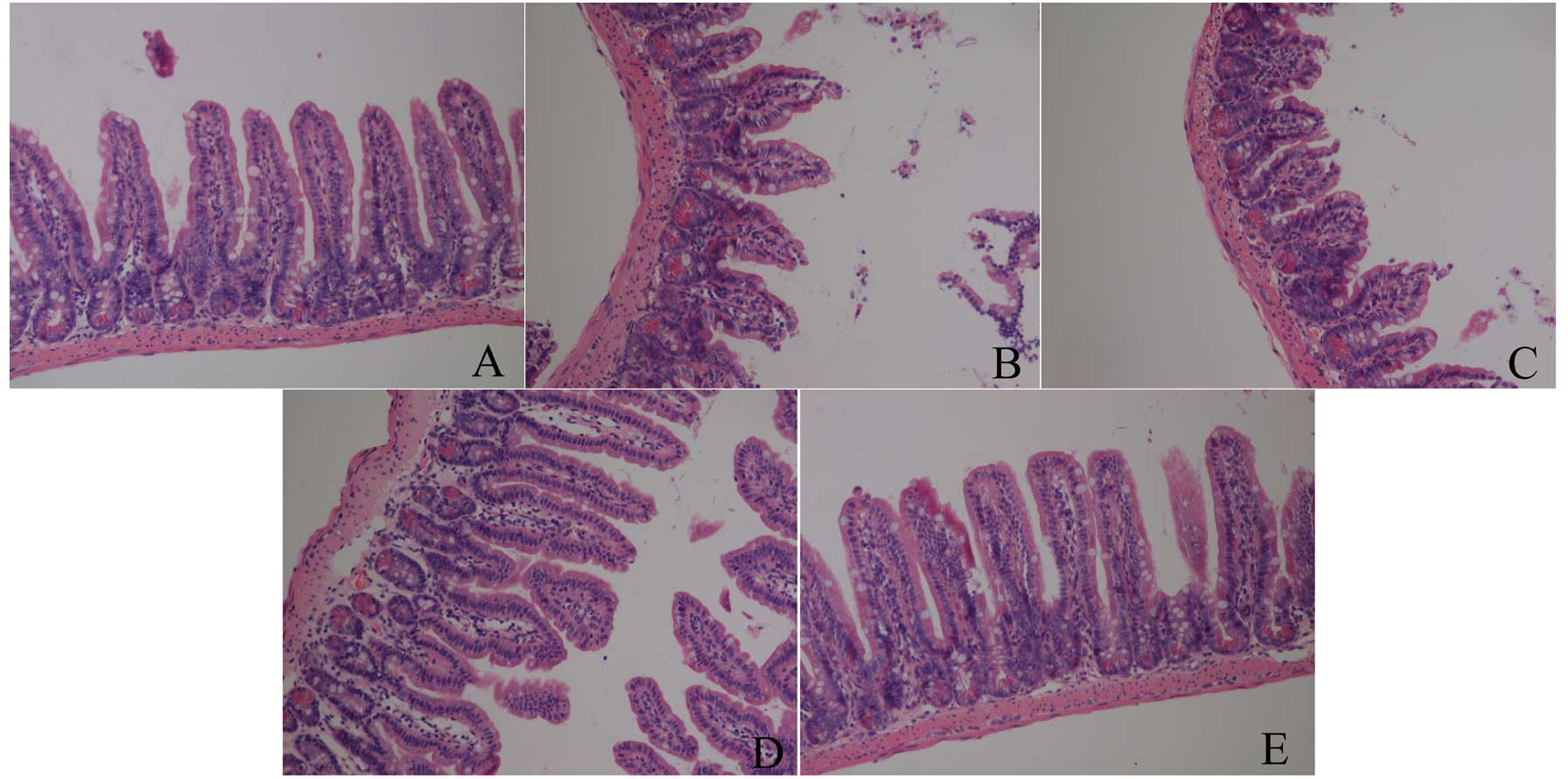
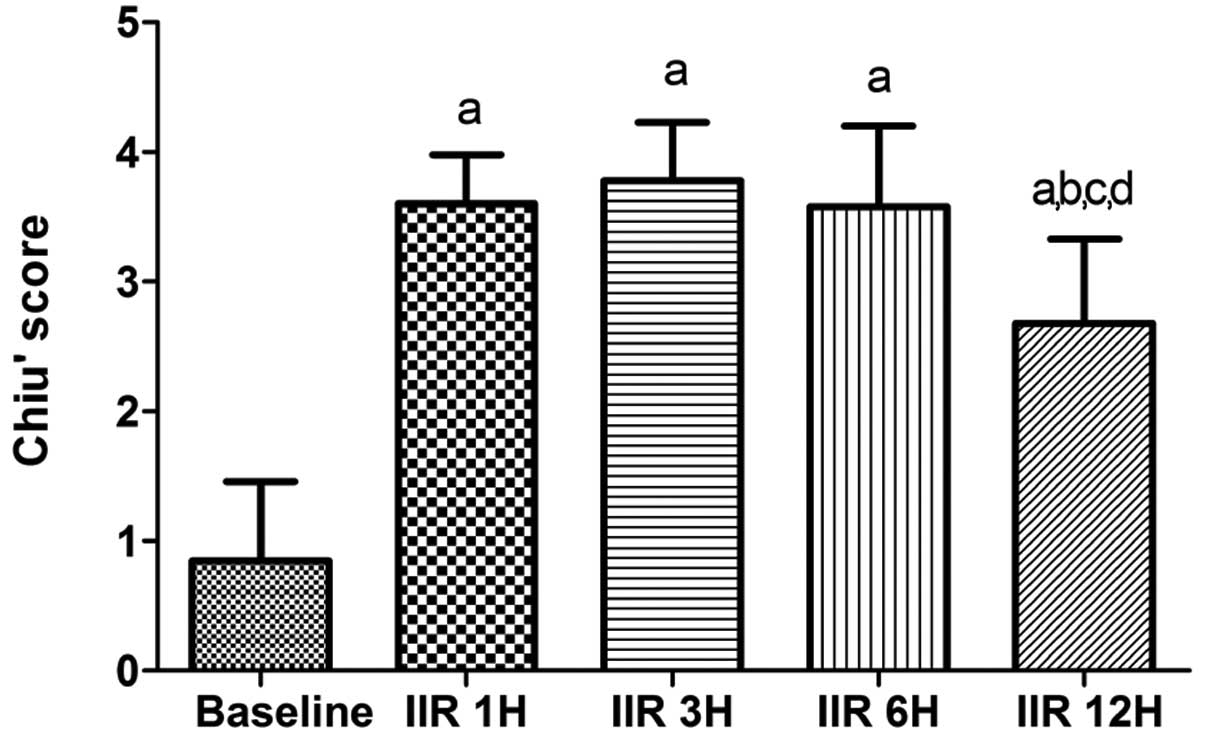
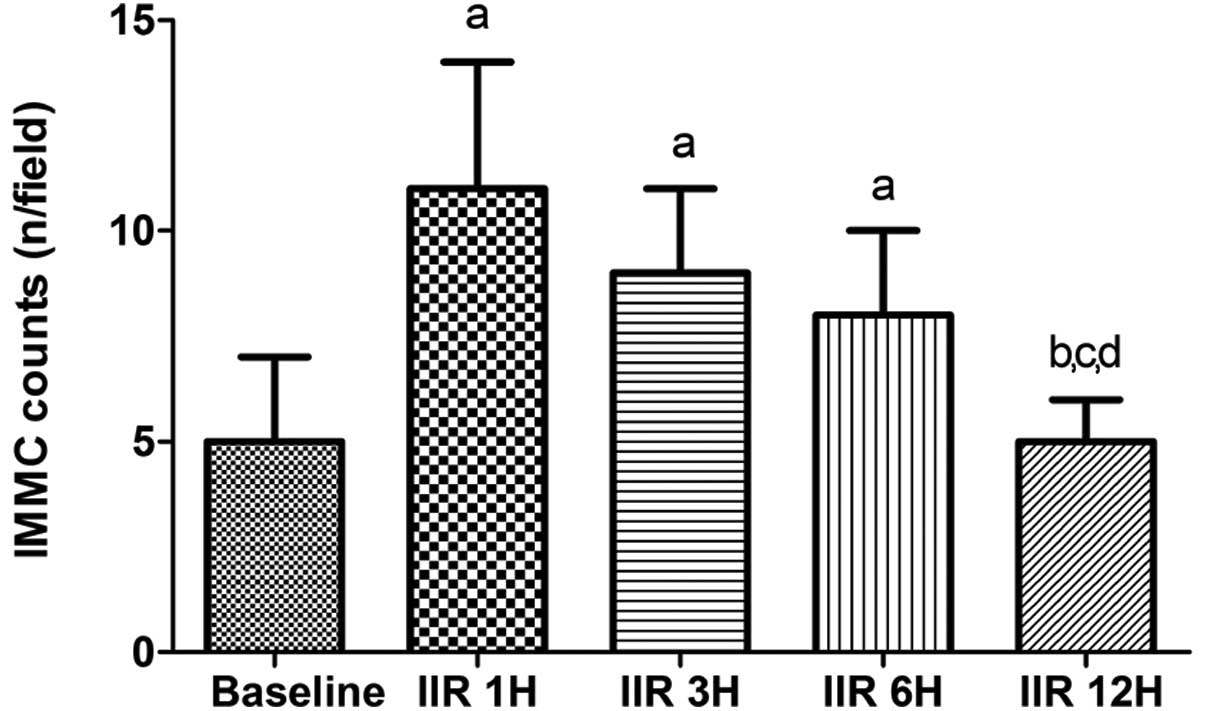
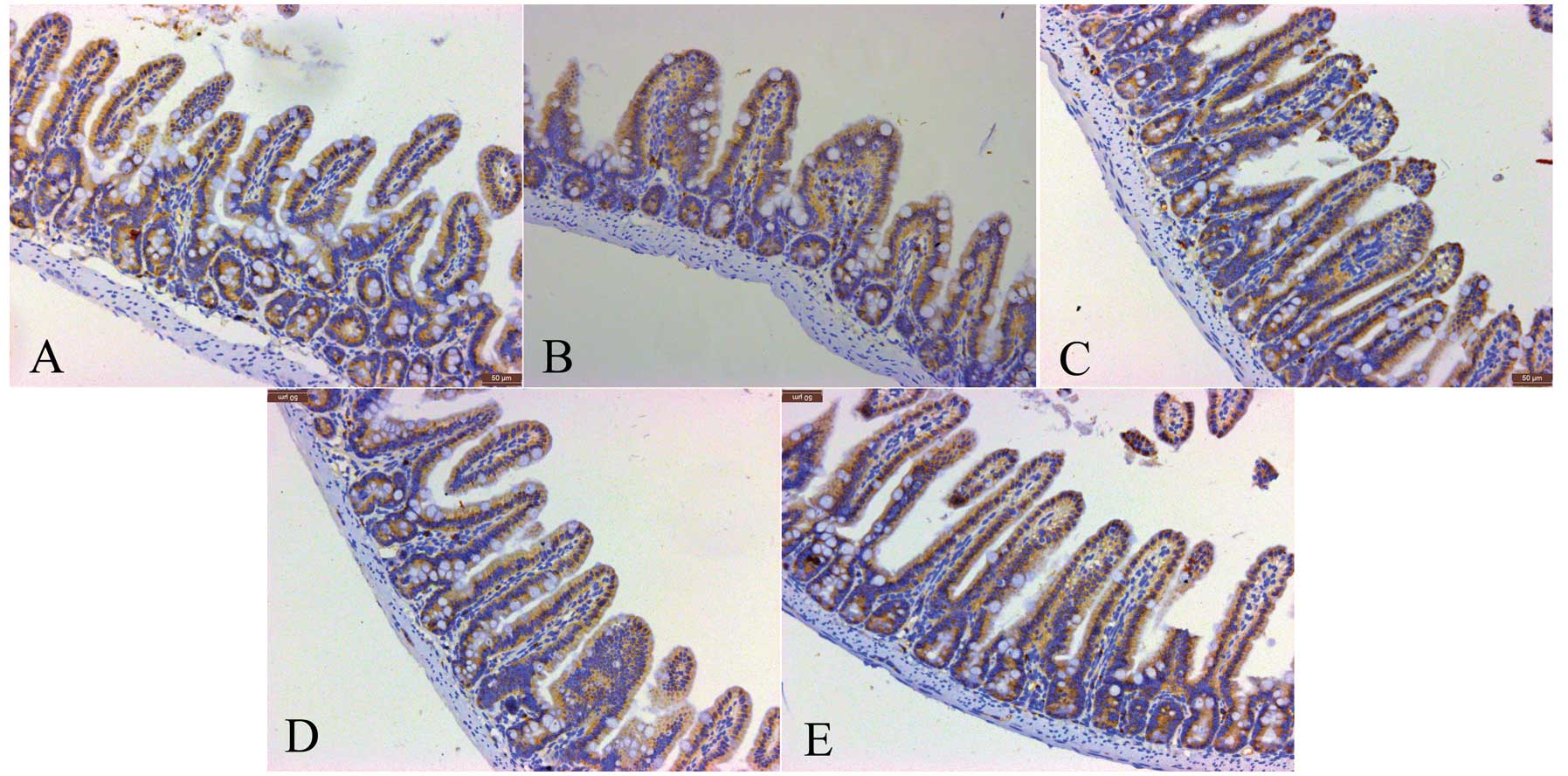
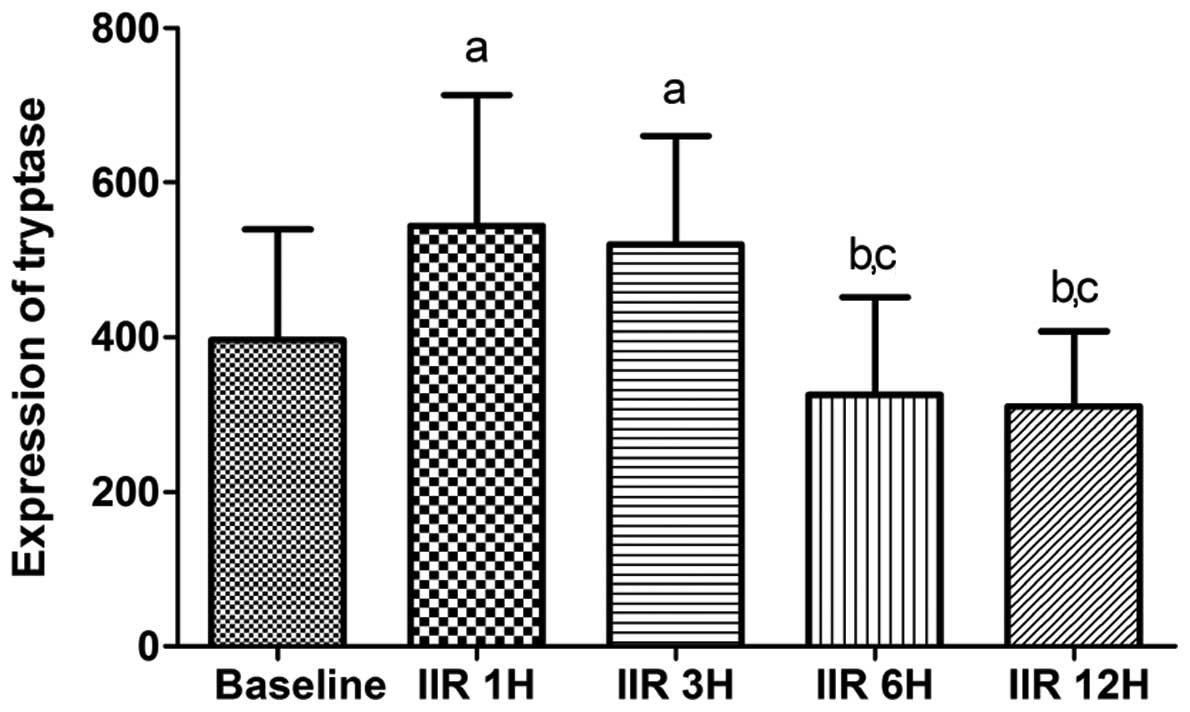
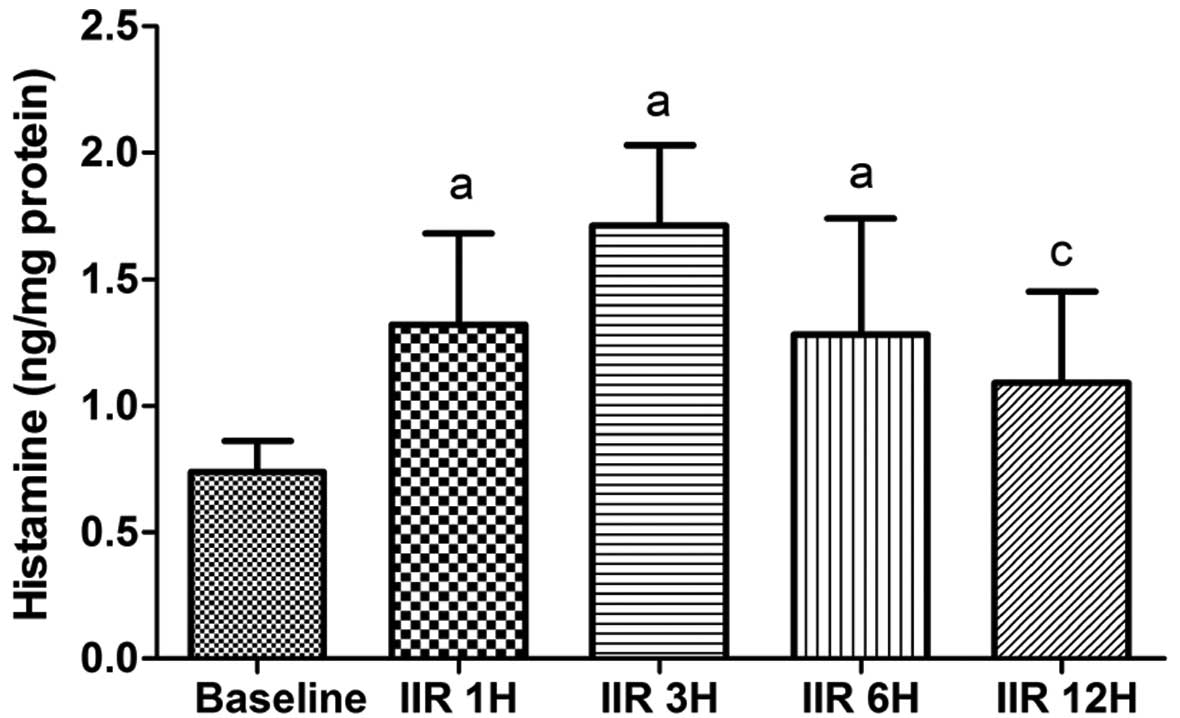
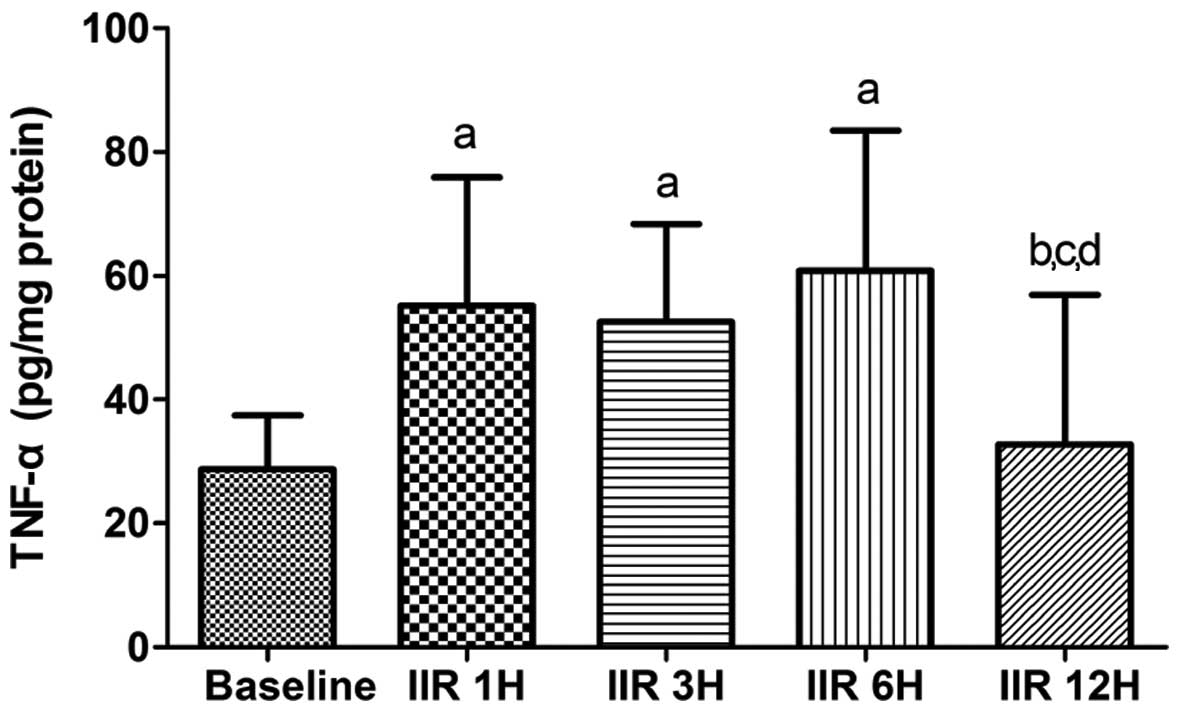
