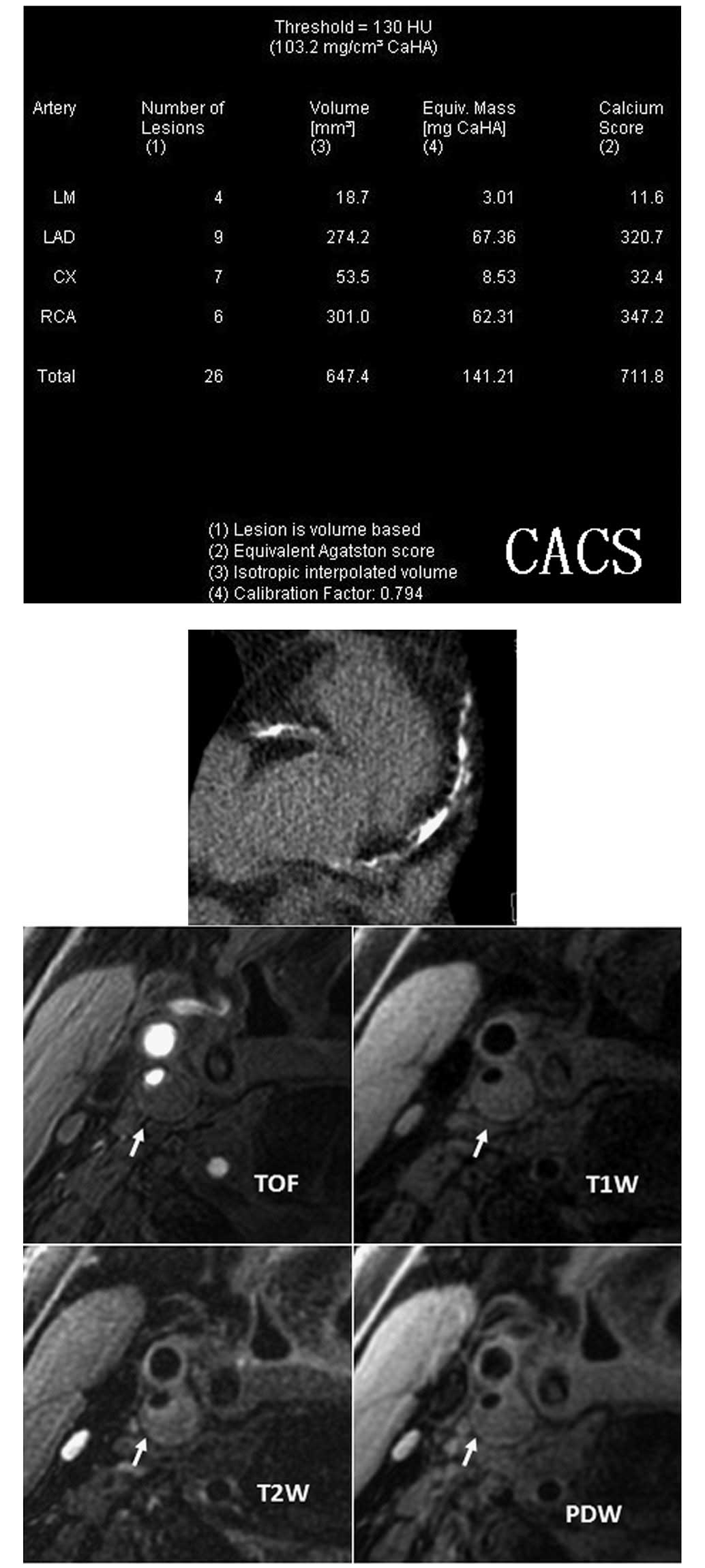
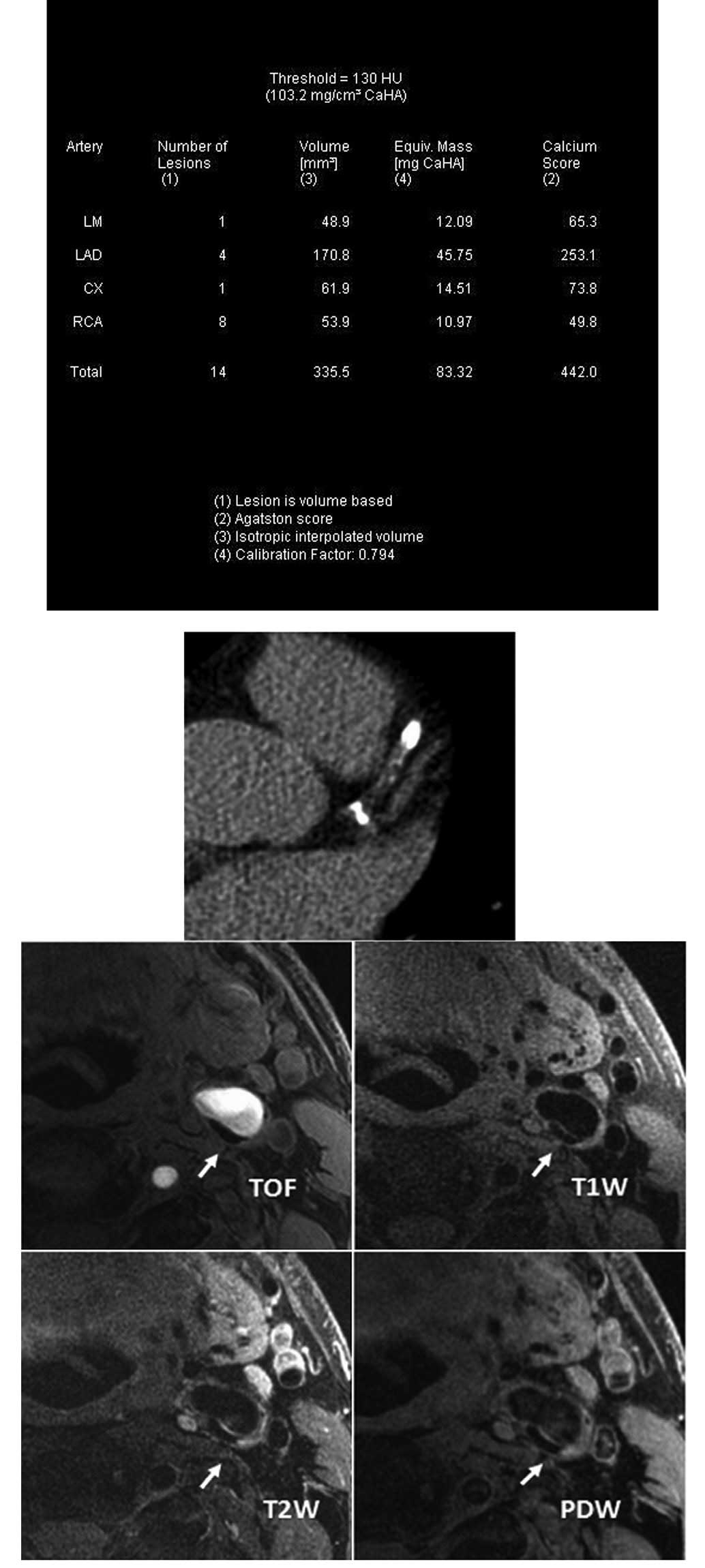
|
1
|
Dalager-Pedersen S, Ravn HB and Falk E:
Atherosclerosis and acute coronary events. Am J Cardiol. 82:37–40.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Iannuzzi A, Wilcosky T, Mercuri M, et al:
Ultrasonographic correlates of carotid atherosclerosis in transient
ischemic attack and stroke. Stroke. 26:614–619. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
CAPRIE Steering Committee. A randomised,
blinded, trial of clopidogrel versus aspirin in patients at risk of
ischaemic events (CAPRIE). CAPRIE Steering Committee. Lancet.
348:1329–1339. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kannel WB and Wolf PA: Peripheral and
cerebral atherothrombosis and cardiovascular events in different
vascular territories: insights from the Framingham Study. Curr
Atheroscler Rep. 8:317–323. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Meco JF, Pintó X, Escribà JM, et al:
Cardiovascular risk factors associated with clinically isolated and
diffuse atherosclerosis in Spanish patients with coronary artery
disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 28:643–650. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rampersaud E, Bielak LF, Parsa A, et al:
The association of coronary artery calcification and carotid artery
intima-media thickness with distinct, traditional coronary artery
disease risk factors in asymptomatic adults. Am J Epidemiol.
168:1016–1023. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Taylor AJ, Bindeman J, Le TP, et al:
Progression of calcified coronary atherosclerosis: relationship to
coronary risk factors and carotid intima-media thickness.
Atherosclerosis. 197:339–345. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Underhill HR, Yuan C, Terry JG, et al:
Differences in carotid arterial morphology and composition between
individuals with and without obstructive coronary artery disease: a
cardiovascular magnetic resonance study. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson.
