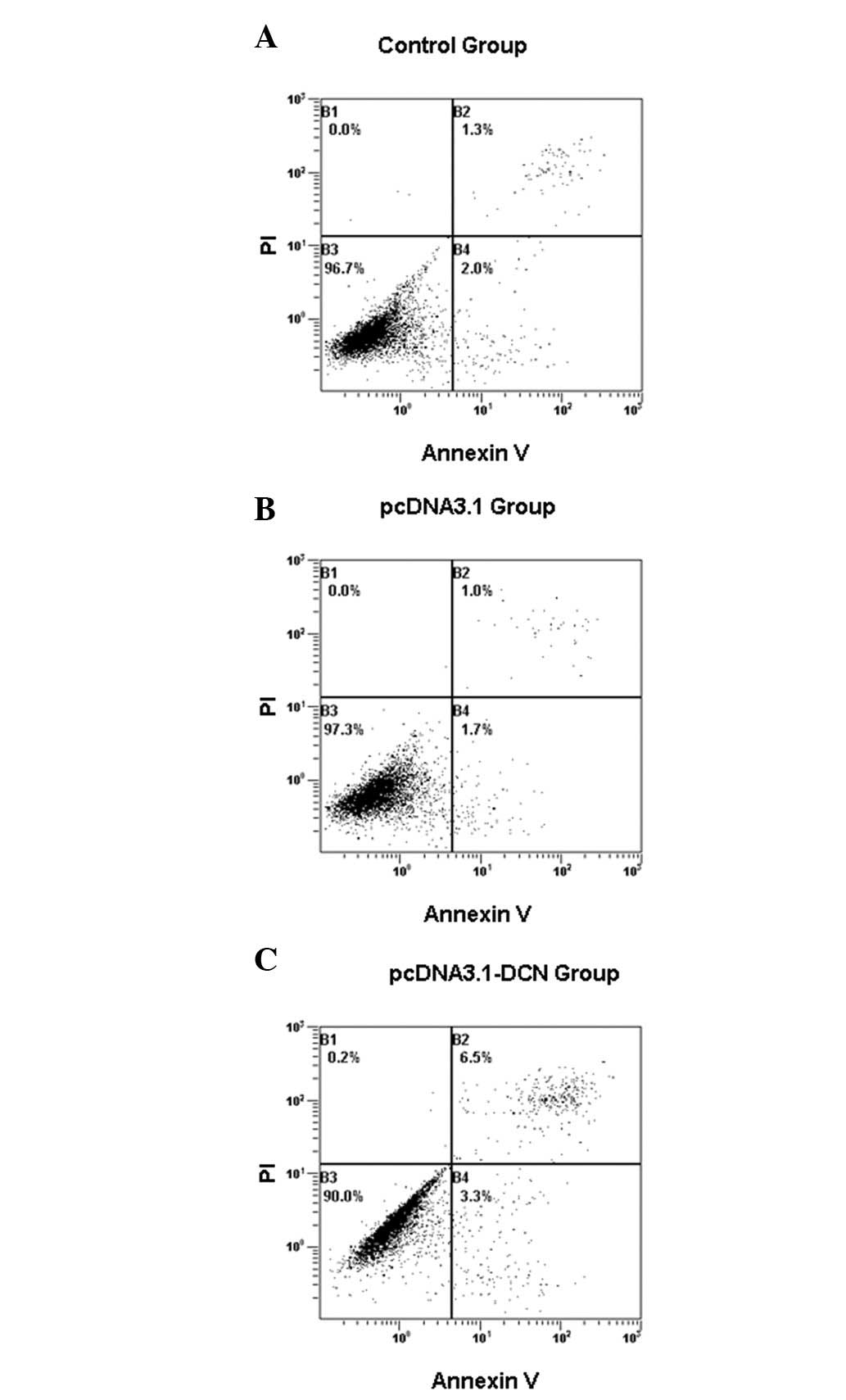
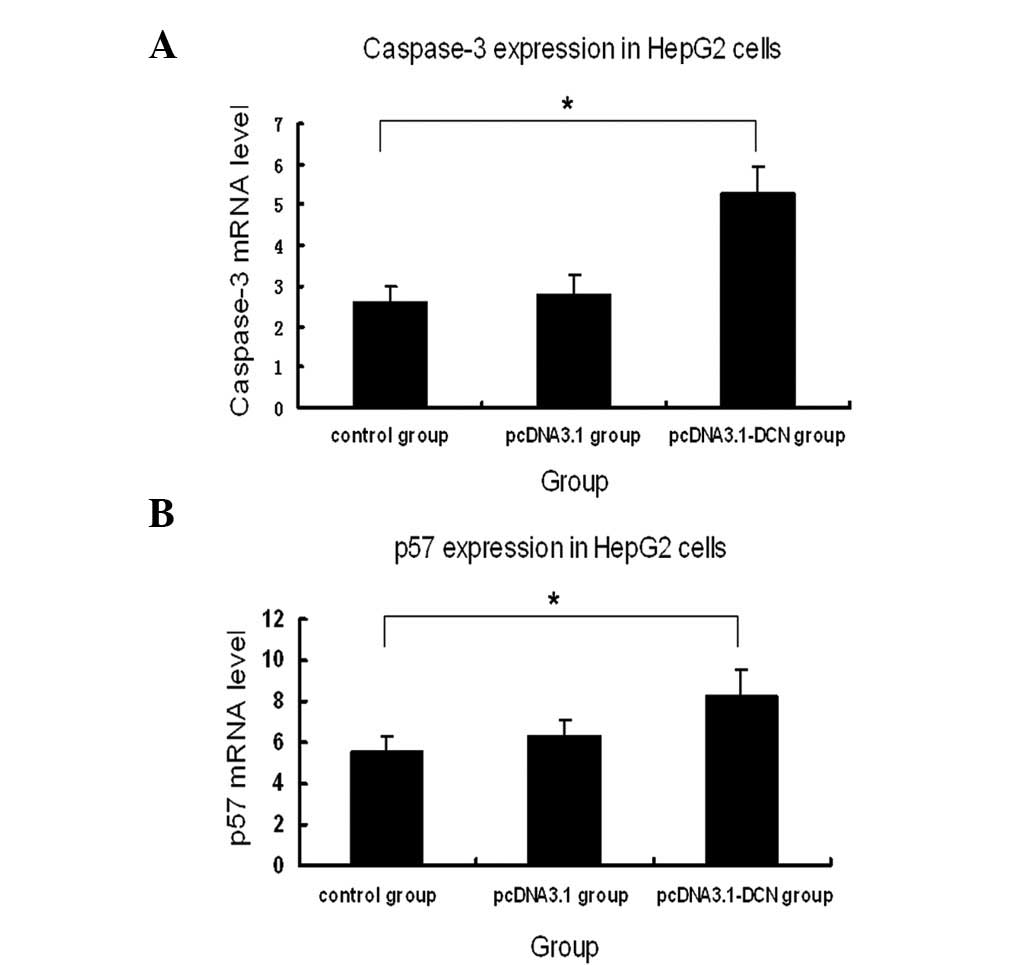
|
1
|
Colak D, Chishti MA, Al-Bakheet AB, et al:
Integrative and comparative genomics analysis of early
hepatocellular carcinoma differentiated from liver regeneration in
young and old. Mol Cancer. 9:1462010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
El-Serag HB, Davila JA, Petersen NJ and
McGlynn KA: The continuing increase in the incidence of
hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States: an update. Ann
Intern Med. 139:817–823. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang MF, Zhang ZY, Fu J, Yang YF and Yun
JP: Correlation between expression of p53, p21/WAF1, and MDM2
proteins and their prognostic significance in primary
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med. 7:1102009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jain S, Singhal S, Lee P and Xu R:
Molecular genetics of hepatocellular neoplasia. Am J Transl Res.
2:105–118. 2010.
|
|
6
|
McGlynn KA and London WT: Epidemiology and
natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 19:3–23. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sherman M: Hepatocellular carcinoma:
epidemiology, risk factors, and screening. Semin Liver Dis.
25:143–154. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Farazi PA and DePinho RA: Hepatocellular
carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:674–687. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Altekruse SF, McGlynn KA and Reichman ME:
Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, mortality, and survival trends
in the United States from 1975 to 2005. J Clin Oncol. 27:1485–1491.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nguyen MH, Whittemore AS, Garcia RT, et
al: Role of ethnicity in risk for hepatocellular carcinoma in
patients with chronic hepatitis C and cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 2:820–824. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Iozzo RV: Matrix proteoglycans: from
molecular design to cellular function. Annu Rev Biochem.
67:609–652. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iozzo RV, Moscatello DK, McQuillan DJ and
Eichstetter I: Decorin is a biological ligand for the epidermal
growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 274:4489–4492. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Reed CC and Iozzo RV: The role of decorin
in collagen fibrillogenesis and skin homeostasis. Glycoconj J.