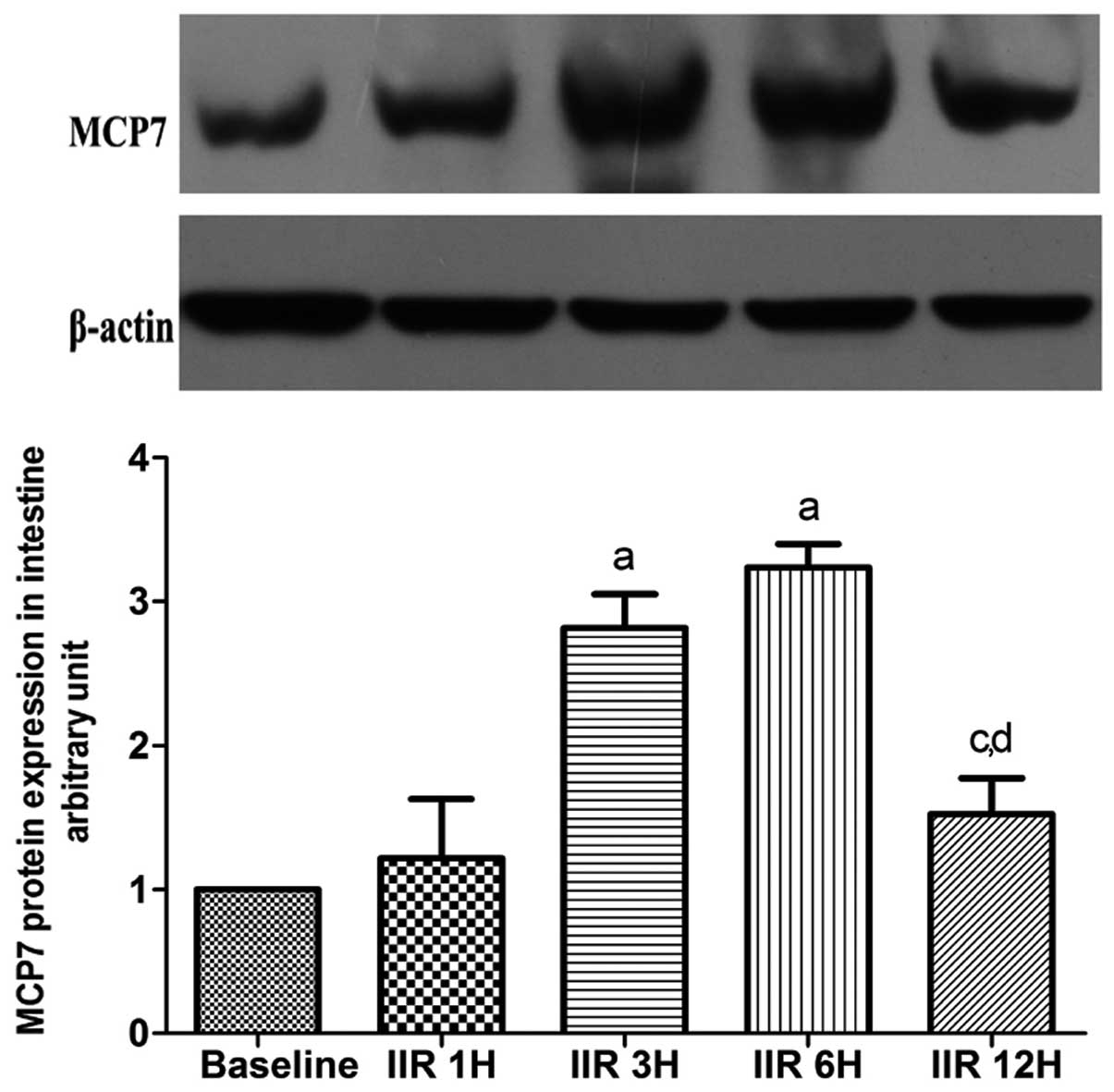
|
1
|
Schoots IG, Koffeman GI, Legemate DA, Levi
M and van Gulik TM: Systematic review of survival after acute
mesenteric ischaemia according to disease aetiology. Br J Surg.
91:17–27. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Acosta-Merida MA, Marchena-Gomez J,
Hemmersbach-Miller M, Roque-Castellano C and Hernandez-Romero JM:
Identification of risk factors for perioperative mortality in acute
mesenteric ischemia. World J Surg. 30:1579–1585. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pierro A and Eaton S: Intestinal ischemia
reperfusion injury and multisystem organ failure. Semin Pediatr
Surg. 13:11–17. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kassahun WT, Schulz T, Richter O and Hauss
J: Unchanged high mortality rates from acute occlusive intestinal
ischemia: six year review. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 393:163–171.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cerqueira NF, Hussni CA and Yoshida WB:
Pathophysiology of mesenteric ischemia/reperfusion: a review. Acta
Cir Bras. 20:336–343. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Haddad JJ: Antioxidant and prooxidant
mechanisms in the regulation of redox(y)-sensitive transcription
factors. Cell Signal. 14:879–897. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vollmar B and Menger MD: Intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion: microcirculatory pathology and functional
consequences. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 396:13–29. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Andoh A, Kimura T, Fukuda M, Araki Y,
Fujiyama Y and Bamba T: Rapid intestinal ischaemia-reperfusion
injury is suppressed in genetically mast cell-deficient Ws/Ws rats.