10:312008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Manolio TA, Arnold AM, Post W, et al:
Ethnic differences in the relationship of carotid atherosclerosis
to coronary calcification: the Multi-Ethnic Study of
Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 197:132–138. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
El-Saed A, Sekikawa A, Edmundowicz D, et
al: Coronary calcification is more predictive of carotid intimal
medial thickness in black compared to white middle aged men.
Atherosclerosis. 196:913–918. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cai J, Hatsukami TS, Ferguson MS, et al:
In vivo quantitative measurement of intact fibrous cap and
lipid-rich necrotic core size in atherosclerotic carotid plaque:
comparison of high-resolution, contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance
imaging and histology. Circulation. 112:3437–3444. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chu BC, Kampschulte A, Ferguson MS, et al:
Hemorrhage in the atherosclerotic carotid plaque: a high-resolution
MRI study. Stroke. 35:1079–1084. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chu B, Phan BA, Balu N, et al:
Reproducibility of carotid atherosclerotic lesion type
characterization using high resolution multicontrast weighted
cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson.
8:793–799. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Agatston AS, Janowitz WR, Hildner FJ, et
al: Quantification of coronary artery calcium using ultrafast
computed tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 15:827–832. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kerwin W, Xu D, Liu F, et al: Magnetic
resonance imaging of carotid atherosclerosis: plaque analysis. Top
Magn Reson Imaging. 18:371–378. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Saam T, Ferguson MS, Yarnykh VL, et al:
Quantitative evaluation of carotid plaque composition by in vivo
MRI. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:234–239. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schenker MP, Dorbala S, Hong EC, et al:
Interrelation of coronary calcification, myocardial ischemia and
outcomes in patients with intermediate likelihood of coronary
artery disease: a combined positron emission tomography/computed
tomography study. Circulation. 117:1693–1700. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Odink AE, van der Lugt A, Hofman A, et al:
Association between calcification in the coronary arteries, aortic
arch and carotid arteries: the Rotterdam study. Atherosclerosis.
193:408–413. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Newman AB, Naydeck BL, Ives DG, et al:
Coronary artery calcium, carotid artery wall thickness, and
cardiovascular disease outcomes in adults 70 to 99 years old. Am J
Cardiol. 101:186–192. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Underhill HR, Kerwin WS, Hatsukami TS and
Yuan C: Automated measurement of mean wall thickness in the common
carotid artery by MRI: a comparison to intima-media thickness by
B-mode ultrasound. J Magn Reson Imaging. 24:379–387. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Salzar RS, Thubrikar MJ and Eppink RT:
Pressure-induced mechanical stress in the carotid artery
bifurcation: a possible correlation to atherosclerosis. J Biomech.
28:1333–1340. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bauer M, Mohlenkamp S, Lehmann N, et al:
The effect of age and risk factors on coronary and carotid artery
atherosclerotic burden in males - results of the Heinz Nixdorf
recall study. Atherosclerosis. 205:595–602. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Allison MA, Criqui MH and Wright CM:
Patterns and risk factors for systemic calcified atherosclerosis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:331–336. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schlieper G, Brandenburg V, Djuric Z, et
al: Risk factors for cardiovascular calcifications in non-diabetic
Caucasian haemodialysis patients. Kidney Blood Press Res.
32:161–168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Demer LL: Effect of calcification on in
vivo mechanical response of rabbit arteries to balloon dilation.
Circulation. 83:2083–2093. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Richardson PD, Davies MJ and Born GV:
Influence of plaque configuration and stress distribution on
fissuring of coronary atherosclerotic plaques. Lancet. 2:941–944.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee RT, Schoen FJ, Loree HM, et al:
Circumferential stress and matrix metalloproteinase 1 in human
coronary atherosclerosis. Implications for plaque rupture.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 16:1070–1073. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cappendijk VC, Kessels AG, Heenemao S, et
al: Comparison of lipid-rich necrotic core size in symptomatic and
asymptomatic carotid atherosclerotic plaque: initial results. J
Magn Reson Imaging. 27:1356–1361. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Altaf N, Daniels L, Morgan PS, et al:
Detection of intraplaque hemorrhage by magnetic resonance imaging
in symptomatic patients with mild to moderate carotid stenosis
predicts recurrent neurological events. J Vasc Surg. 47:337–342.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Altaf N, MacSweeney ST, Gladman J and Auer
DP: Carotid intraplaque hemorrhage predicts recurrent symptoms in
patients with high-grade carotid stenosis. Stroke. 38:1633–1635.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|