19:249–255. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Baghy K, Dezso K, László V, et al:
Ablation of the decorin gene enhances experimental hepatic fibrosis
and impairs hepatic healing in mice. Lab Invest. 91:439–451. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gu Y, Zhang S, Wu Q, et al: Differential
expression of decorin, EGFR and cyclin D1 during mammary gland
carcinogenesis in TA2 mice with spontaneous breast cancer. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 29:62010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moscatello DK, Santra M, Mann DM,
McQuillan DJ, Wong AJ and Iozzo RV: Decorin suppresses tumor cell
growth by activating the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Clin
Invest. 101:406–412. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Csordás G, Santra M, Reed CC, et al:
Sustained down-regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor
by decorin. A mechanism for controlling tumor growth in vivo. J
Biol Chem. 275:32879–32887. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bi X, Tong C, Dockendorff A, et al:
Genetic deficiency of decorin causes intestinal tumor formation
through disruption of intestinal cell maturation. Carcinogenesis.
29:1435–1440. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Besson A, Dowdy SF and Roberts JM: CDK
inhibitors: cell cycle regulators and beyond. Dev Cell. 14:159–169.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kavanagh E and Joseph B: The hallmarks of
CDKN1C (p57, KIP2) in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1816:50–56.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pateras IS, Apostolopoulou K, Koutsami M,
et al: Downregulation of the KIP family members p27(KIP1) and
p57(KIP2) by SKP2 and the role of methylation in p57(KIP2)
inactivation in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer.
119:2546–2556. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Oya M and Schulz WA: Decreased expression
of p57(KIP2)mRNA in human bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 83:626–631.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li JQ, Wu F, Usuki H, et al: Loss of
p57KIP2 is associated with colorectal carcinogenesis. Int J Oncol.
23:1537–1543. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Larson PS, Schlechter BL, King CL, et al:
CDKN1C/p57kip2 is a candidate tumor suppressor gene in human breast
cancer. BMC Cancer. 8:682008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ito Y, Takeda T, Sakon M, Tsujimoto M,
Monden M and Matsuura N: Expression of p57/Kip2 protein in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 61:221–225. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Atasoy P, Yilmaz E, Bozdogan O, Ayva S and
Batislam E: Expression profile and prognostic importance in
prostate lesions of the reverse transcriptase component of human
telomerase (hTERT) and of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p57
(p57kip2a). Int Urol Nephrol. 41:55–60. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Guo H, Lv Y, Tian T, et al: Downregulation
of p57 accelerates the growth and invasion of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 32:1897–1904. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Du Z, et al: Recombinant
human decorin suppresses liver HepG2 carcinoma cells by p21
upregulation. Onco Targets Ther. 5:143–152. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu Y, Sun H, Owens RT, et al: Decorin
suppresses prostate tumor growth through inhibition of epidermal
growth factor and androgen receptor pathways. Neoplasia.
11:1042–1053. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
De Luca A, Santra M, Baldi A, Giordano A
and Iozzo RV: Decorin-induced growth suppression is associated with
up-regulation of p21, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases. J
Biol Chem. 271:18961–18965. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Seidler DG, Goldoni S, Agnew C, et al:
Decorin protein core inhibits in vivo cancer growth and metabolism
by hindering epidermal growth factor receptor function and
triggering apoptosis via caspase-3 activation. J Biol Chem.
281:26408–26418. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K, et al:
Caspases 3 and 7: key mediators of mitochondrial events of
apoptosis. Science. 311:847–851. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ma Y and Cress WD: Transcriptional
upregulation of p57 (Kip2) by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor
BMS-387032 is E2F dependent and serves as a negative feedback loop
limiting cytotoxicity. Oncogene. 26:3532–3540. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Scandura JM, Boccuni P, Massagué J and
Nimer SD: Transforming growth factor beta-induced cell cycle arrest
of human hematopoietic cells requires p57KIP2 up-regulation. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:15231–15236. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nan KJ, Guo H, Ruan ZP, Jing Z and Liu SX:
Expression of p57(kip2) and its relationship with clinicopathology,
PCNA and p53 in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 11:1237–1240. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Biaoxue R, Xiguang C, Hua L, et al:
Decreased expression of decorin and p57(KIP2) correlates with poor
survival and lymphatic metastasis in lung cancer patients. Int J
Biol Markers. 26:9–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shen L, Toyota M, Kondo Y, et al: Aberrant
DNA methylation of p57KIP2 identifies a cell-cycle regulatory
pathway with prognostic impact in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia.
Blood. 101:4131–4136. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nakai S, Masaki T, Shiratori Y, et al:
Expression of p57(KIP2) in hepatocellular carcinoma: relationship
between tumor differentiation and patient survival. Int J Oncol.
20:769–775. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sui L, Dong Y, Ohno M, Watanabe Y,
Sugimoto K and Tokuda M: Expression of p57kip2 and its clinical
relevance in epithelial ovarian tumors. Anticancer Res.
22:3191–3196. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|