Clin Exp Immunol. 116:90–93. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kalia N, Brown NJ, Wood RF and Pockley AG:
Ketotifen abrogates local and systemic consequences of rat
intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
20:1032–1038. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hei ZQ, Gan XL, Huang PJ, Wei J, Shen N
and Gao WL: Influence of ketotifen, cromolyn sodium, and compound
48/80 on the survival rates after intestinal ischemia reperfusion
injury in rats. BMC Gastroenterol. 8:422008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Boros M, Takaichi S, Masuda J, Newlands GF
and Hatanaka K: Response of mucosal mast cells to intestinal
ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat. Shock. 3:125–131. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chang JX, Chen S, Ma LP, et al: Functional
and morphological changes of the gut barrier during the restitution
process after hemorrhagic shock. World J Gastroenterol.
11:5485–5491. 2005.
|
|
13
|
Noda T, Iwakiri R, Fujimoto K, Matsuo S
and Aw TY: Programmed cell death induced by Ischemia-reperfusion in
rat intestinal mucosa. Am J Physiol. 274(2 Pt 1): G270–G276.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chiu CJ, Mcardle AH, Brown R, Scott HJ and
Gurd FN: Intestinal mucosal lesion in low flow states. Arch Surg.
101:478–483. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thakurdas SM, Melicoff E, Sanscores-Garcia
L, Moreira DC, Petrova Y, Stevens RL and Adachi R: The mast
cell-restricted tryptase mMCP-6 has a critical immunoprotective
role in bacterial infections. J Biol Chem. 282:20809–20815. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kemna E, Pickkers P, Nemeth E, van der
Hoeven H and Swinkels D: Time-course analysis of hepcidin, serum
iron, and plasma cytokine levels in humans injected with LPS.
Blood. 106:1864–1866. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bischoff SC: Physiological and
pathophysiological functions of intestinal mast cells. Semin
Immunopathol. 31:185–205. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wierzbicki M and Brzezińska-Błaszczyk E:
The role of mast cells in the development of inflammatory bowel
diseases. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 62:642–650.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bischoff SC and Kramer S: Human mast
cells, bacteria, and intestinal immunity. Immunol Rev. 217:329–337.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hei ZQ, Gan XL, Luo GJ, Li SR and Cai J:
Pretreatment of cromolyn sodium prior to reperfusion attenuates
early reperfusion injury after the small intestine ischemia in
rats. World J Gastroenterol. 13:5139–5146. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lindsberg PJ, Strbian D and
Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML: Mast cells as early responders in the
regulation of acute blood-brain barrier changes after cerebral
ischemia and hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 30:689–702.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morii E: Development of mast cells:
analysis with mutant mice. Int J Hematol. 86:22–26. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Okayama Y and Kawakami T: Development,
migration, and survival of mast cells. Immunol Res. 34:97–115.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
McNeil HP, Reynolds DS, Schiller V, et al:
Isolation, characterization, and transcription of the gene encoding
mouse mast cell protease 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:11174–11178.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Funaba M, Ikeda T, Murakami M, et al:
Transcriptional activation of mouse mast cell protease-7 by activin
and transforming growth factor-beta is inhibited by
microphthalmia-associated transcription factor. J Biol Chem.
278:52032–52041. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Caughey GH: Mast cell tryptases and
chymases in inflammation and host defense. Immunol Rev.
217:141–154. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
He S, Gaca MD and Walls AF: A role for
tryptase in the activation of human mast cells: modulation of
histamine release by tryptase and inhibitors of tryptase. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 286:289–297. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gan XL, Hei ZQ, Huang HQ, Chen LX, Li SR
and Cai J: Effect of Astragalus membranaceus injection on the
activity of the intestinal muscosal mast cells after hemorrhagic
shock-reperfusion in rats. Chin Med J. 119:1892–1898.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pascher A and Klupp J: Biologics in the
treatment of transplant rejection and ischemia/reperfusion injury:
new applications for TNFalpha inhibitors? BioDrugs. 19:211–231.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bischoff SC, Lorentz A, Schwengberg S,
Weier G, Raab R and Manns MP: Mast cells are an important cellular
source of tumour necrosis factor alpha in human intestinal tissue.
Gut. 44:643–652. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|